Mnajdra 01 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mnajdra () is a

 Mnajdra is made of
Mnajdra is made of
 The lowest temple is astronomically aligned and thus was probably used as an astronomical observation and/or calendrical site. On the vernal and the autumnal equinox sunlight passes through the main doorway and lights up the major axis. On the
The lowest temple is astronomically aligned and thus was probably used as an astronomical observation and/or calendrical site. On the vernal and the autumnal equinox sunlight passes through the main doorway and lights up the major axis. On the
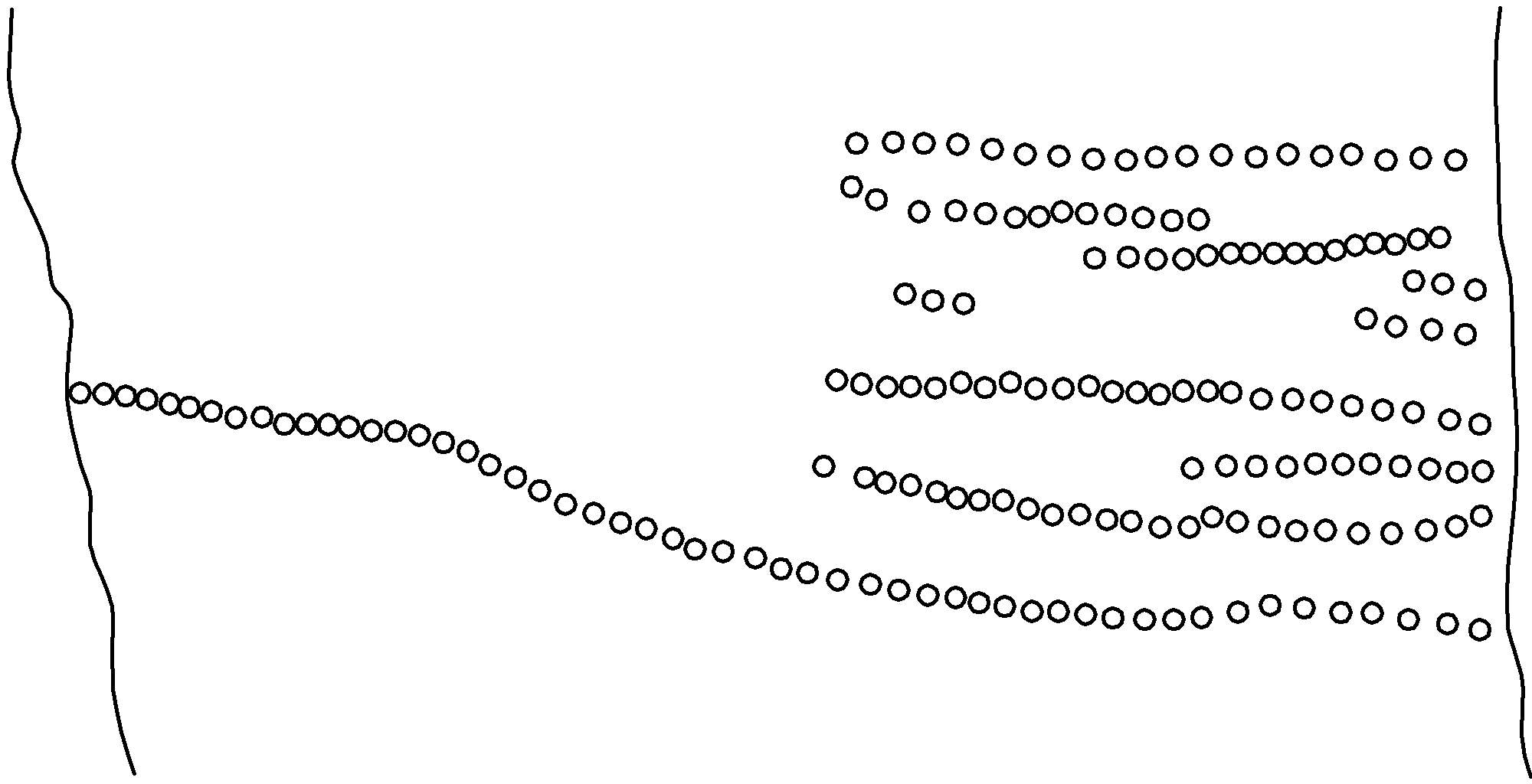 One of the stones displays a lot of drilled holes arranged in different right-aligned rows that can be linked to several periods determined by the moon.
One of the stones displays a lot of drilled holes arranged in different right-aligned rows that can be linked to several periods determined by the moon.
 The excavations of the Mnajdra temples were performed under the direction of J.G. Vance in 1840, one year after the discovery of ń¶agar Qim. In 1871, James Fergusson designed the first plan of the megalithic structure. The plan was quite inaccurate and hence in 1901, Albert Mayr made the first accurate plan which was based on his findings.Alfie Guillaumier, Bliet u Rhula Maltin, Malta 1972 In 1910, Thomas Ashby performed further investigations which resulted in the collection of the important archaeological material. Further excavations were performed in December 1949, in which two small statues, two large bowls, tools and one large spherical stone, which was probably used to move the temple's large stones, were discovered.
The temple was included on the Antiquities List of 1925.
Mnajdra was vandalized on 13 April 2001, when at least three people armed with crowbars toppled or broke about 60 megaliths, and inscribed graffiti on them. The attack was called "the worst act of vandalism ever committed on the island of Malta" by UNESCO. The damage to the temples was initially considered irreparable, but they were restored using new techniques making it difficult to tell where the megaliths had been damaged. The temples were reopened to the public in 2002.
The 1, 2 and 5 cent
The excavations of the Mnajdra temples were performed under the direction of J.G. Vance in 1840, one year after the discovery of ń¶agar Qim. In 1871, James Fergusson designed the first plan of the megalithic structure. The plan was quite inaccurate and hence in 1901, Albert Mayr made the first accurate plan which was based on his findings.Alfie Guillaumier, Bliet u Rhula Maltin, Malta 1972 In 1910, Thomas Ashby performed further investigations which resulted in the collection of the important archaeological material. Further excavations were performed in December 1949, in which two small statues, two large bowls, tools and one large spherical stone, which was probably used to move the temple's large stones, were discovered.
The temple was included on the Antiquities List of 1925.
Mnajdra was vandalized on 13 April 2001, when at least three people armed with crowbars toppled or broke about 60 megaliths, and inscribed graffiti on them. The attack was called "the worst act of vandalism ever committed on the island of Malta" by UNESCO. The damage to the temples was initially considered irreparable, but they were restored using new techniques making it difficult to tell where the megaliths had been damaged. The temples were reopened to the public in 2002.
The 1, 2 and 5 cent
File:Mnajdra.jpg, A total view of the structure
File:Malta 24 Mnajdra.jpg, Ruins of the upper (oldest) temple
File:Mnajdra graffito temple.jpg, An important graffito representing a roofed megalithic temple found in Mnajdra
File:Schematic Angles in the Mnajdra solar temple.tif, Solar angles
File:Map of the Mnajdra temples.tif, Map of the Mnajdra temple
File:Mnajdra tent 2009 06 27.jpg, Protective tent around the site
National Inventory of the Cultural Property of the Maltese Islands
Panoramic View of Mnajdra @ Places of Interest
{{European megaliths Buildings and structures completed in the 4th millennium BC Megalithic Temples of Malta World Heritage Sites in Malta Neolithic sites Qrendi National Inventory of the Cultural Property of the Maltese Islands Sites managed by Heritage Malta
megalithic
A megalith is a large Rock (geology), stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging ...
temple complex found on the southern coast of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
island of Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
. Mnajdra is approximately from the ń¶ań°ar Qim
ń¶ań°ar Qim (; "Standing/Worshipping Stones") is a megalithic temple complex found on the Mediterranean island of Malta, dating from the ń†gantija phase (3600‚Äď3200 BC). The Megalithic Temples of Malta are among the most ancient religio ...
megalithic
A megalith is a large Rock (geology), stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging ...
complex. Mnajdra was built around the fourth millennium BCE; the Megalithic Temples of Malta
The Megalithic Temples of Malta () are several prehistoric temples, some of which are UNESCO World Heritage Sites, built during three distinct periods approximately between 3600 BC and 2500 BC on the island country of Malta. They had been claimed ...
are among the most ancient religious sites on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
, described by the World Heritage Sites committee as "unique architectural masterpieces." In 1992, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
recognized the Mnajdra complex and four other Maltese megalithic structures as UNESCO World Heritage Sites
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
. In 2009, work was completed on a protective tent.
Design

 Mnajdra is made of
Mnajdra is made of coralline limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these ...
, which is much harder than the soft globigerina
''Globigerina'' () is a genus of planktonic Foraminifera, in the order of Rotaliida.Glob ...
limestone of ń¶ań°ar Qim. The main structural systems used in the temples are corbelling
In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal keyed into and projecting from a wall to carry a bearing weight, a type of bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in the wall, whereas a console is a piece applie ...
with smaller stones, and post and lintel
Post and lintel (also called prop and lintel, a trabeated system, or a trilithic system) is a building system where strong horizontal elements are held up by strong vertical elements with large spaces between them. This is usually used to hold ...
construction using large slabs of limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
.
The cloverleaf plan of Mnajdra appears more regular than that of ń¶agar Qim, and seems reminiscent of the earlier complex at ń†gantija
ń†gantija (; "place of giants") is a megalithic temple complex from the Neolithic era (‚Äď2500 BC), on the List of islands in the Mediterranean, Mediterranean island of Gozo in Malta. The ń†gantija temples are the earliest of the Megalithic Temp ...
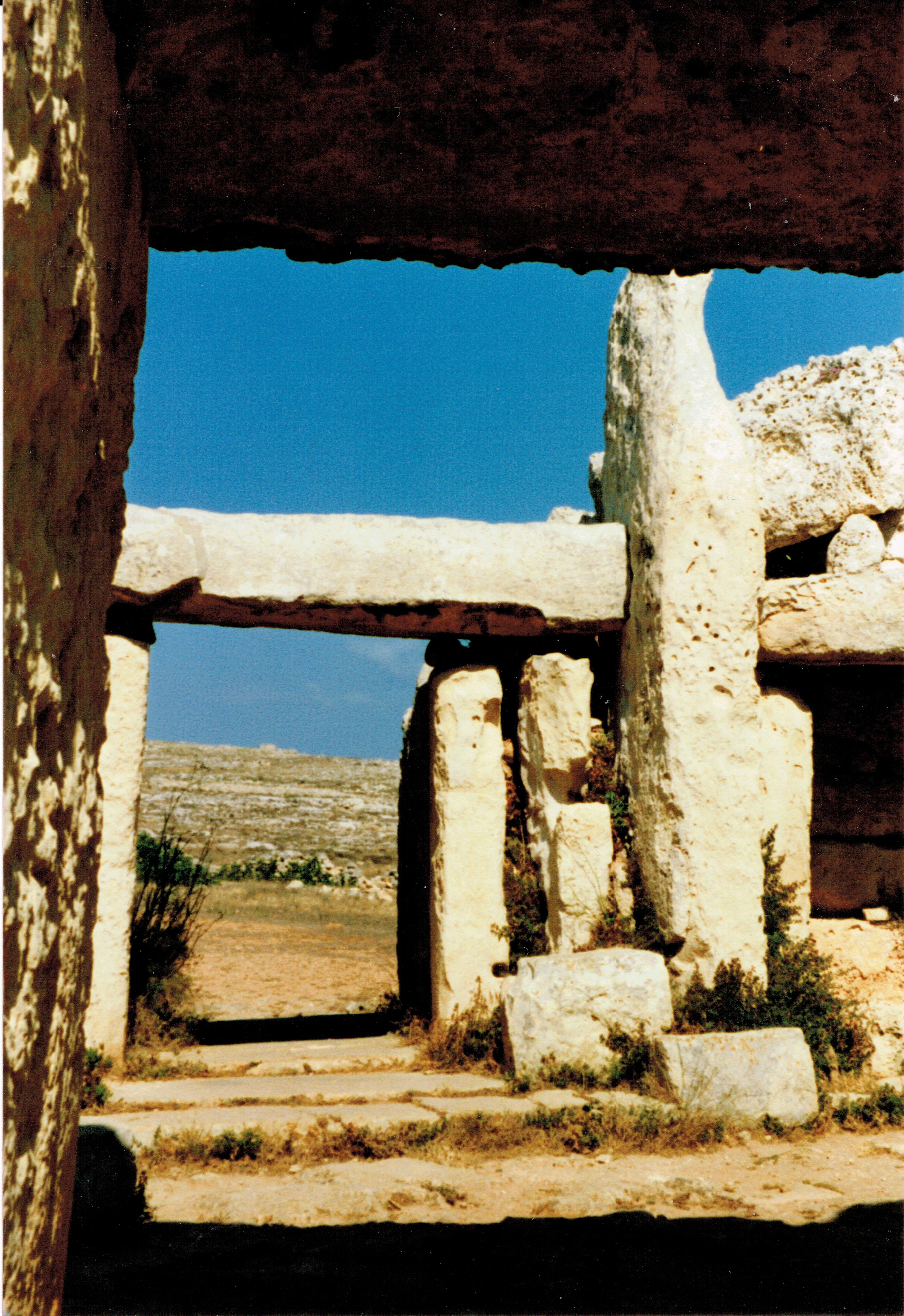
. The prehistoric structure consists of three temples, conjoined, but not connected: the upper, middle, and lower.
The upper temple is the oldest structure in the Mnajdra complex and dates to the ń†gantija phase (3600-3200 BC). It is a three-apse building, the central apse opening blocked by a low screen wall. The pillar-stones were decorated with pitmarks drilled in horizontal rows on the inner surface.
The middle temple was built (or possibly rebuilt) in the late Tarxien
Tarxien ( ) is a town in the Port region of Malta, seat of the Port Regional Council. Its population stood at 8,583 in March 2014.
The town is most notable for the Tarxien Temples, a megalithic temple complex which is among the oldest freestan ...
phase (3150 ‚Äď 2500 BC), the main central doorway of which is formed by a hole cut into a large piece of limestone set upright, a type of construction typical of other megalithic doorways in Malta. This temple appears originally to have had a vaulted ceiling, but only the base of the ceiling now remain on top of the walls and, in fact, is the most recent structure. It is formed of slabs topped by horizontal courses.
The lowest temple, built in the early Tarxien phase, is the most impressive and possibly the best example of Maltese megalithic architecture. It has a large forecourt containing stone benches, an entrance passage covered by horizontal slabs, one of which has survived, and the remains of a possibly domed roof. The temple is decorated with spiral carvings and indentations, and pierced by windows, some into smaller rooms and one onto an arrangement of stones.
Functions
solstice
A solstice is the time when the Sun reaches its most northerly or southerly sun path, excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around 20‚Äď22 June and 20‚Äď22 December. In many countries ...
s sunlight illuminates the edges of megaliths to the left and right of this doorway.
Although there are no written records to indicate the purpose of these structures, archaeologists have inferred their use from ceremonial objects found within them: sacrificial flint knives and rope holes that were possibly used to constrain animals for sacrifice (since various animal bones were found). These structures were not used as tombs since no human remains were found. The temples contain furniture such as stone benches and tables that give clues to their use. Many artifacts were recovered from within the temples suggesting that these temples were used for religious purposes, perhaps to heal illness and/or to promote fertility.
Calendar stone
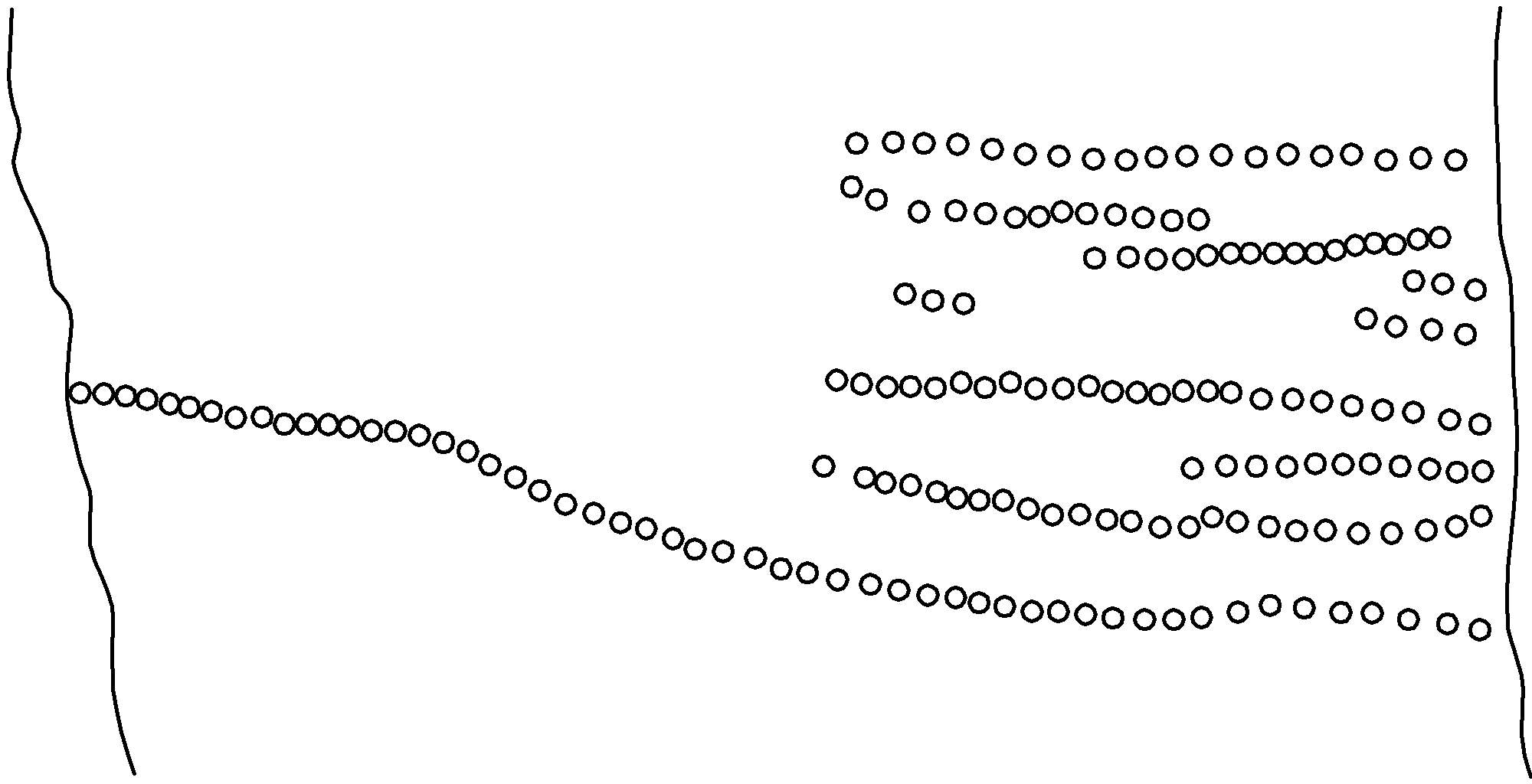 One of the stones displays a lot of drilled holes arranged in different right-aligned rows that can be linked to several periods determined by the moon.
One of the stones displays a lot of drilled holes arranged in different right-aligned rows that can be linked to several periods determined by the moon.
Excavations and recent history
 The excavations of the Mnajdra temples were performed under the direction of J.G. Vance in 1840, one year after the discovery of ń¶agar Qim. In 1871, James Fergusson designed the first plan of the megalithic structure. The plan was quite inaccurate and hence in 1901, Albert Mayr made the first accurate plan which was based on his findings.Alfie Guillaumier, Bliet u Rhula Maltin, Malta 1972 In 1910, Thomas Ashby performed further investigations which resulted in the collection of the important archaeological material. Further excavations were performed in December 1949, in which two small statues, two large bowls, tools and one large spherical stone, which was probably used to move the temple's large stones, were discovered.
The temple was included on the Antiquities List of 1925.
Mnajdra was vandalized on 13 April 2001, when at least three people armed with crowbars toppled or broke about 60 megaliths, and inscribed graffiti on them. The attack was called "the worst act of vandalism ever committed on the island of Malta" by UNESCO. The damage to the temples was initially considered irreparable, but they were restored using new techniques making it difficult to tell where the megaliths had been damaged. The temples were reopened to the public in 2002.
The 1, 2 and 5 cent
The excavations of the Mnajdra temples were performed under the direction of J.G. Vance in 1840, one year after the discovery of ń¶agar Qim. In 1871, James Fergusson designed the first plan of the megalithic structure. The plan was quite inaccurate and hence in 1901, Albert Mayr made the first accurate plan which was based on his findings.Alfie Guillaumier, Bliet u Rhula Maltin, Malta 1972 In 1910, Thomas Ashby performed further investigations which resulted in the collection of the important archaeological material. Further excavations were performed in December 1949, in which two small statues, two large bowls, tools and one large spherical stone, which was probably used to move the temple's large stones, were discovered.
The temple was included on the Antiquities List of 1925.
Mnajdra was vandalized on 13 April 2001, when at least three people armed with crowbars toppled or broke about 60 megaliths, and inscribed graffiti on them. The attack was called "the worst act of vandalism ever committed on the island of Malta" by UNESCO. The damage to the temples was initially considered irreparable, but they were restored using new techniques making it difficult to tell where the megaliths had been damaged. The temples were reopened to the public in 2002.
The 1, 2 and 5 cent Maltese euro coins
Maltese euro coins feature three separate designs for the three series of coins. Malta has been a member of the European Union since 1 May 2004, and is a member of the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union. Malta adopted the euro as it ...
, minted since 2008, bear a representation of the Mnajdra temples on their obverse side.
A protective shelter was constructed around Mnajdra (along with ń¶ań°ar Qim) in 2009.
Contemporary interpretations
Anthropologist Kathryn Rountree has explored how "Malta‚Äôs neolithic temples", including ń†gantija, "have been interpreted, contested and appropriated by different local and foreign interest groups: those working in the tourist industry, intellectuals and Maltese nationalists, hunters, archaeologists, artists, and participants in the globalGoddess movement
The Goddess movement is a Modern Paganism, revivalistic Neopagan New religious movement, religious movement which includes Spirituality, spiritual beliefs and practices that emerged primarily in the United States in the late 1960s and predominant ...
."
One source from the early years of the twenty-first century speculates that the clover-shape of Mnajdra (presumably the Upper Temple) may represent "the present, past and future (or birth, life and death)", while the solar alignment could mean that "the Sun's Male-energy is also given an honored place in these temples", and that "mother earth was represented by statuettes while father sun was venerated through this temple alignment."
Gallery
See also
*ń†gantija
ń†gantija (; "place of giants") is a megalithic temple complex from the Neolithic era (‚Äď2500 BC), on the List of islands in the Mediterranean, Mediterranean island of Gozo in Malta. The ń†gantija temples are the earliest of the Megalithic Temp ...
* ń¶ań°ar Qim
ń¶ań°ar Qim (; "Standing/Worshipping Stones") is a megalithic temple complex found on the Mediterranean island of Malta, dating from the ń†gantija phase (3600‚Äď3200 BC). The Megalithic Temples of Malta are among the most ancient religio ...
* Hypogeum of ń¶al-Saflieni
A hypogeum or hypogaeum ( ; plural hypogea or hypogaea; literally meaning "underground") is an underground temple or tomb.
Hypogea will often contain niches for cremated human remains or loculi for buried remains. Occasionally tombs of thi ...
* List of megalithic sites
This is a list of monoliths organized according to the size of the largest block of stone on the site. A monolith is a large stone which has been used to build a structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. In this list at l ...
* Tarxien Temples
The ń¶al Tarxien Prehistoric Complex ( ) is an archaeological complex in Tarxien, within the Port region of Malta. They date to approximately 3400 BC. The site was accepted as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1992 along with the other Megalithic ...
References
External links
National Inventory of the Cultural Property of the Maltese Islands
Panoramic View of Mnajdra @ Places of Interest
{{European megaliths Buildings and structures completed in the 4th millennium BC Megalithic Temples of Malta World Heritage Sites in Malta Neolithic sites Qrendi National Inventory of the Cultural Property of the Maltese Islands Sites managed by Heritage Malta