Mesoperthite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
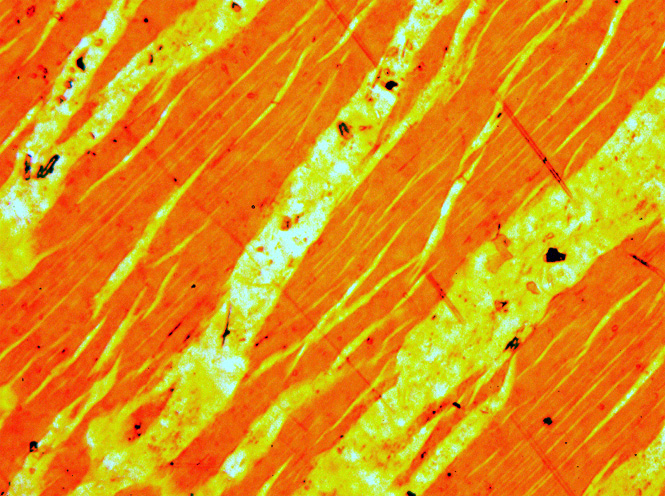 Perthite is used to describe an intergrowth of two
Perthite is used to describe an intergrowth of two
R.V. Dietrich - Perthite
Feldspar Petrology
 Perthite is used to describe an intergrowth of two
Perthite is used to describe an intergrowth of two feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feld ...
s: a host grain of potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosp ...
-rich alkali feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldsp ...
(near K-feldspar, KAlSi3O8, in composition) includes exsolved lamellae
Lamella (plural lamellae) means a small plate or flake in Latin, and in English may refer to:
Biology
* Lamella (mycology), a papery rib beneath a mushroom cap
* Lamella (botany)
* Lamella (surface anatomy), a plate-like structure in an animal
* ...
or irregular intergrowths of sodic alkali feldspar (near albite
Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula . It is a tectosilica ...
, NaAlSi3O8, in composition). Typically, the host grain is orthoclase
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar ( endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture," because its two cleavage planes are at right angl ...
or microcline
Microcline (KAlSi3O8) is an important igneous rock-forming tectosilicate mineral. It is a potassium-rich alkali feldspar. Microcline typically contains minor amounts of sodium. It is common in granite and pegmatites. Microcline forms during slow ...
, and the lamellae are albite. If sodic feldspar is the dominant phase, the result is an antiperthite and where the feldspars are in roughly equal proportions the result is a mesoperthite.
The intergrowth forms by exsolution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word ...
due to cooling of a grain of alkali feldspar with a composition intermediate between K-feldspar and albite. There is complete solid solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The wor ...
between albite and K-feldspar at temperatures near 700 °C and pressures like those within the crust of the Earth, but a miscibility gap A miscibility gap is a region in a phase diagram for a mixture of components where the mixture exists as two or more phases – any region of composition of mixtures where the constituents are not completely miscible.
The IUPAC Gold Book defines ...
is present at lower temperatures. If an alkali feldspar grain with an intermediate composition cools slowly enough, K-rich and more Na-rich feldspar domains separate from one another. In the presence of water, the process occurs quickly.
When megascopically developed, the texture may consist of distinct pink and white lamellae representing exsolved white albite (NaAlSi3O8) in pink microcline
Microcline (KAlSi3O8) is an important igneous rock-forming tectosilicate mineral. It is a potassium-rich alkali feldspar. Microcline typically contains minor amounts of sodium. It is common in granite and pegmatites. Microcline forms during slow ...
. The intergrowths in perthite have a great variety of shapes. If cooling is sufficiently slow, the alkali feldspar may exsolve to form separate grains with near-endmember albite and K-feldspar compositions. The largest documented single crystal of perthite was found in Hugo Mine in South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota peo ...
and measured about x x .
The gem varieties of potassium feldspar, amazonite
Amazonite, also known as Amazonstone, is a green tectosilicate mineral, a variety of the potassium feldspar called microcline. Its chemical formula is KAlSi3O8, which is polymorphic to orthoclase.
Its name is taken from that of the Amazon River ...
and moonstone are variant colored perthites.
References
{{reflistExternal links
R.V. Dietrich - Perthite
Feldspar Petrology