Meretskov on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kirill Afanasievich Meretskov (; – 30 December 1968) was a
on warheroes.ru
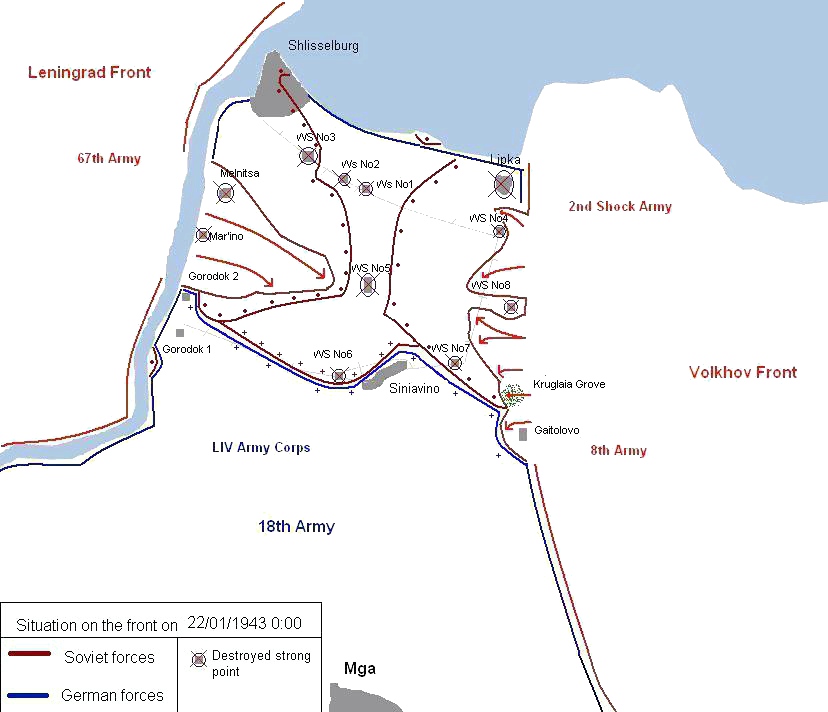 In late November 1942, Govorov commenced planning the next operation to break the blockade of Leningrad. Meretskov soon joined the planning. In December, the plan was approved by the
In late November 1942, Govorov commenced planning the next operation to break the blockade of Leningrad. Meretskov soon joined the planning. In December, the plan was approved by the
 Meretskov's next major command was in
Meretskov's next major command was in
 ;Soviet Union
;Foreign awards
;Soviet Union
;Foreign awards
Kirill Meretskov
(in Russian)
(in Russian) * {{DEFAULTSORT:Meretskov, Kirill 1897 births 1968 deaths People from Zaraysky District People from Ryazan Governorate Old Bolsheviks Candidates of the Central Committee of the 18th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks) Candidates of the Central Committee of the 19th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union Members of the Central Auditing Commission of the 20th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union First convocation members of the Soviet of Nationalities Second convocation members of the Soviet of the Union Third convocation members of the Soviet of the Union Members of the Supreme Soviet of the Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic Marshals of the Soviet Union Frunze Military Academy alumni Military personnel of the 1st Cavalry Army Soviet people of the Spanish Civil War Soviet military personnel of the Winter War Russian people of World War II Soviet military personnel of World War II Heroes of the Soviet Union Recipients of the Order of Victory Recipients of the Order of Suvorov, 1st class Chief Commanders of the Legion of Merit Foreign recipients of the Legion of Merit Recipients of the Order of Lenin Recipients of the Order of the Red Banner Recipients of the Order of Kutuzov, 1st class Order of Saint Olav Burials at the Kremlin Wall Necropolis Military Academy of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union alumni Siege of Leningrad
Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
military commander. Having joined the Communist Party in 1917, he served in the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
from 1920. During the Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
of 1939–1940 against Finland, he had the task of penetrating the Mannerheim Line as commander of the 7th Army. He was awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union () was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society. The title was awarded both ...
shortly afterwards.
The NKVD arrested Meretskov at the start of invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along a ...
. Released two months later, he returned to command the 7th Army and later the Volkhov Front
The Volkhov Front () was a major formation of the Red Army during the first period of the Second World War. It was formed as an expediency of an early attempt to halt the advance of the Wehrmacht Army Group North in its offensive thrust towards L ...
during the 1941–1944 siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad was a Siege, military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) in the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 1941 t ...
. He commanded the Karelian Front
The Karelian Front ) was a front (a formation of Army Group size) of the Soviet Union's Red Army during World War II, and operated in Karelia.
Wartime
The Karelian Front was created in August 1941 when Northern Front was split into Karelian ...
from February 1944, notably the Petsamo–Kirkenes Offensive
The Petsamo–Kirkenes offensive was a major military offensive during World War II, mounted by the Red Army against the ''Wehrmacht'' in 1944 in the Petsamo region, ceded to the Soviet Union by Finland in accordance with the Moscow Armist ...
of October 1944. From April 1945 he was assigned to the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
, where he commanded a front
Front may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''The Front'' (1943 film), a 1943 Soviet drama film
* '' The Front'', 1976 film
Music
* The Front (band), an American rock band signed to Columbia Records and active in the 1980s and ...
during the Soviet invasion of Japanese Manchuria. During the war he reached the rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union
Marshal of the Soviet Union (, ) was the second-highest military rank of the Soviet Union. Joseph Stalin wore the uniform and insignia of Marshal after World War II.
The rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union was created in 1935 and abolished in ...
.Meretskov K. A.on warheroes.ru
Early life and career
Meretskov was born at Nazaryevo inRyazan Governorate
Ryazan Governorate () was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire and the Russian SFSR, which existed from 1796 to 1929. Its capital was in Ryazan.
Administrative division
Ryazan Governorate consisted of the follo ...
(now in Moscow Oblast
Moscow Oblast (, , informally known as , ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). With a population of 8,524,665 (Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census) living in an area of , it is one of the most densely populate ...
), southeast of Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
. His parents were peasants of Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
ethnicity and lived in a rural village. He was a factory worker from 1909, first in Moscow, later near Vladimir
Vladimir (, , pre-1918 orthography: ) is a masculine given name of Slavic origin, widespread throughout all Slavic nations in different forms and spellings. The earliest record of a person with the name is Vladimir of Bulgaria ().
Etymology
...
. He joined the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
(later the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet ...
) in August 1917, and became chief of staff
The title chief of staff (or head of staff) identifies the leader of a complex organization such as the armed forces, institution, or body of persons and it also may identify a principal staff officer (PSO), who is the coordinator of the supportin ...
of Red Guard
The Red Guards () were a mass, student-led, paramilitary social movement mobilized by Chairman Mao Zedong in 1966 until their abolition in 1968, during the first phase of the Cultural Revolution, which he had instituted.Teiwes
According to a ...
militia that helped to organise in the town. During the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
, he was chief of staff of a regiment, and later a division. In 1921, he graduated from the Military Academy (later the M. V. Frunze Military Academy).
From 1922, he held a number of commands as chief of staff, first in a cavalry division, later in various armies and military districts. From September 1936 to May 1937, Meretskov fought for the Republicans during the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War () was a military conflict fought from 1936 to 1939 between the Republican faction (Spanish Civil War), Republicans and the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalists. Republicans were loyal to the Left-wing p ...
under a pseudonym of "General Pavlovich". In 1939, he was appointed commander of the Leningrad Military District
The Order of Lenin Leningrad Military District () is a military district of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. The district was awarded the Order of Lenin in 1968. In 2010, it was merged with the Moscow Military District, the Northern ...
.
World War II
Finland campaign
In November 1939, at the start of theWinter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
, Meretskov initially ran the overall operation against the Finns. However, gross underestimations of the Finnish defenses, the size of their forces and the corresponding overestimations of the capacity of the Red Army, led to serious planning flaws. Only five rifle divisions were initially sent to assault the Mannerheim Line and piecemeal commitment of reinforcements did not achieve any effect.Isayev (2004) p. 19 Meretskov failed and the command was passed on 9 December 1939 to the General Staff Supreme Command, Stavka
The ''Stavka'' ( Russian and Ukrainian: Ставка, ) is a name of the high command of the armed forces used formerly in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union and currently in Ukraine.
In Imperial Russia ''Stavka'' referred to the administrat ...
, directly under Kliment Voroshilov
Kliment Yefremovich Voroshilov ( ; ), popularly known as Klim Voroshilov (; 4 February 1881 – 2 December 1969), was a prominent Soviet Military of the Soviet Union, military officer and politician during the Stalinism, Stalin era (1924–195 ...
(chairman), Nikolai Kuznetsov, Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
and Boris Shaposhnikov
Boris Mikhaylovich Shaposhnikov () ( – 26 March 1945) was a Soviet Union, Soviet military officer, Military theory, theoretician and Marshal of the Soviet Union. He served as the Chief of the General Staff (Russia), Chief of the General St ...
.
Meretskov was appointed to command of the 7th Army. In January 1940, the Leningrad Military District was reformed and renamed "North-Western Front." Semyon Timoshenko
Semyon Konstantinovich Timoshenko (; ; – 31 March 1970) was a Soviet military commander, Marshal of the Soviet Union, and one of the most prominent Red Army commanders during the Second World War.
Born to a Ukrainian family in Bessarabia, ...
was chosen Army Commander to break the Mannerheim Line. This Soviet offensive was checked by the Finnish Army in the Battle of Taipale
The Battle of Taipale was a series of battles fought during the Winter War between Finland and Soviet Union from 6 to 27 December 1939. The battles were part of a Soviet campaign to penetrate the Finnish Mannerheim Line in the Karelian Isthmus ...
. For the next offensive, the Stavka
The ''Stavka'' ( Russian and Ukrainian: Ставка, ) is a name of the high command of the armed forces used formerly in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union and currently in Ukraine.
In Imperial Russia ''Stavka'' referred to the administrat ...
significantly reinforced the 7th Army, deployed the 13th Army Thirteenth Army or 13th Army may refer to:
* Thirteenth Army (Japan)
* Japanese Thirteenth Area Army
* 13th Army (Russian Empire), unit in World War I
*13th Army (RSFSR), a unit in the Russian Civil War
*13th Army (Soviet Union)
The 13th Army (, ...
on its flank and assigned substantial heavy artillery to both armies, including B-4 howitzers and Br-5 mortars.
The next Soviet offensive began in February 1940. The heavy artillery support allowed the Soviet forces to breach the Mannerheim Line. Meretskov's 7th Army proceeded to fight in Viborg which so far had resisted attempts of Soviet conquest. Less than two weeks after the signing of the Moscow Peace Treaty
The Moscow Peace Treaty was signed by Finland and the Soviet Union on 12 March 1940, and the ratifications were exchanged on 21 March. It marked the end of the 105-day Winter War, upon which Finland ceded border areas to the Soviet Union. The ...
, on March 21, 1940, Meretskov was awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union () was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society. The title was awarded both ...
. Afterwards, Meretskov was promoted to rank of army general
Army general or General of the army is the highest ranked general officer in many countries that use the French Revolutionary System. Army general is normally the highest rank used in peacetime.
In countries that adopt the general officer fou ...
and made Deputy Commissar of Defense. From August 1940 to January 1941, he was Chief of the General Staff The Chief of the General Staff (CGS) is a post in many armed forces (militaries), the head of the military staff.
List
* Chief of the General Staff (Abkhazia)
* Chief of General Staff (Afghanistan)
* Chief of the General Staff (Albania)
* C ...
. He was dismissed on 14 January 1941, and on 24 January, Stalin spotted him at the Bolshoi and, in front of witnesses: "You are courageous, capable, but without principles, spineless. You want to be nice, but you should have a plan instead and adhere to it strictly, despite the fact that someone or other is going to be resentful."
Operation Barbarossa
On June 22, 1941, whenOperation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along ...
started, Meretskov was appointed permanent adviser to Stavka. However, on June 23 he was arrested by the NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (, ), abbreviated as NKVD (; ), was the interior ministry and secret police of the Soviet Union from 1934 to 1946. The agency was formed to succeed the Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU) se ...
as a member of an alleged anti-Soviet military conspiracy. The exact reasons are unknown, and the case file was destroyed in 1955. Meretskov's close friendship with General Dmitry Pavlov, the Soviet Commander of the Western Front who had been executed, is often considered a factor, although Pavlov, at the time, was yet to even be relieved of duty, much less arrested. Mark Solonin
Mark Solonin (born May 29, 1958, in Kuybyshev, Soviet Union) is a Russian historian and author of numerous books on the Second World War. An aviation engineer by training, he has lived since 2016 in Estonia. In 2019 he relocated to Ukraine. Si ...
, in his book ''June the 25th: Stupidity or Aggression'', proposes a theory that the actual reason might have been Meretskov's skepticism about the need to start bombardments of Finland, and his later release was due to him turning out to have been right, although he admits that direct evidence is unlikely to be found. After being subjected to two months of torture, including being beaten with rubber rods, and having one of his ribs broken by the notorious torturer Boris Rodos
Boris Veniaminovich Rodos (; 22 June 1905 20 April 1956) was an officer of the OGPU, colonel of the NKVD and Ministry of State Security, deputy head of the Investigative Department of the Main Board of State Security and People's Commissariat o ...
in Lubyanka Prison
Lubyanka (, ) is the popular name for the building which contains the headquarters of the FSB on Lubyanka Square in the Meshchansky District of Moscow, Russia. It is a large Neo-Baroque building with a facade of yellow brick designed by Alex ...
, Meretskov relented and signed a written confession. According to Nikita Khrushchev, "before his arrest, Meretskov had been a strapping young general, very strong and impressive-looking. After his release, he was a shadow of his former self. He had lost so much weight he could hardly speak." Released in September, he was taken before the police chief, Vsevolod Merkulov
Vsevolod Nikolayevich (Boris) Merkulov (; – 23 December 1953) was the head of NKGB from February to July 1941, and again from April 1943 to March 1946. He was a leading member of what was later derisively described as the " Beria gang".
Earl ...
, whom he had known socially: he told Merkulov that their friendship was over. He was then presented to Stalin, in full army dress, and given command of the 7th Separate Army. His confession was used against other commanders arrested in May–July 1941, who were executed on the order of Lavrenty Beria
Lavrentiy Pavlovich Beria ka, ლავრენტი პავლეს ძე ბერია} ''Lavrenti Pavles dze Beria'' ( – 23 December 1953) was a Soviet politician and one of the longest-serving and most influential of Joseph ...
near Kuybyshev on October 28, 1941, or sentenced by the Special Council of the NKVD
Within the administration of the Soviet Union, the Special Council of the USSR NKVD () was created by the same decree of Sovnarkom of July 10, 1934 that introduced the NKVD itself. The decree endowed the Special Council with the right to apply puni ...
and executed on February 23, 1942.
Victory at Tikhvin
Meretskov was appointed Commander of the 4th Army which fought in the defense of Leningrad against theArmy Group North
Army Group North () was the name of three separate army groups of the Wehrmacht during World War II. Its rear area operations were organized by the Army Group North Rear Area.
The first Army Group North was deployed during the invasion of Pol ...
of von Leeb. After stopping the German Tikhvin offensive, his forces, together with the neighboring 52nd and 54th Armies, counterattacked and pushed the German forces back to their starting positions, recapturing Tikhvin on December 10, 1941. This victory was the first Soviet large scale success during the war. The battle also assisted the Battle of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front during World War II, between October 1941 and January 1942. The Soviet defensive effort frustrated H ...
, as significant German forces were tied down in heavy attrition fighting in the marshes and forests between Tikhvin and Tosno and were not able to assist during the Soviet counteroffensive. Notably, the battle locked down two German panzer divisions and two motorized divisions and inflicted serious casualties to the army group overall.
During the counteroffensive of the battle, Stavka
The ''Stavka'' ( Russian and Ukrainian: Ставка, ) is a name of the high command of the armed forces used formerly in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union and currently in Ukraine.
In Imperial Russia ''Stavka'' referred to the administrat ...
ordered Kirill Meretskov to organize a new Volkhov Front
The Volkhov Front () was a major formation of the Red Army during the first period of the Second World War. It was formed as an expediency of an early attempt to halt the advance of the Wehrmacht Army Group North in its offensive thrust towards L ...
, which he commanded until February 1944 (with the exception of May and June 1942).
Defeat at Lyuban
In January 1942, Meretskov started a new offensive near Lyuban, aimed at lifting the siege of Leningrad and encircling a large number of German forces. The advance was very slow, however, as the German forces were well dug in, reinforced and no longer overextended. By March the two Soviet armies trying to close the encirclement were less than apart, but could advance no more. On March 15, German forces began a counteroffensive and cut off the Soviet2nd Shock Army
The 2nd Shock Army (), sometimes translated to English as 2nd Assault Army, was a field army of the Soviet Union during the Second World War. This type of formation was created in accordance with prewar doctrine that called for Shock Armies to ''o ...
. Soviet forces managed to restore communications by March 30 after heavy fighting. However, when Meretskov reported this to the Stavka, he omitted that the corridor that was linking the 2nd Shock Army to the rest of the Soviet forces was no more than wide, under constant German air strikes and artillery bombardment, and therefore, had a very poor transport capacity. As a result, the Stavka did not extract the 2nd Shock Army, when it was still possible. During late April and all of May, the Volkhov front was temporarily subordinated to lieutenant general Khosin's Leningrad Front
The Leningrad Front () was formed during the 1941 German approach on Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg) by dividing the Northern Front into the Leningrad Front and Karelian Front on August 27, 1941.
History
The Leningrad Front was immediately ...
, and Meretskov was sent as deputy high commander to the Western Front.
By May 1942, the 2nd Shock Army was experiencing supply shortages and low morale. On May 30, the German forces began a second offensive and again cut it off. After part of the encircled force broke out on June 5, the rest of the army was systematically destroyed, with 33,000 men becoming prisoners, about the same number killed, and about 10,000 men who broke out.
Immediately after the battle, Meretskov placed the blame on the captured 2nd Shock Army commander, Andrey Vlasov
Andrey Andreyevich Vlasov (, – August 1, 1946) was a Soviet Russian Red Army general. During the Eastern Front (World War II), Axis-Soviet campaigns of World War II, he fought (1941–1942) against the ''Wehrmacht'' in the Battle of Moscow ...
, whom he himself recommended to the post in April, a claim that was echoed in his post-war memoirs. Since Vlasov went on to collaborate with the German forces, there were few attempts to revisit this claim during the Soviet era. However, David Glantz
David M. Glantz (born January 11, 1942) is an American military historian known for his books on the Red Army during World War II and as the chief editor of '' The Journal of Slavic Military Studies''.
Born in Port Chester, New York, Glantz ...
points out that, irrespective of Vlasov's decision to collaborate with German forces, his level of command in May and June 1942 was not different from most other army commanders. Furthermore, Meretskov does bear some responsibility for the defeat as the commander of the front who planned the operation and carried it out. Khosin, the commander of the Leningrad Front, was removed from command on June 8, reduced in rank and never commanded a front again, humiliatingly assigned from March 1944 to the rear line Volga Military District. Meretskov, who was arrested less than a year earlier, knew that his life may be at risk if he accepted responsibility for the disaster.
Breaking the siege of Leningrad
After the defeat at Lyuban, Meretskov remained in command of the Volkhov Front. Together with the new Leningrad Front's commander,Leonid Govorov
Leonid Aleksandrovich Govorov (; – 19 March 1955) was a Soviet Union, Soviet military commander. Trained as an artillery officer, he joined the Red Army in 1920. He graduated from several Soviet military academies, including the Military Aca ...
, Meretskov planned a new offensive to break the siege of the city. Volkhov and Leningrad fronts would break the blockade of the city by eliminating the German positions south of Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg.
It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake ...
, where only separated the Leningrad and Volkhov Fronts. This position was called "the bottleneck". At the same time, German forces were planning Operation Northern Light () to capture the city and link up with Finnish forces. To achieve that, heavy reinforcements arrived from Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
, which the German forces had captured in July 1942. Both sides were unaware of the other's preparations. As a result, the Soviet Sinyavino Offensive
The Sinyavino offensives were a series of Soviet offensives in 1941–1943 during World War II around the Sinyavino Heights, east of Leningrad, to lift the Siege of Leningrad. The area was only fully liberated during the Leningrad–Novgorod offe ...
failed and the 2nd Shock army was decimated for the second time in a year, but the German forces suffered heavy casualties and canceled Operation Northern Light. Meretskov wanted to conduct further local attacks, but this request was categorically denied by the Stavka, in addition to a formal critique he received on October 15, 1942, for his conduct of the operation.
 In late November 1942, Govorov commenced planning the next operation to break the blockade of Leningrad. Meretskov soon joined the planning. In December, the plan was approved by the
In late November 1942, Govorov commenced planning the next operation to break the blockade of Leningrad. Meretskov soon joined the planning. In December, the plan was approved by the Stavka
The ''Stavka'' ( Russian and Ukrainian: Ставка, ) is a name of the high command of the armed forces used formerly in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union and currently in Ukraine.
In Imperial Russia ''Stavka'' referred to the administrat ...
and received the codename Operation Iskra
Operation Iskra (), a Soviet military operation in January 1943 during World War II, aimed to break the Wehrmacht's siege of Leningrad. Planning for the operation began shortly after the failure of the Sinyavino Offensive (1942), Sinyavino Offe ...
(Spark). Operation Iskra began on January 13, 1943, and on January 18, Soviet forces linked up, breaking the blockade. By January 22, the front line stabilized. The operation successfully opened a land corridor 8–10 km wide to the city. A railroad was swiftly built through the corridor that allowed far more supplies to reach the city than the "Road of Life", eliminating the possibility of the capture of the city and a German-Finnish link up. On January 28, both Meretskov and Govorov were awarded the Order of Suvorov
The Order of Suvorov () is a military decoration of the Russian Federation named in honor of Russian Generalissimo Prince Alexander Suvorov (1729–1800).
History
The Order of Suvorov was originally a Soviet Union, Soviet award established on ...
1st Class.
Leningrad and Volkhov Fronts tried to follow up their success with a much more ambitious offensive operation named Operation Polyarnaya Zvezda
Operation Polar Star (Russian: Операция Полярная звезда, ''Operatsia Polyarnaya Zvezda'') was an operation conducted by the Soviet Leningrad, Volkhov and Northwestern Fronts in February and March 1943. The operation was ...
(Polar Star). This operation had the aim of decisively defeating Army Group North
Army Group North () was the name of three separate army groups of the Wehrmacht during World War II. Its rear area operations were organized by the Army Group North Rear Area.
The first Army Group North was deployed during the invasion of Pol ...
, but achieved very modest gains. Several other offensives were conducted by Meretskov in the area in 1943, slowly expanding the corridor, and making other small gains. In November 1943, Meretskov and Govorov began planning the Leningrad-Novgorod Offensive which would drive Army Group North out of the Leningrad region.
On January 14, 1944, the Soviet offensive started. By March 1, the Leningrad, Volkhov and 2nd Baltic Fronts had driven Army Group North back up to on a front, liberating the southern Leningrad region and part of the Kalinin region. Meretskov and Govorov were once again awarded the Order of Suvorov 1st Class together.
Karelian Front and Manchuria
In February 1944, Meretskov was transferred to theKarelian Front
The Karelian Front ) was a front (a formation of Army Group size) of the Soviet Union's Red Army during World War II, and operated in Karelia.
Wartime
The Karelian Front was created in August 1941 when Northern Front was split into Karelian ...
. Here, he participated in the Vyborg–Petrozavodsk Offensive
The Vyborg–Petrozavodsk offensive or Karelian offensive was a strategic operation by the Soviet Leningrad and Karelian Fronts against Finland on the Karelian Isthmus and East Karelia fronts of the Continuation War, on the Eastern Front of Wor ...
that started in June 1944. His front liberated the city of Petrozavodsk
Petrozavodsk (, ; Karelian language, Karelian, Veps language, Vepsian and ) is the capital city of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, which stretches along the western shore of Lake Onega for some . The population of the city is 280,890 as of 2022.
...
and East Karelia. In October, Meretskov was ordered to clear the city of Petsamo Petsamo may refer to:
* Petsamo Province, a province of Finland from 1921 to 1922
* Petsamo, Tampere, a district in Tampere, Finland
* Pechengsky District
Pechengsky District (; ; ; ; ) is an administrative district (raion), one of the six in Mur ...
, in northern Finland, of Germans and to drive the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
army back into Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
. Meretskov was able to use his knowledge of Arctic warfare
Cold-weather warfare, also known as cold-region warfare, arctic warfare or winter warfare, encompasses military operations affected by snow, ice, Mud season, thawing conditions, or cold, both on land and at sea, as well as the strategies and t ...
to launch a co-ordinated offensive called the Petsamo–Kirkenes Offensive
The Petsamo–Kirkenes offensive was a major military offensive during World War II, mounted by the Red Army against the ''Wehrmacht'' in 1944 in the Petsamo region, ceded to the Soviet Union by Finland in accordance with the Moscow Armist ...
that drove the Germans back from their positions. After this offensive Meretskov was promoted to the rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union
Marshal of the Soviet Union (, ) was the second-highest military rank of the Soviet Union. Joseph Stalin wore the uniform and insignia of Marshal after World War II.
The rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union was created in 1935 and abolished in ...
, on October 26, 1944.
 Meretskov's next major command was in
Meretskov's next major command was in Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
in 1945, in the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
, where he was selected to lead the 1st Far East Front
First most commonly refers to:
* First, the ordinal form of the number 1
First or 1st may also refer to:
Acronyms
* Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array
* Far Infrared a ...
during the Soviet invasion of Manchuria
The Soviet invasion of Manchuria, formally known as the Manchurian Strategic Offensive Operation or simply the Manchurian Operation () and sometimes Operation August Storm, began on 9 August 1945 with the Soviet Union, Soviet invasion of the Emp ...
, under the overall command of Aleksandr Vasilevsky
Aleksandr Mikhaylovich Vasilevsky ( 1895 – 5 December 1977) was a Soviet general who served as a top commander during World War II and achieved the rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union. During World War II, he served as the Chief of the General ...
. According to the plan, the main force of the 1st Far East Front Army of set out from Primorsky Krai
Primorsky Krai, informally known as Primorye, is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (a krais of Russia, krai) of Russia, part of the Far Eastern Federal District in the Russian Far East. The types of inhabited localities in Russia, ...
, broke through the Japanese defense line set up in the East Manchuria, and carried out assaults against the Kwantung Army
The Kwantung Army (Japanese language, Japanese: 関東軍, ''Kantō-gun'') was a Armies of the Imperial Japanese Army, general army of the Imperial Japanese Army from 1919 to 1945.
The Kwantung Army was formed in 1906 as a security force for th ...
in Jilin
)
, image_skyline = Changbaishan Tianchi from western rim.jpg
, image_alt =
, image_caption = View of Heaven Lake
, image_map = Jilin in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, mapsize = 275px
, map_al ...
, in order to compete with Marshal Rodion Malinovsky
Rodion Yakovlevich Malinovsky (; ; – 31 March 1967) was a Soviet military commander and Marshal of the Soviet Union. He served as Minister of Defence of the Soviet Union from 1957 to 1967, during which he oversaw the strengthening of the Sov ...
's Transbaikal Front
The Transbaikal Front () was a front formed on September 15, 1941, on the basis of the Transbaikal Military District. Initially, it included the 17th and 36th armies, but in August 1942 the 12th Air Army was added to the front, and, finally, in ...
. The Transbaikal Front Army cooperated and advanced towards Changchun
Changchun is the capital and largest city of Jilin, Jilin Province, China, on the Songliao Plain. Changchun is administered as a , comprising seven districts, one county and three county-level cities. At the 2020 census of China, Changchun ha ...
.K·A·梅列茨科夫. 为人民而战. 王树森等译. 解放军出版社. 1986年8月.
Meretskov's Far East First Front Army and Maksim Purkayev
Maksim Alexeyevich Purkayev (; January 1, 1953) was a Soviet Union, Soviet military leader, reaching service rank of Army General.
Biography
Purkayev was conscripted into the Imperial Russian Army in 1915, and reached the rank of prapor ...
's 2nd Far East Front
__NOTOC__
The 2nd Far Eastern Front () was a Front—a formation equivalent to a Western Army Group—of the Soviet Army. It was formed just prior to the Soviet invasion of Manchuria and was active from August 5, 1945, until October 1, 1945.
Hist ...
jointly enclosed the Kwantung Army at Harbin
Harbin, ; zh, , s=哈尔滨, t=哈爾濱, p=Hā'ěrbīn; IPA: . is the capital of Heilongjiang, China. It is the largest city of Heilongjiang, as well as being the city with the second-largest urban area, urban population (after Shenyang, Lia ...
in an area with a circumference of 1,500 kilometers. Before the attack on August 9, there was a heavy rain. Meretskov decisively ordered the attack without artillery fire as planned. The sudden attack worked and the Soviet army successfully seized the forward position. Within a week, the 1st Far East Front Army broke through the Kwantung Army's 1st Front Army permanently prepared fortifications and penetrated 120 km-150 km. The Japanese headquarters completely lost command of the team and did not organize strong resistance until August 15. After August 15, the Japanese tried to organize heavy resistance in Mudanjiang
Mudanjiang (; Manchu language, Manchu: ''Mudan bira''), postal romanization, alternately romanized as Mutankiang, is a prefecture-level city in the southeast part of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China. It was called ''Botankou'' un ...
, but they still could not stop the advancement of Meretskov's 1st Far East Front Army. On the 18th, the commander of the Kwantung Army Otozō Yamada
was a career officer, convicted war criminal and general in the Imperial Japanese Army, serving from the Russo-Japanese War to the end of World War II.
Biography Early career
Yamada was born in Nagano Prefecture as the third son of Ichikawa Kat ...
did not reply to Meretskov's telegram requesting him to surrender. Meretskov ordered the airborne troops to be dropped at Harbin and other airports. The Kwantung Army surrendered on August 19.
In addition to military work, Meretskov also did political work. At the end of August, he went to the Chinese brigade inspection training led by Zhou Baozhong
Zhou Baozhong (; 1902–1964) was a commander of the 88th Separate Rifle Brigade and Northeast Anti-Japanese United Army resisting the pacification of Manchukuo by the Empire of Japan.
After the Chinese Civil War he was made Vice Governor of Yu ...
and asked his subordinates to provide the report of the North Korean battalion commander by future leader of North Korea
The supreme leader of North Korea () is the ''de facto'' hereditary leadership of the Workers' Party of Korea, the state and the Korean People's Army. The title is honorary, given only after death in the first two cases. More broadly it can ...
Kim Il Sung
Kim Il Sung (born Kim Song Ju; 15 April 1912 – 8 July 1994) was a North Korean politician and the founder of North Korea, which he led as its first Supreme Leader (North Korean title), supreme leader from North Korea#Founding, its establishm ...
. In September, Meretskov inspected the liberated cities of Changchun
Changchun is the capital and largest city of Jilin, Jilin Province, China, on the Songliao Plain. Changchun is administered as a , comprising seven districts, one county and three county-level cities. At the 2020 census of China, Changchun ha ...
, Shenyang
Shenyang,; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; formerly known as Fengtian formerly known by its Manchu language, Manchu name Mukden, is a sub-provincial city in China and the list of capitals in China#Province capitals, provincial capital of Liaonin ...
and Dalian
Dalian ( ) is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China (after Shenyang ...
, and assisted the Chinese Communist Party
The Communist Party of China (CPC), also translated into English as Chinese Communist Party (CCP), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Founded in 1921, the CCP emerged victorious in the ...
in restoring the party organization in the Northeast China
Northeast China () is a geographical region of China, consisting officially of three provinces Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang. The heartland of the region is the Northeast China Plain, the largest plain in China with an area of over . The regi ...
and the establishment of the Northern Manchurian Committee of CCP. Meretskov was awarded the Order of Victory
The Order of Victory () was the highest military decoration awarded for World War II service in the Soviet Union, and one of the rarest orders in the world. The order was awarded only to Generals and Marshals for successfully conducting combat ...
. As commander of Soviet forces in Korea, he launched the career of Kim Il Sung.
Commander and Assistant Minister of Defense
After the war Meretskov commanded a number of military districts until 1955 (including theMoscow Military District
The Order of Lenin Moscow Military District () is a Military districts of Russia, military district of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. Originally it was a district of the Imperial Russian Army until the Russian Empire's collapse in 191 ...
in 1947–49), when he was made the Assistant Minister of Defense, a post he held until 1964. In that year, he was made the Inspector-General Ministry of Defense, a largely ceremonial post.
Death
Meretskov died on December 30, 1968, at the age of 71. The urn containing his ashes is buried in theKremlin Wall Necropolis
The Kremlin Wall Necropolis is the former national cemetery of the Soviet Union, located in Red Square in Moscow beside the Moscow Kremlin Wall, Kremlin Wall. Burials there began in November 1917, when 240 pro-Bolsheviks who died during the Mosc ...
. Streets in Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
, St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
and Petrozavodsk
Petrozavodsk (, ; Karelian language, Karelian, Veps language, Vepsian and ) is the capital city of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, which stretches along the western shore of Lake Onega for some . The population of the city is 280,890 as of 2022.
...
are named after him.
Honours and awards
 ;Soviet Union
;Foreign awards
;Soviet Union
;Foreign awards
In popular culture
Meretskov is a character in the 2009 novel '' The Hundred-Year-Old Man Who Climbed Out the Window and Disappeared''.References
Sources
* * * * * *External links
Kirill Meretskov
(in Russian)
(in Russian) * {{DEFAULTSORT:Meretskov, Kirill 1897 births 1968 deaths People from Zaraysky District People from Ryazan Governorate Old Bolsheviks Candidates of the Central Committee of the 18th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks) Candidates of the Central Committee of the 19th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union Members of the Central Auditing Commission of the 20th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union First convocation members of the Soviet of Nationalities Second convocation members of the Soviet of the Union Third convocation members of the Soviet of the Union Members of the Supreme Soviet of the Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic Marshals of the Soviet Union Frunze Military Academy alumni Military personnel of the 1st Cavalry Army Soviet people of the Spanish Civil War Soviet military personnel of the Winter War Russian people of World War II Soviet military personnel of World War II Heroes of the Soviet Union Recipients of the Order of Victory Recipients of the Order of Suvorov, 1st class Chief Commanders of the Legion of Merit Foreign recipients of the Legion of Merit Recipients of the Order of Lenin Recipients of the Order of the Red Banner Recipients of the Order of Kutuzov, 1st class Order of Saint Olav Burials at the Kremlin Wall Necropolis Military Academy of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union alumni Siege of Leningrad