Mesoamerican Languages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Mesoamerican languages are the
Mesoamerican languages are the
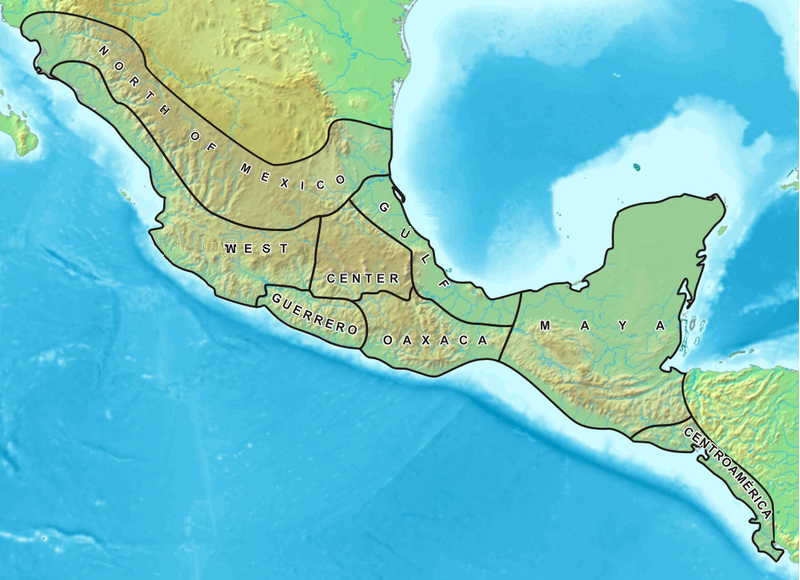 Mesoamerica can be divided into smaller linguistic subareas wherein linguistic diffusion has been especially intense, or where certain families have extended to become predominant.
One such subarea would be the Maya area, roughly covering the
Mesoamerica can be divided into smaller linguistic subareas wherein linguistic diffusion has been especially intense, or where certain families have extended to become predominant.
One such subarea would be the Maya area, roughly covering the
website of the Mesoamerican Language Documentation Project
/ref> Others find Mixe–Zoque an unlikely candidate because no current Mixe–Zoque settlements are found in central Mexico. Around 500–600 CE a new language family entered Mesoamerica when speakers of Proto- Nahuan, a southern Uto-Aztecan language, moved south into central Mexico. Their arrival, which coincides with the decline of Teotihuacan and a period of general turmoil and mass migration in Mesoamerica, has led scientists to speculate that they might have been involved somehow in the fall of the Teotihuacan empire. What is known is that in the years following Teotihuacan's fall Nahuan speakers quickly rose to power in central Mexico and expanded into areas earlier occupied by speakers of Oto-Manguean, Totonacan and Huastec. During this time Oto-Manguean groups of central Mexico such as the Chiapanec, Chorotega and Subtiaba migrated south some of them reaching the southern limits of Mesoamerica in El Salvador and Nicaragua. Also some speakers of Nahuan moved south, some settling on the coast of Oaxaca where their speech became the language Pochutec, and others moving all the way to El Salvador, becoming the ancestors of the speakers of modern Pipil.
 The Spanish arrival in the new world turned the linguistic situation of Mesoamerica upside down. And from then on the indigenous languages have been subject to varying policies imposed on them by the colonial rule. The first impact came from the decimation of the indigenous population by diseases brought by the Europeans. Within the first two centuries of Spanish rule Mesoamerica experienced a dramatic population decline and it is well documented that several small linguistic groups became completely extinct already during the 16th century. The policies that contributed most to a change in the linguistic situation of Mesoamerica were the policies used for conversion of Indians to Christianity. The first victim of this process was the native writing systems which were banned and prohibited and the existing texts destroyed – the pictorial scripts were seen as an idolatry by the Catholic Church. At first missionaries favoured the teaching of Spanish to their prospect converts but from 1555 the first Mexican Council established the policy that the Indians should be converted in their own languages and that parish priests should know the indigenous language of their parishioners. This called for a massive education of clergymen in native languages and the church undertook this task with great zeal. Institutions of learning such as the
The Spanish arrival in the new world turned the linguistic situation of Mesoamerica upside down. And from then on the indigenous languages have been subject to varying policies imposed on them by the colonial rule. The first impact came from the decimation of the indigenous population by diseases brought by the Europeans. Within the first two centuries of Spanish rule Mesoamerica experienced a dramatic population decline and it is well documented that several small linguistic groups became completely extinct already during the 16th century. The policies that contributed most to a change in the linguistic situation of Mesoamerica were the policies used for conversion of Indians to Christianity. The first victim of this process was the native writing systems which were banned and prohibited and the existing texts destroyed – the pictorial scripts were seen as an idolatry by the Catholic Church. At first missionaries favoured the teaching of Spanish to their prospect converts but from 1555 the first Mexican Council established the policy that the Indians should be converted in their own languages and that parish priests should know the indigenous language of their parishioners. This called for a massive education of clergymen in native languages and the church undertook this task with great zeal. Institutions of learning such as the


*'' Mixean''
**E & W Mixe • ''E
*
*'' Huastecan''
** Huastec • ''N
(other branches are outside Mesoamerica)
* Paya (Pech) • ''N
* Miskito • ''
Mesoamerican Languages Project at the University of TexasFAMSI – Mesoamerican Language Texts Digitization ProjectProject for the Documentation of the Languages of Mesoamerica
* ttp://www.peabody.harvard.edu/node/24 Corpus of Maya Hieroglyphic Inscriptions Program at the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology, Harvard Universitybr>Corpus of Maya Hieroglyphic Inscriptions, Volumes 1–9. Published by the Peabody Museum Press and distributed by Harvard University Press
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mesoamerican Languages + + Indigenous languages of North America
 Mesoamerican languages are the
Mesoamerican languages are the language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
s indigenous to the Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
n cultural area, which covers southern Mexico, all of Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
, Belize
Belize is a country on the north-eastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a maritime boundary with Honduras to the southeast. P ...
, El Salvador
El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is S ...
, and parts of Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, ...
, Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America aft ...
and Costa Rica
Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America. It borders Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as Maritime bo ...
. The area is characterized by extensive linguistic diversity containing several hundred different languages and seven major language families. Mesoamerica is also an area of high linguistic diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
in that long-term interaction among speakers of different languages through several millennia has resulted in the convergence of certain linguistic traits across disparate language families. The Mesoamerican sprachbund
A sprachbund (, from , 'language federation'), also known as a linguistic area, area of linguistic convergence, or diffusion area, is a group of languages that share areal features resulting from geographical proximity and language contact. Th ...
is commonly referred to as the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area.
The languages of Mesoamerica were also among the first to evolve independent traditions of writing
Writing is the act of creating a persistent representation of language. A writing system includes a particular set of symbols called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which they encode a particular spoken language. Every written language ...
. The oldest texts date to approximately 1000 BCE (namely Olmec
The Olmecs () or Olmec were an early known major Mesoamerican civilization, flourishing in the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco from roughly 1200 to 400 Before the Common Era, BCE during Mesoamerica's Mesoamerican chronolog ...
and Zapotec), though most texts in the indigenous scripts (such as Maya
Maya may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Mayan languages, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (East Africa), a p ...
) date to c. 600–900 CE. Following the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century, and continuing up until the 19th century, most Mesoamerican languages were written in Latin script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Gree ...
.
The languages of Mesoamerica belong to 6 major families – Mayan, Oto-Mangue, Mixe–Zoque, Totonacan, Uto-Aztecan
The Uto-Aztecan languages are a family of native American languages, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The name of the language family reflects the common ...
and Chibchan languages
The Chibchan languages (also known as Chibchano) make up a language family indigenous to the Isthmo-Colombian Area, which extends from eastern Honduras to northern Colombia and includes populations of these countries as well as Nicaragua, Costa R ...
(only on the southern border of the area) – as well as a few smaller families and isolates – Purépecha
The Purépecha ( ) are a group of Indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of Michoacán, Mexico, mainly in the area of the cities of Cherán and Pátzcuaro.
They are also known by the derogatory term " Tarascan", an exonym, app ...
, Huave, Tequistlatec, Xincan and Lencan. Among these Oto-Manguean and Mayan families account for the largest numbers of speakers by far – each having speakers numbering more than a million. Many Mesoamerican languages today are either endangered or already extinct, but others, including the Mayan languages
The Mayan languages In linguistics, it is conventional to use ''Mayan'' when referring to the languages, or an aspect of a language. In other academic fields, ''Maya'' is the preferred usage, serving as both a singular and plural noun, and a ...
, Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
, Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are Indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica of Guerrero, Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerre ...
and Zapotec, have several hundred thousand speakers and remain viable.
Language vs. dialect
The distinction between relatedlanguage
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
s and dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardize ...
s is notoriously vague in Mesoamerica. The dominant Mesoamerican socio-cultural pattern through millennia has been centered around the town or city as the highest level community rather than the nation, realm or people. This has meant that within Mesoamerica each city-state or town community, called in Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
an , has had its own language standard which, in the typical case, has evolved separately from closely related but geographically remote languages. Even geographically close communities with closely related, mutually intelligible languages have not necessarily seen themselves as being ethnically related, or their language as being a unifying factor between them. The relative endogamy
Endogamy is the cultural practice of marrying within a specific social group, religious denomination, caste, or ethnic group, rejecting any from outside of the group or belief structure as unsuitable for marriage or other close personal relatio ...
of the town community has also resulted in a large linguistic diversification between communities despite geographical and linguistic proximity, often resulting in a low intelligibility between varieties of the same language spoken in adjacent communities. The exception to this rule is when a common “lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
” has evolved to facilitate communication between different linguistic groups. This has been the case for Classical Nahuatl
Classical Nahuatl, also known simply as Aztec or Codical Nahuatl (if it refers to the variants employed in the Mesoamerican Codices through the medium of Aztec Hieroglyphs) and Colonial Nahuatl (if written in Post-conquest documents in the Lat ...
and Classical Maya, both of which, at different times in history, have been used as a common language between different ethnic groups. Further complicating matters are the semi-nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic lifestyle of many Mesoamerican peoples, and political systems which often have used relocation of entire communities as a political tool. Dialect or variant “chaining” is common, where any adjacent two or three towns in a sequence are similar enough in speech to understand each other fairly well, but those separated more widely have trouble understanding each other, and there are no clear breaks naturally separating the continuum into coherent sub-regions.
All of these factors together have made it exceedingly difficult to distinguish between what constitutes a language or a dialect in Mesoamerica. Linguistic isogloss
An isogloss, also called a heterogloss, is the geographic boundary of a certain linguistics, linguistic feature, such as the pronunciation of a vowel, the meaning of a word, or the use of some morphological or syntactic feature. Isoglosses are a ...
es do not coincide often or strongly enough to prove very useful when trying to decide, and sociological factors often further cloud the picture. The significance of measurements of intelligibility (which is itself difficult to measure) depends very much on analysts' purposes and theoretical commitments. In Spanish the word has often been used generically about indigenous languages in order to describe them as inherently inferior to the European languages. In recent years this has caused an aversion to the term “dialect” among Spanish-speaking linguists and others, and the term has often been applied instead.
Many Mesoamerican linguistic groupings have not had different names in common usage for their different languages and some linguistic groups known by a single name show a sufficiently significant variation to warrant division into a number of languages which are quite low in mutual intelligibility. This is the case for example for the Mixtecan, Zapotecan and Nahuan linguistic groups, which all contain distinct languages that are nonetheless referred to by a single name. Sometimes a single name has even been used to describe completely unrelated linguistic groups, as is the case with the terms " Popoluca" or "Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajío region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the same meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" tha ...
". This shortage of language names has meant that the convention within Mesoamerican linguistics when writing about a specific linguistic variety is to always mention the name of the broad linguistic group as well as the name of the community, or geographic location in which it is spoken, for example Isthmus-Mecayapan Nahuatl, Zoogocho Zapotec or Usila Chinantec. Some language groups however have been more adequately named. This is the case of the Mayan languages, with an internal diversity that is arguably comparable to that found between the Nahuatl dialects, but many of whose linguistic varieties have separate names, such as Kʼicheʼ, Tzotzil or Huastec.
Geographical overview
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula ( , ; ) is a large peninsula in southeast Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north and west of the peninsula from the C ...
, Guatemala, Belize, Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
and Tabasco
Tabasco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Tabasco, 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It i ...
, where Mayan languages
The Mayan languages In linguistics, it is conventional to use ''Mayan'' when referring to the languages, or an aspect of a language. In other academic fields, ''Maya'' is the preferred usage, serving as both a singular and plural noun, and a ...
have been highly predominant. The fringes of the area have been home to Xincan (in the southeast) and Mixe-Zoque (along the Pacific coast) speakers, in addition to Nawat
Nawat (academically Pipil, also known as Nahuat) is a Nahuan languages, Nahuan language native to Central America. It is the southernmost extant member of the Uto-Aztecan languages, Uto-Aztecan family. Before Spanish colonization of the Americas ...
(also along the Pacific coast) and the Oto-Manguean Chiapanec language (in the southwest) following postclassic migrations.
Another linguistic area is Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
, which is dominated by speakers of Oto-Manguean languages
The Oto-Manguean or Otomanguean () languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that are now spoken are indigenous to Mexico, but the Manguean branch of th ...
, mainly Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are Indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica of Guerrero, Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerre ...
and Zapotec, both of which are extremely internally diverse. Non-Oto-Manguean languages include Mixe, Tequistlatecan, Huave, and the Nahuan Pochutec language. Huave was the original language of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec
The Isthmus of Tehuantepec () is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Before the opening of the Panama Canal, it was a major overland transport route known simply as the T ...
, but lost territory to Zapotec. Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
is the most linguistically diverse area of Mesoamerica and its contain at least 100 mutually unintelligible linguistic variants.
The subarea commonly called Central Mexico, covering valleys and mountainous areas surrounding the Valley of Mexico
The Valley of Mexico (; ), sometimes also called Basin of Mexico, is a highlands plateau in central Mexico. Surrounded by mountains and volcanoes, the Valley of Mexico was a centre for several pre-Columbian civilizations including Teotihuacan, ...
, originally was mainly host to Oto-Pamean languages
The Oto-Pamean languages are a branch of the Oto-Manguean languages
The Oto-Manguean or Otomanguean () languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that ...
; however, beginning in the late classic these languages were largely gradually displaced by Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
, which was henceforth the predominant indigenous language of the area. Otomi, Matlatzinca, and Mazahua retained significant presences.
The Western area was inhabited mostly by speakers of Purépecha
The Purépecha ( ) are a group of Indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of Michoacán, Mexico, mainly in the area of the cities of Cherán and Pátzcuaro.
They are also known by the derogatory term " Tarascan", an exonym, app ...
in Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo, is one of the 31 states which, together with Mexico City, compose the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The stat ...
, Huichol and Cora in Nayarit
Nayarit, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in Municipalities of Nayarit, 20 municipalit ...
, and Western Peripheral Nahuatl
Western Peripheral Nahuatl is a group of Nahuatl languages of Western Mexico. They are:
*Michoacán Pómaro Nahuatl on the west coast
* Coatepec and Temascaltepec Nahuatl of western México State and northwestern Guerrero
Guerrero, offic ...
in Jalisco
Jalisco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in western Mexico and is bordered by s ...
and Colima
Colima, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Colima, is among the 31 states that make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It shares its name with its capital and main city, Colima.
Colima is a small state of western Mexico on the cen ...
. A host of small undocumented languages were spoken in Colima and southern Jalisco, such as Jalisco Otomi and Jalisco Zapotec.
The Northern Rim area has been inhabited by semi-nomadic Chichimec
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajío region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the same meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" t ...
speakers of Uto-Aztecan languages (probably related to the Tepiman and Corachol groups) as well as Pame (Oto-Mangue), and other undocumented languages that are now extinct, such as Jalisco Otomi.
The Gulf area is traditionally the home of speakers of Totonacan languages in the northern and central area and Mixe–Zoque languages
The Mixe–Zoque (also Mixe–Zoquean, Mije–Soke, Mije–Sokean) languages are a language family whose living members are spoken in and around the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico. The Mexican government recognizes three distinct Mixe–Zoquean ...
in the southern area. However, the northern gulf area became home to the speakers of Huastec in the preclassic period, and the southern area began speaking Isthmus Nahuatl in the post-classic period.
The areas of Central America (excluding the Maya areas) that formed part of Mesoamerica during the preclassic were dominated by Lencan speakers. Based on toponymy, it is possible that Xincan languages
Xinca (or ''Xinka'', Sinca, or ''Szinca'') is a small extinct family of Mesoamerican languages; formerly, the language was regarded as a single language isolate. Xinca was once spoken by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous Xinca p ...
were originally spoken in western El Salvador, but were replaced by Nawat
Nawat (academically Pipil, also known as Nahuat) is a Nahuan languages, Nahuan language native to Central America. It is the southernmost extant member of the Uto-Aztecan languages, Uto-Aztecan family. Before Spanish colonization of the Americas ...
after postclassic migrations. The migrations of Subtiaba and Mangue speakers, possibly also during the postclassic period, expanded the realm of Mesoamerican cultural influence to include the Pacific coast of Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America aft ...
and the Nicoya Peninsula
The Nicoya Peninsula () is a peninsula on the Pacific coast of Costa Rica. It is divided into two provinces: Guanacaste Province in the north, and the Puntarenas Province in the south. It is located at . It varies from in width and is about lon ...
, which were previously part of the Isthmo-Colombian area and probably inhabited by Misumalpan and Chibchan speakers.
The Guerrero subarea has been home to the Oto-Manguean Tlapanec and the unclassified Cuitlatec, and later Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
, as well as a handful of undocumented languages along the Costa Grande.
Linguistic prehistory
The linguistic history of Mesoamerican languages can roughly be divided intopre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era, also known as the pre-contact era, or as the pre-Cabraline era specifically in Brazil, spans from the initial peopling of the Americas in the Upper Paleolithic to the onset of European col ...
, colonial and modern periods.
Pre-Columbian period
The first human presence in Mesoamerica is documented around 8000 BCE, during a period referred to as thePaleo-Indian
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in ...
. Linguistic data, however, including language reconstruction derived from the comparative method
In linguistics, the comparative method is a technique for studying the development of languages by performing a feature-by-feature comparison of two or more languages with common descent from a shared ancestor and then extrapolating backwards ...
, do not reach further back than approximately 5000 years (towards the end of the Archaic period). Throughout the history of Mesoamerica, an unknown number of languages and language families became extinct and left behind no evidence of their existence. What is known about the pre-Columbian history of the Mesoamerican languages is what can be surmised from linguistic, archeological
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology ...
and ethnohistorical evidence. Often, hypotheses concerning the linguistic prehistory of Mesoamerica rely on very little evidence.
Archaic period (–2000 BCE)
Three large language families are thought to have had their most recent common homelands within Mesoamerica. The time frames and locations in which the common ancestors of these families, referred to by linguists asproto-language
In the tree model of historical linguistics, a proto-language is a postulated ancestral language from which a number of attested languages are believed to have descended by evolution, forming a language family. Proto-languages are usually unatte ...
s, were spoken are reconstructed by methods of historical linguistics. The three earliest known families of Mesoamerica are the Mixe–Zoquean languages, the Oto-Manguean languages
The Oto-Manguean or Otomanguean () languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that are now spoken are indigenous to Mexico, but the Manguean branch of th ...
and the Mayan languages
The Mayan languages In linguistics, it is conventional to use ''Mayan'' when referring to the languages, or an aspect of a language. In other academic fields, ''Maya'' is the preferred usage, serving as both a singular and plural noun, and a ...
. Proto-Oto-Manguean is thought to have been spoken in the Tehuacán valley between 5000 and 3000 BCE, although it may only have been one center of Oto-manguean culture, another possible Oto-Manguean homeland being Oaxaca. Proto-Mayan was spoken in the Cuchumatanes highlands of Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
around 3000 BCE. Proto-Mixe–Zoquean was spoken on the gulf coast and on the Isthmus of Tehuantepec
The Isthmus of Tehuantepec () is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Before the opening of the Panama Canal, it was a major overland transport route known simply as the T ...
and on the Guatemalan Pacific coast around 2000 BCE, in a much larger area than its current extension. Totonacan languages, Purépecha, Huave and the Tequistlatecan languages can also be assumed to have been present in Mesoamerica at this point although it is unknown.
Preclassic period (2000 BCE – 200 CE)
The firstcomplex society
A complex society is characterized by the following modern features:
* Organizational society wherein its economy is structured according to specialization and a Division of labour, division of labor. These economic features spawn a bureaucratic c ...
in Mesoamerica was the Olmec civilization, which emerged around 2000 BCE during the Early Preclassic. It is documented that around this time many Mesoamerican languages adopted loanwords from the Mixe–Zoquean languages, particularly loanwords related to such culturally fundamental concepts as agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
and religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
. This has led some linguists to believe that the carriers of Olmec culture spoke a Mixe–Zoquean language and that words spread from their language into others because of their potential cultural dominance in the Preclassic period, though the relationship between the Olmec and other Preclassic groups is still debated (see Olmec influences on Mesoamerican cultures
The causes and degree of Olmec influences on Mesoamerican cultures has been a subject of debate over many decades. Although the Olmecs are considered to be perhaps the earliest Mesoamerican civilization, there are questions concerning how and how ...
). During this time the Oto-Manguean languages diversified and spread into Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
and central Mexico. In the Valley of Oaxaca, the Oto-Manguean Zapotec culture emerges around c. 1000 BCE. The splitting of Proto-Mayan into the modern Mayan languages slowly began at roughly 2000 BCE when the speakers of Huastec moved north into the Mexican Gulf Coast region. Uto-Aztecan languages
The Uto-Aztecan languages are a family of native American languages, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The name of the language family reflects the common ...
were still outside of Mesoamerica during the Preclassic, their speakers living as semi-nomadic
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
hunter-gatherers
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, especially w ...
on the northern rim of the region and co-existing with speakers of Coracholan and Oto-Pamean languages
The Oto-Pamean languages are a branch of the Oto-Manguean languages
The Oto-Manguean or Otomanguean () languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that ...
.
Classic period (200–1000 CE)
During the Classic period the linguistic situation simultaneously becomes both clearer and more obscure. While the Maya actually left examples of their writing, researchers have been unable to determine the linguistic affiliations of several important Classic civilizations, includingTeotihuacan
Teotihuacan (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'', ; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City.
Teotihuacan is ...
, Xochicalco
Xochicalco () is a pre-Columbian archaeological site in Miacatlán in the western part of the Mexican state of Morelos. The name ''Xochicalco'' may be translated from Nahuatl as "in the house of Flowers". The site is located 38 km southwest ...
, Cacaxtla, and El Tajín. During this time it is well established that Mixtec languages were spoken at Tilantongo and Zapotec at Monte Albán
Monte Albán is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site in the Santa Cruz Xoxocotlán Municipality in the southern Mexico, Mexican state of Oaxaca (17.043° N, 96.767°W). The site is located on a low mountainous range rising above the plain i ...
(in the Valley of Oaxaca
The Central Valleys () of Oaxaca, also simply known as the Oaxaca Valley, is a geographic region located within the modern-day state of Oaxaca in southeastern Mexico. In an administrative context, it has been defined as comprising the districts of ...
). The linguistic situation of the Maya area is relatively clear – Proto-Yucatec and Proto-Cholan were established in their respective locations in Yucatán and in the Tabasco area. Around 200 CE speakers of the Tzeltalan branch of Proto-Cholan moved south into Chiapas displacing speakers of Zoquean languages. Throughout the southern part of the Maya area and the highlands the elite
In political and sociological theory, the elite (, from , to select or to sort out) are a small group of powerful or wealthy people who hold a disproportionate amount of wealth, privilege, political power, or skill in a group. Defined by the ...
of the Classic Maya centers spoke a common prestige language based on Cholan, a variant often referred to as Classic Ch'olti'an.
An important question that remains to be answered is what language or languages were spoken by the people and rulers of the empire of Teotihuacan. During the first part of the Classic period Teotihuacan achieved dominance over central Mexico and far into the Maya area. Possible candidates for the language of Teotihuacan have been Nahuatl, Totonac or Mixe–Zoque. Terrence Kaufman
Terrence Kaufman (1937 – March 3, 2022) was an American linguist specializing in documentation of unwritten languages, lexicography, Mesoamerican historical linguistics and language contact phenomena. He was an emeritus professor of linguistic ...
has argued that Nahuatl is an unlikely candidate because Proto-Nahuan did not enter Mesoamerica until around the time of the fall of Teotihuacan (c. 600 AD), and that Totonac or Mixe–Zoque are likely candidates because many Mesoamerican languages have borrowed from these two languages during the Classic period.Kaufman, Terrence, (2001) "Nawa Linguistic Prehistory", paper published awebsite of the Mesoamerican Language Documentation Project
/ref> Others find Mixe–Zoque an unlikely candidate because no current Mixe–Zoque settlements are found in central Mexico. Around 500–600 CE a new language family entered Mesoamerica when speakers of Proto- Nahuan, a southern Uto-Aztecan language, moved south into central Mexico. Their arrival, which coincides with the decline of Teotihuacan and a period of general turmoil and mass migration in Mesoamerica, has led scientists to speculate that they might have been involved somehow in the fall of the Teotihuacan empire. What is known is that in the years following Teotihuacan's fall Nahuan speakers quickly rose to power in central Mexico and expanded into areas earlier occupied by speakers of Oto-Manguean, Totonacan and Huastec. During this time Oto-Manguean groups of central Mexico such as the Chiapanec, Chorotega and Subtiaba migrated south some of them reaching the southern limits of Mesoamerica in El Salvador and Nicaragua. Also some speakers of Nahuan moved south, some settling on the coast of Oaxaca where their speech became the language Pochutec, and others moving all the way to El Salvador, becoming the ancestors of the speakers of modern Pipil.
Postclassic period (1000–1521 CE)
In the Postclassic period Nahuan languages diversified and spread, carried by the culture commonly known asToltec
The Toltec culture () was a Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula (Mesoamerican site), Tula, Hidalgo (state), Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoam ...
. In the early Postclassic period feuds between royal lineages in the Yucatán Peninsula caused the forefathers of the Itza' to move south into the Guatemalan jungle. In northwestern Oaxaca speakers of Mixtec and Chocho- Popolocan languages built successful city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
s, such as Teotitlan del Camino, which did not fall under Nahuan subjugation. Speakers of Otomian languages ( Otomi, Mazahua and Matlatzinca) were routinely displaced to the edges of the Nahuan states. The Otomi of Xaltocan, for example, were forcibly relocated to Otumba by the early Aztec empire.
As Nahuatl, carried by the Toltec and later the Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
culture, became a lingua franca throughout Mesoamerica even some Mayan states such as the Kʼicheʼ Kingdom of Qʼumarkaj adopted Nahuatl as a prestige language. In Oaxaca Zapotec and Mixtec peoples expanded their territories displacing speakers of the Tequistlatecan languages slightly. During this time the Purépecha
The Purépecha ( ) are a group of Indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of Michoacán, Mexico, mainly in the area of the cities of Cherán and Pátzcuaro.
They are also known by the derogatory term " Tarascan", an exonym, app ...
(Tarascans) consolidated their state based at Tzintzuntzan. They were resistant to other states of Mesoamerica and had little contact with the rest of Mesoamerica. Probably as a result of their isolationist policy the Purépecha language is the only language of Mesoamerica to not show any of the traits associated with the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area. In Guerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
the Tlapanecs of Yopitzinco speaking the Oto-Manguean Tlapanec language
Tlapanec , or Mephaa, is an indigenous Mexican language spoken by more than 98,000 Tlapanec people in the state of Guerrero. Like other Oto-Manguean languages, it is tonal and has complex inflectional morphology. The ethnic group themselves ref ...
remained independent of the Aztec empire as did some of the Oaxacan cultures such as the Mixtecs of Tututepec and the Zapotec of Zaachila
Zaachila (the Zapotec name; Nahuatl: ''Teotzapotlan''; Mixtec: ''Ñuhu Tocuisi'') was a powerful Mesoamerican city in what is now Oaxaca, Mexico, from the city of Oaxaca. The city is named after Zaachila Yoo, the Zapotec ruler, in the late 14 ...
. In the late postclassic around 1400 CE Zapotecs of Zaachila moved into the Isthmus of Tehuantepec
The Isthmus of Tehuantepec () is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Before the opening of the Panama Canal, it was a major overland transport route known simply as the T ...
creating a wedge of Zapotec speaking settlements between the former neighbors the Mixe and the Huave who were pushed into their current territories on the edges of the Isthmus.
Colonial period (1521–1821)
 The Spanish arrival in the new world turned the linguistic situation of Mesoamerica upside down. And from then on the indigenous languages have been subject to varying policies imposed on them by the colonial rule. The first impact came from the decimation of the indigenous population by diseases brought by the Europeans. Within the first two centuries of Spanish rule Mesoamerica experienced a dramatic population decline and it is well documented that several small linguistic groups became completely extinct already during the 16th century. The policies that contributed most to a change in the linguistic situation of Mesoamerica were the policies used for conversion of Indians to Christianity. The first victim of this process was the native writing systems which were banned and prohibited and the existing texts destroyed – the pictorial scripts were seen as an idolatry by the Catholic Church. At first missionaries favoured the teaching of Spanish to their prospect converts but from 1555 the first Mexican Council established the policy that the Indians should be converted in their own languages and that parish priests should know the indigenous language of their parishioners. This called for a massive education of clergymen in native languages and the church undertook this task with great zeal. Institutions of learning such as the
The Spanish arrival in the new world turned the linguistic situation of Mesoamerica upside down. And from then on the indigenous languages have been subject to varying policies imposed on them by the colonial rule. The first impact came from the decimation of the indigenous population by diseases brought by the Europeans. Within the first two centuries of Spanish rule Mesoamerica experienced a dramatic population decline and it is well documented that several small linguistic groups became completely extinct already during the 16th century. The policies that contributed most to a change in the linguistic situation of Mesoamerica were the policies used for conversion of Indians to Christianity. The first victim of this process was the native writing systems which were banned and prohibited and the existing texts destroyed – the pictorial scripts were seen as an idolatry by the Catholic Church. At first missionaries favoured the teaching of Spanish to their prospect converts but from 1555 the first Mexican Council established the policy that the Indians should be converted in their own languages and that parish priests should know the indigenous language of their parishioners. This called for a massive education of clergymen in native languages and the church undertook this task with great zeal. Institutions of learning such as the Colegio de Santa Cruz de Tlatelolco
The Colegio de Santa Cruz in Tlatelolco, Mexico City, is the first and oldest European school of higher learning in the Americas and the first major school of interpreters and translators in the New World. It was established by the Franciscans on ...
which was inaugurated in 1536 and which taught both indigenous and classical European languages to both Indians and priests were opened. And missionary grammarians undertook the job of writing grammars for the indigenous languages in order to teach priests. For example, the first grammar of Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
, written by Andrés de Olmos
Andrés de Olmos (c.1485 – 8 October 1571) was a Spanish Franciscan priest and grammarian and ethno-historian of Mexico's indigenous languages and peoples. He was born in Oña, Burgos, Spain and died in Tampico in New Spain (modern-day T ...
, was published in 1547 – three years before the first grammar of French. During this time some literacy in indigenous languages written in the Latin script began to appear. In 1570 Philip II of Spain
Philip II (21 May 152713 September 1598), sometimes known in Spain as Philip the Prudent (), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and List of Sicilian monarchs, Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He ...
decreed that Nahuatl should become the official language of the colonies of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
in order to facilitate communication between the Spanish and natives of the colonies. Throughout the colonial period grammars of indigenous languages were composed, but strangely the quality of these were highest in the initial period and declined towards the ends of the 18th century. In practice the friars found that learning all the indigenous languages was impossible and they began to focus on Nahuatl. During this period the linguistic situation of Mesoamerica was relatively stable. However, in 1696 Charles II made a counter decree banning the use of any languages other than Spanish throughout the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
. And in 1770 a decree with the avowed purpose of eliminating the indigenous languages was put forth by the Royal Cedula. This put an end to the teaching of and writing in indigenous languages and began a strict policy of hispanization of the Indians. However the fact that today around five million people in Mesoamerica still speak indigenous languages suggest that this policy wasn't as effective after all. The most important factor towards the decline of indigenous languages in this period has probably been the social marginalization of the native populations and their languages – and this process has been particularly effective during modern times.
Modern period (1821–)
In the modern period what has affected the indigenous languages most has been the pressure of social marginalization put on the indigenous populations by a growing mestizo class, a growing institutionalization of Hispanic society, and, in some cases, instances of violent suppression and mass murder against indigenous groups in a concerted effort as recorded in El Salvador in 1932. Indigenous languages have been seen by the governing classes as a hindrance to building homogeneous nation states and as an impediment to social progress. These viewpoints sparked a renewed interest in the hispanization of indigenous communities and the introduction of compulsory education in Spanish resulted in a great decline of indigenous languages throughout the 20th century. In a number of indigenous communities it has become practice to learn Spanish first and the indigenous language second. Parents have refrained from teaching their children their own language in order not to subject them to the social stigma of speaking an Indian language – and youths have learned their languages only when they came of age and started taking part in the adult society. Within the last 20 years there has been an overt change in the policies of governments of Mesoamerican countries towards the indigenous languages. There has been official recognition of their right to existence and some kind of governmental support, to the point of recognizing them as national languages. Bilingual (rather than monolingual Spanish) education has been recognized as desirable even if not always actually achieved in practice. In Guatemala the recognition of the indigenous languages as official languages and a valuable part of the country's identity came after theCivil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
which ended in 1996. In Mexico shifting governments had talked about the value of the country's indigenous heritage but it was not until 2003 that the ''Ley General de Derechos Lingüísticos de los Pueblos Indígenas
The General Law on the Linguistic Rights of Indigenous Peoples () was published in the Mexican '' Official Journal of the Federation'' on 13 March 2003Lang, 2008; p.115 during the term of Mexican President Vicente Fox Quesada. It gave rise ...
'' established a framework for the conservation, nurturing and development of indigenous languages.
Despite these official changes, old attitudes persist in many spheres, and indigenous languages are not in any practical sense on a par with Spanish. At present the linguistic situation of Mesoamerican languages is most difficult in the Central American countries like Honduras, El Salvador and Nicaragua where indigenous languages still do not enjoy the rights or privileges now granted them elsewhere, and are still subject to social stigmatization.
Map of current distribution


Writing
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
is one of the relatively few places in the world where writing has developed independently throughout history. The Mesoamerican scripts deciphered to date are logosyllabic combining the use of logograms
In a written language, a logogram (from Ancient Greek 'word', and 'that which is drawn or written'), also logograph or lexigraph, is a written character that represents a semantic component of a language, such as a word or morpheme. Chinese ...
with a syllabary
In the Linguistics, linguistic study of Written language, written languages, a syllabary is a set of grapheme, written symbols that represent the syllables or (more frequently) mora (linguistics), morae which make up words.
A symbol in a syllaba ...
, and they are often called hieroglyphic scripts. Five or six different scripts have been documented in Mesoamerica but archaeological dating methods make it difficult to establish which was earliest and hence the forebear from which the others developed. Candidates for being the first writing system of the Americas are Zapotec writing, the Isthmian or Epi-Olmec script or the scripts of the Izapa
Izapa is a very large pre-Columbian archaeological site located in the Mexican state of Chiapas; it is best known for its occupation during the Late Formative period. The site is situated on the Izapa River, a tributary of the Suchiate River, ...
n culture. The best documented and deciphered Mesoamerican writing system, and hence the most widely known, is the classic Maya script
Maya script, also known as Maya glyphs, is historically the native writing system of the Maya civilization of Mesoamerica and is the only Mesoamerican writing system that has been substantially deciphered. The earliest inscriptions found which ...
. Post-Classic cultures such as the Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
and Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are Indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica of Guerrero, Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerre ...
cultures do not seem to have developed true writing systems, but instead used semasiographic writing although they did use phonetic principles in their writing by the use of the rebus
A rebus ( ) is a puzzle device that combines the use of illustrated pictures with individual letters to depict words or phrases. For example: the word "been" might be depicted by a rebus showing an illustrated bumblebee next to a plus sign (+ ...
principle. Aztec name glyphs for example do combine logographic elements with phonetic readings. From the colonial period on there exists an extensive Mesoamerican literature written in the Latin script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Gree ...
.
Literary traditions
The literature and texts created by indigenous Mesoamericans are the earliest and well known from theAmericas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
for two primary reasons. First, the fact that native populations in Mesoamerica were the first to interact with Europeans assured the documentation and survival of literature samples in intelligible forms. Second, the long tradition of Mesoamerican writing contributed to them readily embracing the Latin script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Gree ...
used by the Spanish and resulted in many literary works written in it during the first centuries after the Spanish conquest of Mexico. Some important literary works in Mesoamerican languages are: The mythological narrative of the Popol Vuh
''Popol Vuh'' (also ''Popul Vuh'' or ''Pop Vuj'') is a text recounting the mythology and history of the Kʼicheʼ people of Guatemala, one of the Maya peoples who also inhabit the Mexican states of Chiapas, Campeche, Yucatan and Quintana Roo, ...
and the theatrical dance-drama the Rabinal Achí both written in Classical Kʼicheʼ Maya. The ethnographical work in the Florentine Codex and the songs of the Cantares Mexicanos both written in Classical Nahuatl
Classical Nahuatl, also known simply as Aztec or Codical Nahuatl (if it refers to the variants employed in the Mesoamerican Codices through the medium of Aztec Hieroglyphs) and Colonial Nahuatl (if written in Post-conquest documents in the Lat ...
. The prophetical and historical accounts of the books of Chilam Balam
The Books of Chilam Balam () are handwritten, chiefly 17th and 18th-centuries Maya miscellanies, named after the small Yucatec towns where they were originally kept, and preserving important traditional knowledge in which indigenous Maya and ea ...
written in the Yucatec Maya language
Yucatec Maya ( ; referred to by its speakers as or ) is a Mayan languages, Mayan language spoken in the Yucatán Peninsula, including part of northern Belize. There is also a significant diasporic community of Yucatec Maya speakers in San Fra ...
. As well as numerous smaller documents written in other indigenous languages throughout the colonial period. No true literary tradition for Mesoamerican languages of the modern period has yet emerged.
Mesoamerican Linguistic Area
Throughout the millennia in which speakers of different Mesoamerican languages were engaged in contact the languages began to change and show similarities with one another. This has resulted in Mesoamerica evolving into a linguistic area of diffusion, a "Sprachbund
A sprachbund (, from , 'language federation'), also known as a linguistic area, area of linguistic convergence, or diffusion area, is a group of languages that share areal features resulting from geographical proximity and language contact. Th ...
", where most languages, even though they have different origins share some important linguistic traits.(Language 62 Vol. 3. 530–58) The traits defining the Mesoamerican sprachbund are few but well established: the languages use relational noun Relational nouns, or relator nouns, are a word class in many languages. They are characterized as functioning syntactically as nouns although they convey the meaning for which other languages use adpositions (prepositions and postpositions). In Me ...
s to express spatial and other relations, they have a base 20 (Vigesimal) numeral system, their syntax is never verb-final and as a consequence of this they don't use switch reference
In linguistics, switch-reference (SR) describes any clause-level morpheme that signals whether certain prominent arguments in 'adjacent' clauses are coreferential. In most cases, it marks whether the subject of the verb in one clause is corefer ...
, they use a distinct pattern for expressing nominal possession and they share a number of semantic calques]. Some other traits are less defining for the area, but still prevalent such as: the presence of whistled language
Whistled speech is a form of speech surrogacy in which whistling is used to mimic speech. Speakers of more than 80 languages have been found to practice various degrees of whistled speech, most of them in rugged topography or dense forests, whe ...
s, incorporation of bodypart nouns into verbs, the derivation of locative
In grammar, the locative case ( ; abbreviated ) is a grammatical case which indicates a location. In languages using it, the locative case may perform a function which in English would be expressed with such prepositions as "in", "on", "at", and " ...
s from bodypart nouns, grammatical indication of inalienable or intimate possession. Terrence Kaufman has worked with documenting the process of this linguistic convergence and he argues that the most probable donor languages of the borrowings into other Mesoamerican languages are the Mixe–Zoquean and Totonacan languages,Campbell and Kaufman 1976 this supports a theory of either or both of these cultures having a prominent role as a dominating power in early Mesoamerican history.
Classification
Uto-Aztecan
The Uto-Aztecan languages are a family of native American languages, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The name of the language family reflects the common ...
(Other branches are outside Mesoamerica.)
*''Corachol'' • ''Nayarit
Nayarit, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in Municipalities of Nayarit, 20 municipalit ...
, Jalisco
Jalisco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in western Mexico and is bordered by s ...
''
** Huichol • 20,000 native speakers
** Cora • 15,000
*''Aztecan''
** Nahuan • 1,380,000
*** Pochutec • ''Coast of Oaxaca'' • EXTINCT
*** General Aztec (Nahuatl)
****Western periphery • ''Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo, is one of the 31 states which, together with Mexico City, compose the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The stat ...
, Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
, Guerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
''
****Eastern periphery • ''S Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
, N Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
, Tabasco
Tabasco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Tabasco, 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It i ...
''
****Huasteca • ''N Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
, Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
, Hidalgo''
****Center • ''México (state)
The State of Mexico, officially just Mexico, is one of the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of the United Mexican States. Colloquially known as Edomex (from , the abbreviation of , and ), to distinguish it from the name o ...
, Morelos
Morelos, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Morelos, is a landlocked state located in south-central Mexico. It is one of the 32 states which comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Mun ...
, Tlaxcala
Tlaxcala, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tlaxcala, is one of the 32 federal entities that comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Tlaxcala, 60 municipalities and t ...
, Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
, Hidalgo''
*** Pipil • ''Pacific coast of Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
, Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
, El Salvador
El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is S ...
''
Oto-Manguean
The Oto-Manguean or Otomanguean () languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that are now spoken are indigenous to Mexico, but the Manguean languages, Ma ...
*''Otopamean''
** Otomian
*** Otomi • '' Hidalgo, Guanajuato
Guanajuato, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato, is one of the 32 states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guanajuato, 46 municipalities and its cap ...
, N México (state)
The State of Mexico, officially just Mexico, is one of the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of the United Mexican States. Colloquially known as Edomex (from , the abbreviation of , and ), to distinguish it from the name o ...
, Querétaro
Querétaro, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Querétaro, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Querétaro, 18 municipalities. Its capital city is Querétaro Cit ...
'' • 350,000
*** Mazahua • ''Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo, is one of the 31 states which, together with Mexico City, compose the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The stat ...
, W México (state)
The State of Mexico, officially just Mexico, is one of the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of the United Mexican States. Colloquially known as Edomex (from , the abbreviation of , and ), to distinguish it from the name o ...
'' • 150,000
**Pamean
***Chichimec
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajío region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the same meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" t ...
• ''Guanajuato
Guanajuato, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato, is one of the 32 states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guanajuato, 46 municipalities and its cap ...
''
*** Pame • ''San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí, officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí, is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 59 municipalities and is named after its capital city, San Luis Potosí.
It ...
, NW Hidalgo'' • 4200
*** Chichimeca Jonaz
**Matlatzinca-Ocuilteco
*** Matlatzinca • ''SW México (state)
The State of Mexico, officially just Mexico, is one of the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of the United Mexican States. Colloquially known as Edomex (from , the abbreviation of , and ), to distinguish it from the name o ...
'' • 3,000
*** Ocuilteco
*'' Chinantecan'' (perhaps closest to Otopamean)
** Chinantec • ''N Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 100,000
*''Supanecan''
** Tlapanec (Yopi) • ''Guerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
'' • 44,000
** Subtiaba • ''Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America aft ...
, El Salvador
El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is S ...
'' • EXTINCT
*'' Manguean'' (perhaps closest to Supanecan)
** Chiapanec • ''Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
'' • EXTINCT
** Chorotegan • ''Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, ...
'' • EXTINCT
** Mangue • ''Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America aft ...
'' • EXTINCT
** Nicoyan • ''Costa Rica
Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America. It borders Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as Maritime bo ...
'' • EXTINCT
*'' Popolocan''
** Mazatec • ''SE Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
, N Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 145,000
** Ixcatec
** Popoluca • ''SE Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
, NW Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 37,000
** Chocho
*''Zapotecan languages
The Zapotecan languages are a group of related Oto-Manguean languages which descend from the common proto-Zapotecan language spoken by the Zapotec people during the era of the dominance of Monte Albán.
The Zapotecan language group contains ...
'' (perhaps closest to Popolocan)
** Zapotec • ''Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 500,000
** Chatino • ''SW Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 28,000
** Soltec • ''Elotepec Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • EXTINCT
** Papabuco • ''Elotepec Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • EXTINCT
*'' Mixtecan''
** Mixteco-Cuicateco
***Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are Indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica of Guerrero, Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerre ...
• ''E Guerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
, S Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
, W Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 500,000
*** Cuicatec • ''NE Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 20,000
** Trique • ''W Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 19,000
*''Amuzgo'' (perhaps closest to Mixtecan)
** Amuzgo • ''E Guerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
, W Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 20,000
Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 75,000
** Olutec& Sayultec • ''S Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
'' • EXTINCT?
** Tapachultec • '' SE Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
'' • EXTINCT
*''Zoquean''
** Zoque languages • ''Tabasco
Tabasco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Tabasco, 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It i ...
, Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
, E Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 35,000
** Sierra Popoluca & Texistepec Popoluca • ''S Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
'' • 25,000
** Chimalapa
Totonac
The Totonac are an Indigenous people of Mexico who reside in the states of Veracruz, Puebla, and Hidalgo. They are one of the possible builders of the pre-Columbian city of El Tajín, and further maintained quarters in Teotihuacán (a cit ...
• ''Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
, Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
'' • 250,000
* Tepehua • '' Hidalgo, Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
'' • 10,000
Tequistlatecan (Chontal)
* Huamelultec (Lowland Oaxaca Chontal) • ''SEOaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 1000
* Tequistlatec • EXTINCT?
* Highland Oaxaca Chontal • 3600
Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
, San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí, officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí, is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 59 municipalities and is named after its capital city, San Luis Potosí.
It ...
, NE Hidalgo'' • 120,000
** Chicomuceltec • ''S Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
'' • EXTINCT
*'' Yucatecan''
** Yucatec • ''Yucatán
Yucatán, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, constitute the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate municipalities, and its capital city is Mérida.
...
, Campeche
Campeche, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Campeche, is one of the 31 states which, with Mexico City, make up the Administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. Located in southeast Mexico, it is bordered by the sta ...
, Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Quintana Roo, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, constitute the 32 administrative divisions of Mexico, federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into municipalities of ...
, Belize
Belize is a country on the north-eastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a maritime boundary with Honduras to the southeast. P ...
, N Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
'' • 750,000
** Mopán • ''N Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
, Belize
Belize is a country on the north-eastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a maritime boundary with Honduras to the southeast. P ...
'' • 11,000
** Itzá • ''N Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
'' • EXTINCT?
** Lacandón • ''Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
'' • 1000
*''Western''
**Greater Tzeltalan
*** Cholan
**** Chol • ''Tabasco
Tabasco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Tabasco, 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It i ...
, Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
'' • 135,000
**** Chontal • ''Tabasco
Tabasco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Tabasco, 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It i ...
'' • 55,000
**** Chorti • ''Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, ...
, E Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
'' • 30,000
***Tzeltalan • ''Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
''
**** Tzeltal • 215,000
**** Tzotzil • 265,000
**Greater Kanjolabalan • ''NW Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
, Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
''
***Chujean
**** Chuj • ''NW Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
'' • 50,000
**** Tojolabal • ''Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
'' • 35,000
***Kanjolabal (Q’anhob’al) • ''NW Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
''
**** Solomec • 80,000
**** Acatec • 60,000
**** Jacaltec • 100,000
**Mochó (Cotoque) • ''SE Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
''
*** Motozintlec • EXTINCT?
*** Tuzantec • EXTINCT?
*''Eastern''
**Greater Mamean
***Mamean
**** Mam • ''W Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
'' • 535,000
**** Tektiteco • '' Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
-Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
border'' • 2300
***Ixilan • ''NW Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
''
**** Ixil • 70,000
**** Aguacatec (Awakateko) • 18,000
**Greater Quichean
*** Quichean • ''C Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
''
**** Quiché • 2,420,000
**** Cakchiquel • 450,000
**** Tz'utujil • 85,000
**** Sacapultec • 35,000
**** Sipacapan • 8000
*** Kekchi • ''C & E Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
'' • 420,000
***Pocom • ''C & E Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
''
**** Pocomchi • 90,000
**** Pocomam • 50,000
*** Uspantec • ''NW Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
'' • 3000
Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, ...
'' • 1000
Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America aft ...
'' • 185,000
*Sumo
is a form of competitive full-contact wrestling where a ''rikishi'' (wrestler) attempts to force his opponent out of a circular ring (''dohyō'') or into touching the ground with any body part other than the soles of his feet (usually by th ...
• 7000
* Matagalpa • EXTINCT
Isolates
*Purépecha
The Purépecha ( ) are a group of Indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of Michoacán, Mexico, mainly in the area of the cities of Cherán and Pátzcuaro.
They are also known by the derogatory term " Tarascan", an exonym, app ...
• ''SW Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo, is one of the 31 states which, together with Mexico City, compose the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The stat ...
'' • 120,000
* Cuitlatec • ''Guerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
'' • EXTINCT
* Huave (Wabe) • ''SE Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
'' • 14,000
* Xinca • ''SE Guatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
'' • EXTINCT
*Lenca
The Lenca,are an Indigenous people from present day southwest Honduras and eastern El Salvador in Central America. They historically spoke various dialects of the Lencan languages such as Chilanga, Putun (Potón), and Kotik, but today are nat ...
• ''SW Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, ...
, El Salvador
El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is S ...
'' • EXTINCT?
Proposed stocks
* Hokan *Penutian
Penutian is a proposed grouping of language family, language families that includes many Native Americans in the United States, Native American languages of western North America, predominantly spoken at one time in British Columbia, Washington ( ...
* Macro-Mayan
**'' Mayan''
**'' Mixe–Zoque''
**'' Totonacan''
**'' Huave''
* Macro-Chibchan
**'' Chibchan''
**'' Misumalpan''
**'' Xinca''
**''Lenca
The Lenca,are an Indigenous people from present day southwest Honduras and eastern El Salvador in Central America. They historically spoke various dialects of the Lencan languages such as Chilanga, Putun (Potón), and Kotik, but today are nat ...
''
* Tolatecan
**'' Tequistlatecan''
**'' Jicaque''
* Totozoquean
**'' Mixe–Zoque''
**'' Totonacan''
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Mesoamerican Languages Project at the University of Texas
* ttp://www.peabody.harvard.edu/node/24 Corpus of Maya Hieroglyphic Inscriptions Program at the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology, Harvard Universitybr>Corpus of Maya Hieroglyphic Inscriptions, Volumes 1–9. Published by the Peabody Museum Press and distributed by Harvard University Press
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mesoamerican Languages + + Indigenous languages of North America