Mobile High-Definition Link on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mobile High-Definition Link (MHL) is an industry standard for a mobile audio/video interface that allows the connection of
 MHL is an adaptation of
MHL is an adaptation of
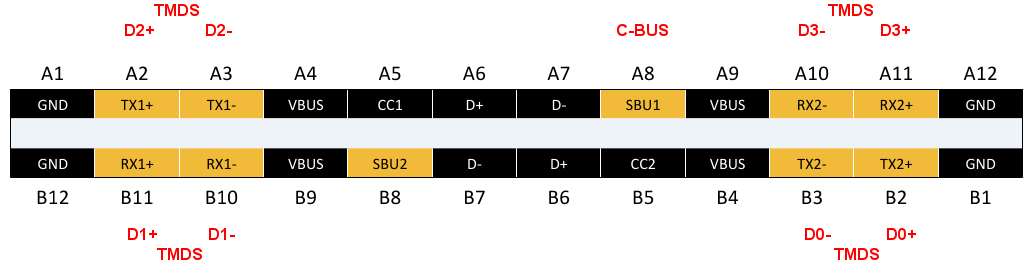 In common MHL Alternate Mode implementations, the video from the GPU will be converted to an MHL signal by using an MHL transmitter chip. The transmitter chips often accept video in MIPI ( DSI/ DPI) or
In common MHL Alternate Mode implementations, the video from the GPU will be converted to an MHL signal by using an MHL transmitter chip. The transmitter chips often accept video in MIPI ( DSI/ DPI) or
smartphone
A smartphone is a mobile phone with advanced computing capabilities. It typically has a touchscreen interface, allowing users to access a wide range of applications and services, such as web browsing, email, and social media, as well as multi ...
s, tablets, and other portable consumer electronics
Consumer electronics, also known as home electronics, are electronic devices intended for everyday household use. Consumer electronics include those used for entertainment, Communication, communications, and recreation. Historically, these prod ...
devices to high-definition television
High-definition television (HDTV) describes a television or video system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since at least 1933; in more recent times, it ref ...
s (HDTVs), audio receivers, and projectors. The standard was designed to share existing mobile device connectors, such as Micro-USB
The initial versions of the USB standard specified connectors that were easy to use and that would have high life spans; revisions of the standard added smaller connectors useful for compact portable devices. Higher-speed development of the USB ...
, and avoid the need to add video connectors on devices with limited space for them.
MHL connects to display devices either directly through special HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary digital interface used to transmit high-quality video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect devices such as televisions, computer monitors, projectors, gam ...
inputs that are MHL-enabled, or indirectly through standard HDMI inputs using MHL-to-HDMI adapters. MHL was developed by a consortium
A consortium () is an association of two or more individuals, companies, organizations, or governments (or any combination of these entities) with the objective of participating in a common activity or pooling their resources for achieving a ...
of five companies: Nokia
Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporation, originally established as a pulp mill in 1 ...
, Samsung
Samsung Group (; stylised as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean Multinational corporation, multinational manufacturing Conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered in the Samsung Town office complex in Seoul. The group consists of numerous a ...
, Silicon Image, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Toshiba
is a Japanese multinational electronics company headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, elevators and escalators, electronic components, semiconductors ...
.
History
Silicon Image, one of the founding companies of theHDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary digital interface used to transmit high-quality video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect devices such as televisions, computer monitors, projectors, gam ...
standard, originally demonstrated a mobile interconnect
In telecommunications, interconnection is the physical linking of a carrier's network with equipment or facilities not belonging to that network. The term may refer to a connection between a carrier's facilities and the equipment belonging to its ...
at the January 2008 Consumer Electronics Show
CES (; formerly an initialism for Consumer Electronics Show) is an annual trade show organized by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). Held in January at the Las Vegas Convention Center in Winchester, Nevada, United States, the event typi ...
(CES), based on its transition-minimized differential signaling (TMDS) technology. This interface was termed "Mobile High Definition Link" at the time of the demonstration, and is a direct precursor of the implementation announced by the MHL Consortium. The company is quoted as saying it did not ship that original technology in any volume, but used it as a way to get a working group
A working group is a group of experts working together to achieve specified goals. Such groups are domain-specific and focus on discussion or activity around a specific subject area. The term can sometimes refer to an interdisciplinary collab ...
started.
The working group was announced in September 2009, and the MHL Consortium founded in April 2010 by Nokia
Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications industry, telecommunications, technology company, information technology, and consumer electronics corporation, originally established as a pulp mill in 1 ...
, Samsung
Samsung Group (; stylised as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean Multinational corporation, multinational manufacturing Conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered in the Samsung Town office complex in Seoul. The group consists of numerous a ...
, Silicon Image, Sony
is a Japanese multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate headquartered at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The Sony Group encompasses various businesses, including Sony Corporation (electronics), Sony Semiconductor Solutions (i ...
and Toshiba
is a Japanese multinational electronics company headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, elevators and escalators, electronic components, semiconductors ...
. The MHL specification version 1.0 was released in June 2010, and the Compliance Test Specification (CTS) was released in December 2010. May 2011 marked the first retail availability of MHL-enabled products.
The first mobile device to feature the MHL standard was the Samsung Galaxy S II
The Samsung Galaxy S II (also unofficially known as the Samsung Galaxy S2) is a touchscreen-enabled, Slate phone, slate-format Android (operating system), Android smartphone developed and marketed by Samsung Electronics, as the second smartphon ...
, announced at the 2011 Mobile World Congress
MWC Barcelona (formerly but still commonly referred to as Mobile World Congress) is an annual trade show dedicated to the mobile communications industry.
The event is held in L'Hospitalet de Llobregat, Spain, at the Fira de Barcelona Gran ...
.
MHL announced in 2014 that more than half a billion MHL-capable products had been shipped since the standard was created.
Overview
HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary digital interface used to transmit high-quality video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect devices such as televisions, computer monitors, projectors, gam ...
intended for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Unlike DVI, which is compatible with HDMI using only passive cables and adapters, MHL requires that the HDMI socket be MHL-enabled. (To deliver an MHL signal to a non-MHL HDMI socket, one can use an adapter device that receives the signal on an MHL-enabled socket, converts it to HDMI, and transmits the HDMI signal to the non-MHL socket). It has several aspects in common with HDMI, such as the ability to carry uncompressed
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression ...
HDCP
High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) is a form of digital copy protection developed by Intel Corporation to prevent copying of digital audio and video content as it travels across connections. Types of connections include DisplayPort ...
encrypted high-definition video
High-definition video (HD video) is video of higher resolution and quality than standard-definition. While there is no standardized meaning for ''high-definition'', generally any video image with considerably more than 480 vertical scan lines ( ...
, eight-channel surround sound
Surround sound is a technique for enriching the fidelity and depth of sound reproduction by using multiple audio channels from speakers that surround the listener ( surround channels). Its first application was in movie theaters. Prior to ...
, and control remote devices with Consumer Electronics Control
Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) is a feature of HDMI designed to control HDMI connected devices by using only one remote controller; individual CEC enabled devices can command and control each other without user intervention, for up to 15 device ...
(CEC).
There are a total of five pins used in MHL rather than the 19 used in HDMI, namely: a differential pair for data, a bi-directional control channel (CBUS), power charging supply, and ground. This permits a much lighter cable and a much smaller connector on the mobile device, as a typical MHL source will be shared with USB 2.0 on a standard 5-pin Micro-USB
The initial versions of the USB standard specified connectors that were easy to use and that would have high life spans; revisions of the standard added smaller connectors useful for compact portable devices. Higher-speed development of the USB ...
receptacle. (Although MHL ports can be dedicated to MHL alone, the standard is designed to permit port sharing with the most commonly used ports.) The USB port switches from USB to MHL when it recognizes an MHL-qualified sink (e.g., a TV) detected on the control wire. A typical MHL sink will be shared with HDMI on a standard 19-pin HDMI receptacle.
Because the same five-pin Micro-USB port is also typically used for charging the device, the sink is required to provide power to maintain the state of charge (or even recharge) while it is being used (although this is dependent on the power available being sufficient e.g., MHL 2 & 3 provide a minimum of 4.5 W / 900 mA, while superMHL can provide up to 40 W). The use of the power line in this way differs from HDMI, which expects the source to provide 55 mA for the purpose of reading the EDID
Extended Display Identification Data (EDID) and Enhanced EDID (E-EDID) are metadata formats for display devices to describe their capabilities to a video source (e.g., graphics card or set-top box). The data format is defined by a standard publish ...
of a display.
Because of to the low pin count of MHL versus HDMI, the functions that are carried on separate dedicated pins on HDMI, namely: the Display Data Channel (DDC) (pins 15 & 16) and CEC (pin 13) are instead carried on the bi-directional control bus (CBUS). The CBUS both emulates the function of the DDC bus and also carries an MHL sideband channel (MSC), which emulates the CEC bus function, and allows a TV remote to control the media player on a phone with its Remote Control Protocol (RCP).
Bandwidth
MHL uses the same Transition-minimized differential signaling (TMDS) as HDMI to carry video, audio, and auxiliary data. However, MHL differs from HDMI in that there is only one differential pair to carry the TMDS data lane, compared to HDMI's four (three data lanes, plus the clock). Therefore these three logical data channels are instead time-division multiplexed into the single physical MHL data lane (i.e., with the logical channels sent sequentially), and the clock signal carried as a common mode signal of this pair. From MHL 3 onwards, the method for carrying the clock signal changed to being carried separately on the MHL CBUS pin instead. The normal (24 bit) mode operates at 2.25 Gbit/s, and multiplexes the same three channel, 24 bit color signal as HDMI, at a pixel clock rate of up to 75 MHz, sufficient for1080i
In high-definition television (HDTV) and video display technology, 1080i is a video display format with 1080 lines of vertical resolution and Interlaced video, interlaced scanning method. This format was once a standard in HDTV. It was particular ...
and 720p
720p (720 lines progressive) is a progressive HD signal format with 720 horizontal lines/1280 columns and an aspect ratio (AR) of 16:9, normally known as widescreen HD (1.78:1). All major HD broadcasting standards (such as SMPTE 292M) includ ...
at 60 Hz. One period of the MHL clock equals one period of the pixel clock, and each period of the MHL clock transmits three 10-bit TMDS characters (i.e., a 24-bit pixel, where each 10-bit TMDS character represents an encoded byte – 8-bits).
MHL can also operate in PackedPixel mode at 3 Gbit/s, catering for 1080p
1080p (1920 × 1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the sc ...
, in this case only two channels are multiplexed, as the color signal is changed to a chroma subsampled (YCbCr 4:2:2) pair of adjacent 16-bit pixels (i.e., where two adjacent pixels share chroma values and are represented with only 36-bits), and the pixel clock is doubled to 150 MHz. In this mode, one clock period of the MHL clock now equals two periods of the pixel clock, so each period of the MHL clock transmits twice the number of channels i.e., four 10-bit TMDS characters (a pair of 16-bit pixels).
Version 3 of MHL changed from being frame-based to a packet-based technology, and operates at 6 Gbit/s. superMHL extends this by carrying the data signal over more than one differential pair (up to four with USB Type-C, or a total of six using a superMHL cable) allowing up to 36 Gbit/s.
Versions
All MHL specifications are backward compatible to previous versions of the standard. MHL is connection agnostic (i.e., not tied to a specific type of hardware connector). The first implementations used the 5-pin MHL-USB connector described below, and all are supported over USB Type-C MHL Alternate Mode. Other proprietary and custom connections are also allowed.MHL 1
Version 1.0 was introduced in June 2010, supporting uncompressed HD video up to 720p/1080i 60 Hz (with RGB and YCbCr 4:2:2/4:4:4 pixel encoding). Support for1080p
1080p (1920 × 1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the sc ...
60 Hz (YCbCr 4:2:2) was introduced in version 1.3. The specification supports standard SD ( Rec. 601) and HD ( Rec. 709) color spaces, as well as those introduced in HDMI 1.3 and 1.4 (xvYCC
xvYCC or extended-gamut YCbCr is a color space that can be used in the video electronics of television sets to support a gamut 1.8 times as large as that of the sRGB color space. xvYCC was proposed by Sony, specified by the IEC in October 2005 ...
, sYCC601, Adobe RGB
Adobe (from arabic: الطوب Attub ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for mudbrick. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used ...
, and AdobeYCC601). Other features include 192 kHz 24-bit LPCM 8-channel surround sound
Surround sound is a technique for enriching the fidelity and depth of sound reproduction by using multiple audio channels from speakers that surround the listener ( surround channels). Its first application was in movie theaters. Prior to ...
audio, HDCP
High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) is a form of digital copy protection developed by Intel Corporation to prevent copying of digital audio and video content as it travels across connections. Types of connections include DisplayPort ...
1.4 content protection, and a minimum of 2.5 W (500 mA) power between sink (e.g., TV) and source (e.g., mobile phone) for charging. The MHL sideband channel (MSC) includes a built-in Remote Control Protocol (RCP) function allowing the remote control
A remote control, also known colloquially as a remote or clicker, is an consumer electronics, electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operat ...
of the TV to operate the MHL mobile device through TV's Consumer Electronics Control
Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) is a feature of HDMI designed to control HDMI connected devices by using only one remote controller; individual CEC enabled devices can command and control each other without user intervention, for up to 15 device ...
(CEC) function, or allowing a mobile device to manage the playback of its content on the TV.
MHL 2
Version 2.0 was introduced in April 2012, and raised the minimum charging supply to 4.5 W (900 mA), with an optional 7.5 W (1.5 A) maximum allowed. Support for 3D video was also introduced, permitting 720p/1080i 60 Hz, and 1080p 24 Hz 3D video modes. The specification also included additional MHL sideband channel (MSC) commands.MHL 3
Version 3.0 was introduced in August 2013, and added support for 4K Ultra HD (3840 × 2160) 30 Hz video, increasing the maximum bandwidth from 3 Gbit/s to 6 Gbit/s. An additional YCbCr 4:2:0 pixel encoding for 4K resolution was also introduced, while the maximum charging supply was increased to 10 W (2 A). Support for compressed lossless audio formats was added with support forDolby TrueHD
Dolby TrueHD is a lossless, multi-channel audio codec developed by Dolby Laboratories for home video, used principally in Blu-ray Disc and compatible hardware. Dolby TrueHD, along with Dolby Digital Plus (E-AC-3) and Dolby AC-4, is one of th ...
and DTS-HD Master Audio
DTS-HD Master Audio (DTS-HD MA; known as DTS++ before 2004) is a multi-channel, lossless audio codec developed by DTS as an extension of the lossy DTS Coherent Acoustics codec (DTS CA; usually itself referred to as just DTS). Rather than be ...
.
The specification increased the speed of the bi-directional data channel from 1 Mbit/s to 75 Mbit/s to enable concurrent 4K video and human interface device
A human interface device (HID) is a type of computer device usually used by humans that takes input from or provides output to humans.
The term "HID" most commonly refers to the USB HID specification. The term was coined by Mike Van Flandern ...
(HID) support, such as mice, keyboards, touchscreens, and game controllers. Other features include support for simultaneous multiple displays, improved Remote Control Protocol (RCP) with new commands, and HDCP 2.2 content protection.
superMHL
superMHL 1.0 was introduced in January 2015, supporting 8K Ultra HD (7680 × 4320) 120 Hz High Dynamic Range (HDR) video with wide color gamut ( Rec. 2020) and 48-bit deep color. Support for object-based audio formats were added, such asDolby Atmos
Dolby Atmos is a surround sound technology developed by Dolby Laboratories. It expands on existing surround sound systems by adding height channels as well as free-moving sound objects, interpreted as three-dimensional objects with neither horiz ...
and DTS:X, with an audio-only mode also available. The Remote Control Protocol (RCP) was also extended to link multiple MHL devices together (e.g., TV, AVR, Blu-ray Disc player) and control them via one remote.
The specification introduces a reversible 32-pin superMHL connector, which (along with USB Type-C) supports a higher charging power of up to 40 W (20 V / 2 A), and is designed for future bandwidth expansion. The increase in bandwidth over previous MHL versions is achieved by using multiple A/V lanes, each operating at 6 Gbit/s, with a maximum of six A/V lanes supported depending on device and connector type. For example, Micro-USB and HDMI Type-A support one A/V lane, USB Type-C supports up to four A/V lanes, and the superMHL connector supports up to six A/V lanes (36 Gbit/s).
In addition to supporting a variable number of lanes, the specification supports VESA
VESA (), formally known as Video Electronics Standards Association, is an American standards organization, technical standards organization for computer display standards. The organization was incorporated in California in July 1989To retrieve ...
Display Stream Compression
Display Stream Compression (DSC) is a VESA-developed video compression algorithm designed to enable increased display resolutions and frame rates over existing physical interfaces, and make devices smaller and lighter, with longer battery life. ...
(DSC) 1.1, a "visually lossless" (but mathematically lossy) video compression standard. In cases when the bandwidth of the available lane(s) is unable to meet the rate of the uncompressed video stream, bandwidth savings of up to 3:1 can be achieved with a DSC compression rate of 3.0×. For example, 4K 60 Hz is possible using a single lane (e.g., Micro-USB / HDMI Type-A) with a DSC rate of 3.0×.
superMHL can use a variety of source and sink connectors with certain limitations: micro-USB or proprietary connectors can be used for the source only, HDMI Type-A for the sink only, while the USB Type-C and the superMHL connectors can be used for the source or sink.
Connectors
Micro-USB–to–HDMI (five-pin)
The first implementations used the most common connection for non-Apple mobile phones at the time, (Micro-USB
The initial versions of the USB standard specified connectors that were easy to use and that would have high life spans; revisions of the standard added smaller connectors useful for compact portable devices. Higher-speed development of the USB ...
), and the most common TV connection (HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary digital interface used to transmit high-quality video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect devices such as televisions, computer monitors, projectors, gam ...
). There are two types of connection, depending on whether the display device directly supports MHL.
Passive cable
Passive cables allow MHL devices to connect directly to MHL-enabled TVs (i.e. display devices or AV receivers with an MHL-enabled HDMI port) while providing charging power upstream to the mobile device. Other than the physical connectors, no USB or HDMI technology is being used. Exclusively MHL signaling is used through the connectors and over the cable.Active adapter
With an active adapter, MHL devices are able to connect to HDMI display devices that do not have MHL capability by actively converting the signal to HDMI. These adapters often feature an additional Micro-USB port on them to provide charging power to the mobile device because standard HDMI ports do not supply sufficient current.Samsung Micro-USB–to–HDMI adapter and tip (eleven-pin)
TheSamsung Galaxy S III
The Samsung Galaxy S III (unofficially known as the Samsung Galaxy S3) is an Android smartphone developed and marketed by Samsung Electronics. Launched in 2012, it had sold more than 80 million units overall, making it the most sold ph ...
, and later Galaxy Note II and Galaxy S4, use an 11-pin connector and the six additional connector pins in order to achieve functional improvements over the 5-pin design (like simultaneous USB-OTG use). However, if consumers have a standard MHL-to-HDMI adapter all they need to purchase is a tip. With the launch of the Samsung Galaxy S4, Samsung also released MHL 2.0 smart adapter with a built-in 11-pin connector. The first Samsung MHL 1.0 smart adapter released with the Galaxy S III requires external power and is able to work with HDMI TVs at 1080p at 24 Hz. The MHL 2.0 adapter released with the Galaxy S4 can output 1080p at 60 Hz and does not need external power.
USB Type-C (MHL Alternate Mode)
The MHL Alternate Mode for USB 3.1 specification allows MHL enabled source and display devices to be connected through a USB Type-C port. The standard was released on November 17, 2014, and is backward compatible with existing MHL specifications: supporting MHL 1, 2, 3 and superMHL. The standard supports the simultaneous transfer of data (at least USB 2.0, and depending on video resolution: USB 3.1 Gen 1 or 2) and power charging (up to 40 W viaUSB Power Delivery
The initial versions of the USB standard specified connectors that were easy to use and that would have high life spans; revisions of the standard added smaller connectors useful for compact portable devices. Higher-speed development of the USB ...
), in addition to MHL audio/video. This allows the connection to be used with mobile docks
The word dock () in American English refers to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near a shore). In British English, the term is not used the same way as in American Engli ...
, allowing devices to connect to other peripherals while charging. The use of passive cables is possible when both devices support the standard, e.g., when connecting to superMHL, USB Type-C, and MHL-enabled HDMI, otherwise, an active cable adapter is necessary to connect to standard HDMI devices.
Depending on the bandwidth requirement, the standard makes use of a variable number of USB Type-C's four SuperSpeed differential pairs to carry each TMDS lane: a single lane is required for resolutions up to 4K/60 Hz, two lanes for 4K/120 Hz, and all four lanes for 8K/60 Hz. The MHL eCBUS signal is sent over a side-band (SBU) pin on the USB Type-C connector. When one or two lanes are used, USB 3.1 data transfer is supported.
 In common MHL Alternate Mode implementations, the video from the GPU will be converted to an MHL signal by using an MHL transmitter chip. The transmitter chips often accept video in MIPI ( DSI/ DPI) or
In common MHL Alternate Mode implementations, the video from the GPU will be converted to an MHL signal by using an MHL transmitter chip. The transmitter chips often accept video in MIPI ( DSI/ DPI) or HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary digital interface used to transmit high-quality video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect devices such as televisions, computer monitors, projectors, gam ...
format and convert it to MHL format. The USB Type-C port controller functions as a switch and multiplexer, passing the MHL signal through to the external devices. The dock or display device may use an MHL bridge chip to convert the MHL signal to HDMI signal format.
superMHL (32-pin)
In conjunction with the release of the superMHL specification in January 2015, MHL introduced a reversible 32-pin superMHL connector. The connector can carry six A/V lanes over six differential pairs, catering for the full 36 Gbit/s bandwidth available from the superMHL standard. The connector also enables 40 W of charging power at a higher voltage and current.Alternatives
SlimPort is a proprietary alternative to MHL, based on theDisplayPort
DisplayPort (DP) is a digital interface used to connect a video source, such as a Personal computer, computer, to a display device like a Computer monitor, monitor. Developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA), it can also car ...
standard integrated into common Micro-USB ports, and supports up to 1080p60 or 1080p30 with 3D content over HDMI 1.4 (up to 5.4 Gbit/s of bandwidth), in addition to support for DVI, VGA (up to 1920 × 1080 at 60 Hz), and DisplayPort.
See also
* SlimPort ( Mobility DisplayPort), also known as MyDP *Miracast
Miracast is a Wireless, wireless communications standard created by the Wi-Fi Alliance which is designed to transmit video and sound from devices (such as laptops or smartphones) to display receivers (such as TVs, monitors, or projectors). It uses ...
(wireless display technology)
* Chromecast
Chromecast is a discontinued line of digital media players developed by Google. The devices, designed as small dongles, can play Internet-streaming media, streamed audio-visual content on a high-definition television or home audio system. The u ...
(proprietary media broadcast over IP: Google Cast for audio or audiovisual playback)
* AirPlay
Airplay is how frequently a song is being played through broadcasting on radio stations. A song which is being played several times every day (spins) would have a significant amount of airplay. Music which became very popular on jukeboxes, in n ...
(proprietary IP-based)
* Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) (IP-based)
* WiDi version 3.5 to 6.0 supports Miracast
Miracast is a Wireless, wireless communications standard created by the Wi-Fi Alliance which is designed to transmit video and sound from devices (such as laptops or smartphones) to display receivers (such as TVs, monitors, or projectors). It uses ...
; discontinued
* Wireless HDMI
* WirelessHD proprietary
* Wireless Home Digital Interface
Wireless Home Digital Interface (WHDI) is a consumer electronic specification for wireless HDTV connectivity throughout the home.
WHDI enables delivery of uncompressed high-definition digital video over a wireless radio channel connecting any vid ...
References
External links
* {{High-definition Computer-related introductions in 2008 Computer-related introductions in 2010 Digital display connectors High-definition television Standards Television technology Ultra-high-definition television Serial buses