Mirror Mount on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A mirror mount is a device that holds a
A mirror mount is a device that holds a
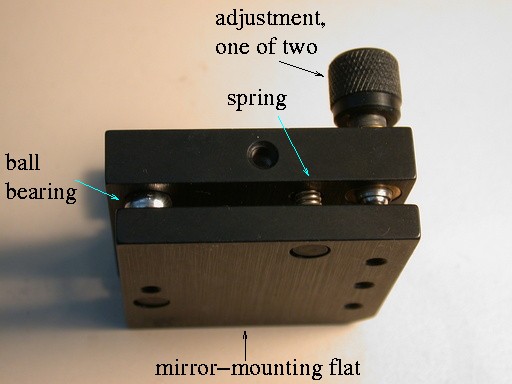 The most common type of mirror mount is the
The most common type of mirror mount is the  One way of eliminating this translation along the axis is to set the first ball on a fine-thread screw as well. By appropriate adjustment of all three screws, the mirror can be tilted in either direction without translation. The screws can be driven by a
One way of eliminating this translation along the axis is to set the first ball on a fine-thread screw as well. By appropriate adjustment of all three screws, the mirror can be tilted in either direction without translation. The screws can be driven by a
 Laser cavity end mirrors need very precise alignment. Due to their low divergence laser beams need precise steering mirrors. For prototyping optical systems on an optical table mirror mounts can be used to hold other elements besides mirrors, for example lenses often need to be aligned for minimal
Laser cavity end mirrors need very precise alignment. Due to their low divergence laser beams need precise steering mirrors. For prototyping optical systems on an optical table mirror mounts can be used to hold other elements besides mirrors, for example lenses often need to be aligned for minimal
 A mirror mount is a device that holds a
A mirror mount is a device that holds a mirror
A mirror, also known as a looking glass, is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror forms an image of whatever is in front of it, which is then focused through the lens of the eye or a camera ...
. In optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
research, these can be quite sophisticated devices, due to the need to be able to tip and tilt the mirror by controlled amounts, while still holding it in a precise position when it is not being adjusted.
An optical mirror mount generally consists of a movable front plate which holds the mirror, and a fixed back plate with adjustment screws. Adjustment screws drive the front plate about the axes of rotation in the pitch (vertical) and yaw (horizontal) directions. An optional third actuator often enables z-axis translation.
Precision mirror mounts can be quite expensive, and a notable amount of engineering goes into their design. Such sophisticated mounts are often required for lasers
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
, interferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the '' interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber opt ...
s, and optical delay line
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviol ...
s.
Types of mirror mount
 The most common type of mirror mount is the
The most common type of mirror mount is the kinematic
In physics, kinematics studies the geometrical aspects of motion of physical objects independent of forces that set them in motion. Constrained motion such as linked machine parts are also described as kinematics.
Kinematics is concerned with s ...
mount. This type of mount is designed according to the principles of kinematic determinacy
Kinematic determinacy is a term used in structural mechanics to describe a structure where material compatibility conditions alone can be used to calculate deflections. A kinematically determinate structure can be defined as a structure where, ...
. Typically, the movable frame that holds the mirror pivots on a ball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
which is set into a hole in the fixed frame. Ideally, this hole should be trihedral (pyramid-shaped). Often a conical hole is used due to easier manufacture. The frame is pivoted by means of two micrometer Micrometer can mean:
* Micrometer (device), used for accurate measurements by means of a calibrated screw
* Micrometre
The micrometre (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English as used by the International Bureau of Weights ...
s or fine-thread screws, tipped with steel ball bearings. One of these ball bearings rests in a V-groove, the other rests on a flat surface. On cheaper mounts, the flat surface may be simply the material of the mount. In more expensive mounts, the flat surface (and perhaps the hole and v-groove too) may be made out of a much harder material (often sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, cobalt, lead, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, boron, and silicon. The name ''sapphire ...
), set into the frame.
The reason for this strange mechanism is that the first ball (ideally) makes contact with the fixed frame at exactly three points, the second ball at two, and the third ball at just one. These six points of contact exactly constrain the six degrees of freedom
In many scientific fields, the degrees of freedom of a system is the number of parameters of the system that may vary independently. For example, a point in the plane has two degrees of freedom for translation: its two coordinates; a non-infinite ...
for motion of the movable frame. This leads to precise movement of the frame when the micrometers or screws are turned, without unnecessary wobble or friction.
A disadvantage of kinematic mounts is that the center of the mirror moves along its normal
Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson
* ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie
* ''Norma ...
axis, when the mirror is rotated. This is because the center of rotation is the middle of the first ball bearing, not the center of the mirror. For optical cavities and interferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the '' interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber opt ...
s, it is often desirable to be able to align the mirrors separately from adjustments to the length of the cavity. For these applications and others, a more sophisticated mount is required.
motor
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power gene ...
under computer control to make this seem to the operator like simple rotation about a virtual pivot point in the center of the mirror surface. The translation can instead be eliminated mechanically by using a gimbal
A gimbal is a pivoted support that permits rotation of an object about an axis. A set of three gimbals, one mounted on the other with orthogonal pivot axes, may be used to allow an object mounted on the innermost gimbal to remain independent of ...
mount, which uses two rings that each pivot about a line running through the center of the mirror. This gives kinematically correct two-axis rotation about the center of the mirror.
With both types of mount, springs are needed to keep the frame pressed against the ball bearings, unless the mount is designed to be used only in an orientation where gravity will keep the frame in place. Following the cantilever
A cantilever is a rigid structural element that extends horizontally and is unsupported at one end. Typically it extends from a flat vertical surface such as a wall, to which it must be firmly attached. Like other structural elements, a cantilev ...
principle, a large mount allows finer control than a smaller one. The frames are ideally made of a light material, to make the resonant
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
frequency of the structure high. This reduces vibration, since many common sources of vibration are relatively low frequency. For stability, the fixed frame is supported by a rigid mount that is securely bolted to a supporting surface. In a laboratory environment, this is typically an optical table
An optical table is a vibration control platform that is used to support systems used for laser- and optics-related experiments in science, engineering and manufacturing. The surfaces of these tables are designed to be very rigid with minimum defl ...
. A shock can cause the mount to move away from the ball bearings, but because there are only 6, hard contacts, the mirror will return to the original position, preserving the alignment.
The mount itself has to avoid deformation of the mounted optics. Stress from mounting can introduce aberration in the light reflected from a mirror, or photoelasticity
In materials science, photoelasticity describes changes in the optical properties of a material under mechanical deformation. It is a property of all dielectric media and is often used to experimentally determine the stress distribution in a ...
inside a lens. In some lasers the mirrors have to be easily replaced, in which case the mount needs to be designed to allow the mirror to be removed and replaced without losing the correct alignment.
Operation
The fine-thread screws show a slip and stick behaviour; when used manually, a torque is applied with two fingers until the thread slips a bit, then the new position is read on a scale. Inexpensive screws do long slips and lack a scale. Precision micrometers perform better and provide a scale for reference. When used remotely, anelectric motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to gene ...
is used to apply short pulses of torque. The motor is firmly connected with the screw and the thread and nothing else so that the pulse is absorbed by friction. To read out the position electronically, a rotary encoder
A rotary encoder, also called a shaft encoder, is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angle, angular position or motion of a shaft or axle to Analog signal, analog or Digital signal, digital output signals.
There are two main types of ...
is attached. When the ball is not completely centered on the screw and the axis of the screw is not normal to the mirror surface (which is an explicit feature of some high-end mirror mounts), a small cosine error in the movement of the mirror is overlaid onto the linear movement of the screw, which a controller could compensate for. If finer control over the position of the mirror is required, piezo driven mirrors can be employed with a movement distance of a few μm, and without the stick-slip phenomenon of a mechanical screw.
Applications
 Laser cavity end mirrors need very precise alignment. Due to their low divergence laser beams need precise steering mirrors. For prototyping optical systems on an optical table mirror mounts can be used to hold other elements besides mirrors, for example lenses often need to be aligned for minimal
Laser cavity end mirrors need very precise alignment. Due to their low divergence laser beams need precise steering mirrors. For prototyping optical systems on an optical table mirror mounts can be used to hold other elements besides mirrors, for example lenses often need to be aligned for minimal coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate ...
. Sometimes prism
PRISM is a code name for a program under which the United States National Security Agency (NSA) collects internet communications from various U.S. internet companies. The program is also known by the SIGAD . PRISM collects stored internet ...
s only need two axes alignment and can be mounted on a mirror mount rather than a three-axis prism table.
Critical phase matched crystals can be aligned and tuned precisely with a standard mirror mount. The same is true for small etalons, retarders and polarizer
A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that lets light waves of a specific polarization (waves), polarization pass through while attenuation, blocking light waves of other polarizations. It can filter a beam of light of undefined or mixed ...
s. Furthermore, mirror mounts using magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, ...
s instead of springs allow the mobile frame to be removed and later replaced in exactly the same position.
Related devices
*Althoughrotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
can be achieved by a semi gimbal mount most rotation stages are not designed based on the principles of kinematic determinacy.
*A linear motion bearing
A linear-motion bearing or linear slide is a bearing designed to provide free motion in one direction. There are many different types of linear motion bearings.
Motorized linear slides such as machine slides, X-Y tables, roller tables and some ...
or linear stage
A linear stage or translation stage is a component of a precise motion system used to restrict an object to a single axis of motion. The term linear slide is often used interchangeably with "linear stage", though technically "linear slide" refer ...
having kinematic determinacy uses two V-grooves sliding on a cylinder, a flat surface sliding on a second parallel cylinder, and a flat surface joining the screw.
*The hexapod known from flight simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies, for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they rea ...
s allows motion with six degrees of freedom. For kinematic determinacy each leg consists of a ball set in a trihedral hole in the fixed frame, a ball joining a flat plate in the fixed frame, and a ball joining a trihedral hole in the mobile frame. The mobile part of the leg is connected with a thread which runs in thread of the fixed part.
*A screw thread
A screw thread is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a ''straight'' thread and t ...
join gets kinematic determinacy the same way as any other rotation bearing.
*The ball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
and cylindrical roller bearing are overdetermined, having more points of contact than required for kinematic determinacy. This leads to decreased precision as the joints wear.
*The flexure bearing
A flexure bearing is a category of flexure which is engineered to be compliant in one or more angular degrees of freedom. Flexure bearings are often part of compliant mechanisms. Flexure bearings serve much of the same function as conventional be ...
and piezoelectric element offer higher precision than other mechanical bearings.
See also
*Mirror support cell
In astronomy, a mirror support cell - more commonly mirror cell - is a component of a reflecting telescope that supports the mirror in place to hold optical alignment, allow collimation adjustment, and protect it from falling out. The common usa ...
* PLate OPtimizer
PLate OPtimizer, or PLOP is a CAD program used by amateur telescope makers to design primary mirror support cells for reflecting telescopes. It was developed by telescope maker David Lewis, first described in 1999, and used to simplify calculati ...
* Kinematic coupling
Kinematic coupling describes fixtures designed to exactly constrain the part in question, providing precision and certainty of location. A canonical example of a kinematic coupling consists of three radial v-grooves in one part that mate with thre ...
References
{{reflist, 1 Optomechanics Positioning instruments Holders