Messier 3 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Messier 3 (M3; also NGC 5272) is a
 Many amateur astronomers consider it one of the finest northern globular clusters, following only Messier 13. M3 has an
Many amateur astronomers consider it one of the finest northern globular clusters, following only Messier 13. M3 has an
SEDS Messier pages on M3
M3, Galactic Globular Clusters Database page
M3 Photo detail Dark Atmospheres
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Messier 3 Messier 003 Messier 003 003 Messier 003 17640503 Discoveries by Charles Messier
globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars that is bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards its center. It can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars, all orbiting ...
located 33.9 thousand light years from Earth in the northern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
of Canes Venatici. It is one of the largest and brightest globular clusters discovered with around 500,000 stars.
Discovery
It was discovered on May 3, 1764, and was the first Messier object to be discovered by Charles Messier himself. Messier originally mistook the object for a nebula without stars. This mistake was corrected after the stars were resolved byWilliam Herschel
Frederick William Herschel ( ; ; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel. Born in the Electorate of Hanover ...
around 1784. Since then, it has become one of the best-studied globular clusters. Identification of the cluster's unusually large variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are ...
population was begun in 1913 by American astronomer Solon Irving Bailey and new variable members continue to be identified up through 2004.
Visibility
 Many amateur astronomers consider it one of the finest northern globular clusters, following only Messier 13. M3 has an
Many amateur astronomers consider it one of the finest northern globular clusters, following only Messier 13. M3 has an apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), ...
of 6.2, making it a difficult naked eye
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnification, magnifying, Optical telescope#Light-gathering power, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microsc ...
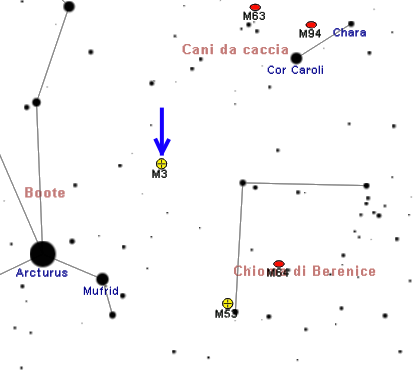
target even with dark conditions with averted vision. However, with a moderate-sized telescope, the cluster can be seen as a cloudy smudge even in severely light-polluted skies, and can be further defined in darker conditions. It can be found by looking almost exactly halfway along the north-west line that would join Arcturus (α Boötis) to Cor Caroli (α Canum Venaticorum). Using a telescope with a aperture, the cluster has a bright core with a diameter of about 6 arcminutes and spans a total of double that.
Characteristics
This cluster is one of the largest and brightest, and is made up of around 500,000 stars. It is estimated to be 11.4 billion years old. It is centered at 32,600light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year (ly or lyr), is a unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equal to exactly , which is approximately 9.46 trillion km or 5.88 trillion mi. As defined by the International Astr ...
s (10.0 kpc) away from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
.
Messier 3 is quite isolated as it is above the Galactic plane
The galactic plane is the plane (geometry), plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms ''galactic plane'' and ''galac ...
and roughly from the center of the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
. It contains 274 known variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are ...
s, by far the most found in any globular cluster. These include 133 RR Lyrae variables, of which about a third display the Blazhko effect of long-period modulation. The overall abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium, what astronomers term the metallicity, is in the range of −1.34 to −1.50 dex. This value gives the logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , the ...
of the abundance relative to the Sun; the actual proportion is 3.2–4.6% of the solar abundance. Messier 3 is the prototype for the Oosterhoff type I cluster, which is considered "metal-rich". That is, for a globular cluster, Messier 3 has a relatively high abundance of heavier elements.

References
See also
* List of Messier objectsExternal links
SEDS Messier pages on M3
M3, Galactic Globular Clusters Database page
M3 Photo detail Dark Atmospheres
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Messier 3 Messier 003 Messier 003 003 Messier 003 17640503 Discoveries by Charles Messier