Merck Sharp and Dohme on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Merck & Co., Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in
 The company develops
The company develops
 Merck & Co. traces its origins to its former German parent company Merck Group, which was established by the Merck family in 1668 when Friedrich Jacob Merck purchased a pharmacy in
Merck & Co. traces its origins to its former German parent company Merck Group, which was established by the Merck family in 1668 when Friedrich Jacob Merck purchased a pharmacy in
NobelPrize.org In 1982, the company formed a
 In May 2002, The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation purchased stock in Merck.
From 2002 through 2005, the Australian affiliate of Merck paid publishing house
In May 2002, The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation purchased stock in Merck.
From 2002 through 2005, the Australian affiliate of Merck paid publishing house
Prometheus Biosciences
Inc for $10.8 billion. In December 2023, Merck announced it had partnered with Owkin to develop artificial intelligence-powered digital pathology diagnostics that could be used to identify patients suitable for immunotherapies. The aim is to come up with tools that can pre-screen patients with four tumour types for the MSI-H biomarker, namely endometrial, gastric, small intestinal, and biliary cancers. In January 2024, the company announced it would acquire Harpoon Therapeutics for $680 million. With this purchase, Merck expands its portfolio of oncological drugs. The main positions are HPN328, an activator of
Africa Recovery, Vol. 17 No. 1 (May 2003), p. 6 and the decision to donate the entirety of the drug to all those in need of it is used as part of the Mectizan Donation Program that covers countries such as Yemen and African countries. More than 700 million people have been treated since the inception of the program with 80 million people still undergoing treatment in Africa, Latin America, and Yemen. Blindness caused by onchocerciasis is decreasing, and there are regions of Latin America and Africa that have been shown to have eliminated the disease altogether.
Rahway, New Jersey
Rahway () is a city (New Jersey), city in southern Union County, New Jersey, Union County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. A bedroom community of New York City, it is centrally located in the Rahway River, Rahway Valley region, in the New ...
. The company does business as Merck Sharp & Dohme or MSD outside the United States and Canada. It is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world, generally ranking in the global top five by revenue.
Merck & Co. was originally established as the American affiliate of Merck Group in 1891. Merck develops and produces medicines, vaccines, biologic therapies and animal health products. It has several blockbuster products, including cancer immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncotherapy) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the basic research, fundamental research of cancer im ...
, anti-diabetic medications, and vaccines for HPV and chickenpox, each generating significant revenue as of 2020.
The company is ranked 71st on the 2022 ''Fortune'' 500 and 87th on the 2022 ''Forbes'' Global 2000, both based on 2021 revenues. In 2023, the company’s seat in the ''Forbes'' Global 2000 was 73.
Products
 The company develops
The company develops medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
s, vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
s, biologic therapies and animal health products. In 2020, the company had 6 blockbuster drugs or products, each with over $1 billion in revenue: ''Keytruda'' ( pembrolizumab), a humanized antibody used in cancer immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncotherapy) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the basic research, fundamental research of cancer im ...
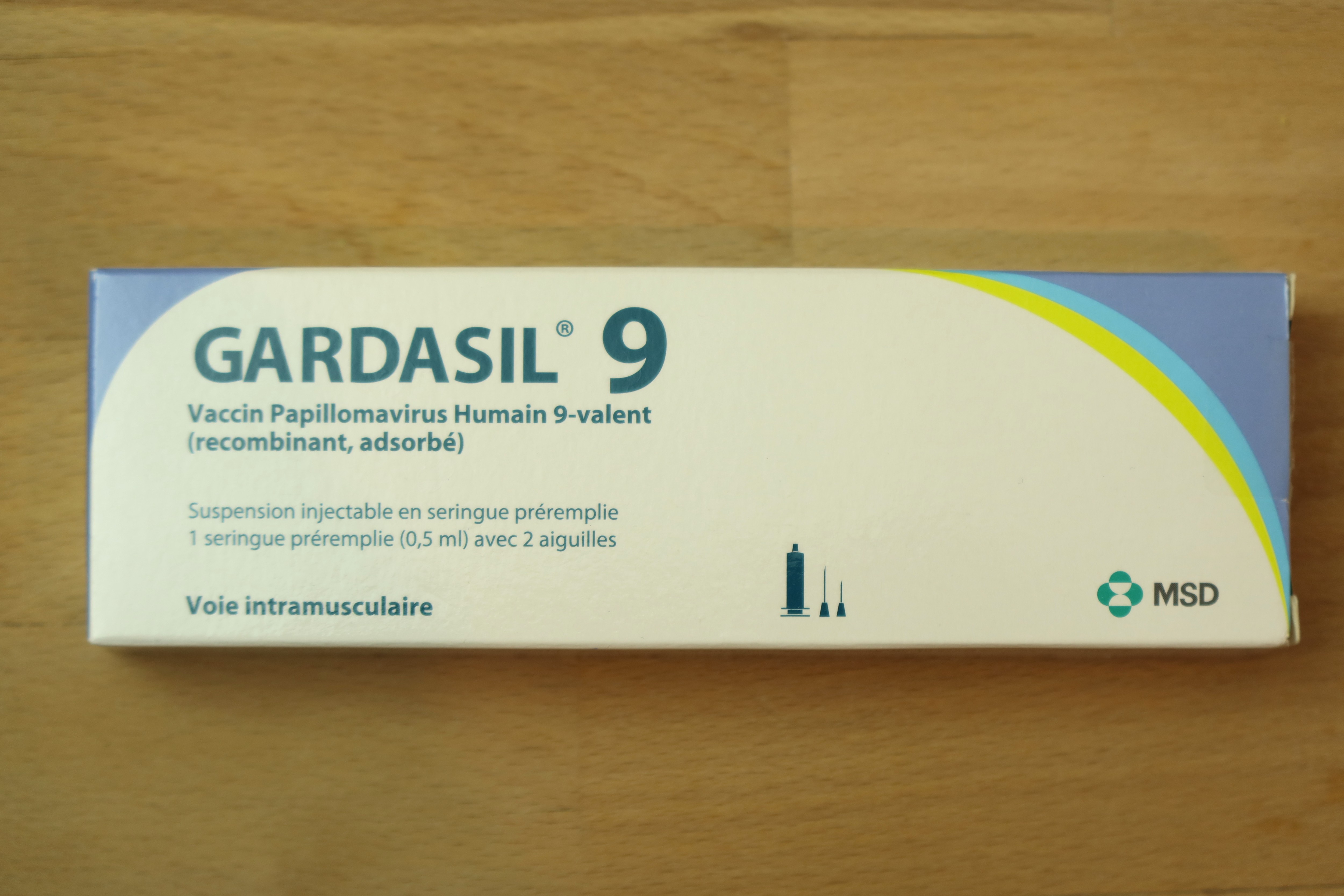
that had $14.3 billion in 2020 revenue; ''Januvia'' ( sitagliptin), an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes that had $5.3 billion in 2020 revenue; Gardasil, an HPV vaccine
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines are vaccines intended to provide acquired immunity against infection by certain types of human papillomavirus. The first HPV vaccine became available in 2006. Currently there are six licensed HPV vaccines: ...
that had $3.9 billion in 2020 revenue; Varivax, a varicella vaccine used to protect against chickenpox that had $1.9 billion in 2020 revenues; ''Bridion'' ( Sugammadex), a neuromuscular-blocking drug that had $1.2 billion in 2020 revenue; and ''Pneumovax 23'', a pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine that had $1.1 billion in 2020 revenue. Other major products by the company include ''Isentress'' ( raltegravir), an antiretroviral medication used to treat HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
that had $857 million in 2020 revenue; ''Simponi'' ( golimumab), a human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
monoclonal antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodie ...
used as an immunosuppressive drug that had $838 million in 2020 revenue; RotaTeq, a rotavirus vaccine that had $797 million in 2020 revenue; and ''Lynparza'' ( olaparib), a medication for the maintenance treatment of BRCA-mutated advanced ovarian cancer in adults that generated $725 million in 2020 revenue for the company.
Details of Merck's major products are as follows:
* Januvia (sitagliptin) is a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. In 2013, Januvia was the second largest selling diabetes drug worldwide. Januvia is commonly paired with the generic anti-diabetes drug metformin. It has been popular due in part because unlike many other diabetes drugs, it causes little or no weight gain and is not associated with hypoglycemic episodes. Merck also sells a single pill combination drug containing both Januvia and metformin under the trade name Janumet. There has been some concern that treatment with Januvia and other DPP-IV inhibitors may be associated with a modestly increased risk of pancreatitis.
* Zetia (ezetimibe) is a drug for hypercholesterolemia that acts by inhibiting the absorption of dietary cholesterol. Zetia has been controversial, as it was initially approved based on its impact on serum cholesterol levels without proof that it actually impacted the incidence of cardiovascular disease. Results of the IMPROVE-IT study, however, introduced at the 2014 Scientific Sessions of the American Heart Association, showed a statistically significant, albeit modest, benefit in adding Zetia to simvastatin for high-risk, post-acute-coronary-syndrome patients.
* Remicade (infliximab) is a monoclonal antibody directed toward the cytokine TNF-alpha and used for the treatment of a wide range of autoimmune disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
, ankylosing spondylitis, plaque psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete b ...
, and others. Remicade and other TNF-alpha inhibitors exhibit additive therapeutic effects with methotrexate and improve quality of life. Adverse effects include increased risk of infection and certain cancers. Merck had rights to the drug in certain areas, while Janssen Biotech had rights in other areas; in 2017, Merck announced a biosimilar to Remicade, Renflexis.
* Gardasil (recombinant human papilloma virus vaccine) is a vaccine against multiple serotypes of human papilloma virus (HPV), which is responsible for most cases of cervical cancer worldwide.
* Isentress (raltegravir) is a human immunodeficiency virus integrase inhibitor for the treatment of HIV infection. It is the first anti-HIV compound having this mechanism of action. It is part of one of several first line treatment regimens recommended by the United States Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
.
* Keytruda (pembrolizumab) is an immune modulator for the treatment of cancer. On September 4, 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Pembrolizumab (MK-3475) as a breakthrough therapy for melanoma treatment. In clinical trials, pembrolizumab provided partial tumor regression in about one quarter of patients, many of whom have not seen further progression of their disease in over 6 months of follow-up.
* Invanz ( Ertapenem) is an injectable antibiotic, rights to which Merck has owned since 1999. Merck was in a legal dispute with the Taiwanese company Savior Lifetec over their attempt to secure rights to sell a generic drug version in the United States. Savior has since obtained approval to market generic ertapenem.
* Mexsana is an antiseptic medicated powder.
* Mectizan (ivermectin) is an anti-parasitic medicine traditionally used to treat river blindness. It is the focus of Merck's Mectizan Donation Program, wherein Merck has donated doses of the drug to treat millions of people in countries such as Yemen and African nations.
* Molnupiravir is an antiviral pill to treat COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
, developed in partnership with Ridgeback Biotherapeutics.
Merck & Co. publishes '' The Merck Manuals'', a series of medical reference books for physicians, nurses, technicians, and veterinarians. These include the '' Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy'', the world's best-selling medical reference. '' The Merck Index'', a compendium of chemical compounds, was published by Merck & Co. until it was acquired by the Royal Society of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society and professional association in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the ...
in 2012.
History
Roots and early history
 Merck & Co. traces its origins to its former German parent company Merck Group, which was established by the Merck family in 1668 when Friedrich Jacob Merck purchased a pharmacy in
Merck & Co. traces its origins to its former German parent company Merck Group, which was established by the Merck family in 1668 when Friedrich Jacob Merck purchased a pharmacy in Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it the ...
. In 1827, Merck Group evolved from a pharmacy to a drug manufacturer company with the commercial manufacture of morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
. Merck perfected the chemical process of deriving morphine from opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
and later introduced cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, used to treat sinus problems and to add to beverages to boost energy levels.
In 1887 a German-born, long-time Merck employee, Theodore Weicker, went to the United States to represent Merck Group. In 1891, with $200,000 received from E. Merck, Weicker started Merck & Co., with headquarters in lower Manhattan. That year George Merck, the 23-year-old son of the then head of E. Merck (and grandson of the founder) joined Weicker in New York. Merck & Co. operated from 1891 to 1917 as the US subsidiary of the Merck Group.
Nationalization
After the U.S. enteredWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, due to its German connections, Merck & Co. was the subject of expropriation under the Trading with the Enemy Act of 1917. The government seized 80 percent of the shares owned by the German parent company and sold it. In 1919, George F. Merck (head of the American branch of the Merck family), in partnership with Goldman Sachs
The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. ( ) is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company. Founded in 1869, Goldman Sachs is headquartered in Lower Manhattan in New York City, with regional headquarters in many internationa ...
and Lehman Brothers, bought the company back at a U.S. government auction for $3.5 million, but Merck & Co. remained a separate company from its former German parent. Merck & Co. holds the trademark rights to the "Merck" name in the United States and Canada, while its former parent company retains the rights in the rest of the world; the right to use the Merck name was the subject of litigation between the two companies in 2016.
In 1925, George W. Merck succeeded his father George F. Merck as president. In 1927, the corporation merged with the Powers- Weightman-Rosengarten Company, a Philadelphia quinine manufacturer. George Merck remained president and Frederic Rosengarten became chairman of the board. In 1929, H. K. Mulford Company merged with Sharp and Dohme, Inc. and brought vaccine technology, including immunization of cavalry horses in World War I and delivery of a diphtheria antitoxin to Merck & Co.
In 1943, streptomycin
Streptomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, Burkholderia infection, ''Burkholderia'' i ...
was discovered during a Merck-funded research program in Selman Waksman's laboratory at Rutgers University
Rutgers University ( ), officially Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, is a Public university, public land-grant research university consisting of three campuses in New Jersey. Chartered in 1766, Rutgers was originally called Queen's C ...
. It became the first effective treatment for tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
. At the time of its discovery, sanatorium
A sanatorium (from Latin '' sānāre'' 'to heal'), also sanitarium or sanitorium, is a historic name for a specialised hospital for the treatment of specific diseases, related ailments, and convalescence.
Sanatoriums are often in a health ...
s for the isolation of tuberculosis-infected people were a ubiquitous feature of cities in developed countries, with 50% dying within 5 years of admission. Although Merck's agreement with Rutgers gave it exclusive rights to streptomycin, at Waksman's request the company renegotiated the agreement, returning the rights to the university in exchange for a royalty. The university then set up non-exclusive licenses with seven companies to ensure a reliable supply of the antibiotic.
1950–2000
In the 1950s, thiazide diuretics were developed by Merck scientists Karl H. Beyer, James M. Sprague, John E. Baer, and Frederick C. Novello and led to the marketing of the first drug of this class, chlorothiazide, under the trade name Diuril in 1958. The research leading to the discovery of chlorothiazide, leading to "the saving of untold thousands of lives and the alleviation of the suffering of millions of victims of hypertension" was recognized by a special Public Health Award from the Lasker Foundation in 1975. In 1953, Merck & Co. merged with Philadelphia-based Sharp & Dohme, Inc., becoming the largest U.S. drugmaker. Sharp and Dohme had acquired H. K. Mulford Company in 1929, addingsmallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
vaccines to its portfolio. The combined company kept the trade name Merck in the United States and Canada, and as Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD) outside North America.
In 1965, Merck & Co. acquired Charles Frosst Ltd. of Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
(founded 1899), creating Merck-Frosst Canada, Inc., as its Canadian subsidiary and pharmaceutical research facility. Merck & Co. closed this facility in July 2010 but remerged in 2011 as Merck Canada.
Maurice Hilleman, a scientist at Merck, developed the first mumps vaccine in 1967, the first rubella vaccine in 1969, and the first trivalent measles, mumps, rubella ( MMR vaccine) in 1971. The incidence of rubella-associated birth defects fell from up to 10,000 per year in the U.S. to zero in the aftermath of the rubella vaccine's development. Hilleman also developed the first Hepatitis B vaccine and the first varicella vaccine, for chickenpox.
The company was incorporated in New Jersey in 1970. John J. Horan became CEO and Chairman in 1976, serving until 1985. Under his leadership, the company's investment in R&D grew threefold, and Merck became the largest pharmaceutical company in the world.
In 1979, Merck scientists developed lovastatin (''Mevacor''), the first drug of the statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play ...
class.
Merck scientist William C. Campbell and Satoshi Ōmura developed ivermectin for veterinary use in 1981, and later put it to human use against Onchocerciasis
Onchocerciasis, also known as river blindness, is a disease caused by infection with the parasitic worm ''Onchocerca volvulus''. Symptoms include severe itching, bumps under the skin, and blindness. It is the second-most common cause of blindne ...
in 1987–88 with the name Mectizan; today the compound is used against river blindness, lymphatic filariasis, scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious human skin infestation by the tiny (0.2–0.45 mm) mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei'', variety ''hominis''. The word is from . The most common symptoms are severe itchiness a ...
and other parasitic infections.Press releaseNobelPrize.org In 1982, the company formed a
joint venture
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties, generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, and shared governance. Companies typically pursue joint ventures for one of four reasons: to acce ...
, KBI Inc., with AstraZeneca
AstraZeneca plc () (AZ) is a British-Swedish multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with its headquarters at the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridge, UK. It has a portfolio of products for major diseases in areas includi ...
. During the late 1980s and 1990s, the company also established joint ventures with DuPont
Dupont, DuPont, Du Pont, duPont, or du Pont may refer to:
People
* Dupont (surname) Dupont, also spelled as DuPont, duPont, Du Pont, or du Pont is a French surname meaning "of the bridge", historically indicating that the holder of the surname re ...
to access research and development expertise, and with Johnson & Johnson to sell over-the-counter consumer medications.
In 1985, Merck received approval for imipenem, the first member of the carbapenem
Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Si ...
class of antibiotics. Antibiotics of the carbapenem class play an important role in treatment guidelines for certain hospital-acquired and multi-drug resistant infections. P. Roy Vagelos became CEO and Chairman that year, succeeding Horan.
In 1991, Merck's Kelco subsidiary was responsible for volatile organic compound
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature. They are common and exist in a variety of settings and products, not limited to Indoor mold, house mold, Upholstery, upholstered furnitur ...
(VOC) emission pollution in the San Diego area. In 1996 Merck paid $1.8 million for polluting the air. New machines were installed to reduce smog emissions by a year.
In November 1993, Merck & Co. acquired Medco Containment Services for $6 billion. Merck & Co. spun Medco off ten years later.
Merck's supply chain
A supply chain is a complex logistics system that consists of facilities that convert raw materials into finished products and distribute them to end consumers or end customers, while supply chain management deals with the flow of goods in distri ...
reduction programme has been referred to as an example of successful change. Merck reduced its number of global suppliers from 40,000 to less than 10,000 during the period from 1992 to 1997.
2001–2019
 In May 2002, The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation purchased stock in Merck.
From 2002 through 2005, the Australian affiliate of Merck paid publishing house
In May 2002, The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation purchased stock in Merck.
From 2002 through 2005, the Australian affiliate of Merck paid publishing house Elsevier
Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, ...
an undisclosed amount to produce eight issues of a medical journal, the '' Australasian Journal of Bone and Joint Medicine''. Although it gave the appearance of being an independent peer-reviewed journal, without any indication that Merck had paid for it, the journal actually reprinted articles that originally appeared in other publications and that were favorable to Merck. The misleading publication came to light in 2009 during a personal injury lawsuit filed over Vioxx; 9 of 29 articles in the journal's second issue referred positively to Vioxx. The CEO of Elsevier's Health Sciences Division, Michael Hansen, admitted that the practice was "unacceptable".
In 2005, CEO Raymond Gilmartin retired following Merck's voluntary worldwide withdrawal of Vioxx. Former president of manufacturing Richard Clark was named CEO and company president.
In November 2009, Merck & Co. completed a merger with Schering-Plough
Schering-Plough Corporation was an American pharmaceutical company. It was originally the U.S. subsidiary of the German company Schering AG, which was founded in 1851 by Ernst Christian Friedrich Schering. As a result of nationalization, it becam ...
in a US$41 billion deal. Although Merck & Co. was in reality acquiring Schering-Plough, the purchase was declared a "reverse merger", in which "Old" Merck & Co. was renamed Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Schering-Plough renamed as "Merck & Co., Inc. The maneuver was an attempt avoid a "change-of-control" in order to preserve Schering-Plough's rights to market Remicade. A settlement with Johnson & Johnson was reached in 2011, in which Merck agreed to pay $500 million. Merck Sharp & Dohme remains a subsidiary of the Merck & Co. parent.
Richard Clark retired as CEO and company president in October 2011 and Kenneth Frazier became CEO.
In October 2013, Merck announced it would cut 8,500 jobs in an attempt to cut $2.5 billion from its costs by 2015. Combined with 7,500 job cuts announced in 2011 and 2012, the layoffs amounted to 20% of its workforce.
By 2014, research performed at Merck has led to U.S. FDA approval of 63 new molecular entities.
In August 2014, Merck acquired Idenix Pharmaceuticals for $3.85 billion.
In December 2014, the company acquired Swiss biotechnology company OncoEthix for up to $375 million.
Between 2010 and 2015, the company cut around 36,450 jobs. During that time, the company sold its consumer health business to Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
and narrowed the company's focus to immunology, vaccines, diabetes, emerging markets and medicines used in hospitals, like certain antibiotics.
In January 2015, Merck acquired Cubist Pharmaceuticals for $102 per share in cash or about $9.5 billion in total.
In July 2015, Merck and Ablynx expanded their 18-month-old immuno-oncology collaboration by four years, generating a potential $4.4 billion in milestone payments for the Abylnx. The company also announced it would spend $95 million up front collaborating with cCAM Biotherapeutics and its early-stage treatment similar to Keytruda. Merck & Co. will bring in CM-24, an antibody designed to block the immune checkpoint CEACAM1.
In January 2016, Merck announced two new partnerships; the first with Quartet Medicine and its small molecule pain treatments, the second with Complix investigating intracellular cancer targets, with both collaborations potentially generating up to $595 million and $280 million respectively. Days later the company announced it would acquire IOmet Pharma, with IOmet becoming a wholly owned subsidiary of Merck & Co. The acquisition includes IOmets indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO), tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO), and dual-acting inhibitors.
In July 2016, the company acquired Afferent Pharmaceuticals, developer of a candidate used to block P2RX3 receptors, for approximately $1 billion, plus up to $750 million in milestone payments.
In 2017, Merck bought the PARP inhibitor Lynparza from AstraZeneca.
In April 2017, Merck Animal Health acquired Vallée S.A., a Brazilian animal health product manufacturer.
In September 2017, the company announced it would acquire Rigontec, developer of a candidate to target the retinoic acid-inducible gene I pathway, for $554 million.
In October 2017, the company granted the inaugural Merck-AGITG Clinical Research Fellowship in Gastro-Intestinal (GI) Cancer to David Lau, a professional in Melbourne, Australia.
In June 2018, Merck acquired Viralytics, an Australian viral cancer drug company, for AUD$502 million.
In 2018, Merck began the submission process for a Biologics License Application to the Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
under the Breakthrough Therapy Designation for an investigational vaccine, called V920, to fight the Zaire strain of the Ebola virus.
In April 2019, the company acquired Immune Design for approximately $300 million, gaining access to its immunotherapy programs. It also acquired Antelliq Group for $2.4 billion, or $3.7 billion including debt.
In May 2019, Merck announced it would acquire Peloton Therapeutics, developer of a HIF-2alpha inhibitor for Von Hippel–Lindau disease-associated renal cell carcinoma, for up to $2.2 billion.
In June 2019, Merck announced it would acquire Tilos Therapeutics for up to $773 million.
In November 2019, the company acquired Calporta, which focused on Parkinsons and Alzheimers treatments.
In December 2019, Merck Animal Health acquired Vaki, an aquaculture company, from Pentair
Pentair plc (PNR) is an American water treatment company incorporated in Ireland with tax residency in UK, with its main U.S. office in Golden Valley, Minnesota, Golden Valley, Minnesota. Pentair was founded in the US, with 65% of company's reve ...
.
2020–present
In January 2020, Merck acquired ArQule, developer of ARQ 531, an oral Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, for $2.7 billion. In March 2020, Merck was one of ten companies recognised at the inaugural Manufacturing Awards by New Jersey Business magazine and the New Jersey Business and Industry Association. In June 2020, Merck acquired Themis Bioscience, a company focused on vaccines and immune-modulation therapies for infectious diseases includingCOVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
.
Also in June 2020, Merck Animal Health acquired Quantified Ag, a data and analytics company that monitors cattle body temperature and movement in order to detect illness early.
In August 2020, Merck Animal Health acquired IdentiGEN, engaged in DNA-based animal traceability.
In September 2020, Merck acquired $1 billion of Seattle Genetics common stock, and agreed to co-develop ladiratuzumab vedotin.
In November 2020, Merck announced it would acquire VelosBio for $2.75 billion, developer of VLS-101, an antibody-drug conjugate designed to target Tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1) in both hematological and solid tumors. VLS-101 is currently Phase I and Phase II clinical trials. The company also announced it would acquire OncoImmune for $425 million and its phase 3 candidate, CD24Fc, used in the treatment of patients with severe and critical COVID-19.
In February 2021, Merck Animal Health acquired PrognostiX Poultry.
In April 2021, Merck acquired Pandion Therapeutics for $1.85 billion, expanding its offering in treating autoimmune diseases.
In June 2021, the U.S. government agreed to spend $1.2 billion to purchase 1.7 million doses of Molnupiravir, a Merck product, if it were to be approved by regulators to treat COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
. In October 2021, the company said that the drug reduces the risk of hospitalization or death by around 50% for patients with mild or moderate cases of COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
and that it would seek Emergency Use Authorization for the drug.
In July 2021, Robert M. Davis became CEO, succeeding Kenneth Frazier, who became executive chairman.
In July 2021, Merck completed the corporate spin-off of Organon & Co.
In September 2021, Merck announced it would acquire Acceleron Pharma for $11.5 billion, gaining control over Sotatercept, used in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include dypsnea, shortness of breath, Syncope (medicine), fainting, tiredness, chest pain, pedal edema, swell ...
, and luspatercept-aamt.
In September 2022, the company announced it would acquire Vence, a livestock management company for an undisclosed sum, incorporating it within Merck Animal Health.
In December 2022, the company announced a licensing deal with Kelun-Biotech of China whereby it would expand its early cancer pipeline with a set of antibody-drug conjugates; this follows an earlier agreement between the two companies to co-develop such drugs.
In April 2023, Merck announced it would acquirPrometheus Biosciences
Inc for $10.8 billion. In December 2023, Merck announced it had partnered with Owkin to develop artificial intelligence-powered digital pathology diagnostics that could be used to identify patients suitable for immunotherapies. The aim is to come up with tools that can pre-screen patients with four tumour types for the MSI-H biomarker, namely endometrial, gastric, small intestinal, and biliary cancers. In January 2024, the company announced it would acquire Harpoon Therapeutics for $680 million. With this purchase, Merck expands its portfolio of oncological drugs. The main positions are HPN328, an activator of
T-cells
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
that is being researched to treat advanced cancer patients associated with DLL3 expression (delta-like ligand 3), an inherent small cell lung cancer (SCLC), neuroendocrine tumors, and several other species. Merck’s portfolio will also be complemented by T-cell attractions using the patented Harpoon Tri-specific design for T cell activation (TriTAC). According to engineering protein technology, tumor cells are destroyed by the patient’s own immune cells, and the ProTriTAC platform works with the TriTAC platform to develop a therapeutic agent that attracts T-cells, but is inactive until it reaches the tumor.
In April 2024, Merck completed the acquisition of Abceutics for $208m.
In July 2024, Merck completed the acquisition of EyeBio for $3bn.
In October 2024, Merck announced the acquisition of Modifi Biosciences for $1.3bn.
Acquisition history
*Merck & Co **Merck & Co ***Merck & Co ****H. K. Mulford Company ****Sharp & Dohme, Inc ****Charles E. Frosst Ltd ****Medco Containment Services Inc ***Schering‑Plough ****Schering-Plough
Schering-Plough Corporation was an American pharmaceutical company. It was originally the U.S. subsidiary of the German company Schering AG, which was founded in 1851 by Ernst Christian Friedrich Schering. As a result of nationalization, it becam ...
*****Schering Corporation
*****Plough, Inc
****Organon International
*****Alydia Health
****Intervet
****Diosynth
****Nobilon
**Imperial Blue Corporation
***Idenix Pharmaceuticals
**Maven Corporation
*** Cubist Pharmaceuticals
**** Trius Therapeutics
****Optimer Pharmaceuticals
**OncoEthix
**IOmet Pharma
**Afferent Pharmaceuticals
**Merck Animal Health
***Vallée S.A.
***Vaki
***Quantified Ag
***IdentiGEN
***PrognostiX Poultry Ltd
***Vence
**Rigontec
** Viralytics
**Antelliq Group
**Cascade Merger Sub, Inc.
***Immune Design Corp
**Peloton Therapeutics
**Tilos Therapeutics
**Calporta
**Argon Merger Sub, Inc.
***ArQule, Inc.
**Themis Bioscience
**VelosBio
**OncoImmune
**Astros Merger Sub, Inc.
*** Acceleron Pharma
**Prometheus Biosciences
**Caraway Therapeutics
**Harpoon Therapeutics
**Abceutics
**EyeBio
**Modifi Biosciences
**Emergent BioSolutions (Acq 2025)
Philanthropy
Merck Company Foundation
Since it was founded in 1957, the Merck Company Foundation has distributed $740 million in overall charitable distributions including more than $480 million to educational and non-profit organizations. On December 7, 2012, the foundation announced that it was ending its donations to theBoy Scouts of America
Scouting America is the largest scouting organization and one of the largest List of youth organizations, youth organizations in the United States, with over 1 million youth, including nearly 200,000 female participants. Founded as the Boy Sco ...
citing its discrimination against gay people.
Patient assistance programs
Merck & Co. was one of the first American pharmaceutical companies to offer assistance to those unable to afford its medications, beginning a program in the 1950s. Merck & Co. offers seven patient assistance programs, each with specific eligibility requirements.Hilleman Laboratories
Merck and the Wellcome trust jointly fund the Hilleman Laboratories, an India-based non-profit research organization dedicated to the development of low-cost vaccines for use in developing countries. Current projects include the development of low cost, thermostable vaccines for the prevention of cholera, rotavirus, and meningitis.Merck for Mothers
Merck for Mothers is Merck's global initiative to help create a world where no woman has to die while giving life.Mectizan donation program
In 1987, Merck began a program withUNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
to donate its new drug Mectizan to "all that need it for as long as needed" in an effort to combat onchocerciasis
Onchocerciasis, also known as river blindness, is a disease caused by infection with the parasitic worm ''Onchocerca volvulus''. Symptoms include severe itching, bumps under the skin, and blindness. It is the second-most common cause of blindne ...
, also known as river blindness, primarily in Africa. Up to that point, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
had fought the disease through the use of insecticides to lower the population of its primary vector, the Black Fly
A black fly or blackfly (sometimes called a buffalo gnat, turkey gnat, or white socks) is any member of the family Simuliidae of the Culicomorpha infraorder. It is related to the Ceratopogonidae, Chironomidae, and Thaumaleidae. Over 2,200 s ...
. However, when studies in the 1980s showed how effective the drug was at treating and preventing the disease, the WHO agreed to use it instead of its previous strategies. Merck's involvement is considered a key factor in the success against the disease all over the world,Onchocerciasis: Africa's victory over river blindnessAfrica Recovery, Vol. 17 No. 1 (May 2003), p. 6 and the decision to donate the entirety of the drug to all those in need of it is used as part of the Mectizan Donation Program that covers countries such as Yemen and African countries. More than 700 million people have been treated since the inception of the program with 80 million people still undergoing treatment in Africa, Latin America, and Yemen. Blindness caused by onchocerciasis is decreasing, and there are regions of Latin America and Africa that have been shown to have eliminated the disease altogether.
Lawsuits and controversies
Vioxx
In 1999, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Vioxx (known generically as rofecoxib), a Merck product for treating arthritis. Vioxx was designed as a selective inhibitor of the enzyme cyclooxygenase-2. Such compounds were expected to cause less gastrointestinal bleeding than olderanti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation, fever or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs reduce pain by inhibiting mechan ...
drugs such as naproxen, which were associated with 20,000 hospitalizations and 2000 deaths each year. Vioxx became one of the most prescribed drugs in history.
Thereafter, studies by Merck and by others found an increased risk of heart attack associated with Vioxx use when compared with naproxen. Merck adjusted the labeling of Vioxx to reflect possible cardiovascular risks in 2002.
On September 23, 2004, Merck received information about results from a clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
it was conducting that included findings of increased risk of heart attacks among Vioxx users who had been using the medication for over eighteen months. On September 28, 2004, Merck notified the FDA that it was voluntarily withdrawing Vioxx from the market, and it publicly announced the withdrawal on September 30. An analysis for the period 1999–2004, based on U.S. Medical Expenditure Survey data, reported that Vioxx was associated with 46,783 heart attacks, and along with the other popular COX-2 inhibitor Celebrex, an estimated 26,603 deaths from both.
About 50,000 people sued Merck, claiming they or their family members had suffered medical problems such as heart attacks or strokes after taking Vioxx. In November 2007, Merck agreed to pay $4.85 billion to settle most of the pending Vioxx lawsuits. The settlement required that claimants provide medical and pharmacy records confirming the occurrence of a heart attack, ischemic stroke, or sudden cardiac death; the receipt of at least 30 Vioxx pills within 60 days prior to the injury or death; and confirmation of Vioxx being used within 14 days of the Vioxx-related event. The settlement was generally viewed by industry analysts and investors as a victory for Merck, considering that original estimates of Merck's liability reached between $10 billion and $25 billion. As of mid-2008, when the plaintiff class had reached the threshold percentage required by Merck to go through with the settlement, plaintiffs had prevailed in only three of the twenty cases that had reached juries, all with relatively small awards.
Merck has refused to consider compensation for Vioxx victims and their families outside the US. This is particularly true in the UK where there are at least 400 victims and the legal protection afforded to the victims and their families is particularly weak.
According to internal e-mail traffic released at a later lawsuit, Merck had a list of doctors critical of Vioxx to be "neutralized" or "discredited". "We may need to seek them out and destroy them where they live," wrote an employee. A Stanford Medical School professor said that Merck was engaged in intimidation of researchers and infringement upon academic freedom
Academic freedom is the right of a teacher to instruct and the right of a student to learn in an academic setting unhampered by outside interference. It may also include the right of academics to engage in social and political criticism.
Academic ...
.
On May 20, 2008, Merck settled for $58 million with 30 states alleging that Merck engaged in deceptive marketing tactics to promote Vioxx. All its new television pain-advertisements must be vetted by the Food and Drug Administration and changed or delayed upon request until 2018.
Fosamax
Fosamax ( alendronate) is abisphosphonate
Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone density, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed to treat osteoporosis.
Evidence shows that they reduce the risk of fracture in ...
used for the treatment of post-menopausal osteoporosis and for the prevention of skeletal problems in certain cancers. The American College of Clinical Endocrinology, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) is a professional association of physicians specializing in obstetrics and gynecology in the United States. Several Latin American countries are also represented within Districts of ...
, the North American Menopause Society and the UK National Osteoporosis Guideline Group recommend alendronate and certain other bisphosphonates as first line treatments for post-menopausal osteopotosis. Long-term treatment with bisphosponates produces anti-fracture and bone mineral density effects that persist for 3–5 years after an initial 3–5 years of treatment. Alendronate reduces the risk of hip, vertebral, and wrist fractures by 35-39%.
In December 2013, Merck agreed to pay a total of $27.7 million to 1,200 plaintiffs in a class action lawsuit alleging that the company's osteoporosis drug had caused them to develop osteonecrosis of the jaw. Prior to the settlement, Merck had prevailed in 3 of 5 so-called bellwether trials. Approximately 4000 cases still await adjudication or settlement as of August 2014.
There have also been thousands of lawsuits alleging that Fosamax increased the risk of thigh-bone fractures. In March 2022, Merck defeated approximately 500 lawsuits over Fosamax in New Jersey when U.S. District Judge
The United States district courts are the trial courts of the United States federal judiciary, U.S. federal judiciary. There is one district court for each United States federal judicial district, federal judicial district. Each district cov ...
Freda L. Wolfson ruled that the plaintiffs' lawsuit was preempted by federal law. On September 20, 2024, the United States Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit overturned that decision, holding that federal law did not block plaintiffs' state law claims against Merck over Fosamax. As of June 30, 2024, about 3,115 lawsuits over Fosamax were still pending against Merck in both federal and state courts in the United States.
Medicaid overbilling
A fraud investigation by theUnited States Department of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a United States federal executive departments, federal executive department of the U.S. government that oversees the domestic enforcement of Law of the Unite ...
began in 2000 when allegations were brought in two separate lawsuits filed by whistleblowers under the False Claims Act. They alleged that Merck failed to pay proper rebates to Medicaid
Medicaid is a government program in the United States that provides health insurance for adults and children with limited income and resources. The program is partially funded and primarily managed by U.S. state, state governments, which also h ...
and other health care programs and paid illegal remuneration to health care providers. On February 7, 2008, Merck agreed to pay more than $650 million to settle charges that it routinely overbilled Medicaid for its most popular medicines. The settlement was one of the largest pharmaceutical settlements in history. The federal government received more than $360 million, plus 49 states and Washington, DC, received over $290 million. One whistleblower received a $68 million reward. Merck made the settlement without an admission of liability or wrongdoing.
"Merck" name legal dispute
In 191 of 193 countries, the original Merck company, the Merck Group of Darmstadt, owns the rights to the "Merck" name. In the United States and Canada, the company trades under the name EMD (an abbreviation of Emanuel Merck, Darmstadt), its legal name here says ''Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany'', and instead of "Merck Group", the "EMD Group" name is used. In the United States and Canada, Merck & Co. holds the rights to the trademark "Merck", while in the rest of the world the company trades under the name MSD (an abbreviation of Merck, Sharp & Dohme) and its legal name says here ''Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc. Kenilworth, NJ, USA''. In 2015 the Merck Group adopted a new logo and said it will be "much more aggressive" about protecting the brand of "the real Merck". Merck of Darmstadt has initiated litigation against its former subsidiary, Merck & Co. (MSD) of Kenilworth, in several countries over infringing use of the Merck name. In 2016, theHigh Court of Justice
The High Court of Justice in London, known properly as His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England, together with the Court of Appeal (England and Wales), Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Courts of England and Wales, Senior Cour ...
in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
ruled that MSD had breached an agreement with its former parent company and that only Merck of Darmstadt is entitled to use the Merck name in the United Kingdom. The judge also held that MSD's use of "Merck" as part of branding on its global websites were directed to the UK and infringed Merck's trade mark rights in the UK.
In response to the ruling, MSD initiated counter-litigation in the United States in January 2016 by filing a federal lawsuit which accused its former parent company of "infringing on its trademark" through actions that included the increased usage of "Merck KGaA" and "MERCK" in branding in the US as well as on its social media presence. Further Merck & Co. has also accused the Merck Group of federal trademark dilution, unfair competition, false advertising, deceptive trade practices, breach of contract, and cybersquatting. The case came to a head when a research scientist believed he was communicating with Merck & Co regarding a research grant in oncology, when in fact he was talking with the Merck Group. As a result, Merck & Co. asked the federal court to stop the Merck Group from using "Merck" on any products or marketing materials in the United States. As a direct result, Merck & Co is seeking "''all monetary gains, profits, and advantages''" made by the Merck Group and three-times the damage, plus additional punitive damages.
In April 2020, in the course of litigation of Merck against MSD in Switzerland, the Federal Supreme Court of Switzerland ruled that MSD's use of the "Merck" brand in its global websites could, absent geotargeting mechanisms, have "commercial effect" in Switzerland and could therefore violate Merck's rights (if any) to the "Merck" brand in Switzerland.
Tax fraud
In 2007, Merck paid $2.3 billion to settle allegations of offshore tax fraud between 1993 and 2001.Propecia
In 2021, an investigation byReuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency ...
revealed that Merck's baldness drug Propecia caused persistent sexual dysfunction in men. The drug has been linked to over 700 incidences of suicidal thoughts and 110 deaths. Merck has been receiving reports since 1998, but never included the risks on the label. In 2015, Merck was sued by consumer-rights law firm Hagens Berman over a wrongful death linked to Propecia.
Environmental violations
Merck & Co. once used methylene chloride, an animal carcinogen on theUnited States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on De ...
's list of pollutants, as a solvent in some of its manufacturing processes. Merck chemists and engineers subsequently replaced the compound with others having fewer negative environmental effects. Merck has also modified its equipment to protect the environment, installing a distributed control system that coordinates chemical reactions more efficiently and expedites manufacturing by 50 percent, eliminating the need for the disposal and storage of harmful waste. Biological oxygen demand has also been reduced. In 2011, Merck paid a $1.5 million civil penalty to settle alleged violations of federal environmental laws at its pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities in Riverside, Pennsylvania and West Point, Pennsylvania.
Public-private engagement
Conferences
Merck was a Conference Supporter for the Virtual ISPOR Asia Pacific conference in September 2020.Political lobbying
Merck is a contributing member of AcademyHealth, a health research advocacy network that also includesgovernment agencies
A government agency or state agency, sometimes an appointed commission, is a permanent or semi-permanent organization in the machinery of government (bureaucracy) that is responsible for the oversight and administration of specific functions, ...
, universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
, pharmaceutical companies and lobbying groups.
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Merck and Co. Biotechnology companies of the United States Pharmaceutical companies of the United States Veterinary companies of the United States Vaccine producers Multinational companies headquartered in the United States Pharmaceutical companies based in New Jersey Companies based in Union County, New Jersey Kenilworth, New Jersey American companies established in 1891 Pharmaceutical companies established in 1891 1891 establishments in New Jersey Companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average Companies in the Dow Jones Global Titans 50 Companies listed on the New York Stock Exchange Bayer Schering-Plough