Mississippi Attorney General 2023 Election Map on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mississippi ( ) is a
 Descendant Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture in the Southeast include the
Descendant Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture in the Southeast include the
 During the
During the
 On January 9, 1861, Mississippi became the second state to declare its secession from the Union, and it was one of the founding members of the
On January 9, 1861, Mississippi became the second state to declare its secession from the Union, and it was one of the founding members of the
 In 1900, blacks made up more than half of the state's population. By 1910, a majority of black farmers in the Delta had lost their land and became
In 1900, blacks made up more than half of the state's population. By 1910, a majority of black farmers in the Delta had lost their land and became
, The Morris W. H. (Bill) Collins Speaker Series, Mississippi State University, accessed June 10, 2015 In 1966, the state was the last to repeal officially statewide In 1987, 20 years after the
In 1987, 20 years after the


 Mississippi is bordered to the north by
Mississippi is bordered to the north by
 Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 50,000 (
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 50,000 (
 The late summer and fall is the seasonal period of risk for
The late summer and fall is the seasonal period of risk for

 Mississippi is heavily forested, with over half of the state's area covered by wild or cultivated trees. The southeastern part of the state is dominated by
Mississippi is heavily forested, with over half of the state's area covered by wild or cultivated trees. The southeastern part of the state is dominated by
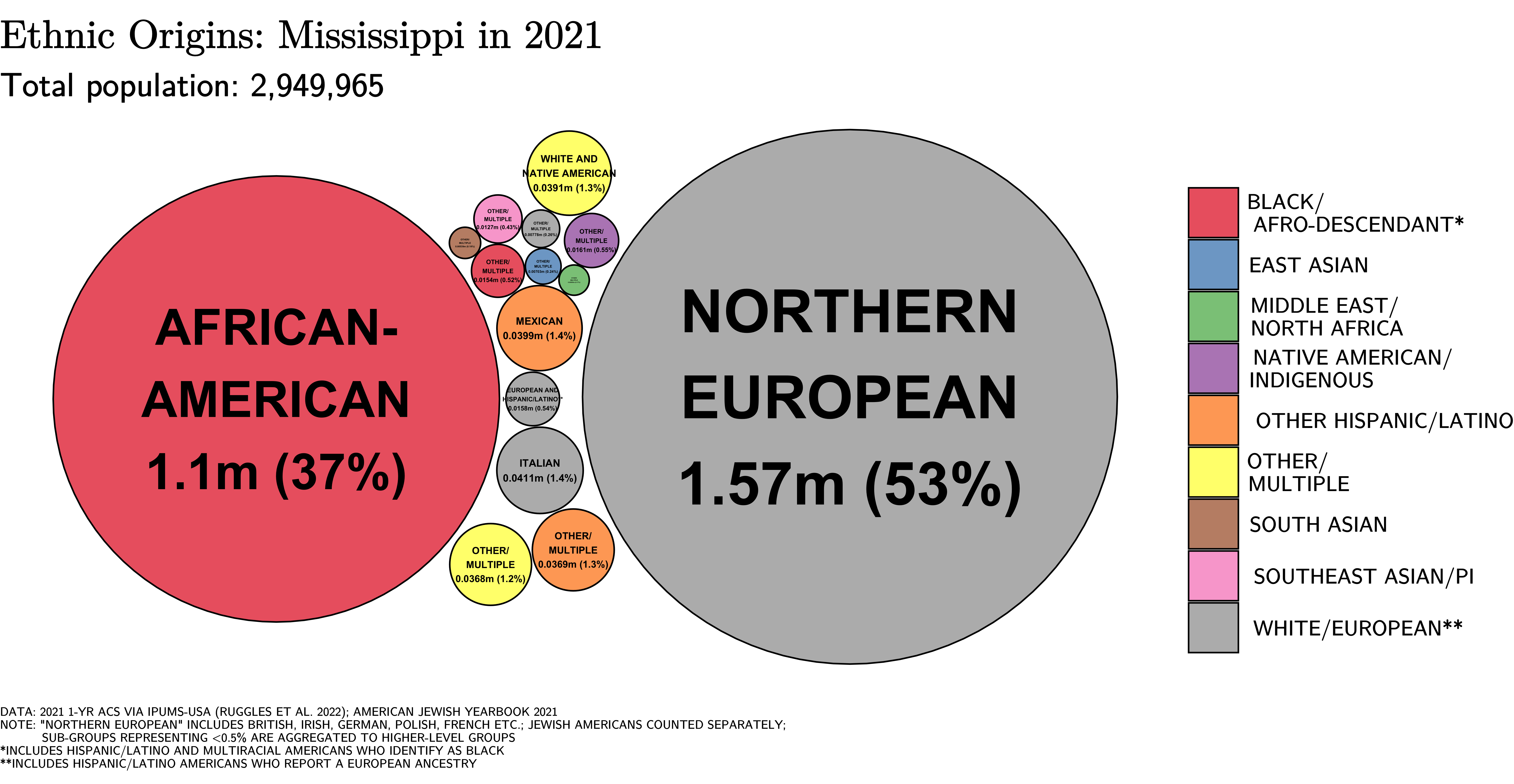
 Mississippi's population has remained from 2 million people at the 1930 U.S. census, to 2.9 million at the 2020 census. In contrast with
Mississippi's population has remained from 2 million people at the 1930 U.S. census, to 2.9 million at the 2020 census. In contrast with
''The New York Times'', March 20, 2011, accessed October 25, 2012 In addition, Mississippi led the nation for most of the last decade in the growth of mixed marriages among its population. The total population has not increased significantly, but is young. Some of the above change in identification as mixed-race is due to new births. But, it appears mostly to reflect those residents who have chosen to identify as more than one race, who in earlier years may have identified by just one race or ethnicity. A binary racial system had been in place since slavery times and the days of official government
 Americans of Scots-Irish, English and
Americans of Scots-Irish, English and
 ''Note: Births in table do not add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
*Since 2016, data for births of
''Note: Births in table do not add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
*Since 2016, data for births of
 The revivals of the
The revivals of the
 Before the Civil War, Mississippi was the fifth-wealthiest state in the nation, its wealth generated by the labor of slaves in cotton plantations along the rivers.
Slaves were counted as property and the rise in the cotton markets since the 1840s had increased their value. By 1860, a majority—55 percent—of the population of Mississippi was enslaved. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were undeveloped and the state had low overall density of population.
Largely due to the domination of the
Before the Civil War, Mississippi was the fifth-wealthiest state in the nation, its wealth generated by the labor of slaves in cotton plantations along the rivers.
Slaves were counted as property and the rise in the cotton markets since the 1840s had increased their value. By 1860, a majority—55 percent—of the population of Mississippi was enslaved. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were undeveloped and the state had low overall density of population.
Largely due to the domination of the
''Bacon's Rebellion''. The facility was shut down in January 2017. GreenTech had promised to invest $60 million in the manufacturing plant, but it produced few cars if any. A Mississippi state auditor's review begun in 2016 found documentation reflecting only $3 million spent by GreenTech on automotive assembly equipment and parts. While the company had promised to create 350 full-time jobs, it was found to never have created more than 94 active, full-time jobs in Mississippi at any time."Chinese investors sue McAuliffe, Rodham over green-car investments ,"
''Politico''. In July 2017, the Mississippi state auditor demanded that GreenTech and its CEO
''The Journal Record''. The auditor said: "I would venture that there isn’t really much of an operation in Tunica at all. This appears to have been a game of smoke and mirrors, and a corporate entity that never had any intention to deliver on the promises it made." In November 2017, Mississippi Attorney General
 As with all other U.S. states and the federal government, Mississippi's government is based on the separation of legislative, executive and judicial power. Executive authority in the state rests with the Governor, currently
As with all other U.S. states and the federal government, Mississippi's government is based on the separation of legislative, executive and judicial power. Executive authority in the state rests with the Governor, currently
 Mississippi is served by nine
Mississippi is served by nine
 *
*
 In the 21st century, 91% of white children and most of the black children in the state attend public schools. In 2008, Mississippi was ranked last among the fifty states in academic achievement by the
In the 21st century, 91% of white children and most of the black children in the state attend public schools. In 2008, Mississippi was ranked last among the fifty states in academic achievement by the
 While Mississippi has been especially known for its music and literature, it has embraced other forms of art. Its strong religious traditions have inspired striking works by
While Mississippi has been especially known for its music and literature, it has embraced other forms of art. Its strong religious traditions have inspired striking works by
online edition
* Swain, Martha H. ed. ''Mississippi Women: Their Histories, Their Lives'' (2003). 17 short biographies
Mississippi Travel and TourismMississippi Development AuthorityThe "Mississippi Believe It" CampaignUSDA Mississippi State Facts
University Press of MississippiEcoregions of MississippiMississippi as Metaphor State, Region, and Nation in Historical Imagination
, ''Southern Spaces'', October 23, 2006. *
Mississippi State Databases
an annotated list of searchable databases compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association. {{coord, 33, -90, dim:300000_region:US-MS_type:adm1st, name=State of Mississippi, display=title 1817 establishments in the United States Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former French colonies Southern United States States and territories established in 1817 States of the Confederate States of America States of the Gulf Coast of the United States States of the United States Contiguous United States
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
in the Southeastern and Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
to the north, Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
to the east, the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
to the south, Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
to the southwest, and Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
to the northwest. Mississippi's western boundary is largely defined by the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
, or its historical course. Mississippi is the 32nd largest by area and 35th-most populous of the 50 U.S. states and has the lowest per-capita income. Jackson
Jackson may refer to:
Places Australia
* Jackson, Queensland, a town in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson North, Queensland, a locality in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson South, Queensland, a locality in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson oil field in Durham, ...
is both the state's capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
and largest city. Greater Jackson is the state's most populous metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region consisting of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories which share Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport network ...
, with a population of 591,978 in 2020. Other major cities include Gulfport, Southaven
Southaven is a city in DeSoto County, Mississippi, United States. It is a principal city in Greater Memphis. The 2020 census reported a population of 54,648, making it the 3rd most populous city in Mississippi and the largest suburb of Memp ...
, Hattiesburg
Hattiesburg is a city in the U.S. state of Mississippi, located primarily in Forrest County (where it is the county seat and most populous city) and extending west into Lamar County. The city population was 48,730 in 2020, making it the 5th m ...
, Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. It lies on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, bordering the city of Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport to its west. The adjacent cities ar ...
, Olive Branch
The olive branch, a ramus of '' Olea europaea'', is a symbol of peace. It is generally associated with the customs of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, and is connected with supplication to divine beings and persons in power. Likewise, it is f ...
, Tupelo
Tupelo commonly refers to:
* Tupelo (tree), a small genus of deciduous trees with alternate, simple leaves
* Tupelo, Mississippi, the county seat and the largest city of Lee County, Mississippi
Tupelo may also refer to:
Places
* Tupelo, Arka ...
, Meridian, and Greenville.
The state's history traces back to around 9500 BC with the arrival of Paleo-Indians
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in ...
, evolving through periods marked by the development of agricultural societies, rise of the Mound Builders
Many pre-Columbian cultures in North America were collectively termed "Mound Builders", but the term has no formal meaning. It does not refer to specific people or archaeological culture but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks that in ...
, and flourishing of the Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building la ...
. European exploration began with the Spanish in the 16th century, followed by French colonization in the 17th century. Mississippi's strategic location along the Mississippi River made it a site of significant economic and strategic importance, especially during the era of cotton plantation agriculture, which led to its wealth pre-Civil War, but entrenched slavery and racial segregation. On December 10, 1817, Mississippi became the 20th state admitted to the Union. By 1860, Mississippi was the nation's top cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
-producing state and slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
accounted for 55% of the state population. Mississippi declared its secession
Secession is the formal withdrawal of a group from a Polity, political entity. The process begins once a group proclaims an act of secession (such as a declaration of independence). A secession attempt might be violent or peaceful, but the goal i ...
from the Union on January 9, 1861, and was one of the seven original Confederate States
The Confederate States of America (CSA), also known as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or Dixieland, was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States from 1861 to 1865. It comprised eleven U.S. states th ...
, which constituted the largest slaveholding states in the nation. Following the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
, it was restored to the Union on February 23, 1870. Mississippi's political and social landscape was dramatically shaped by the Civil War, Reconstruction era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abol ...
, and civil rights movement, with the state playing a pivotal role in the struggle for civil rights. From the Reconstruction era to the 1960s, Mississippi was dominated by socially conservative
Social conservatism is a political philosophy and a variety of conservatism which places emphasis on traditional social structures over social pluralism. Social conservatives organize in favor of duty, traditional values and social institu ...
and segregationist
Racial segregation is the separation of people into racial or other ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, such as schools and hospitals by peopl ...
Southern Democrats
Southern Democrats are members of the U.S. Democratic Party who reside in the Southern United States.
Before the American Civil War, Southern Democrats mostly believed in Jacksonian democracy. In the 19th century, they defended slavery in the ...
dedicated to upholding white supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
.
Despite progress, Mississippi continues to grapple with challenges related to health, education, and economic development, often ranking among the lowest in the United States in national metrics for wealth, health care quality, and educational attainment. Economically, it relies on agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, manufacturing, and an increasing focus on tourism, highlighted by its casinos and historical sites. Mississippi produces more than half of the country's farm-raised catfish, and is a top producer of sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its sizeable, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable, which is a staple food in parts of ...
es, cotton and pulpwood
Pulpwood can be defined as timber that is ground and processed into a fibrous pulp. It is a versatile natural resource commonly used for Papermaking, paper-making but also made into low-grade wood and used for chips, energy, pellets, and engineered ...
. Others include advanced manufacturing, utilities
A public utility company (usually just utility) is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service (often also providing a service using that infrastructure). Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and r ...
, transport
Transport (in British English) or transportation (in American English) is the intentional Motion, movement of humans, animals, and cargo, goods from one location to another. Mode of transport, Modes of transport include aviation, air, land tr ...
ation, and health services
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
. Mississippi is almost entirely within the east Gulf Coastal Plain
The Gulf Coastal Plain extends around the Gulf of Mexico in the Southern United States and eastern Mexico.
This coastal plain reaches from the Florida Panhandle, southwest Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, the southern two-thirds of Alabama, over m ...
, and generally consists of lowland
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland.
Definitions
Upland and lowland are portions of a ...
plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ...
s and low hills. The northwest remainder of the state consists of the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazo ...
. Mississippi's highest point is Woodall Mountain
Woodall Mountain is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Mississippi at 806 feet (246 m). It is located just off Mississippi Highway 25, south of Iuka in Tishomingo County in the northeast part of the state and is part of the Appala ...
at 807 feet (246 m) above sea level adjacent to the Cumberland Plateau
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms " Al ...
; the lowest is the Gulf of Mexico. Mississippi has a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
classification.
Mississippi is known for its deep religious roots, which play a central role in its residents' lives. The state ranks among the highest of U.S. states
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its so ...
in religiosity
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' defines religiosity as: "Religiousness; religious feeling or belief. ..Affected or excessive religiousness". Different scholars have seen this concept as broadly about religious orientations and degrees of inv ...
. Mississippi is also known for being the state with the highest proportion of African-American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa. ...
residents. The state's governance structure is based on the traditional separation of powers, with political trends showing a strong alignment with conservative values. Mississippi boasts a rich cultural heritage, especially in music, being the birthplace of the blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
and contributing significantly to the development of the music of the United States
The United States' multi-ethnic population is reflected through a diverse array of styles of music. It is a mixture of music influenced by the music of Europe, Indigenous peoples, West Africa, Latin America, Middle East, North Africa, amongst ...
as a whole.
Etymology
The state's name is derived from theMississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
, which flows along and defines its western boundary. European-American settlers named it after the Ojibwe
The Ojibwe (; Ojibwe writing systems#Ojibwe syllabics, syll.: ᐅᒋᐺ; plural: ''Ojibweg'' ᐅᒋᐺᒃ) are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland (''Ojibwewaki'' ᐅᒋᐺᐘᑭ) covers much of the Great Lakes region and the Great Plains, n ...
word ().
History
Near 9500 BC Native Americans orPaleo-Indians
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in ...
arrived in what today is referred to as the American South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is census regions United States Census Bureau. It is between the Atlantic Ocean and the ...
.
Paleo-Indians in the South were hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s who pursued the megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
that became extinct following the end of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
age. In the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazo ...
, Native American settlements and agricultural fields were developed on the natural levees, higher ground in the proximity of rivers. The Native Americans developed extensive fields near their permanent villages. Together with other practices, they created some localized deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
but did not alter the ecology of the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazo ...
as a whole.
After thousands of years, succeeding cultures of the Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunli ...
and Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building la ...
eras developed rich and complex agricultural societies, in which surplus supported the development of specialized trades. Both were mound builder
Many pre-Columbian cultures in North America were collectively termed "Mound Builders", but the term has no formal meaning. It does not refer to specific people or archaeological culture but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks that in ...
cultures. Those of the Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building la ...
were the largest and most complex, constructed beginning about 950 AD. The peoples had a trading network spanning the continent from the Great Lakes to the Gulf Coast. Their large earthworks, which expressed their cosmology of political and religious concepts, still stand throughout the Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
and Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
valleys.
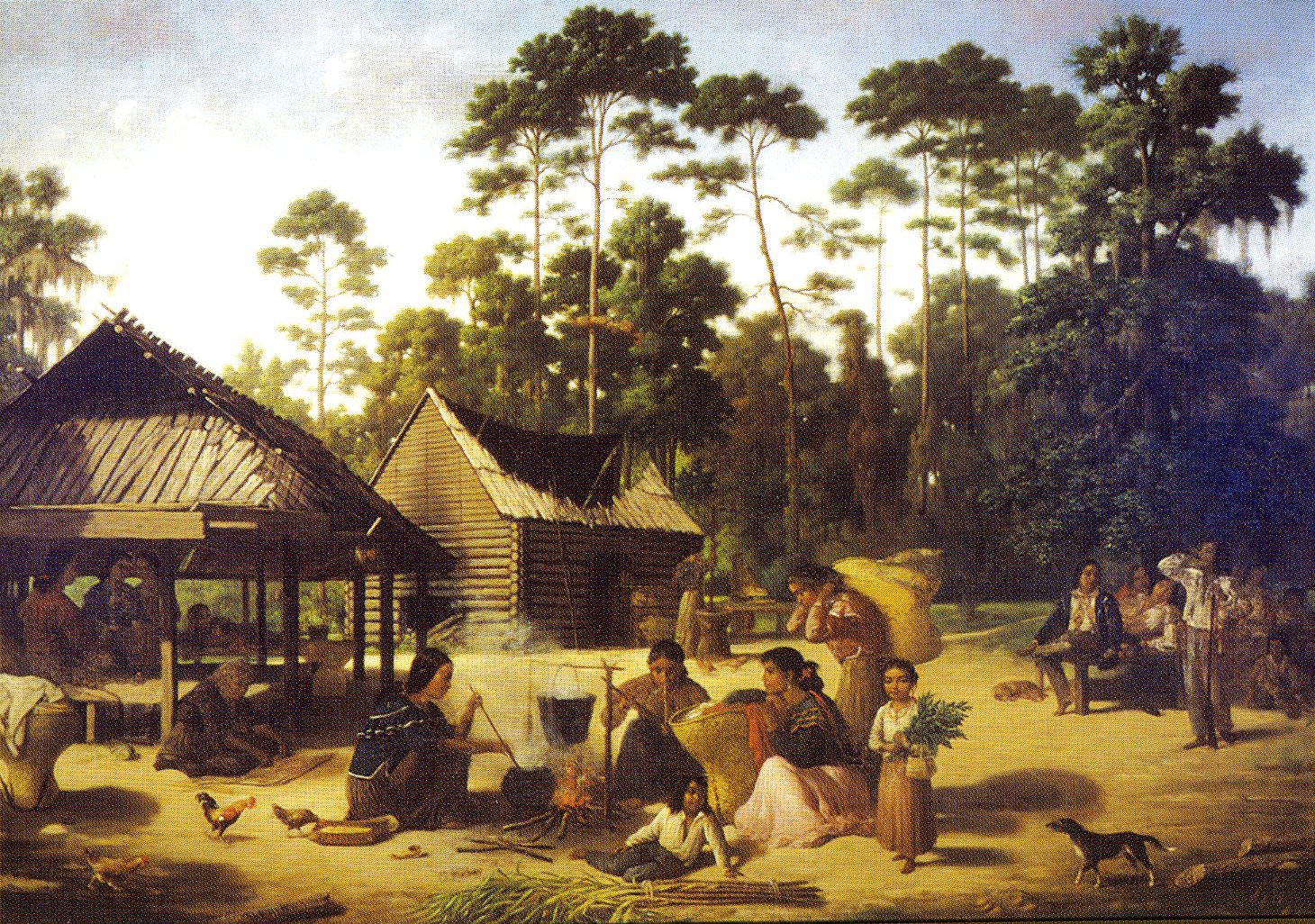
 Descendant Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture in the Southeast include the
Descendant Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture in the Southeast include the Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, United States. Their traditional territory was in northern Mississippi, northwestern and northern Alabama, western Tennessee and southwestern Kentucky. Their language is ...
and Choctaw
The Choctaw ( ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States, originally based in what is now Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama. The Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choct ...
. Other tribes who inhabited the territory of Mississippi (and whose names were honored by colonists in local towns) include the Natchez, the Yazoo, and the Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. It lies on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, bordering the city of Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport to its west. The adjacent cities ar ...
.
The first major European expedition into the territory that became Mississippi was that of the Spanish explorer, Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1497 – 21 May 1542) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, ...
, who passed through the northeast part of the state in 1540, in his second expedition to the New World.
Colonial era
In April 1699, French colonists established the first European settlement at ''Fort Maurepas
Fort Maurepas, later known as Old Biloxi,
"Pierre Le Moyne, Sieur d'Iberville" (biography),
''Catholic Encyclopedia'', 1907, webpage:
gives dates: 13 Feb. 1699, went to the mainland Biloxi,
with fort completion May 1, 1699; sailed f ...
'' (also known as Old Biloxi), built in the vicinity of present-day Ocean Springs
Ocean Springs is a city in Jackson County, Mississippi, United States, approximately east of Biloxi and west of Gautier. It is part of the Pascagoula metropolitan area. The population was 18,429 at the 2020 U.S Census, down from 18,434 in 201 ...
on the Gulf Coast. It was settled by Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville
Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (16 July 1661 – 9 July 1706) or Sieur d'Iberville was a French soldier, explorer, colonial administrator, and trader. He is noted for founding the colony of Louisiana in New France. He was born in Montreal to French ...
. In 1716, the French founded Natchez on the Mississippi River (as '' Fort Rosalie''); it became the dominant town and trading post of the area. The French called the greater territory "New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
"; the Spanish continued to claim part of the Gulf coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South or the South Coast, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Tex ...
area (east of Mobile Bay
Mobile Bay ( ) is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. T ...
) of present-day southern Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
, in addition to the entire area of present-day Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
. The British assumed control of the French territory after the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
.
 During the
During the colonial era Colonial period (a period in a country's history where it was subject to management by a colonial power) may refer to:
Continents
*European colonization of the Americas
* Colonisation of Africa
* Western imperialism in Asia
Countries
* Col ...
, European (chiefly French and Spanish) settlers imported enslaved Africans
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were once commonplace in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the rest of the Ancient history, ancient and Post-classical history, medieval world. When t ...
to work on cash crop plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
s. Under French and Spanish rule, there developed a class of free people of color
In the context of the history of slavery in the Americas, free people of color (; ) were primarily people of mixed African, European, and Native American descent who were not enslaved. However, the term also applied to people born free who we ...
(''gens de couleur libres''), mostly multiracial
The term multiracial people refers to people who are mixed with two or more
races (human categorization), races and the term multi-ethnic people refers to people who are of more than one ethnicity, ethnicities. A variety of terms have been used ...
descendants of European men and enslaved or free black women, and their mixed-race
The term multiracial people refers to people who are mixed with two or more
races and the term multi-ethnic people refers to people who are of more than one ethnicities. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mul ...
children. In the early days the French and Spanish colonists were chiefly men. Even as more European women joined the settlements, the men had interracial unions among women of African descent (and increasingly, multiracial descent), both before and after marriages to European women. Often the European men would help their multiracial children get educated or gain apprenticeships for trades, and sometimes they settled property on them; they often freed the mothers and their children if enslaved, as part of contracts of ''plaçage
Plaçage was a recognized extralegal system in French slave colonies of North America (including the Caribbean) by which ethnic European men entered into civil unions with non-Europeans of African, Native American and mixed-race descent. The term ...
''. With this social capital
Social capital is a concept used in sociology and economics to define networks of relationships which are productive towards advancing the goals of individuals and groups.
It involves the effective functioning of social groups through interper ...
, the free people of color became artisans, and sometimes educated merchants and property owners, forming a third class between the Europeans and most enslaved Africans in the French and Spanish settlements, although not so large a free community as in the city of New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
, Louisiana.
After Great Britain's victory in the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
(Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
), the French surrendered the Mississippi area to them under the terms of the Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Kingdom of France, France and Spanish Empire, Spain, with Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal in agree ...
. They also ceded their areas to the north that were east of the Mississippi River, including the Illinois Country and Quebec. After the Peace of Paris (1783)
The Peace of Paris of 1783 was the set of treaties that ended the American Revolutionary War. On 3 September 1783, representatives of King George III of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain signed a treaty in Paris with representatives of the ...
, the lower third of Mississippi came under Spanish rule as part of West Florida
West Florida () was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. Great Britain established West and East Florida in 1763 out of land acquired from France and S ...
. In 1819 the United States completed the purchase of West Florida and all of East Florida
East Florida () was a colony of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of the Spanish Empire from 1783 to 1821. The British gained control over Spanish Florida in 1763 as part of the Treaty of Paris (1763), Tre ...
in the Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Spanish Cession, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p. 168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to ...
, and in 1822 both were merged into the Florida Territory
The Territory of Florida was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 30, 1822, until March 3, 1845, when it was admitted to the Union as the state of Florida. Originally the major portion of the Spanish ...
.
United States territory
After theAmerican Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
(1775–83), Britain ceded this area to the new United States of America. The Mississippi Territory
The Territory of Mississippi was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that was created under an organic act passed by the United States Congress, Congress of the United States. It was approved and signed into law by Presiden ...
was organized on April 7, 1798, from territory ceded by Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
and South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
to the United States. Their original colonial charters theoretically extended west to the Pacific Ocean. The Mississippi Territory was later twice expanded to include disputed territory claimed by both the United States and Spain.
From 1800 to about 1830, the United States purchased some lands (Treaty of Doak's Stand
The Treaty of Doak's Stand (7 Stat. 210, also known as Treaty with the Choctaw) was signed on October 18, 1820 (proclaimed and legally binding on January 8, 1821) between the United States and the Choctaw Indian tribe. The Treaty of Doak's Stan ...
) from Native American tribes for new settlements of European Americans. The latter were mostly migrants from other Southern states, particularly Virginia and North Carolina, where soils were exhausted. New settlers kept encroaching on Choctaw land, and they pressed the federal government to expel the Native Americans. On September 27, 1830, the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek
The Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek was a treaty which was signed on September 27, 1830, and proclaimed on February 24, 1831, between the Choctaw American Indian tribe and the United States government. This treaty was the first removal treaty wh ...
was signed between the U.S. Government and the Choctaw
The Choctaw ( ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States, originally based in what is now Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama. The Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choct ...
. The Choctaw agreed to sell their traditional homelands in Mississippi and Alabama, for compensation and removal to reservations in Indian Territory
Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United States, ...
(now Oklahoma). This opened up land for sale to European-American
European Americans are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes both people who descend from the first European settlers in the area of the present-day United States and people who descend from more recent European arrivals. Since th ...
migrant settlement.
Article 14 in the treaty allowed those Choctaw who chose to remain in the states to become U.S. citizens, as they were considered to be giving up their tribal membership. They were the second major Native American ethnic group to do so (some Cherokee were the first, who chose to stay in North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
and other areas during rather than join the removal).
Today their descendants include approximately 9,500 persons identifying as Choctaw, who live in Neshoba, Newton, Leake, and Jones counties. The Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians
The Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians () is one of three federally recognized tribes of Choctaw, an indigenous Indian people, and the only one in the state of Mississippi. On April 20, 1945, this tribe was organized under the Indian Reorgan ...
reorganized in the 20th century and is a Federally recognized tribe.
Many slaveholders brought enslaved African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
with them or purchased them through the domestic slave trade, especially in New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
. Through the trade, an estimated nearly one million slaves were forcibly transported to the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
, including Mississippi, in an internal migration that broke up many slave families of the Upper South, where planters
Planters Nut & Chocolate Company is an American snack food company now owned by Hormel Foods. Planters is best known for its processed nuts and for the Mr. Peanut icon that symbolizes them. Mr. Peanut was created by grade schooler Antonio Gent ...
were selling excess slaves. The Southerners imposed slave laws in the Deep South and restricted the rights of free blacks.
Beginning in 1822, slaves in Mississippi were protected by law from cruel and unusual punishment by their owners. The Southern slave codes
The slave codes were laws relating to slavery and enslaved people, specifically regarding the Atlantic slave trade and chattel slavery in the Americas.
Most slave codes were concerned with the rights and duties of free people in regards to ensla ...
made the willful killing of a slave illegal in most cases. For example, the 1860 Mississippi case of ''Oliver v. State'' charged the defendant with murdering his own slave.
Statehood to Civil War
Mississippi became the 20th state on December 10, 1817. David Holmes was the first governor. The state was still occupied as ancestral land by several Native American tribes, including Choctaw, Natchez, Houma, Creek, and Chickasaw. Plantations were developed primarily along the major rivers, where the waterfront provided access to the major transportation routes. This is also where early towns developed, linked by thesteamboats
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. The term ''steamboat'' is used to refer to small steam-powered vessels worki ...
that carried commercial products and crops to markets. The remainder of Native American ancestral land remained largely undeveloped but was sold through treaties until 1826, when the Choctaws and Chickasaws refused to sell more land. The combination of the Mississippi state legislature's abolition of Choctaw Tribal Government in 1829, President Andrew Jackson's Indian Removal Act
The Indian Removal Act of 1830 was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States president Andrew Jackson. The law, as described by Congress, provided "for an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, ...
and the Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek
The Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek was a treaty which was signed on September 27, 1830, and proclaimed on February 24, 1831, between the Choctaw American Indian tribe and the United States government. This treaty was the first removal treaty wh ...
of 1830, the Choctaw were effectively forced to sell their land and were transported to Oklahoma Territory. The forced migration of the Choctaw, together with other southeastern tribes removed as a result of the Act, became known as the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was the forced displacement of about 60,000 people of the " Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850, and the additional thousands of Native Americans and their black slaves within that were ethnically cleansed by the U ...
.
When cotton was king during the 1850s, Mississippi plantation owners—especially those of the Delta and Black Belt central regions—became wealthy due to the high fertility of the soil, the high price of cotton on the international market, and free labor gained through their holding enslaved African Americans. They used some of their profits to buy more cotton land and more slaves. The planters' dependence on hundreds of thousands of slaves for labor and the severe wealth imbalances among whites, played strong roles both in state politics and in planters' support for secession
Secession is the formal withdrawal of a group from a Polity, political entity. The process begins once a group proclaims an act of secession (such as a declaration of independence). A secession attempt might be violent or peaceful, but the goal i ...
. Mississippi was a slave society, with the economy dependent on slavery. The state was thinly settled, with population concentrated in the riverfront areas and towns.
By 1860, the enslaved African-American population numbered 436,631 or 55% of the state's total of 791,305 persons. Fewer than 1000 were free people of color
In the context of the history of slavery in the Americas, free people of color (; ) were primarily people of mixed African, European, and Native American descent who were not enslaved. However, the term also applied to people born free who we ...
. The relatively low population of the state before the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
reflected the fact that land and villages were developed only along the riverfronts, which formed the main transportation corridors. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were still frontier and undeveloped.John C. Willis, ''Forgotten Time: The Yazoo-Mississippi Delta after the Civil War''. Charlottesville: University of Virginia Press, 2000, . The state needed many more settlers for development. The land further away from the rivers was cleared by freedmen and white migrants during Reconstruction and later.
Civil War through late 19th century
 On January 9, 1861, Mississippi became the second state to declare its secession from the Union, and it was one of the founding members of the
On January 9, 1861, Mississippi became the second state to declare its secession from the Union, and it was one of the founding members of the Confederate States
The Confederate States of America (CSA), also known as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or Dixieland, was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States from 1861 to 1865. It comprised eleven U.S. states th ...
. The first six states to secede were those with the highest number of slaves. During the war, Union and Confederate forces struggled for dominance on the Mississippi River, critical to supply routes and commerce. More than 80,000 Mississippians fought in the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
for the Confederate Army
The Confederate States Army (CSA), also called the Confederate army or the Southern army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fi ...
. Around 17,000 black and 545 white Mississippians would serve in the Union Army. Pockets of Unionism in Mississippi were in places such as the northeastern corner of the state and Jones County, where Newton Knight formed a revolt with Unionist leanings, known as the "Free State of Jones". Union General Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
's long siege of Vicksburg finally gained the Union control of the river in 1863.
In the postwar period, freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, slaves were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their owners), emancipation (granted freedom as part of a larger group), or self- ...
withdrew from white-run churches to set up independent congregations. The majority of blacks left the Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC), alternatively the Great Commission Baptists (GCB), is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist organization, the largest Protestant, and the second-largest Chr ...
, sharply reducing its membership. They created independent black Baptist congregations. By 1895 they had established numerous black Baptist state associations and the National Baptist Convention of black churches.
In addition, independent black denominations, such as the African Methodist Episcopal Church
The African Methodist Episcopal Church, usually called the AME Church or AME, is a Methodist denomination based in the United States. It adheres to Wesleyan theology, Wesleyan–Arminian theology and has a connexionalism, connexional polity. It ...
(established in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
in the early 19th century) and the African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church
The African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church, or the AME Zion Church (AMEZ) is a historically African-American Christian denomination based in the United States. It was officially formed in 1821 in New York City, but operated for a number of y ...
(established in New York City), sent missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group who is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Miss ...
to the South in the postwar years. They quickly attracted hundreds of thousands of converts and founded new churches across the South. Southern congregations brought their own influences to those denominations as well.
During Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Union ...
, the first Mississippi constitutional convention in 1868, with delegates both black and white, framed a constitution whose major elements would be maintained for 22 years. The convention was the first political organization in the state to include African-American representatives, 17 among the 100 members (32 counties had black majorities at the time). Some among the black delegates were freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, slaves were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their owners), emancipation (granted freedom as part of a larger group), or self- ...
, but others were educated free blacks who had migrated from the North. The convention adopted universal suffrage; did away with property qualifications for suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to v ...
or for office, a change that also benefited both blacks and poor whites; provided for the state's first public school system; forbade race distinctions in the possession and inheritance of property; and prohibited limiting civil rights in travel. Under the terms of Reconstruction, Mississippi was restored to the Union on February 23, 1870.
Because the Mississippi Delta contained so much fertile bottomland that had not been developed before the American Civil War, 90 percent of the land was still frontier. After the Civil War, tens of thousands of migrants were attracted to the area by higher wages offered by planters trying to develop land. In addition, black and white workers could earn money by clearing the land and selling timber, and eventually advance to ownership. The new farmers included many freedmen, who by the late 19th century achieved unusually high rates of land ownership in the Mississippi bottomlands. In the 1870s and 1880s, many black farmers succeeded in gaining land ownership.
Around the start of the 20th century, two-thirds of the Mississippi farmers who owned land in the Delta were African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
. But many had become overextended with debt during the falling cotton prices of the difficult years of the late 19th century. Cotton prices fell throughout the decades following the Civil War. As another agricultural depression lowered cotton prices into the 1890s, numerous African-American farmers finally had to sell their land to pay off debts, thus losing the land which they had developed by hard, personal labor.
Democrats had regained control of the state legislature in 1875, after a year of expanded violence against blacks and intimidation of whites in what was called the "white line" campaign, based on asserting white supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
. Democratic whites were well armed and formed paramilitary
A paramilitary is a military that is not a part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. The Oxford English Dictionary traces the use of the term "paramilitary" as far back as 1934.
Overview
Though a paramilitary is, by definiti ...
organizations such as the Red Shirts to suppress black voting. From 1874 to the elections of 1875, they pressured whites to join the Democrats, and conducted violence against blacks in at least 15 known "riots" in cities around the state to intimidate blacks. They killed a total of 150 blacks, although other estimates place the death toll at twice as many. A total of three white Republicans and five white Democrats were reported killed. In rural areas, deaths of blacks could be covered up. Riots (better described as massacres of blacks) took place in Vicksburg, Clinton, Macon, and in their counties, as well-armed whites broke up black meetings and lynched
Lynching is an extrajudicial killing by a group. It is most often used to characterize informal public executions by a mob in order to punish an alleged or convicted transgressor or to intimidate others. It can also be an extreme form of in ...
known black leaders, destroying local political organizations. Seeing the success of this deliberate "Mississippi Plan
The Mississippi Plan of 1874–1875 was developed by white Southern Democrats as part of the white insurgency during the Reconstruction era in the Southern United States. It was devised by the Democratic Party in that state to overthrow the Repub ...
", South Carolina and other states followed it and also achieved white Democratic dominance. In 1877 by a national compromise, the last of federal troops were withdrawn from the region.
Even in this environment, black Mississippians continued to be elected to local office. However, black residents were deprived of all political power after white legislators passed a new state constitution in 1890 specifically to "eliminate the nigger from politics", according to the state's Democratic governor, James K. Vardaman. It erected barriers to voter registration and instituted electoral provisions that effectively disenfranchised
Disfranchisement, also disenfranchisement (which has become more common since 1982) or voter disqualification, is the restriction of suffrage (the right to vote) of a person or group of people, or a practice that has the effect of preventing someo ...
most black Mississippians and many poor whites. Estimates are that 100,000 black and 50,000 white men were removed from voter registration rolls in the state over the next few years.
The loss of political influence contributed to the difficulties of African Americans in their attempts to obtain extended credit in the late 19th century. Together with imposition of Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced racial segregation, " Jim Crow" being a pejorative term for an African American. The last of the ...
and racial segregation laws, whites increased violence against blacks, with lynchings occurring through the period of the 1890s and extending to 1930.
20th century to present
 In 1900, blacks made up more than half of the state's population. By 1910, a majority of black farmers in the Delta had lost their land and became
In 1900, blacks made up more than half of the state's population. By 1910, a majority of black farmers in the Delta had lost their land and became sharecropper
Sharecropping is a legal arrangement in which a landowner allows a tenant (sharecropper) to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on that land. Sharecropping is not to be conflated with tenant farming, providing the tenant a ...
s. By 1920, the third generation after freedom, most African Americans in Mississippi were landless laborers again facing poverty. Starting about 1913, tens of thousands of black Americans left Mississippi for the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
in the Great Migration to industrial cities such as St. Louis
St. Louis ( , sometimes referred to as St. Louis City, Saint Louis or STL) is an independent city in the U.S. state of Missouri. It lies near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a populatio ...
, Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, Detroit
Detroit ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Michigan, most populous city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated on the bank of the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario. It had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 United State ...
, Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
, Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
and New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. They sought jobs, better education for their children, the right to vote, relative freedom from discrimination, and better living. In the migration of 1910–1940, they left a society that had been steadily closing off opportunity. Most migrants from Mississippi took trains directly north to Chicago and often settled near former neighbors.
Cotton crops failed due to boll weevil
The boll weevil (''Anthonomus grandis'') is a species of beetle in the family Curculionidae. The boll weevil
feeds on cotton buds and flowers. Thought to be native to Central Mexico, it migrated into the United States from Mexico in the late 19 ...
infestation and successive severe flooding in 1912 and 1913, creating crisis conditions for many African Americans. With control of the ballot box and more access to credit, white planters bought out such farmers, expanding their ownership of Delta bottomlands. They also took advantage of new railroads sponsored by the state. Blacks also faced violence in the form of lynching, shooting, and the burning of churches. In 1923, the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) is an American civil rights organization formed in 1909 as an interracial endeavor to advance justice for African Americans by a group including W. E. B. Du&nbs ...
stated "the Negro feels that life is not safe in Mississippi and his life may be taken with impunity at any time upon the slightest pretext or provocation by a white man".
In the early 20th century, some industries were established in Mississippi, but jobs were generally restricted to whites, including child workers. The lack of jobs also drove some southern whites north to cities such as Chicago and Detroit, seeking employment, where they also competed with European immigrants. The state depended on agriculture, but mechanization put many farm laborers out of work.
By 1900, many white ministers, especially in the towns, subscribed to the Social Gospel
The Social Gospel is a social movement within Protestantism that aims to apply Christian ethics to social problems, especially issues of social justice such as economic inequality, poverty, alcoholism, crime, racial tensions, slums, unclean en ...
movement, which attempted to apply Christian ethics to social and economic needs of the day. Many strongly supported Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic b ...
, believing it would help alleviate and prevent many sins. Mississippi became a dry state
A dry state was a state in the United States in which the manufacture, distribution, importation, and sale of alcoholic beverages was prohibited or tightly restricted. Some states, such as North Dakota, entered the United States as dry states, and ...
in 1908 by an act of the state legislature
A state legislature is a Legislature, legislative branch or body of a State (country subdivision), political subdivision in a Federalism, federal system.
Two federations literally use the term "state legislature":
* The legislative branches of ...
. It remained dry until the legislature passed a local option
A local option is the ability of local political jurisdictions, typically counties or municipalities, to allow decisions on certain controversial issues within their borders, usually referring to a popular vote. It usually relates to the issue of ...
bill in 1966.
African-American Baptist churches grew to include more than twice the number of members as their white Baptist counterparts. The African-American call for social equality resonated throughout the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
in the 1930s and World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
in the 1940s.
The Second Great Migration from the South started in the 1940s, lasting until 1970. Almost half a million people left Mississippi in the second migration, three-quarters of them black. Nationwide during the first half of the 20th century, African Americans became rapidly urbanized and many worked in industrial jobs. The Second Great Migration included destinations in the West
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
, especially California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, where the buildup of the defense industry offered higher-paying jobs to both African Americans and whites.
Blacks and whites in Mississippi generated rich, quintessentially American music traditions: gospel music
Gospel music is a traditional genre of Christian music and a cornerstone of Christian media. The creation, performance, significance, and even the definition of gospel music vary according to culture and social context. Gospel music is compo ...
, country music
Country (also called country and western) is a popular music, music genre originating in the southern regions of the United States, both the American South and American southwest, the Southwest. First produced in the 1920s, country music is p ...
, jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
, blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
and rock and roll
Rock and roll (often written as rock & roll, rock-n-roll, and rock 'n' roll) is a Genre (music), genre of popular music that evolved in the United States during the late 1940s and early 1950s. It Origins of rock and roll, originated from African ...
. All were invented, promulgated or heavily developed by Mississippi musicians, many of them African American, and most came from the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazo ...
. Many musicians carried their music north to Chicago, where they made it the heart of that city's jazz and blues.
So many African Americans left in the Great Migration that after the 1930s, they became a minority in Mississippi. In 1960 they made up 42% of the state's population. The whites maintained their discriminatory voter registration processes established in 1890, preventing most blacks from voting, even if they were well educated. Court challenges were not successful until later in the century. After World War II, African-American veterans returned with renewed commitment to be treated as full citizens of the United States and increasingly organized to gain enforcement of their constitutional rights.
The Civil Rights movement had many roots in religion, and the strong community of churches helped supply volunteers and moral purpose for their activism. Mississippi was a center of activity, based in black churches, to educate and register black voters, and to work for integration. In 1954 the state had created the Mississippi State Sovereignty Commission
The Mississippi State Sovereignty Commission (also called the MSSC or Sov-Com) was a state agency in Mississippi active from 1956 to 1973 and tasked with fighting integration and controlling civil rights activism. It was overseen by the List of G ...
, a tax-supported agency, chaired by the Governor, that claimed to work for the state's image but effectively spied on activists and passed information to the local White Citizens' Councils to suppress black activism. White Citizens Councils
The White Citizens' Councils were an associated network of white supremacist, segregationist organizations in the United States, concentrated in the South and created as part of a white backlash against the US Supreme Court's landmark ''Brown v ...
had been formed in many cities and towns to resist integration of schools following the unanimous 1954 United States Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that turn on question ...
ruling (''Brown v. Board of Education
''Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the ...
'') that segregation of public schools was unconstitutional. They used intimidation and economic blackmail against activists and suspected activists, including teachers and other professionals. Techniques included loss of jobs and eviction from rental housing.
In the summer of 1964 students and community organizers from across the country came to help register black voters in Mississippi and establish Freedom Schools
Freedom Schools were temporary, alternative, and free schools for African Americans mostly in the South. They were originally part of a nationwide effort during the Civil Rights Movement to organize African Americans to achieve social, political a ...
. The Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party
The Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party (MFDP), also referred to simply as the Freedom Democratic Party, was an American political party that existed in the state of Mississippi from 1964 to 1968 during the Civil Rights Movement. Created as t ...
was established to challenge the all-white Democratic Party of the Solid South
The Solid South was the electoral voting bloc for the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party in the Southern United States between the end of the Reconstruction era in 1877 and the Civil Rights Act of 1964. In the aftermath of the Co ...
. Most white politicians resisted such changes. Chapters of the Ku Klux Klan
The Ku Klux Klan (), commonly shortened to KKK or Klan, is an American Protestant-led Christian terrorism, Christian extremist, white supremacist, Right-wing terrorism, far-right hate group. It was founded in 1865 during Reconstruction era, ...
and its sympathizers used violence against activists, most notably the murders of Chaney, Goodman, and Schwerner
On June 21, 1964, three Civil Rights Movement activists, James Chaney, Andrew Goodman, and Michael Schwerner, were murdered by local members of the Ku Klux Klan. They had been arrested earlier in the day for speeding, and after being releas ...
in 1964 during the Freedom Summer
Freedom Summer, also known as Mississippi Freedom Summer (sometimes referred to as the Freedom Summer Project or the Mississippi Summer Project), was a campaign launched by civil rights movement, American civil rights activists in June 1964 to r ...
campaign. This was a catalyst for Congressional passage the following year of the Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights move ...
. Mississippi earned a reputation in the 1960s as a reactionary state.
After decades of disenfranchisement, African Americans in the state gradually began to exercise their right to vote again for the first time since the 19th century, following the passage of federal civil rights legislation in 1964 and 1965, which ended ''de jure'' segregation and enforced constitutional voting rights. Registration of African-American voters increased and black candidates ran in the 1967 elections for state and local offices. The Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party fielded some candidates. Teacher Robert G. Clark of Holmes County was the first African American to be elected to the State House since Reconstruction. He continued as the only African American in the state legislature until 1976 and was repeatedly elected into the 21st century, including three terms as Speaker of the House."Robert G. Clark, 26 October 2000 (video)", The Morris W. H. (Bill) Collins Speaker Series, Mississippi State University, accessed June 10, 2015 In 1966, the state was the last to repeal officially statewide
prohibition of alcohol
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic b ...
. Before that, Mississippi had taxed the illegal alcohol brought in by bootleggers. Governor Paul Johnson urged repeal and the sheriff "raided the annual Junior League
The Association of Junior Leagues International, Inc. (Junior League or JL) is a private, nonprofit educational women's volunteer organization aimed at improving communities and the social, cultural, and political fabric of civil society. With ...
Mardi Gras
Mardi Gras (, ; also known as Shrove Tuesday) is the final day of Carnival (also known as Shrovetide or Fastelavn); it thus falls on the day before the beginning of Lent on Ash Wednesday. is French for "Fat Tuesday", referring to it being ...
ball at the Jackson Country Club, breaking open the liquor cabinet and carting off the Champagne before a startled crowd of nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. T ...
and high-ranking state officials".
The end of legal segregation and Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced racial segregation, " Jim Crow" being a pejorative term for an African American. The last of the ...
led to the integration of some churches, but most today remain divided along racial and cultural lines, having developed different traditions. After the Civil War, most African Americans left white churches to establish their own independent congregations, particularly Baptist churches, establishing state associations and a national association by the end of the 20th century. They wanted to express their own traditions of worship and practice. In more diverse communities, such as Hattiesburg
Hattiesburg is a city in the U.S. state of Mississippi, located primarily in Forrest County (where it is the county seat and most populous city) and extending west into Lamar County. The city population was 48,730 in 2020, making it the 5th m ...
, some churches have multiracial congregations.
On August 17, 1969, Category 5 Hurricane Camille
Hurricane Camille was a powerful, deadly and destructive tropical cyclone which became the second most intense on record to strike the United States (behind the 1935 Labor Day hurricane) and is one of the four Category 5 hurricanes to make ...
hit the Mississippi coast, killing 248 people and causing US$1.5 billion in damage (1969 dollars). Mississippi ratified the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Nineteenth Amendment (Amendment XIX) to the United States Constitution prohibits the United States and its U.S. state, states from denying the Suffrage, right to vote to citizens of the United States on the basis of sex, in effect recogni ...
, in March 1984, which had already entered into force by August 1920; granting women the right to vote.
 In 1987, 20 years after the
In 1987, 20 years after the U.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that turn on question ...
had ruled in 1967's ''Loving v. Virginia
''Loving v. Virginia'', 388 U.S. 1 (1967), was a landmark civil rights decision of the U.S. Supreme Court that ruled that the laws banning interracial marriage violate the Equal Protection and Due Process Clauses of the Fourteenth Amendment to ...
'' that a similar Virginian law was unconstitutional, Mississippi repealed its ban on interracial marriage (also known as miscegenation
Miscegenation ( ) is marriage or admixture between people who are members of different races or ethnicities. It has occurred many times throughout history, in many places. It has occasionally been controversial or illegal. Adjectives describin ...
), which had been enacted in 1890. It also repealed the segregationist
Racial segregation is the separation of people into racial or other ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, such as schools and hospitals by peopl ...
-era poll tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources. ''Poll'' is an archaic term for "head" or "top of the head". The sen ...
in 1989. In 1995, the state symbolically ratified the Thirteenth Amendment, which had abolished slavery in 1865. In 2009, the legislature passed a bill to repeal other discriminatory civil rights laws, which had been enacted in 1964, the same year as the federal Civil Rights Act
Civil Rights Act may refer to several civil right acts in the United States. These acts of the United States Congress are meant to protect rights to ensure individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private ...
, but ruled unconstitutional in 1967 by federal courts. Republican Governor Haley Barbour
Haley Reeves Barbour (born October 22, 1947) is an American attorney, politician, and lobbyist who served as the 63rd governor of Mississippi from 2004 to 2012. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he previously ser ...
signed the bill into law.
On August 29, 2005, Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a powerful, devastating and historic tropical cyclone that caused 1,392 fatalities and damages estimated at $125 billion in late August 2005, particularly in the city of New Orleans and its surrounding area. ...
, though a Category 3 storm upon final landfall, caused even greater destruction across the entire of the Mississippi Gulf Coast
The Mississippi Gulf Coast, also known as Mississippi Coast, Mississippi Gulf Coast region, Coastal Mississippi, and The Coast, is the area of Mississippi along the Mississippi Sound at the northern extreme of the Gulf of Mexico.
Geography
At t ...
from Louisiana to Alabama.
The previous flag of Mississippi
The flag of the U.S. state of Mississippi consists of a white magnolia blossom surrounded by 21 stars and the words "In God We Trust" written below, all put over a blue Canadian pale with two vertical gold borders on a red Glossary of vexillolo ...
, used until June 30, 2020, featured the Confederate battle flag
The flags of the Confederate States of America have a history of three successive designs during the American Civil War. The flags were known as the "Stars and Bars", used from 1861 to 1863; the "Stainless Banner", used from 1863 to 1865; and ...
. Mississippi became the last state to remove the Confederate battle flag as an official state symbol on June 30, 2020, when Governor Tate Reeves
Jonathan Tate Reeves (born June 5, 1974) is an American politician serving as the 65th List of governors of Mississippi, governor of Mississippi since 2020. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, Reeves served as the ...
signed a law officially retiring the second state flag. The current flag, The "New Magnolia" flag, was selected via referendum as part of the general election on November 3, 2020. It officially became the state flag on January 11, 2021, after being signed into law by the state legislature and governor.
Geography


Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
, to the east by Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
, to the south by Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
and a narrow coast on the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
; and to the west, across the Mississippi River, by Louisiana and Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
.
In addition to its namesake, major rivers in Mississippi include the Big Black River, the Pearl River
The Pearl River (, or ) is an extensive river system in southern China. "Pearl River" is often also used as a catch-all for the watersheds of the Pearl tributaries within Guangdong, specifically the Xi ('west'), Bei ('north'), and Dong ( ...
, the Yazoo River
The Yazoo River is a river primarily in the U.S. state of Mississippi. It is considered by some to mark the southern boundary of what is called the Mississippi Delta, a broad floodplain that was cultivated for cotton plantations before the Ame ...
, the Pascagoula River
The Pascagoula River is a river, about 80 miles (130 km) long, in southeastern Mississippi in the United States. The river drains an area of about 8,800 square miles (23,000 km²) and flows into Mississippi Sound of the Gulf of Mexico. ...
, and the Tombigbee River
The Tombigbee River is a tributary of the Mobile River, approximately 200 mi (325 km) long, in the U.S. states of Mississippi and Alabama. Together with the Alabama, it merges to form the short Mobile River before the latter empties i ...
. Major lakes include Ross Barnett Reservoir
The Ross Barnett Reservoir, often called the Rez, is a reservoir of the Pearl River between Madison and Rankin counties in the U.S. state of Mississippi. The lake serves as the state's largest drinking water resource, and is managed by the P ...
, Arkabutla, Sardis
Sardis ( ) or Sardes ( ; Lydian language, Lydian: , romanized: ; ; ) was an ancient city best known as the capital of the Lydian Empire. After the fall of the Lydian Empire, it became the capital of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Lydia (satrapy) ...
, and Grenada
Grenada is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. The southernmost of the Windward Islands, Grenada is directly south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and about north of Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidad and the So ...
, with the largest being Sardis Lake.
Mississippi is entirely composed of lowland
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland.
Definitions
Upland and lowland are portions of a ...
s, the highest point being Woodall Mountain
Woodall Mountain is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Mississippi at 806 feet (246 m). It is located just off Mississippi Highway 25, south of Iuka in Tishomingo County in the northeast part of the state and is part of the Appala ...
, at above sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
, in the northeastern part of the state. The lowest point is sea level at the Gulf Coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South or the South Coast, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Tex ...
. The state's mean elevation is above sea level.
Most of Mississippi is part of the east Gulf Coastal Plain
The Gulf Coastal Plain extends around the Gulf of Mexico in the Southern United States and eastern Mexico.
This coastal plain reaches from the Florida Panhandle, southwest Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, the southern two-thirds of Alabama, over m ...
. The coastal plain
A coastal plain (also coastal plains, coastal lowland, coastal lowlands) is an area of flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and an upland area.
Formation
Coastal plains can f ...
is generally composed of low hills, such as the Pine Hills in the south and the North Central Hills. The Pontotoc Ridge and the Fall Line
A fall line (or fall zone) is the area where an upland region and a coastal plain meet and is noticeable especially the place rivers cross it, with resulting rapids or waterfalls. The uplands are relatively hard crystalline basement rock, and the ...
Hills in the northeast have somewhat higher elevations. Yellow-brown loess
A loess (, ; from ) is a clastic rock, clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loesses or similar deposition (geology), deposits.
A loess ...
soil is found in the western parts of the state. The northeast is a region of fertile black earth uplands, a geology that extend into the Alabama Black Belt.
The coastline includes large bays at Bay St. Louis, Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. It lies on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, bordering the city of Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport to its west. The adjacent cities ar ...
, and Pascagoula
The Pascagoula (also Pascoboula, Pacha-Ogoula, Pascagola, Pascaboula, Paskaguna) were an indigenous group living in coastal Mississippi on the Pascagoula River.
The name ''Pascagoula'' is a Choctaw term meaning "bread eater". Choctaw native Am ...
. It is separated from the Gulf of Mexico proper by the shallow Mississippi Sound
The Mississippi Sound is a sound along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It runs east-west along the southern coasts of Mississippi and Alabama, from the mouth of the Pearl River at the Mississippi-Louisiana state border to the Dauphin Islan ...
, which is partially sheltered by Petit Bois Island
Petit Bois Island is a barrier island off the Mississippi Gulf Coast, south of Pascagoula, and one of the Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands. It is part of Jackson County, Mississippi. Since 1971 it has been a part of Gulf Islands National Seas ...
, Horn Island, East and West Ship Islands, Deer Island, Round Island, and Cat Island.
The northwest remainder of the state consists of the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazo ...
, a section of the Mississippi Alluvial Plain
The Mississippi River Alluvial Plain is an alluvial plain created by the Mississippi River on which lie parts of seven U.S. states, from southern Louisiana to southern Illinois (Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, Lo ...
. The plain is narrow in the south and widens north of Vicksburg. The region has rich soil, partly made up of silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension (chemistry), suspension with water. Silt usually ...
which had been regularly deposited by the flood waters of the Mississippi River.
Areas under the management of the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List ...
include:
* Brices Cross Roads National Battlefield Site
Brices Cross Roads National Battlefield Site memorializes the Battle of Brice's Cross Roads, in which a U.S. Army force was defeated by a smaller Confederate force commanded by Major-General Nathan Bedford Forrest on June 10, 1864, but noneth ...
near Baldwyn
* Gulf Islands National Seashore
Gulf Islands National Seashore is an American National seashore that offers recreation opportunities and preserves natural and historic resources along the Gulf of Mexico barrier islands of Florida and Mississippi. In 2023, it was the fifth-mos ...
* Natchez National Historical Park
Natchez National Historical Park commemorates the history of Natchez, Mississippi, and is managed by the National Park Service.
The park consists of four separate sites:
Fort Rosalie is the site of a former fortification from the 18th century ...
in Natchez
* Natchez Trace National Scenic Trail in Tupelo
Tupelo commonly refers to:
* Tupelo (tree), a small genus of deciduous trees with alternate, simple leaves
* Tupelo, Mississippi, the county seat and the largest city of Lee County, Mississippi
Tupelo may also refer to:
Places
* Tupelo, Arka ...
* Natchez Trace Parkway
The Natchez Trace Parkway is a limited-access national parkway in the Southeastern United States that commemorates the historic Natchez Trace and preserves sections of that original trail. Its central feature is a two-lane road that extends 44 ...
* Tupelo National Battlefield
Tupelo National Battlefield commemorates the Battle of Tupelo, also known as the Battle of Harrisburg, fought from July 14 to 15, 1864, near Tupelo, Mississippi during the American Civil War. The Union victory over Confederate forces in nor ...
in Tupelo
* Vicksburg National Military Park and Cemetery in Vicksburg
Major cities and towns
 Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 50,000 (
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 50,000 (United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
as of 2017): Retrieved September 20, 2013
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 20,000 but fewer than 50,000 (United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
as of 2017):
Mississippi City Population Rankings of at least 10,000 but fewer than 20,000 (United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
as of 2017):
''(See: Lists of municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
, census-designated places
A census-designated place (CDP) is a concentration of population defined by the United States Census Bureau for statistical purposes only.
CDPs have been used in each decennial census since 1980 as the counterparts of incorporated places, such ...
, metropolitan areas
A metropolitan area or metro is a region consisting of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories which share industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metropolitan area usually ...
, micropolitan areas, and counties
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
in Mississippi)''
Climate
Mississippi has ahumid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a subtropical -temperate climate type, characterized by long and hot summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between ...
with long, hot and humid summers, and short, mild winters. Temperatures average about in July and about in January. The temperature varies little statewide in the summer; however, in winter, the region near Mississippi Sound
The Mississippi Sound is a sound along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It runs east-west along the southern coasts of Mississippi and Alabama, from the mouth of the Pearl River at the Mississippi-Louisiana state border to the Dauphin Islan ...
is significantly warmer than the inland portion of the state. The recorded temperature in Mississippi has ranged from , in 1966, at Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
in the northeast, to , in 1930, at Holly Springs in the north. Snowfall is scant throughout the state, occurring only rarely in the south. Yearly precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
generally increases from north to south, with the regions closer to the Gulf being the most humid. Thus, Clarksdale, in the northwest, gets about of precipitation annually and Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. It lies on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, bordering the city of Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport to its west. The adjacent cities ar ...
, in the south, about . Small amounts of snow fall in northern and central Mississippi; snow is occasional in the southern part of the state.
 The late summer and fall is the seasonal period of risk for
The late summer and fall is the seasonal period of risk for hurricanes
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
moving inland from the Gulf of Mexico, especially in the southern part of the state. Hurricane Camille
Hurricane Camille was a powerful, deadly and destructive tropical cyclone which became the second most intense on record to strike the United States (behind the 1935 Labor Day hurricane) and is one of the four Category 5 hurricanes to make ...
in 1969 and Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a powerful, devastating and historic tropical cyclone that caused 1,392 fatalities and damages estimated at $125 billion in late August 2005, particularly in the city of New Orleans and its surrounding area. ...
in 2005, which killed 238 people in the state, were the most devastating hurricanes to hit the state. Both caused nearly total storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the ...
destruction of structures in and around Gulfport, Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. It lies on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, bordering the city of Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport to its west. The adjacent cities ar ...
, and Pascagoula
The Pascagoula (also Pascoboula, Pacha-Ogoula, Pascagola, Pascaboula, Paskaguna) were an indigenous group living in coastal Mississippi on the Pascagoula River.
The name ''Pascagoula'' is a Choctaw term meaning "bread eater". Choctaw native Am ...
.
As in the rest of the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion of the Southern United States. The term is used to describe the states which were most economically dependent on Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, plant ...
, thunderstorms are common in Mississippi, especially in the southern part of the state. On average, Mississippi has around 27 tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the ...
es annually; the northern part of the state has more tornadoes earlier in the year and the southern part a higher frequency later in the year. Two of the five deadliest tornadoes in United States history have occurred in the state. These storms struck Natchez, in southwest Mississippi (see The Great Natchez Tornado) and Tupelo
Tupelo commonly refers to:
* Tupelo (tree), a small genus of deciduous trees with alternate, simple leaves
* Tupelo, Mississippi, the county seat and the largest city of Lee County, Mississippi
Tupelo may also refer to:
Places
* Tupelo, Arka ...
, in the northeast corner of the state. About seven F5 tornadoes have been recorded in the state.
Climate change
Ecology, flora, and fauna

 Mississippi is heavily forested, with over half of the state's area covered by wild or cultivated trees. The southeastern part of the state is dominated by
Mississippi is heavily forested, with over half of the state's area covered by wild or cultivated trees. The southeastern part of the state is dominated by longleaf pine
The longleaf pine (''Pinus palustris'') is a pine species native to the Southeastern United States, found along the coastal plain from East Texas to southern Virginia, extending into northern and central Florida. In this area it is also known as ...
, in both uplands and lowland flatwoods
Flatwoods, pineywoods, pine savannas and longleaf pine–wiregrass ecosystem are terms that refer to an ecological community in the southeastern coastal plain of North America. Flatwoods are an ecosystem maintained by wildfire or prescribed fir ...
and Sarracenia
''Sarracenia'' ( or ) is a genus comprising 8 to 11 species of North American pitcher plants, commonly called trumpet pitchers. The genus belongs to the family Sarraceniaceae, which also contain the closely allied genera '' Darlingtonia'' and '' ...
bogs
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main Wetland#Types, types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagm ...
. The Mississippi Alluvial Plain, or Delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
, is primarily farmland and aquaculture ponds but also has sizeable tracts of cottonwood, willows
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, of the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 350 species (plus numerous hybrids) of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions.
Most species are known ...
, bald cypress
''Taxodium distichum'' (baldcypress, bald-cypress, bald cypress, swamp cypress; ;
''cipre'' in Louisiana) is a deciduous conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is native to the southeastern United States. Hardy and tough, this tree adapts to a w ...
, and oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
s. A belt of loess
A loess (, ; from ) is a clastic rock, clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loesses or similar deposition (geology), deposits.
A loess ...
extends north to south in the western part of the state, where the Mississippi Alluvial Plain reaches the first hills; this region is characterized by rich, mesic mixed hardwood forests, with some species disjunct from Appalachian forests. Two bands of historical prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
, the Jackson Prairie and the Black Belt, run northwest to southeast in the middle and northeastern part of the state. Although these areas have been highly degraded by conversion to agriculture, a few areas remain, consisting of grassland with interspersed woodland of eastern redcedar, oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
s, hickories, osage-orange, and sugarberry. The rest of the state, primarily north of Interstate 20
Interstate 20 (I‑20) is a major east–west Interstate Highway in the Southern United States. I-20 runs beginning at an interchange with I-10 in Reeves County, Texas, and ending at an interchange with I-95 in Florence, South Carolina. B ...
not including the prairie regions, consists of mixed pine-hardwood forest, common species being loblolly pine
''Pinus taeda'', commonly known as loblolly pine, is one of several pines native to the Southeastern United States, from East Texas to Florida, and north to southern New Jersey. The wood industry classifies the species as a southern yellow pi ...
, oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
s (e.g., water oak), hickories, sweetgum
''Liquidambar'', commonly called sweetgum (star gum in the UK), gum, redgum, satin-walnut, styrax or American storax, is the only genus in the flowering plant family Altingiaceae and has 15 species. They were formerly often treated as a part of ...
, and elm
Elms are deciduous and semi-deciduous trees comprising the genus ''Ulmus'' in the family Ulmaceae. They are distributed over most of the Northern Hemisphere, inhabiting the temperate and tropical- montane regions of North America and Eurasia, ...
. Areas along large rivers are commonly inhabited by bald cypress
''Taxodium distichum'' (baldcypress, bald-cypress, bald cypress, swamp cypress; ;
''cipre'' in Louisiana) is a deciduous conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is native to the southeastern United States. Hardy and tough, this tree adapts to a w ...
, water tupelo
''Nyssa aquatica'', commonly called the water tupelo, cottongum, wild olive, large tupelo, tupelo-gum, or water-gum, is a large, long-lived tree in the tupelo genus ''(Nyssa)'' that grows in swamps and floodplains in the Southeastern United Stat ...
, water elm, and bitter pecan. Commonly cultivated trees include loblolly pine, longleaf pine, cherrybark oak, and cottonwood.
There are approximately 3000 species of vascular plants
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes (, ) or collectively tracheophyta (; ), are plants that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue ( ...
known from Mississippi. As of 2018, a project funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation
The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) is an Independent agencies of the United States government#Examples of independent agencies, independent agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that su ...
aims to update that checklist of plants with museum (herbarium
A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a collection of preserved plant biological specimen, specimens and associated data used for scientific study.
The specimens may be whole plants or plant parts; these will usually be in dried form mounted on a sh ...
) vouchers and create an online atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
of each species's distribution.
About 420 species of birds are known to inhabit Mississippi.
Mississippi has one of the richest fish faunas in the United States, with 204 native fish species.
Mississippi also has a rich freshwater mussel
Freshwater bivalves are molluscs of the order Bivalvia that inhabit freshwater ecosystems. They are one of the two main groups of freshwater molluscs, along with freshwater snails.
The majority of bivalve molluscs are saltwater species that l ...
fauna, with about 90 species in the primary family of native mussels (Unionidae
The Unionidae are a Family (biology), family of freshwater mussels, the largest in the order Unionida, the bivalve molluscs sometimes known as river mussels, or simply as unionids.
The range of distribution for this family is world-wide. It is a ...
). Several of these species were extirpated during the construction of the Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway.
Mississippi is home to 63 crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some spe ...
species, including at least 17 endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
species.
Mississippi is home to eight winter stonefly species.
Ecological problems
Flooding
Due to seasonal flooding, possible from December to June, theMississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
and Yazoo rivers and their tributaries created a fertile floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrolog ...
in the Mississippi Delta. The river's flooding created natural levees, which planters had built higher to try to prevent flooding of land cultivated for cotton crops. Temporary workers built levees
A levee ( or ), dike (American English), dyke (British English; see spelling differences), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is an elevated ridge, natural or artificial, alongside the banks of a river, often intended to protect against fl ...
along the Mississippi River on top of the natural levees that formed from dirt deposited after the river flooded.
From 1858 to 1861, the state took over levee building, accomplishing it through contractors and hired labor. In those years, planters considered their slaves too valuable to hire out for such dangerous work. Contractors hired gangs of Irish immigrant laborers to build levees and sometimes clear land. Many of the Irish were relatively recent immigrants from the famine years who were struggling to get established. Before the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, the earthwork levees averaged six feet in height, although in some areas they reached twenty feet.
Flooding has been an integral part of Mississippi history, but clearing of the land for cultivation and to supply wood fuel for steamboats took away the absorption of trees and undergrowth. The banks of the river were denuded, becoming unstable and changing the character of the river. After the Civil War, major floods swept down the valley in 1865, 1867, 1874 and 1882. Such floods regularly overwhelmed levees damaged by Confederate and Union fighting during the war, as well as those constructed after the war. In 1877, the state created the Mississippi Levee District for southern counties.
In 1879, the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
created the Mississippi River Commission
The United States Army Corps of Engineers Mississippi Valley Division (MVD) is responsible for the Corps water resources programs within 370,000-square-miles of the Mississippi River Valley, as well as the watershed portions of the Red River ...
, whose responsibilities included aiding state levee boards in the construction of levees. Both white and black transient workers were hired to build the levees in the late 19th century. By 1882, levees averaged seven feet in height, but many in the southern Delta were severely tested by the flood that year. After the 1882 flood, the levee system was expanded. In 1884, the Yazoo-Mississippi Delta Levee District was established to oversee levee construction and maintenance in the northern Delta counties; also included were some counties in Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
which were part of the Delta.
Flooding overwhelmed northwestern Mississippi in 1912–1913, causing heavy damage to the levee districts. Regional losses and the Mississippi River Levee Association's lobbying for a flood control bill helped gain passage of national bills in 1917 and 1923 to provide federal matching funds for local levee districts, on a scale of 2:1. Although U.S. participation in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
interrupted funding of levees, the second round of funding helped raise the average height of levees in the Mississippi-Yazoo Delta to in the 1920s. Scientists now understand the levees have increased the severity of flooding by increasing the flow speed of the river and reducing the area of the floodplains. The region was severely damaged due to the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927
The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 was the most destructive river flood in the history of the United States, with inundated in depths of up to over the course of several months in early 1927. The period cost of the damage has been estimate ...
, which broke through the levees. There were losses of millions of dollars in property, stock and crops. The most damage occurred in the lower Delta, including Washington
Washington most commonly refers to:
* George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States
* Washington (state), a state in the Pacific Northwest of the United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A ...
and Bolivar counties.
Even as scientific knowledge about the Mississippi River has grown, upstream development and the consequences of the levees have caused more severe flooding in some years. Scientists now understand that the widespread clearing of land and building of the levees have changed the nature of the river. Such work removed the natural protection and absorption of wetlands and forest cover, strengthening the river's current. The state and federal governments have been struggling for the best approaches to restore some natural habitats in order to best interact with the original riverine ecology.
Demographics
 Mississippi's population has remained from 2 million people at the 1930 U.S. census, to 2.9 million at the 2020 census. In contrast with
Mississippi's population has remained from 2 million people at the 1930 U.S. census, to 2.9 million at the 2020 census. In contrast with Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
to its east, and Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
to its west, Mississippi has been the slowest growing of the three Gulf coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South or the South Coast, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Tex ...
states by population. According to the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the U ...
, Mississippi's center of population
In Demography, demographics, the center of population (or population center) of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several ways of defining such a "center point", leading to dif ...
is located in Leake County, in the town of Lena
Lena or LENA may refer to:
Places
* Léna Department, a department of Houet Province in Burkina Faso
* Lena, Manitoba, an unincorporated community located in Killarney-Turtle Mountain municipality in Manitoba, Canada
* Lena, Norway, a village in ...
.
According to HUD's 2022 Annual Homeless Assessment Report, there were an estimated 1,196 homeless people in Mississippi.
From 2000 to 2010, the United States Census Bureau reported that Mississippi had the highest rate of increase in people identifying as mixed-race, up 70 percent in the decade; it amounts to a total of 1.1 percent of the population.Susan Saulny, "Black and White and Married in the Deep South: A Shifting Image"''The New York Times'', March 20, 2011, accessed October 25, 2012 In addition, Mississippi led the nation for most of the last decade in the growth of mixed marriages among its population. The total population has not increased significantly, but is young. Some of the above change in identification as mixed-race is due to new births. But, it appears mostly to reflect those residents who have chosen to identify as more than one race, who in earlier years may have identified by just one race or ethnicity. A binary racial system had been in place since slavery times and the days of official government
racial segregation
Racial segregation is the separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Segregation can involve the spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, ...
. In the civil rights era, people of African descent banded together in an inclusive community to achieve political power and gain restoration of their civil rights.
As the demographer William H. Frey noted, "In Mississippi, I think it's dentifying as mixed racechanged from within." Historically in Mississippi, after Indian removal in the 1830s, the major groups were designated as black (African American), who were then mostly enslaved, and white (primarily European American). Matthew Snipp, also a demographer, commented on the increase in the 21st century in the number of people identifying as being of more than one race: "In a sense, they're rendering a more accurate portrait of their racial heritage that in the past would have been suppressed."
After having accounted for a majority of the state's population since well before the American Civil War and through the 1930s, today African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
s constitute approximately 37.8 percent of the state's population. Most have ancestors who were enslaved, with many forcibly transported from the Upper South in the 19th century to work on the area's new plantations. Many of these slaves were mixed race, with European ancestors, as there were many children born into slavery with white fathers. Some also have Native American ancestry. During the first half of the 20th century, a total of nearly 400,000 African Americans left the state during the Great Migration, for opportunities in the North, Midwest and West. They became a minority in the state for the first time since early in its development.
In 2018, the top countries of origin for Mississippi's immigrants were Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
, Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
and Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
.
Race and ethnicity
Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
ancestry are present throughout the state. It is believed that there are more people with such ancestry than identify as such on the census, in part because their immigrant ancestors are more distant in their family histories. English, Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
and Scots-Irish are generally the most under-reported ancestry groups in both the South Atlantic states and the East South Central states. The historian David Hackett Fischer
David Hackett Fischer (born December 2, 1935) is University Professor of History Emeritus at Brandeis University. Fischer's major works have covered topics ranging from large macroeconomic and cultural trends ('' Albion's Seed,'' '' The Great Wave ...
estimated that a minimum 20% of Mississippi's population is of English ancestry, though the figure is probably much higher, and another large percentage is of Scottish ancestry. Many Mississippians of such ancestry identify simply as American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, p ...
on questionnaires, because their families have been in North America for centuries. In the 1980 U.S. census, 656,371 Mississippians of a total of 1,946,775 identified as being of English ancestry, making them 38% of the state at the time.
The state in 2010 had the highest proportion of African Americans in the nation. The African American percentage of population has begun to increase due mainly to a younger population than the whites (the total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
s of the two races are approximately equal). Due to patterns of settlement and whites putting their children in private schools, in almost all of Mississippi's public school districts, a majority of students are African American. African Americans are the majority ethnic group in the northwestern Yazoo Delta, and the southwestern and the central parts of the state. These are areas where, historically, African Americans owned land as farmers in the 19th century following the Civil War, or worked on cotton plantations and farms.
People of French Creole ancestry form the largest demographic group in Hancock County on the Gulf Coast. The African American, Choctaw
The Choctaw ( ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States, originally based in what is now Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama. The Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choct ...
(mostly in Neshoba County), and Chinese American
Chinese Americans are Americans of Chinese ancestry. Chinese Americans constitute a subgroup of East Asian Americans which also constitute a subgroup of Asian Americans. Many Chinese Americans have ancestors from mainland China, Hong Kong ...
portions of the population are also almost entirely native born.
The Chinese first came to Mississippi as contract workers from Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
and California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
in the 1870s, and they originally worked as laborers on the cotton plantations. However, most Chinese families came later between 1910 and 1930 from other states, and most operated small family-owned groceries stores in the many small towns of the Delta. In these roles, the ethnic Chinese carved out a niche in the state between black and white, where they were concentrated in the Delta. These small towns have declined since the late 20th century, and many ethnic Chinese have joined the exodus to larger cities, including Jackson. Their population in the state overall has increased in the 21st century.
In the early 1980s many Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese people living outside Vietna ...
immigrated to Mississippi and other states along the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
, where they became employed in fishing-related work.
Italians were one of the largest immigrant groups in the state during the first three decades of the twentieth century.
Mexicans
Mexicans () are the citizens and nationals of the Mexico, United Mexican States. The Mexican people have varied origins with the most spoken language being Spanish language, Spanish, but many also speak languages from 68 different Languages o ...
have been in the state since the early 20th century.
There is also a German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
community in the state.
As of 2011, 53.8% of Mississippi's population younger than age 1 were minorities, meaning that they had at least one parent who was not non-Hispanic white.
Birth data
 ''Note: Births in table do not add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
*Since 2016, data for births of
''Note: Births in table do not add up, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
*Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic
White Hispanic and Latin Americans, also called Euro-Hispanics, Euro-Latinos, White Hispanics, or White Latinos, are Americans who self-identify as white of European (diaspora) or West Asian descent with origins from Hispanic countries or Lat ...
origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
In 2022, Mississippi had the highest teen birth rate of any state, at 26.4 births per 1,000 females ages 15 to 19 years of age.
LGBT community
The 2010 United States census counted 6,286 same-sex unmarried-partner households in Mississippi, an increase of 1,512 since the 2000 United States census. Of those same-sex couples roughly 33% contained at least one child, giving Mississippi the distinction of leading the nation in the percentage of same-sex couples raising children. Mississippi has the largest percentage ofAfrican American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
same-sex couples among total households. The state capital, Jackson, ranks tenth in the nation in concentration of African American same-sex couples. The state ranks fifth in the nation in the percentage of Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
same-sex couples among all Hispanic households and ninth in the highest concentration of same-sex couples who are seniors.
Language
In 2000, 96.4% of Mississippi residents five years old and older spoke only English in the home, a decrease from 97.2% in 1990. English is largelySouthern American English
Southern American English or Southern U.S. English is a regional dialect or collection of dialects of American English spoken throughout the Southern United States, primarily by White Southerners and increasingly concentrated in more rural areas ...
, with some South Midland speech in northern and eastern Mississippi. There is a common absence of final /r/, particularly in the elderly natives and African Americans, and the lengthening and weakening of the diphthongs /aɪ/ and /ɔɪ/ as in 'ride' and 'oil'. South Midland terms in northern Mississippi include: tow sack (burlap bag), dog irons (andirons), plum peach (clingstone peach), snake doctor (dragonfly), and stone wall (rock fence).
Religion
Under French and Spanish rule beginning in the 17th century, European colonists were mostlyRoman Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
. The growth of the cotton culture after 1815 brought in tens of thousands of Anglo-American settlers each year, most of whom were Protestants from Southeastern states. Due to such migration, there was rapid growth in the number of Protestant denominations and churches, especially among the Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother ...
s, Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
s and Baptist
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
s.
 The revivals of the
The revivals of the Great Awakening
The Great Awakening was a series of religious revivals in American Christian history. Historians and theologians identify three, or sometimes four, waves of increased religious enthusiasm between the early 18th century and the late 20th cent ...
in the late 18th and early 19th centuries initially attracted the "plain folk" by reaching out to all members of society, including women and blacks. Both slaves and free blacks were welcomed into Methodist and Baptist churches. Independent black Baptist churches were established before 1800 in Virginia, Kentucky, South Carolina and Georgia, and later developed in Mississippi as well.
In the post-Civil War years, religion became more influential as the South became known as the "Bible Belt
The Bible Belt is a region of the Southern United States and the Midwestern state of Missouri (which also has significant Southern influence), where evangelical Protestantism exerts a strong social and cultural influence. The region has been de ...
". By 2014, the Pew Research Center determined 83% of its population was Christian. In a separate study by the Public Religion Research Institute in 2020, 80% of the population was Christian. In another Public Religion study in 2022, 84% of the population was Christian spread throughout Protestants (74%), Catholics (8%), Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a Christian denomination that is an outgrowth of the Bible Student movement founded by Charles Taze Russell in the nineteenth century. The denomination is nontrinitarian, millenarian, and restorationist. Russell co-fou ...
(1%), and Mormons
Mormons are a Religious denomination, religious and ethnocultural group, cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's d ...
(1%).
Since the 1970s, fundamentalist conservative churches have grown rapidly, fueling Mississippi's conservative political trends among whites. In 1973 the Presbyterian Church in America
The Presbyterian Church in America (PCA) is the second-largest Presbyterian church body, behind the Presbyterian Church (USA), and the largest conservative Calvinist denomination in the United States. The PCA is Calvinist, Reformed in theolog ...
attracted numerous conservative congregations. As of 2010, Mississippi remained a stronghold of the denomination, which originally was brought by Scots immigrants. The state has the highest adherence rate of the PCA in 2010, with 121 congregations and 18,500 members. It is among the few states where the PCA has higher membership than the PC(USA).
According to the Association of Religion Data Archives
The Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) is a free source of online information related to American and international religion. One of the primary goals of the archive is to democratize access to academic information on religion by making t ...
(ARDA), in 2010 the Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC), alternatively the Great Commission Baptists (GCB), is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist organization, the largest Protestant, and the second-largest Chr ...
had 907,384 adherents and was the largest religious denomination in the state, followed by the United Methodist Church
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant Christian denomination, denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was ...
with 204,165, and the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
with 112,488. Other religions have a small presence in Mississippi; as of 2010, there were 5,012 Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
; 4,389 Hindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
; and 816 of the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
.
According to the Pew Research Center in 2014, with evangelical Protestantism
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of the Christian g ...
as the predominant Christian affiliation, the Southern Baptist Convention remained the largest denomination in the state. Non-denominational Evangelicals were the second-largest, followed by historically African American denominations such as the National Baptist Convention, USA
The National Baptist Convention, USA, more commonly known as the National Baptist Convention (NBC USA or NBC), is a Baptist Christian denomination headquartered at the Baptist World Center in Nashville, Tennessee and affiliated with the Baptist ...
and Progressive National Baptist Convention
The Progressive National Baptist Convention (PNBC), incorporated as the Progressive National Baptist Convention, Inc., is a Baptist denomination emphasizing civil rights and social justice. The headquarters of the Progressive National Baptist Co ...
.
Public opinion polls have consistently ranked Mississippi as the most religious state in the United States, with 59% of Mississippians considering themselves "very religious". The same survey also found that 11% of the population were non-Religious. In a 2009 Gallup poll, 63% of Mississippians said that they attended church weekly or almost weekly—the highest percentage of all states (U.S. average was 42%, and the lowest percentage was in Vermont at 23%). Another 2008 Gallup poll found that 85% of Mississippians considered religion an important part of their daily lives, the highest figure among all states (U.S. average 65%).
Health
The state is ranked 50th or last place among all the states for health care, according to theCommonwealth Fund
The Commonwealth Fund is a private American foundation whose stated purpose is to "promote a high-performing health care system that achieves better access, improved quality, and greater efficiency, particularly for society's most vulnerable, inc ...
, a nonprofit foundation working to advance performance of the health care system.
Mississippi has the highest rate of infant and neonatal deaths of any U.S. state. Age-adjusted data also shows Mississippi has the highest overall death rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
, and the highest death rate from heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
, hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
and hypertensive renal disease, influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
and pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
.
In 2011, Mississippi (and Arkansas) had the fewest dentists per capita in the United States.
For three years in a row, more than 30 percent of Mississippi's residents have been classified as obese
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classified as obese when ...
. In a 2006 study, 22.8 percent of the state's children were classified as such. Mississippi had the highest rate of obesity of any U.S. state from 2005 to 2008, and also ranks first in the nation for high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, and adult inactivity. In a 2008 study of African-American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa. ...
women, contributing risk factors were shown to be: lack of knowledge about body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
(BMI), dietary behavior, physical inactivity and lack of social support, defined as motivation and encouragement by friends. A 2002 report on African-American adolescents noted a 1999 survey which suggests that a third of children were obese, with higher ratios for those in the Delta.
The study stressed that "obesity starts in early childhood extending into the adolescent years and then possibly into adulthood". It noted impediments to needed behavioral modification, including the Delta likely being "the most underserved region in the state" with African Americans the major ethnic group; lack of accessibility and availability of medical care; and an estimated 60% of residents living below the poverty level
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line, or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for ...
. Additional risk factors were that most schools had no physical education
Physical education is an academic subject taught in schools worldwide, encompassing Primary education, primary, Secondary education, secondary, and sometimes tertiary education. It is often referred to as Phys. Ed. or PE, and in the United Stat ...
curriculum and nutrition education
__NOTOC__
Nutrition education is a combination of learning experiences designed to teach individuals or groups about the principles of a balanced diet, the importance of various nutrients, how to make healthy food choices, and how both dietary an ...
is not emphasized. Previous intervention strategies may have been largely ineffective due to not being culturally sensitive
Cultural sensitivity, also referred to as cross-cultural sensitivity or cultural awareness, is the knowledge, awareness, and acceptance of other cultures and others' cultural identities. It is related to cultural competence (the skills needed fo ...
or practical. A 2006 survey found nearly 95 percent of Mississippi adults considered childhood obesity
Childhood obesity is a condition where excess adipose tissue, body fat negatively affects a child's health or well-being. As methods to determine body fat directly are difficult, the diagnosis of obesity is often based on Body mass index, BMI. ...
to be a serious problem.
A 2017 study found that Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Mississippi was the leading health insurer with 53% followed by UnitedHealth Group
UnitedHealth Group Incorporated is an American Multinational corporation, multinational for-profit company specializing in health insurance and health care services based in Eden Prairie, Minnesota. Selling insurance products under UnitedHealth ...
at 13%.
Economy
TheBureau of Economic Analysis
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) of the United States Department of Commerce is a U.S. government agency that provides official macroeconomic and industry statistics, most notably reports about the gross domestic product (GDP) of the United ...
estimates that Mississippi's total state product in 2024 was $150 billion. GDP growth was .5 percent in 2015 and is estimated to be 2.4 in 2016 according to Darrin Webb, the state's chief economist, who noted it would make two consecutive years of positive growth since the recession.Pender, 2017. Per capita personal income in 2006 was $26,908, the lowest per capita personal income of any state, but the state also has the nation's lowest living costs. 2015 data records the adjusted per capita personal income at $40,105. Mississippians consistently rank as one of the highest per capita in charitable contributions.
At 56 percent, the state has one of the lowest workforce participation rates in the country. Approximately 70,000 adults are disabled, which is 10 percent of the workforce.
Mississippi's rank as one of the poorest states is related to its dependence on cotton agriculture before and after the Civil War, late development of its frontier bottomlands in the Mississippi Delta, repeated natural disasters of flooding in the late 19th and early 20th century that required massive capital investment in levees, and ditching and draining the bottomlands, and slow development of railroads to link bottomland towns and river cities.John Otto Solomon,''The Final Frontiers, 1880–1930: Settling the Southern Bottomlands''. Westport: Greenwood Press, 1999, pp.10–11, 42–43, 50–51, and 70 In addition, when Democrats regained control of the state legislature, they passed the 1890 constitution that discouraged corporate industrial development in favor of rural agriculture, a legacy that would slow the state's progress for years.
 Before the Civil War, Mississippi was the fifth-wealthiest state in the nation, its wealth generated by the labor of slaves in cotton plantations along the rivers.
Slaves were counted as property and the rise in the cotton markets since the 1840s had increased their value. By 1860, a majority—55 percent—of the population of Mississippi was enslaved. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were undeveloped and the state had low overall density of population.
Largely due to the domination of the
Before the Civil War, Mississippi was the fifth-wealthiest state in the nation, its wealth generated by the labor of slaves in cotton plantations along the rivers.
Slaves were counted as property and the rise in the cotton markets since the 1840s had increased their value. By 1860, a majority—55 percent—of the population of Mississippi was enslaved. Ninety percent of the Delta bottomlands were undeveloped and the state had low overall density of population.
Largely due to the domination of the plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
economy, focused on the production of agricultural
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created f ...
cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, the state's elite was reluctant to invest in infrastructure such as roads and railroads. They educated their children privately. Industrialization
Industrialisation (British English, UK) American and British English spelling differences, or industrialization (American English, US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an i ...
did not reach many areas until the late 20th century. The planter aristocracy, the elite of antebellum
Antebellum, Latin for "before war", may refer to:
United States history
* Antebellum South, the pre-American Civil War period in the Southern US
** Antebellum Georgia
** Antebellum South Carolina
** Antebellum Virginia
* Antebellum architectu ...
Mississippi, kept the tax structure low for their own benefit, making only private improvements. Before the war the most successful planters, such as Confederate
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
President Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the only President of the Confederate States of America, president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the Unite ...
, owned riverside properties along the Mississippi and Yazoo rivers in the Mississippi Delta. Away from the riverfronts, most of the Delta was undeveloped frontier.
During the Civil War, 30,000 Mississippi soldiers, mostly white, died from wounds and disease, and many more were left crippled and wounded. Changes to the labor structure and an agricultural depression throughout the South caused severe losses in wealth. In 1860 assessed valuation of property in Mississippi had been more than $500 million, of which $218 million (43 percent) was estimated as the value of slaves. By 1870, total assets had decreased in value to roughly $177 million.
Poor white
Poor White is a sociocultural classification used to describe economically disadvantaged Whites in the English-speaking world, especially White Americans with low incomes.
In the United States, Poor White is the historical classification f ...
s and landless former slaves suffered the most from the postwar economic depression. The constitutional convention of early 1868 appointed a committee to recommend what was needed for relief of the state and its citizens. The committee found severe destitution among the laboring classes. It took years for the state to rebuild levees damaged in battles. The upset of the commodity system impoverished the state after the war. By 1868 an increased cotton crop began to show possibilities for free labor in the state, but the crop of 565,000 bales produced in 1870 was still less than half of prewar figures.
Blacks cleared land, selling timber and developing bottomland to achieve ownership. In 1900, two-thirds of farm owners in Mississippi were blacks, a major achievement for them and their families. Due to the poor economy, low cotton prices and difficulty of getting credit, many of these farmers could not make it through the extended financial difficulties. Two decades later, the majority of African Americans were sharecroppers. The low prices of cotton into the 1890s meant that more than a generation of African Americans lost the result of their labor when they had to sell their farms to pay off accumulated debts.
After the Civil War, the state refused for years to build human capital by fully educating all its citizens. In addition, the reliance on agriculture grew increasingly costly as the state suffered loss of cotton crops due to the devastation of the boll weevil
The boll weevil (''Anthonomus grandis'') is a species of beetle in the family Curculionidae. The boll weevil
feeds on cotton buds and flowers. Thought to be native to Central Mexico, it migrated into the United States from Mexico in the late 19 ...
in the early 20th century, devastating floods in 1912–1913 and 1927, collapse of cotton prices after 1920, and drought in 1930.
It was not until 1884, after the flood of 1882, that the state created the Mississippi-Yazoo Delta District Levee Board and started successfully achieving longer-term plans for levees in the upper Delta. Despite the state's building and reinforcing levees for years, the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927
The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 was the most destructive river flood in the history of the United States, with inundated in depths of up to over the course of several months in early 1927. The period cost of the damage has been estimate ...
broke through and caused massive flooding of throughout the Delta, homelessness for hundreds of thousands, and millions of dollars in property damages. With the Depression coming so soon after the flood, the state suffered badly during those years. In the Great Migration, hundreds of thousands of African Americans migrated North and West for jobs and chances to live as full citizens.
Energy
Solar power
Entertainment and tourism
The legislature's 1990 decision to legalize casino gambling along the Mississippi River and the Gulf Coast has led to increased revenues and economic gains for the state. Gambling towns in Mississippi have attracted increased tourism: they include the Gulf Coast resort towns of Bay St. Louis, Gulfport andBiloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. It lies on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, bordering the city of Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport to its west. The adjacent cities ar ...
, and the Mississippi River towns of Tunica (the third largest gaming area in the United States), Greenville, Vicksburg and Natchez.
Before Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a powerful, devastating and historic tropical cyclone that caused 1,392 fatalities and damages estimated at $125 billion in late August 2005, particularly in the city of New Orleans and its surrounding area. ...
struck the Gulf Coast, Mississippi was the second-largest gambling state in the Union, after Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, th ...
and ahead of New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
. In August 2005, an estimated $500,000 per day in tax revenue, , was lost following Hurricane Katrina's severe damage to several coastal casinos in Biloxi. Because of the destruction from this hurricane, on October 17, 2005, Governor Haley Barbour
Haley Reeves Barbour (born October 22, 1947) is an American attorney, politician, and lobbyist who served as the 63rd governor of Mississippi from 2004 to 2012. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he previously ser ...
signed a bill into law that allows casinos in Hancock and Harrison counties to rebuild on land (but within of the water). The only exception is in Harrison County, where the new law states that casinos can be built to the southern boundary of U.S. Route 90
U.S. Route 90 or U.S. Highway 90 (US 90) is an east–west major United States highway in the Southern United States. Despite the "0" in its route number, US 90 never was a full coast-to-coast route. It generally travels near Int ...
.
In 2012, Mississippi had the sixth largest gambling revenue of any state, at $2.25 billion. The federally recognized Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians
The Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians () is one of three federally recognized tribes of Choctaw, an indigenous Indian people, and the only one in the state of Mississippi. On April 20, 1945, this tribe was organized under the Indian Reorgan ...
has established a gaming casino on its reservation, which yields revenue to support education and economic development. While regulated sports betting has been active since 2018, the lack of mobile sports betting laws has limited the tax revenue paid by sportsbooks to the state. From 2018 to September 2024, Mississippi sports betting was responsible for $37 million in tax benefits.
Momentum Mississippi, a statewide, public–private partnership dedicated to the development of economic and employment opportunities in Mississippi, was adopted in 2005.
Manufacturing
Mississippi, like the rest of its southern neighbors, is aright-to-work state
In the context of labor law in the United States, the term right-to-work laws refers to state laws that prohibit union security agreements between employers and labor unions. Such agreements can be incorporated into union contracts to require ...
. It has some major automotive factories, such as the Toyota Mississippi Plant in Blue Springs and a Nissan Automotive plant in Canton. The latter produces the Nissan Titan.
GreenTech Automotive
GreenTech Automotive (also known as WM GreenTech Automotive Corp.) was a United States automotive manufacturer founded in 2009 that planned to develop and produce ultralow-power electric cars resembling very small cars or large golf carts. It wa ...
received $6 million of incentive financing from the state of Mississippi and Tunica County to build an automotive plant in the county."Where Did $140 Million in GreenTech Money Go?,"''Bacon's Rebellion''. The facility was shut down in January 2017. GreenTech had promised to invest $60 million in the manufacturing plant, but it produced few cars if any. A Mississippi state auditor's review begun in 2016 found documentation reflecting only $3 million spent by GreenTech on automotive assembly equipment and parts. While the company had promised to create 350 full-time jobs, it was found to never have created more than 94 active, full-time jobs in Mississippi at any time."Chinese investors sue McAuliffe, Rodham over green-car investments ,"
''Politico''. In July 2017, the Mississippi state auditor demanded that GreenTech and its CEO
Charlie Wang
GreenTech Automotive (also known as WM GreenTech Automotive Corp.) was a United States automotive manufacturer founded in 2009 that planned to develop and produce ultralow-power electric cars resembling very small cars or large golf carts. It wa ...
pay Mississippi $6 million because Greentech had not lived up to its promises."Mississippi demands $6.4M back from electric car maker, CEO,"''The Journal Record''. The auditor said: "I would venture that there isn’t really much of an operation in Tunica at all. This appears to have been a game of smoke and mirrors, and a corporate entity that never had any intention to deliver on the promises it made." In November 2017, Mississippi Attorney General
Jim Hood
James Matthew Hood (born May 15, 1962) is an American lawyer and politician who served as the 39th Attorney General of Mississippi from 2004 to 2020.
Hood was first elected Attorney General in 2003, defeating Republican Scott Newton. A former ...
sued the company. GreenTech declared bankruptcy in February 2018. In a 2020 final settlement, it paid Mississippi and Tunica County only $575,000.
Taxation
, Mississippi collects personalincome tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
at a flat rate of 5% for all income over $10,000. The retail sales tax
A sales tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services. Usually laws allow the seller to collect funds for the tax from the consumer at the point of purchase. When a tax on goods or services is paid to a govern ...
rate in Mississippi is 7%. This rate is applied also to groceries, making it the highest grocery tax in the United States. Tupelo levies a local sales tax of 2.5%. State sales tax growth was 1.4 percent in 2016 and estimated to be slightly less in 2017. For purposes of assessment for ad valorem tax
An ''ad valorem'' tax (Latin for "according to value") is a tax whose amount is based on the value of a transaction or of a property. It is typically imposed at the time of a transaction, as in the case of a sales tax or value-added tax (VAT) ...
es, taxable property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, re ...
is divided into five classes.
On August 30, 2007, a report by the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, econ ...
indicated that Mississippi was the poorest state in the country. Major cotton farmers in the Delta have large, mechanized plantations, and they receive the majority of extensive federal subsidies going to the state, yet many other residents still live as poor, rural, landless laborers. The state's sizable poultry industry has faced similar challenges in its transition from family-run farms to large mechanized operations. Of $1.2 billion from 2002 to 2005 in federal subsidies to farmers in the Bolivar County area of the Delta, only 5% went to small farmers. There has been little money apportioned for rural development. Small towns are struggling. More than 100,000 people have left the region in search of work elsewhere. The state had a median household income of $34,473.
Employment
As of February 2023, the state's unemployment rate was 3.7%, the eleventh-highest in the country, tied withArizona
Arizona is a U.S. state, state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States, sharing the Four Corners region of the western United States with Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. It also borders Nevada to the nort ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, and West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
. This is an improvement over the 3.9% rate in January 2023, and 4% over the previous year. The highest unemployment rate recorded in the state was in April 2020, during the start of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, at 15.6%.
Federal subsidies and spending
Mississippi ranks as having the second-highest ratio of spending to tax receipts of any state. In 2005, Mississippi citizens received approximately $2.02 per dollar of taxes in the way of federal spending. This ranks the state second-highest nationally, and represents an increase from 1995, when Mississippi received $1.54 per dollar of taxes in federal spending and was 3rd highest nationally. This figure is based on federal spending after large portions of the state were devastated byHurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a powerful, devastating and historic tropical cyclone that caused 1,392 fatalities and damages estimated at $125 billion in late August 2005, particularly in the city of New Orleans and its surrounding area. ...
, requiring large amounts of federal aid from the Federal Emergency Management Agency
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS), initially created under President Jimmy Carter by Presidential Reorganization Plan No. 3 of 1978 and implemented by two Exec ...
(FEMA). However, from 1981 to 2005, it was at least number four in the nation for federal spending vs. taxes received.
A proportion of federal spending in Mississippi is directed toward large federal installations such as Camp Shelby
Camp Shelby is a U.S. Army post whose south gate is located at the southern boundary of Hattiesburg, Mississippi, along U.S. Highway 49. It was originally established during World War I, and has served almost continuously since then as a trai ...
, John C. Stennis Space Center
The John C. Stennis Space Center (SSC) is a NASA rocket testing facility in Hancock County, Mississippi, United States, on the banks of the Pearl River (Mississippi–Louisiana), Pearl River at the Mississippi–Louisiana border. , it is NASA ...
, Meridian Naval Air Station, Columbus Air Force Base
Columbus Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in Columbus, Mississippi. The host unit at Columbus AFB is the 14th Flying Training Wing (14 FTW), which is a part of Air Education and Training Command (AETC).
The resident ...
, and Keesler Air Force Base
Keesler Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in Biloxi, a city along the Gulf Coast in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. The base is named in honor of aviator 2d Lt Samuel Reeves Keesler Jr., a Mississippi nati ...
. Three of these installations are located in the area affected by Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a powerful, devastating and historic tropical cyclone that caused 1,392 fatalities and damages estimated at $125 billion in late August 2005, particularly in the city of New Orleans and its surrounding area. ...
.
Politics and government
 As with all other U.S. states and the federal government, Mississippi's government is based on the separation of legislative, executive and judicial power. Executive authority in the state rests with the Governor, currently
As with all other U.S. states and the federal government, Mississippi's government is based on the separation of legislative, executive and judicial power. Executive authority in the state rests with the Governor, currently Tate Reeves
Jonathan Tate Reeves (born June 5, 1974) is an American politician serving as the 65th List of governors of Mississippi, governor of Mississippi since 2020. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, Reeves served as the ...
( R). The lieutenant governor, currently Delbert Hosemann
Charles Delbert Hosemann Jr. (born June 30, 1947) is an American attorney and politician serving as the 33rd lieutenant governor of Mississippi since 2020. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as the secretary of state of Miss ...
( R), is elected on a separate ballot. Both the governor and lieutenant governor are elected to four-year terms of office. Unlike the federal government, but like many other U.S. states, most of the heads of major executive departments are elected by the citizens of Mississippi rather than appointed by the governor.
Mississippi is one of five states that elects its state officials in odd-numbered years (the others are Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
). Mississippi holds elections for these offices every four years, always in the year preceding presidential elections.
In a 2020 study, Mississippi was ranked as the 4th hardest state for citizens to vote in. Mississippi has the highest rate of disenfranchisement in the United States and around 16% of the African American voting age population is disenfranchised.
Mississippi is also the last state in the United States to have never elected a woman to the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
. However, it has elected one
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sp ...
to the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
.
Laws
In 2004, Mississippi voters approved a stateconstitutional amendment
A constitutional amendment (or constitutional alteration) is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly alt ...
banning same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same legal Legal sex and gender, sex. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 38 countries, with a total population of 1.5 ...
and prohibiting Mississippi from recognizing same-sex marriages performed elsewhere. The amendment passed 86% to 14%, the largest margin in any state. Same-sex marriage became legal in Mississippi on June 26, 2015, when the United States Supreme Court invalidated all state-level bans on same-sex marriage as unconstitutional in the landmark case ''Obergefell v. Hodges
''Obergefell v. Hodges'', ( ), is a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court which ruled that the fundamental right to marry is guaranteed to same-sex couples by both the Due Process Clause and the Equal Protection Clause of th ...
''.
With the passing of HB 1523 in April 2016, from July it became legal in Mississippi to refuse service to same-sex couples, based on one's religious beliefs. The bill has become the subject of controversy. A federal judge blocked the law in July of that year; however, it was challenged, and a federal appeals court ruled in favor of the law in October 2017.
Mississippi's regulations on abortion
Abortion is the early termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. Abortions that occur without intervention are known as miscarriages or "spontaneous abortions", and occur in roughly 30–40% of all pregnan ...
are among the most restrictive in the United States. A 2014 poll by Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
found that 59% of the state's population thinks abortion
Abortion is the early termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. Abortions that occur without intervention are known as miscarriages or "spontaneous abortions", and occur in roughly 30–40% of all pregnan ...
should be illegal in all/most cases, while only 36% of the state's population thinks abortion should be legal in all/most cases.
Mississippi has banned sanctuary cities
A sanctuary city is a municipality that limits or denies its cooperation with the national government in enforcing immigration law.
Proponents of sanctuary cities cite motives such as reducing the fear of persons which illegally immigrated fr ...
. Mississippi retains the death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in s ...
(see also: capital punishment in Mississippi). The preferred form of execution is the lethal injection
Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person (typically a barbiturate, paralytic, and potassium) for the express purpose of causing death. The main application for this procedure is capital punishment, but t ...
.
Section 265 of the Constitution of the State of Mississippi declares that "No person who denies the existence of a Supreme Being shall hold any office in this state." However, this religious test restriction was held to be unconstitutional by the U.S. Supreme Court in '' Torcaso v. Watkins'' (1961).
Gun laws in Mississippi are among the most permissive in the country, with no license or background check required to openly carry handguns in most places in the state.
In 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in a 6−3 decision in '' Jones v. Mississippi'' that a Mississippi law allowing mandatory sentencing of children to life imprisonment without parole is valid and that states and judges can impose such sentences without separately deciding if the child can be rehabilitated.
Political alignment
Mississippi led the South in developing a disenfranchising constitution, passing it in 1890. By raising barriers to voter registration, the state legislature disenfranchised most blacks and many poor whites, excluding them from politics until the late 1960s. It established a one-party state dominated by white Democrats, particularly those politicians who supported poor whites and farmers. Although the state was dominated by one party, there were a small number of Democrats who fought against most legislative measures that disenfranchised most blacks. They also side with the small group of Mississippi Republicans that still existed in the state and Republicans at the federal level on legislative measures that benefited them. Most blacks were still disenfranchised under the state's 1890 constitution and discriminatory practices, until passage of theVoting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights move ...
and concerted grassroots efforts to achieve registration and encourage voting. In the 1980s, whites divided evenly between the parties. In the 1990s, those voters largely shifted their allegiance to the Republican Party, first for national and then for state offices.
Gubernatorial elections
In 2019, a federal lawsuit claiming the provisions to be elected Governor are racially biased was filed against an 1890 election law known as ''The Mississippi Plan'', which requires that candidates must win the popular vote and a majority of districts. In the following year, 79% of Mississippians voted to remove the requirement of doing so. Under the new law, any candidate who receives a majority of statewide votes will be elected; if no candidate receives more than 50% of the vote, a statewide runoff election between the top two candidates will be held. These provisions were put in place with the 1890 Mississippi Constitution, itself established by the segregationistRedeemers
The Redeemers were a political coalition in the Southern United States during the Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction Era that followed the American Civil War. Redeemers were the Southern wing of the Democratic Party (Unite ...
and overturning the Reconstruction-era 1868 Constitution, as part of Jim Crow Era
The Jim Crow laws were U.S. state, state and local laws introduced in the Southern United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that enforced Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, "Jim Crow (character), Ji ...
policy to minimize the power of African Americans in politics. Because of this, as well as present gerrymandering
Gerrymandering, ( , originally ) defined in the contexts of Representative democracy, representative electoral systems, is the political manipulation of Boundary delimitation, electoral district boundaries to advantage a Political party, pa ...
that packs African Americans into a small number of districts, the plaintiffs claimed that the provisions should be struck down on the basis of racial bias.
The 2023 Mississippi gubernatorial election
The 2023 Mississippi gubernatorial election was held on November 7, 2023, to elect the governor of Mississippi. Incumbent Mississippi Republican Party, Republican governor Tate Reeves won re-election to a second term, defeating Mississippi ...
was the first Mississippi gubernatorial election since the 2020 referendum altered the election process. Previously, under a provision crafted as part of the 1890 Constitution of Mississippi
The Constitution of Mississippi is the primary organizing law for the U.S. state of Mississippi delineating the duties, powers, structures, and functions of the state government. Mississippi's original constitution was adopted at a constituti ...
, a candidate needed a majority of voters across the state and a majority of voters in a majority of state House of Representatives districts; if no candidates achieved such a result, the state House of Representatives would choose between the top two finishers, something that only happened in 1999
1999 was designated as the International Year of Older Persons.
Events January
* January 1 – The euro currency is established and the European Central Bank assumes its full powers.
* January 3 – The Mars Polar Lander is launc ...
. This structure was referred to as Mississippi's version of the electoral college
An electoral college is a body whose task is to elect a candidate to a particular office. It is mostly used in the political context for a constitutional body that appoints the head of state or government, and sometimes the upper parliament ...
; it was originally crafted, in the words of the Mississippi Historical Society, as part of "the legal basis and bulwark of the design of white supremacy". In the 21st century, because the state House districts favor Republican candidates, the provision was seen as helping Republican gubernatorial candidates as well.
Transportation
Air
Mississippi has six airports with commercial passenger service, the busiest in Jackson ( Jackson-Evers International Airport).Roads
Mississippi is the only American state where people in cars may legally consume beer. Some localities have laws restricting the practice. In 2018, the state was ranked number eight in the Union in terms of impaired driving deaths. Mississippi is served by nine
Mississippi is served by nine interstate highways
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, or the Eisenhower Interstate System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National H ...
:
*
**
*
**
*
*
*
*
**
and fourteen main U.S. Routes:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
*
*
*
*
as well as a system of State Highways
A state highway, state road, or state route (and the equivalent provincial highway, provincial road, or provincial route) is usually a road that is either Route number, numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered ...
.
Rail
Passenger
Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak (; ), is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates intercity rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
provides scheduled passenger service along two routes, the ''Crescent
A crescent shape (, ) is a symbol or emblem used to represent the lunar phase (as it appears in the northern hemisphere) in the first quarter (the "sickle moon"), or by extension a symbol representing the Moon itself.
In Hindu iconography, Hind ...
'' and '' City of New Orleans''. Prior to severe damage from Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a powerful, devastating and historic tropical cyclone that caused 1,392 fatalities and damages estimated at $125 billion in late August 2005, particularly in the city of New Orleans and its surrounding area. ...
, the ''Sunset Limited
The ''Sunset Limited'' is a long-distance passenger train run by Amtrak, operating on a route between New Orleans and Los Angeles. Major stops include Houston, San Antonio and El Paso in Texas, as well as Tucson, Arizona. Opening in 1894 thr ...
'' traversed the far south of the state; the route originated in Los Angeles, California
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
and it terminated in Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
. Restoration of services on the portion of this line from New Orleans, LA to Mobile, AL has been approved but actual resumption of services have been delayed.
Freight
All but one of the United StatesClass I railroad
Railroad classes are the system by which Rail freight transport, freight railroads are designated in the United States. Railroads are assigned to Class I, II or III according to annual revenue criteria originally set by the Surface Transportatio ...
s serve Mississippi (the exception is the Union Pacific):
*Canadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company () is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.
CN is Canada's largest railway, in terms of both revenue a ...
's Illinois Central Railroad
The Illinois Central Railroad , sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, is a railroad in the Central United States. Its primary routes connected Chicago, Illinois, with New Orleans, New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama, and thus, ...
subsidiary provides north–south service.
*BNSF Railway
BNSF Railway is the largest freight railroad in the United States. One of six North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 36,000 employees, of track in 28 states, and over 8,000 locomotives. It has three Transcontinental railroad, transcontine ...
has a northwest–southeast line across northern Mississippi.
* Canadian Pacific Kansas City Southern Railway provides east–west service in the middle of the state and north–south service along the Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
state line.
*Norfolk Southern Railway
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States. Headquartered in Atlanta, the company was formed in 1982 with the merger of the Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. The comp ...
provides service in the extreme north and southeast.
*CSX
CSX Transportation , known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Railroad classes, Class I freight railroad company operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. Operating about 21,000 route miles () of trac ...
has a line along the Gulf Coast.
Water
Major rivers
*Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
* Big Black River
*Pascagoula River
The Pascagoula River is a river, about 80 miles (130 km) long, in southeastern Mississippi in the United States. The river drains an area of about 8,800 square miles (23,000 km²) and flows into Mississippi Sound of the Gulf of Mexico. ...
*Pearl River
The Pearl River (, or ) is an extensive river system in southern China. "Pearl River" is often also used as a catch-all for the watersheds of the Pearl tributaries within Guangdong, specifically the Xi ('west'), Bei ('north'), and Dong ( ...
* Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway
*Yazoo River
The Yazoo River is a river primarily in the U.S. state of Mississippi. It is considered by some to mark the southern boundary of what is called the Mississippi Delta, a broad floodplain that was cultivated for cotton plantations before the Ame ...
Major bodies of water
 *
*Arkabutla Lake
Arkabutla Lake is a reservoir on the Coldwater River in the U.S. state of Mississippi. It was created following the construction of the Arkabutla Dam in 1940 on the Coldwater River.
The dam is located on Arkabutla Dam Rd ( Mississippi Highway ...
of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
* Bay Springs Lake of water and of shoreline; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
* Grenada Lake of water; became operational in 1954; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Ross Barnett Reservoir
The Ross Barnett Reservoir, often called the Rez, is a reservoir of the Pearl River between Madison and Rankin counties in the U.S. state of Mississippi. The lake serves as the state's largest drinking water resource, and is managed by the P ...
of water; named for Ross Barnett
Ross Robert Barnett (January 22, 1898November 6, 1987) was an American politician and segregationist who served as the 53rd governor of Mississippi from 1960 to 1964. He was a Southern Democrat who supported racial segregation.
Early life
Ba ...
, the 52nd Governor of Mississippi
The governor of Mississippi is the head of government of Mississippi and the commander-in-chief of the U.S. state, state's Mississippi National Guard, military forces. The governor has a duty to enforce state laws, and the power to either appro ...
; became operational in 1966; constructed and managed by The Pearl River Valley Water Supply District, a state agency; provides water supply for the City of Jackson.
* Sardis Lake of water; became operational in October 1940; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Vicksburg District
*Enid Lake
Enid Lake is a lake that is located mostly in Yalobusha County in the U.S. state of Mississippi. Parts of it extend into Panola and Lafayette counties. Common fish species include crappie, largemouth bass, catfish and bream. Enid Lake holds ...
of water; constructed and managed by the U.S. Army
Education
Until theCivil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
era, Mississippi had a small number of schools and no educational institutions for African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
. The first school for black students was not established until 1862.
During Reconstruction in 1871, black and white Republicans drafted a constitution that was the first to provide for a system of free public education
A state school, public school, or government school is a primary school, primary or secondary school that educates all students without charge. They are funded in whole or in part by taxation and operated by the government of the state. State-f ...
in the state. The state's dependence on agriculture and resistance to taxation limited the funds it had available to spend on any schools. In the early 20th century, there were still few schools in rural areas, particularly for black children. With seed money from the Julius Rosenwald
Julius Rosenwald (August 12, 1862 – January 6, 1932) was an American businessman and philanthropist. He is best known as a part-owner and leader of Sears, Roebuck and Company, and for establishing the Rosenwald Fund, which donated millions i ...
Fund, many rural black communities across Mississippi raised matching funds and contributed public funds to build new schools for their children. Essentially, many black adults taxed themselves twice and made significant sacrifices to raise money for the education of children in their communities, in many cases donating land or labor to build such schools.
Blacks and whites attended separate, segregated public schools in Mississippi until the late 1960s, although such segregation had been declared unconstitutional by the United States Supreme Court in its 1954 ruling in ''Brown v. Board of Education
''Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the ...
''. In the majority-black Mississippi Delta counties, white parents worked through White Citizens' Councils
The White Citizens' Councils were an associated network of White supremacy, white supremacist, Racial segregation in the United States, segregationist organizations in the United States, concentrated in the Southern United States, South and crea ...
to set up private segregation academies
Segregation academies are private schools in the Southern United States that were founded in the mid-20th century by white parents to avoid having their children attend desegregated public schools. They were founded between 1954, when the U.S ...
, where they enrolled their children. Often funding declined for the public schools. But in the state as a whole, only a small minority of white children were withdrawn from public schools. State officials believed they needed to maintain public education to attract new businesses. Many black parents complained that they had little representation in school administration, and that many of their former administrators and teachers had been pushed out. They have had to work to have their interests and children represented.Bolton, Charles C. '' The Hardest Deal of All: The Battle Over School Integration in Mississippi, 1870–1980''. University Press of Mississippi
The University Press of Mississippi (UPM), founded in 1970, is a university press that is sponsored by the eight state universities in Mississippi (i.e., Alcorn State University, Delta State University, Jackson State University, Mississippi Sta ...
, 2005, pp. 136, 178–179. , 9781604730609.
In the late 1980s, Mississippi's 954 public schools enrolled about 369,500 elementary and 132,500 secondary students. Some 45,700 students attended private school
A private school or independent school is a school not administered or funded by the government, unlike a State school, public school. Private schools are schools that are not dependent upon national or local government to finance their fina ...
s.
American Legislative Exchange Council
The American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) is a nonprofit organization of conservatism in the United States, conservative state legislature (United States), state legislators and private sector representatives who draft and share Model act, ...
's ''Report Card on Education'', with the lowest average ACT scores and sixth-lowest spending per pupil in the nation. In contrast, Mississippi had the 17th-highest average SAT
The SAT ( ) is a standardized test widely used for college admissions in the United States. Since its debut in 1926, its name and Test score, scoring have changed several times. For much of its history, it was called the Scholastic Aptitude Test ...
scores in the nation. As an explanation, the Report noted that 92% of Mississippi high school graduates took the ACT, but only 3% of graduates took the SAT, apparently a self-selection of higher achievers. This breakdown compares to the national average of high school graduates taking the ACT and SAT, of 43% and 45%, respectively.
Generally prohibited in the West
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
at large, school corporal punishment
Corporal punishment in schools is the deliberate infliction of physical pain as a response to undesired behavior by students. The term corporal punishment derives from , the Latin word for the body. In schools it may involve striking the student o ...
is not unusual in Mississippi, with 31,236 public school students paddled at least one time . A greater percentage of students were paddled in Mississippi than in any other state, according to government data for the 2011–2012 school year.
In 2007, Mississippi students scored the lowest of any state on the National Assessments of Educational Progress in both math and science.
Jackson
Jackson may refer to:
Places Australia
* Jackson, Queensland, a town in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson North, Queensland, a locality in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson South, Queensland, a locality in the Maranoa Region
* Jackson oil field in Durham, ...
, the state's capital city, is the site of the state residential school for deaf and hard of hearing students. The Mississippi School for the Deaf was established by the state legislature in 1854 before the civil war.
Culture
 While Mississippi has been especially known for its music and literature, it has embraced other forms of art. Its strong religious traditions have inspired striking works by
While Mississippi has been especially known for its music and literature, it has embraced other forms of art. Its strong religious traditions have inspired striking works by outsider art
Outsider art is Fine art, art made by Autodidacticism, self-taught individuals who are untrained and untutored in the traditional arts with typically little or no contact with the Convention (norm), conventions of the art worlds.
The term ''ou ...
ists who have been shown nationally.
Jackson established the USA International Ballet Competition The USA International Ballet Competition, or USA IBC, is one of the world's top competitions for ballet. Located in Jackson, Mississippi, this competition is attended by dancers from all over the world to represent their country for bronze, silver, ...
, which is held every four years. This ballet competition attracts the most talented young dancers from around the world.
The Magnolia Independent Film Festival
The Magnolia Independent Film Festival or The Mag, a film festival based in Mississippi, was founded by Ron Tibbett in 1997 in West Point, Mississippi. It was the first film festival to take place in Mississippi. Three years later it was moved ...
, still held annually in Starkville, is the first and oldest in the state.
George Ohr, known as the "Mad Potter of Biloxi" and the father of abstract expressionism in pottery, lived and worked in Biloxi, MS.
Music
Musicians of the state's Delta region were historically significant to the development of theblues
Blues is a music genre and musical form that originated among African Americans in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues has incorporated spiritual (music), spirituals, work songs, field hollers, Ring shout, shouts, cha ...
. Although by the end of the 19th century, two-thirds of the farm owners were black, continued low prices for cotton and national financial pressures resulted in most of them losing their land. More problems built up with the boll weevil infestation, when thousands of agricultural jobs were lost.
Jimmie Rodgers
James Charles Rodgers ( – ) was an American singer, songwriter, and musician who rose to popularity in the late 1920s. Widely regarded as the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, Father of Country Music", he is best known for his di ...
, a native of Meridian and guitarist/singer/songwriter known as the "Father of Country Music", played a significant role in the development of the blues. He and Chester Arthur Burnett were friends and admirers of each other's music. Their friendship and respect is an important example of Mississippi's musical legacy. While the state has had a reputation for being racist, Mississippi musicians created new forms by combining and creating variations on musical traditions from African American traditions, and the musical traditions of white Southerners strongly shaped by Scots-Irish and other styles.
The state is creating a Mississippi Blues Trail
The Mississippi Blues Trail was created by the Mississippi Blues Commission in 2006 to place interpretive markers at the most notable historical sites related to the birth, growth, and influence of the blues throughout (and in some cases beyond) t ...
, with dedicated markers explaining historic sites significant to the history of blues music, such as Clarksdale's Riverside Hotel, where Bessie Smith
Bessie Smith (April 15, 1892 – September 26, 1937) was an African-American blues singer widely renowned during the Jazz Age. Nicknamed the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, Empress of the Blues" and formerly Queen of the Blues, she was t ...
died after her auto accident on Highway 61. The Riverside Hotel is just one of many historical blues sites in Clarksdale. The Delta Blues Museum
The Delta Blues Museum in Clarksdale, Mississippi, United States, is a museum dedicated to collecting, preserving, and providing public access to and awareness of the musical genre known as the blues. Along with holdings of significant blues-r ...
there is visited by tourists from all over the world. Close by is "Ground Zero", a contemporary blues club and restaurant co-owned by actor Morgan Freeman
Morgan Freeman (born June 1, 1937) is an American actor, producer, and narrator. In a career spanning six decades, he has received numerous accolades, including an Academy Award and a Golden Globe Award, as well as a nomination for a Tony ...
.
Elvis Presley
Elvis Aaron Presley (January 8, 1935 – August 16, 1977) was an American singer and actor. Referred to as the "King of Rock and Roll", he is regarded as Cultural impact of Elvis Presley, one of the most significant cultural figures of the ...
, who created a sensation in the 1950s as a crossover artist and contributed to rock 'n' roll, was a native of Tupelo
Tupelo commonly refers to:
* Tupelo (tree), a small genus of deciduous trees with alternate, simple leaves
* Tupelo, Mississippi, the county seat and the largest city of Lee County, Mississippi
Tupelo may also refer to:
Places
* Tupelo, Arka ...
. From opera star Leontyne Price
Leontyne Price ( born Mary Violet Leontine Price February 10, 1927) is an American spinto soprano who was the first African-American soprano to receive international acclaim. From 1961 she began a long association with the Metropolitan Opera. ...
to the alternative rock
Alternative rock (also known as alternative music, alt-rock or simply alternative) is a category of rock music that evolved from the independent music underground of the 1970s. Alternative rock acts achieved mainstream success in the 1990s w ...
band 3 Doors Down
3 Doors Down is an American Rock music, rock band from Escatawpa, Mississippi that formed in 1996. The band's music is described as post-grunge, alternative rock, and hard rock.
The band's 2000 debut single "Kryptonite (3 Doors Down song), Kr ...
, to Gulf and Western
Gulf and Western Industries, Inc. (stylized as Gulf+Western) was an American conglomerate. The company originally focused on manufacturing and resource extraction, but it began purchasing a number of entertainment companies beginning in 1966 ...
singer Jimmy Buffett
James William Buffett (December 25, 1946 – September 1, 2023) was an American singer-songwriter, author, and businessman. He was known for his tropical rock sound and persona, which often portrayed a lifestyle described as "island escapis ...
, modern rock/jazz/world music guitarist-producer Clifton Hyde
Clifton Hyde (born November 27, 1976) is an American multi-instrumentalist, composer, and producer currently working from and residing in Nashville. He has composed multiple film scores and is a frequent collaborator of filmmaker Miles Doleac. ...
, to rappers David Banner
Lavell William Crump (born April 11, 1974), known professionally as David Banner, is an American rapper, record producer, and actor.
Born in Brookhaven, Mississippi, Banner's family moved to Jackson, Mississippi, where he was raised. Banner gra ...
, Big K.R.I.T.
Justin Lewis Scott (born August 26, 1986), known professionally as Big K.R.I.T. (a backronym for King Remembered in Time), is an American rapper and record producer. Born in Meridian, Mississippi, he began his musical career in 2005. He was sign ...
and Afroman
Joseph Edgar Foreman (born July 28, 1974), better known by his stage name Afroman, is an American rapper. His debut studio album, '' The Good Times'' (2001), featured the singles " Because I Got High" and " Crazy Rap". He was nominated for a Gr ...
, Mississippi musicians have been significant in all genres.
Sports
*Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. It lies on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, bordering the city of Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport to its west. The adjacent cities ar ...
is home to the Biloxi Shuckers
The Biloxi Shuckers are a Minor League Baseball team of the Southern League (1964–present), Southern League and the Double-A (baseball), Double-A affiliate of the Milwaukee Brewers. They are located in Biloxi, Mississippi, and are named in ref ...
baseball team, the Double-A minor league
Minor leagues are professional sports leagues which are not regarded as the premier leagues in those sports. Minor league teams tend to play in smaller, less elaborate venues, often competing in smaller cities/markets. This term is used in Nort ...
affiliate of the Milwaukee Brewers
The Milwaukee Brewers are an American professional baseball team based in Milwaukee. The Brewers compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (baseball), National League (NL) National League Central, Central Di ...
and member of the Southern League playing at Keesler Federal Park
Keesler Federal Park, formerly known as MGM Park, is a baseball park in Biloxi, Mississippi. The home of the Double-A (baseball), Double-A Biloxi Shuckers of the Southern League (1964–present), Southern League, it opened on June 6, 2015, and ca ...
, and the Mississippi Sea Wolves
The Mississippi Sea Wolves were a professional hockey team based in Biloxi, Mississippi, and played in the Mississippi Coast Coliseum. The Sea Wolves were members of the ECHL.
The Sea Wolves were founded in 1996 and had considerable success ove ...
hockey team, a member of the Federal Prospects Hockey League
The Federal Prospects Hockey League (FPHL) is a professional ice hockey independent minor league with teams in the Midwestern, Southern, and Northeastern United States. The FPHL began operations in November 2010 as the Federal Hockey League. ...
playing at Mississippi Coast Coliseum
Mississippi Coast Coliseum is an 11,500-seat reserved seating, 15,000 festival seating, multi-purpose arena in Biloxi, Mississippi. It was built in 1977. It hosted the World Championship Wrestling, WCW Beach Blast in 1993 and the Sun Belt Confere ...
.
* Clinton is home to the Mississippi Brilla FC
Mississippi Brilla is an amateur American soccer club based in Clinton, Mississippi, United States. Founded in 2006, the team plays in USL League Two. The team's colors are sky blue, navy and white.
Brilla is associated with Brilla Soccer Minis ...
, a USL League Two
USL League Two (USL2), formerly the Premier Development League (PDL), is a semi-professional soccer league sponsored by United Soccer Leagues in the United States, forming part of the United States soccer league system. The league will featu ...
soccer team.
*Southaven
Southaven is a city in DeSoto County, Mississippi, United States. It is a principal city in Greater Memphis. The 2020 census reported a population of 54,648, making it the 3rd most populous city in Mississippi and the largest suburb of Memp ...
is home to the Memphis Hustle
The Memphis Hustle are an American professional basketball team of the NBA G League based in the Greater Memphis suburb of Southaven, Mississippi, and are affiliated with the Memphis Grizzlies. The team plays their home games at the Landers C ...
basketball team. The Hustle are an affiliate of the Memphis Grizzlies
The Memphis Grizzlies (referred to locally as the Grizz) are an American professional basketball team based in Memphis, Tennessee. The Grizzlies compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Southwest Division of the ...
. They play in the NBA G League
The NBA G League, or simply the G League, is a professional basketball league in North America that serves as the Minor league#Basketball, developmental league of the National Basketball Association (NBA). The league comprises 31 teams; as of ...
.
See also
*Index of Mississippi-related articles
The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the U.S. state of Mississippi.
0–9
*.ms.us – Internet second-level domain for the state of Mississippi
*20th State, 20th state to join the United States of America
A
*Aborti ...
* Outline of Mississippi
* List of people from Mississippi
* Mississippi literature
Notes
References
Further reading
* Busbee, Westley F. ''Mississippi: A History'' (2005). * Gonzales, Edmond, ed. ''A Mississippi Reader: Selected Articles from the Journal of Mississippi History'' (1980) * Krane, Dale and Stephen D. Shaffer. ''Mississippi Government & Politics: Modernizers versus Traditionalists'' (1992), government textbook * Loewen, James W. and Charles Sallis, eds. ''Mississippi: Conflict and Change'' (2nd ed. 1980), high school textbook * McLemore, Richard, ed. ''A History of Mississippi'' 2 vols. (1973), thorough coverage by scholars * Mitchell, Dennis J., ''A New History of Mississippi'' (2014) * Ownby, ted et al. eds. ''The Mississippi Encyclopedia'' (2017) * Skates, John Ray. ''Mississippi: A Bicentennial History'' (1979), popular * Sparks, Randy J. ''Religion in Mississippi'' (2001) 374 ponline edition
* Swain, Martha H. ed. ''Mississippi Women: Their Histories, Their Lives'' (2003). 17 short biographies
External links
*Mississippi Travel and Tourism
University Press of Mississippi
, ''Southern Spaces'', October 23, 2006. *
Mississippi State Databases
an annotated list of searchable databases compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association. {{coord, 33, -90, dim:300000_region:US-MS_type:adm1st, name=State of Mississippi, display=title 1817 establishments in the United States Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas Former French colonies Southern United States States and territories established in 1817 States of the Confederate States of America States of the Gulf Coast of the United States States of the United States Contiguous United States