Methylation Specific Oligonucleotide Microarray on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Methylation specific oligonucleotide microarray, also known as MSO microarray, was developed as a technique to map epigenetic methylation changes in 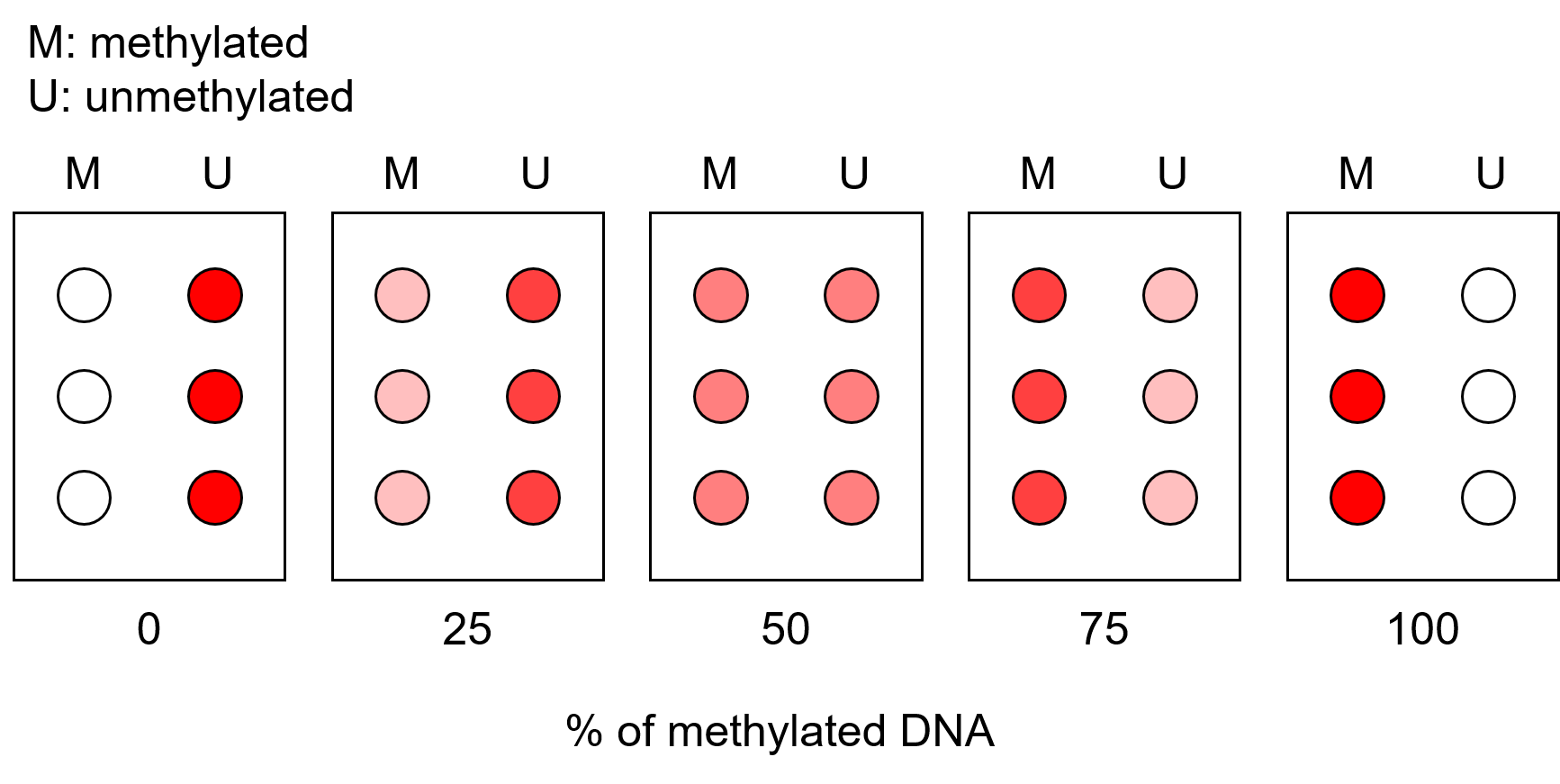
Resources, information and specific protocols for DNA Methylation Analysis Software for DNA Methylation Analysis
Cancer research Microarrays {{oncology-stub
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
cells.
The general process starts with modification of DNA with bisulfite
The bisulfite ion (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogensulfite) is the ion . Salts containing the ion are also known as "sulfite lyes". Sodium bisulfite is used interchangeably with sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5). Sodium metabisulfite diss ...
, specifically to convert ''unmethylated'' cytosine in CpG sites to uracil, while leaving ''methylated'' cytosines untouched. The modified DNA region of interest is amplified via PCR and during the process, uracils are converted to thymine. The amplicons are labelled with a fluorescent dye
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescence, fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromaticity, aromatic groups, or planar o ...
and hybridized to oligonucleotide probes that are fixed to a glass slide. The probes differentially bind to cytosine and thymine residues, which ultimately allows discrimination between methylated and unmethylated CpG sites, respectively.
A calibration curve is produced and compared with the microarray results of the amplified DNA samples. This allows a general quantification of the proportion of methylation present in the region of interest.
This microarray technique was developed by Tim Hui-Ming Huang and his laboratory and was officially published in 2002.

Implications for cancer research
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
cells often develop atypical methylation
Methylation, in the chemistry, chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate (chemistry), substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replac ...
patterns, at CpG sites in promoters of tumour suppressor genes. High levels of methylation at a promoter leads to downregulation of the corresponding genes and is characteristic of carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cell (biology), cells are malignant transformation, transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, G ...
. It is one of the most consistent changes observed in early stage tumour cells. Methylation specific oligonucleotide microarray allows for the high resolution and high throughput detection of numerous methylation events on multiple gene promoters. Therefore, this technique can be used to detect aberrant methylation in tumour suppressor promoters at an early stage and has been used in gastric and colon cancers and multiple others. Because it allows one to detect presence of atypical methylations in cancer cells, it can also be used to reveal the major cause behind the malignancy, whether its main contributor is mutations on chromosomes or epigenetic modifications, as well as which tumour suppressor genes' transcription levels are affected. An interesting use of this microarray includes specific classification of cancers based on the methylation patterns alone, such as differentiating between classes of leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
, suggesting that different classes of cancer show relatively unique methylation patterns. This technique has also been proposed to monitor cancer treatments that involve modifying the methylation patterns in mutant cancer cells.
References
External links
Resources, information and specific protocols for DNA Methylation Analysis
Cancer research Microarrays {{oncology-stub