Mendelian inheritance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of
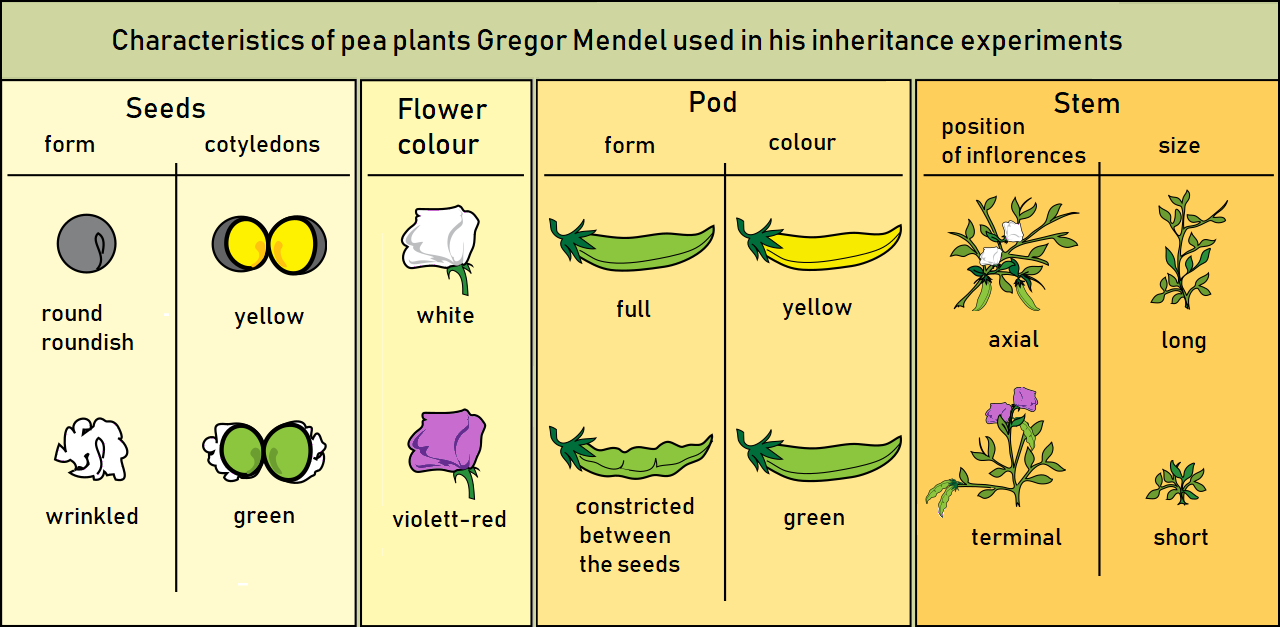
 Mendel selected for the experiment the following characters of pea plants:
* Form of the ripe seeds (round or roundish, surface shallow or wrinkled)
* Colour of the seed–coat (white, gray, or brown, with or without violet spotting)
* Colour of the
Mendel selected for the experiment the following characters of pea plants:
* Form of the ripe seeds (round or roundish, surface shallow or wrinkled)
* Colour of the seed–coat (white, gray, or brown, with or without violet spotting)
* Colour of the
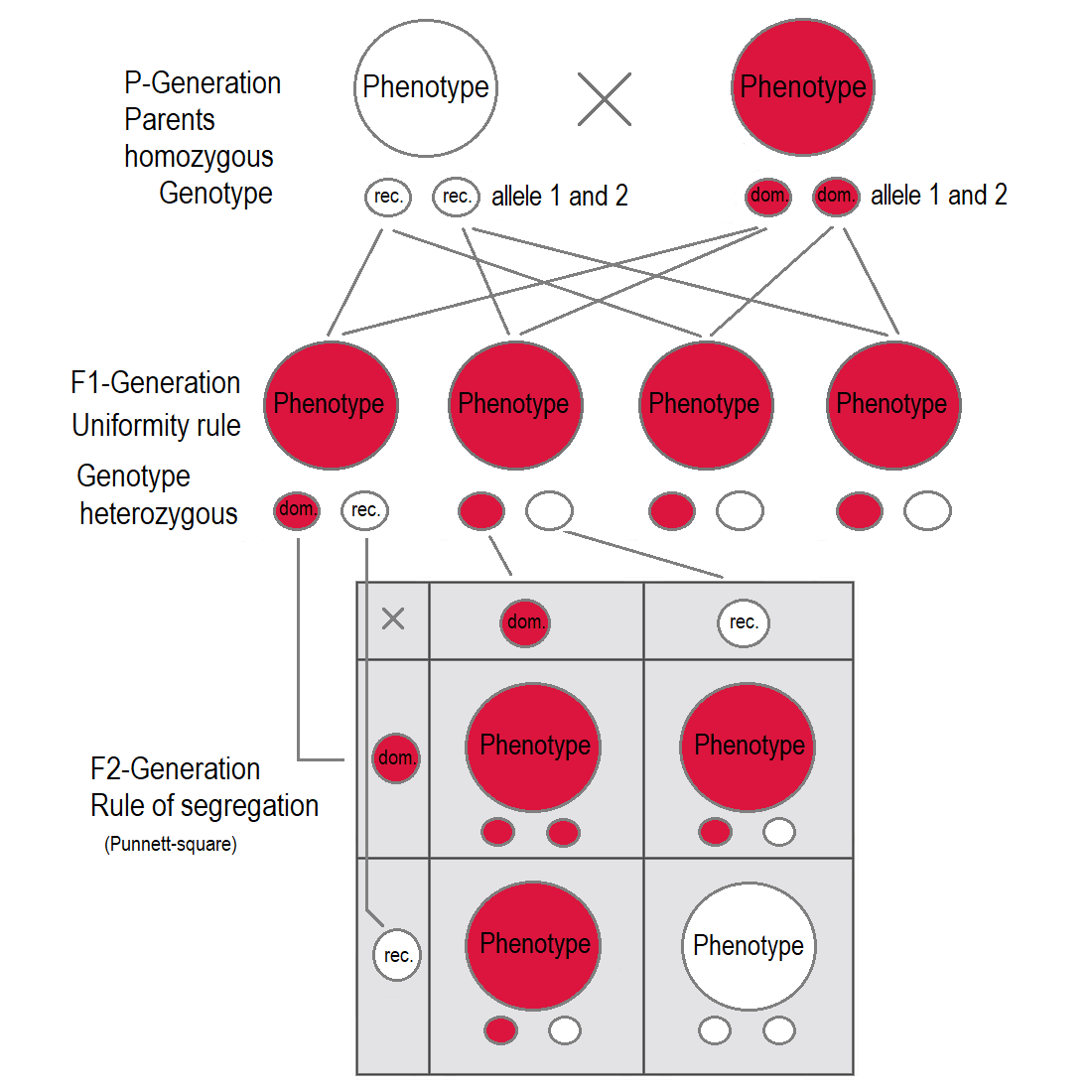 If two parents are mated with each other who differ in one genetic characteristic for which they are both homozygous (each pure-bred), all offspring in the first generation (F1) are equal to the examined characteristic in
If two parents are mated with each other who differ in one genetic characteristic for which they are both homozygous (each pure-bred), all offspring in the first generation (F1) are equal to the examined characteristic in
 The Law of Segregation of genes applies when two individuals, both heterozygous for a certain trait are crossed, for example hybrids of the F1-generation. The offspring in the F2-generation differ in genotype and phenotype, so that the characteristics of the grandparents (P-generation) regularly occur again. In a dominant-recessive inheritance an average of 25% are homozygous with the dominant trait, 50% are heterozygous showing the dominant trait in the phenotype ( genetic carriers), 25% are homozygous with the recessive trait and therefore express the recessive trait in the phenotype. The genotypic ratio is 1 : 2 : 1, the phenotypic ratio is 3 : 1.
In the pea plant example, the capital "B" represents the dominant allele for purple blossom and lowercase "b" represents the recessive allele for white blossom. The pistil plant and the
The Law of Segregation of genes applies when two individuals, both heterozygous for a certain trait are crossed, for example hybrids of the F1-generation. The offspring in the F2-generation differ in genotype and phenotype, so that the characteristics of the grandparents (P-generation) regularly occur again. In a dominant-recessive inheritance an average of 25% are homozygous with the dominant trait, 50% are heterozygous showing the dominant trait in the phenotype ( genetic carriers), 25% are homozygous with the recessive trait and therefore express the recessive trait in the phenotype. The genotypic ratio is 1 : 2 : 1, the phenotypic ratio is 3 : 1.
In the pea plant example, the capital "B" represents the dominant allele for purple blossom and lowercase "b" represents the recessive allele for white blossom. The pistil plant and the

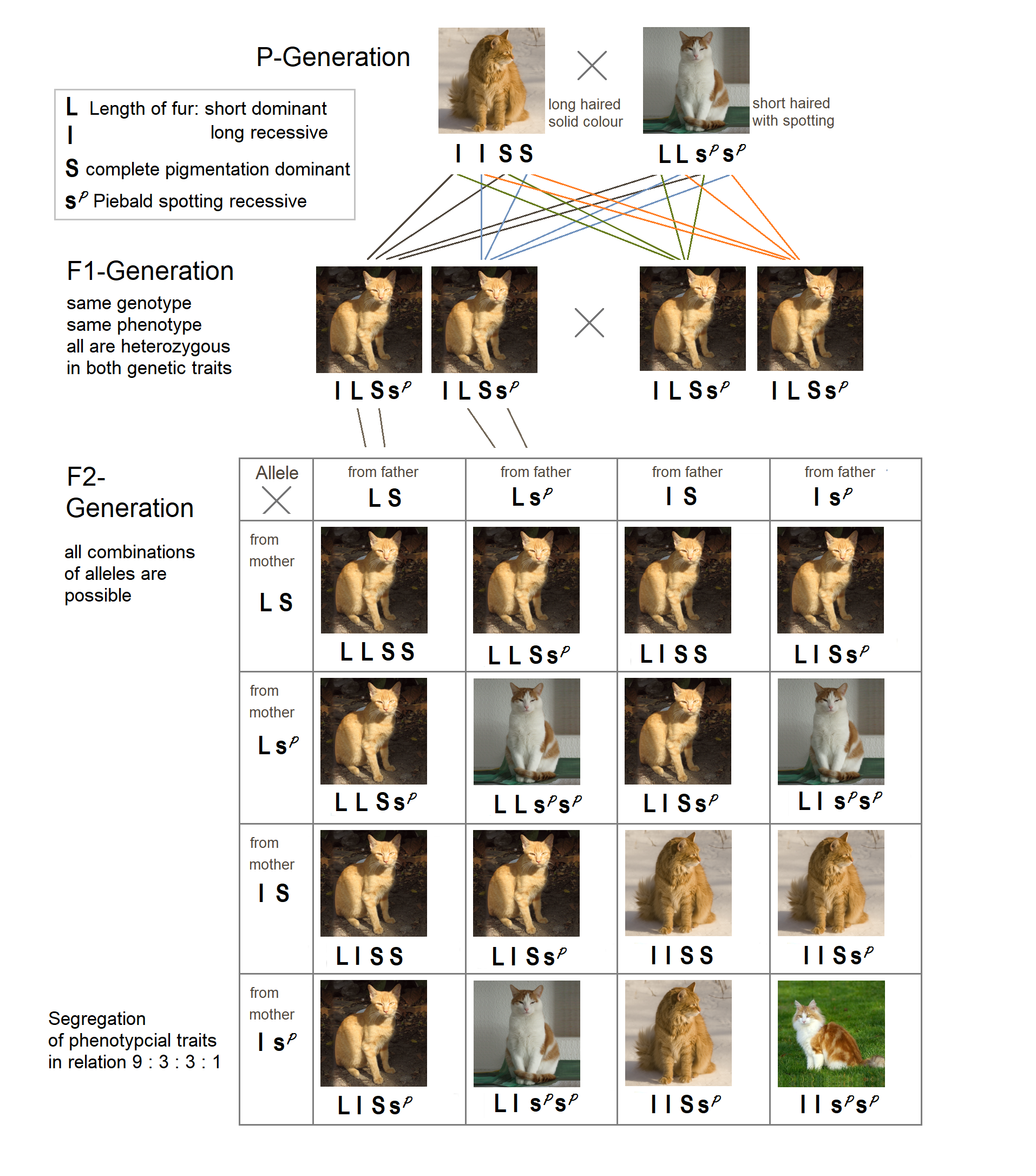 The Law of Independent Assortment states that alleles for separate traits are passed independently of one another. That is, the biological selection of an allele for one trait has nothing to do with the selection of an allele for any other trait. Mendel found support for this law in his dihybrid cross experiments. In his monohybrid crosses, an idealized 3:1 ratio between dominant and recessive phenotypes resulted. In dihybrid crosses, however, he found a 9:3:3:1 ratios. This shows that each of the two alleles is inherited independently from the other, with a 3:1 phenotypic ratio for each.
Independent assortment occurs in
The Law of Independent Assortment states that alleles for separate traits are passed independently of one another. That is, the biological selection of an allele for one trait has nothing to do with the selection of an allele for any other trait. Mendel found support for this law in his dihybrid cross experiments. In his monohybrid crosses, an idealized 3:1 ratio between dominant and recessive phenotypes resulted. In dihybrid crosses, however, he found a 9:3:3:1 ratios. This shows that each of the two alleles is inherited independently from the other, with a 3:1 phenotypic ratio for each.
Independent assortment occurs in
Variations on Mendel's laws (overview)
/ref> For example, Mendel focused on traits whose genes have only two alleles, such as "A" and "a". However, many genes have more than two alleles. He also focused on traits determined by a single gene. But some traits, such as height, depend on many genes rather than just one. Traits dependent on multiple genes are called
Khan Academy, video lecture
Mendel's principles of Inheritance
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mendelian Inheritance Classical genetics
 Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary ...
inheritance following the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel, OSA (; cs, Řehoř Jan Mendel; 20 July 1822 – 6 January 1884) was a biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinian friar and abbot of St. Thomas' Abbey in Brünn (''Brno''), Margraviate of Moravia. Mendel wa ...
in 1865 and 1866, re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns, and later popularized by William Bateson. These principles were initially controversial. When Mendel's theories were integrated with the Boveri–Sutton chromosome theory of inheritance by Thomas Hunt Morgan in 1915, they became the core of classical genetics. Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962) was a British polymath who was active as a mathematician, statistician, biologist, geneticist, and academic. For his work in statistics, he has been described as "a genius who ...
combined these ideas with the theory of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
in his 1930 book '' The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection'', putting evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
onto a mathematical
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
footing and forming the basis for population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and pop ...
within the modern evolutionary synthesis.
History
The principles of Mendelian inheritance were named for and first derived by Gregor Johann Mendel, a nineteenth-century Moravian monk who formulated his ideas after conducting simple hybridisation experiments with pea plants ('' Pisum sativum'') he had planted in the garden of his monastery. Between 1856 and 1863, Mendel cultivated and tested some 5,000 pea plants. From these experiments, he induced two generalizations which later became known as ''Mendel's Principles of Heredity'' or ''Mendelian inheritance''. He described his experiments in a two-part paper, ''Versuche über Pflanzen-Hybriden'' ('' Experiments on Plant Hybridization''), that he presented to the Natural History Society of Brno on 8 February and 8 March 1865, and which was published in 1866. Mendel's results were at first largely ignored. Although they were not completely unknown to biologists of the time, they were not seen as generally applicable, even by Mendel himself, who thought they only applied to certain categories of species or traits. A major roadblock to understanding their significance was the importance attached by 19th-century biologists to the apparent blending of many inherited traits in the overall appearance of the progeny, now known to be due to multi-gene interactions, in contrast to the organ-specific binary characters studied by Mendel. In 1900, however, his work was "re-discovered" by three European scientists, Hugo de Vries, Carl Correns, and Erich von Tschermak. The exact nature of the "re-discovery" has been debated: De Vries published first on the subject, mentioning Mendel in a footnote, while Correns pointed out Mendel's priority after having read De Vries' paper and realizing that he himself did not have priority. De Vries may not have acknowledged truthfully how much of his knowledge of the laws came from his own work and how much came only after reading Mendel's paper. Later scholars have accused Von Tschermak of not truly understanding the results at all. Regardless, the "re-discovery" made Mendelism an important but controversial theory. Its most vigorous promoter in Europe was William Bateson, who coined the terms "genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar worki ...
" and "allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
" to describe many of its tenets. The model of heredity was contested by other biologists because it implied that heredity was discontinuous, in opposition to the apparently continuous variation observable for many traits. Many biologists also dismissed the theory because they were not sure it would apply to all species. However, later work by biologists and statisticians such as Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962) was a British polymath who was active as a mathematician, statistician, biologist, geneticist, and academic. For his work in statistics, he has been described as "a genius who ...
showed that if multiple Mendelian factors were involved in the expression of an individual trait, they could produce the diverse results observed, thus demonstrating that Mendelian genetics is compatible with natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
. Thomas Hunt Morgan and his assistants later integrated Mendel's theoretical model with the chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
theory of inheritance, in which the chromosomes of cells were thought to hold the actual hereditary material, and created what is now known as classical genetics, a highly successful foundation which eventually cemented Mendel's place in history.
Mendel's findings allowed scientists such as Fisher and J.B.S. Haldane to predict the expression of traits on the basis of mathematical probabilities. An important aspect of Mendel's success can be traced to his decision to start his crosses only with plants he demonstrated were true-breeding. He only measured discrete (binary) characteristics, such as color, shape, and position of the seeds, rather than quantitatively variable characteristics. He expressed his results numerically and subjected them to statistical analysis. His method of data analysis and his large sample size gave credibility to his data. He had the foresight to follow several successive generations (P, F1, F2, F3) of pea plants and record their variations. Finally, he performed "test crosses" ( backcrossing descendants of the initial hybridization to the initial true-breeding lines) to reveal the presence and proportions of recessive characters.
Mendel's genetic discoveries
Five parts of Mendel's discoveries were an important divergence from the common theories at the time and were the prerequisite for the establishment of his rules. # Characters are unitary, that is, they are discrete e.g.: purple ''vs''. white, tall ''vs''. dwarf. There is no medium-sized plant or light purple flower. # Genetic characteristics have alternate forms, each inherited from one of two parents. Today these are calledallele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
s.
# One allele is dominant over the other. The phenotype reflects the dominant allele.
# Gametes are created by random segregation. Heterozygotic individuals produce gametes with an equal frequency of the two alleles.
# Different traits have independent assortment. In modern terms, genes are unlinked.
According to customary terminology, the principles of inheritance discovered by Gregor Mendel are here referred to as Mendelian laws, although today's geneticists also speak of ''Mendelian rules'' or ''Mendelian principles'', as there are many exceptions summarized under the collective term Non-Mendelian inheritance
Non-Mendelian inheritance is any pattern in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendel's laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. In Mendelian inheritance, each pare ...
.

 Mendel selected for the experiment the following characters of pea plants:
* Form of the ripe seeds (round or roundish, surface shallow or wrinkled)
* Colour of the seed–coat (white, gray, or brown, with or without violet spotting)
* Colour of the
Mendel selected for the experiment the following characters of pea plants:
* Form of the ripe seeds (round or roundish, surface shallow or wrinkled)
* Colour of the seed–coat (white, gray, or brown, with or without violet spotting)
* Colour of the seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
s and cotyledon
A cotyledon (; ; ; , gen. (), ) is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant, and is defined as "the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or more of which are the first to appear from a germinating seed." The num ...
s (yellow or green)
* Flower colour (white or violet-red)
* Form of the ripe pods (simply inflated, not contracted, or constricted between the seeds and wrinkled)
* Colour of the unripe pods (yellow or green)
* Position of the flowers (axial or terminal)
* Length of the stem
When he crossed purebred white flower and purple flower pea plants (the parental or P generation) by artificial pollination, the resulting flower colour was not a blend. Rather than being a mix of the two, the offspring in the first generation ( F1-generation) were all purple-flowered. Therefore, he called this biological trait dominant. When he allowed self-fertilization in the uniform looking F1-generation, he obtained both colours in the F2 generation with a purple flower to white flower ratio of 3 : 1. In some of the other characters also one of the traits was dominant.
He then conceived the idea of heredity units, which he called hereditary "factors". Mendel found that there are alternative forms of factors—now called gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s—that account for variations in inherited characteristics. For example, the gene for flower color in pea plants exists in two forms, one for purple and the other for white. The alternative "forms" are now called allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
s. For each trait, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent. These alleles may be the same or different. An organism that has two identical alleles for a gene is said to be homozygous for that gene (and is called a homozygote). An organism that has two different alleles for a gene is said be heterozygous for that gene (and is called a heterozygote).
Mendel hypothesized that allele pairs separate randomly, or segregate, from each other during the production of the gametes in the seed plant (egg cell
The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is ...
) and the pollen plant ( sperm). Because allele pairs separate during gamete production, a sperm or egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
carries only one allele for each inherited trait. When sperm and egg unite at fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
, each contributes its allele, restoring the paired condition in the offspring. Mendel also found that each pair of alleles segregates independently of the other pairs of alleles during gamete formation.
The genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
of an individual is made up of the many alleles it possesses. The phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological prop ...
is the result of the expression of all characteristics that are genetically determined by its alleles as well as by its environment. The presence of an allele does not mean that the trait will be expressed in the individual that possesses it. If the two alleles of an inherited pair differ (the heterozygous condition), then one determines the organism's appearance and is called the dominant allele; the other has no noticeable effect on the organism's appearance and is called the recessive allele.
Law of Dominance and Uniformity
 If two parents are mated with each other who differ in one genetic characteristic for which they are both homozygous (each pure-bred), all offspring in the first generation (F1) are equal to the examined characteristic in
If two parents are mated with each other who differ in one genetic characteristic for which they are both homozygous (each pure-bred), all offspring in the first generation (F1) are equal to the examined characteristic in genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
and phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological prop ...
showing the dominant trait. This ''uniformity rule'' or ''reciprocity rule'' applies to all individuals of the F1-generation.
The principle of dominant inheritance discovered by Mendel states that in a heterozygote the dominant allele will cause the recessive allele to be "masked": that is, not expressed in the phenotype. Only if an individual is homozygous with respect to the recessive allele will the recessive trait be expressed. Therefore, a cross between a homozygous dominant and a homozygous recessive organism yields a heterozygous organism whose phenotype displays only the dominant trait.
The F1 offspring of Mendel's pea crosses always looked like one of the two parental varieties. In this situation of "complete dominance," the dominant allele had the same phenotypic effect whether present in one or two copies.
But for some characteristics, the F1 hybrids have an appearance ''in between'' the phenotypes of the two parental varieties. A cross between two four o'clock ('' Mirabilis jalapa'') plants shows an exception to Mendel's principle, called ''incomplete dominance''. Flowers of heterozygous plants have a phenotype somewhere between the two homozygous genotypes. In cases of intermediate inheritance (incomplete dominance) in the F1-generation Mendel's principle of uniformity in genotype and phenotype applies as well. Research about intermediate inheritance was done by other scientists. The first was Carl Correns with his studies about Mirabilis jalapa.
Law of Segregation of genes
pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametop ...
plant are both F1-hybrids with genotype "B b". Each has one allele for purple and one allele for white. In the offspring, in the F2-plants in the Punnett-square, three combinations are possible. The genotypic ratio is 1 ''BB'' : 2 ''Bb'' : 1 ''bb''. But the phenotypic ratio of plants with purple blossoms to those with white blossoms is 3 : 1 due to the dominance of the allele for purple. Plants with homozygous "b b" are white flowered like one of the grandparents in the P-generation.
In cases of incomplete dominance the same segregation of alleles takes place in the F2-generation, but here also the phenotypes show a ratio of 1 : 2 : 1, as the heterozygous are different in phenotype from the homozygous because the genetic expression of one allele compensates the missing expression of the other allele only partially. This results in an intermediate inheritance which was later described by other scientists.
In some literature sources the principle of segregation is cited as "first law". Nevertheless, Mendel did his crossing experiments with heterozygous plants after obtaining these hybrids by crossing two purebred plants, discovering the principle of dominance and uniformity first. Neil A. Campbell, Jane B. Reece: Biologie. Spektrum-Verlag 2003, page 293-315.
Molecular proof of segregation of genes was subsequently found through observation of meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately ...
by two scientists independently, the German botanist Oscar Hertwig
Oscar Hertwig (21 April 1849 in Friedberg, Hesse, Friedberg – 25 October 1922 in Berlin) was a German embryologist and zoologist known for his research in developmental biology and evolution. Hertwig is credited as the first man to observe se ...
in 1876, and the Belgian zoologist Edouard Van Beneden in 1883. Most alleles are located in chromosomes
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are ...
in the cell nucleus. Paternal and maternal chromosomes get separated in meiosis, because during spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the t ...
the chromosomes are segregated on the four sperm cells that arise from one mother sperm cell, and during oogenesis
Oogenesis, ovogenesis, or oögenesis is the differentiation of the ovum (egg cell) into a cell competent to further develop when fertilized. It is developed from the primary oocyte by maturation. Oogenesis is initiated in the embryonic stage.
O ...
the chromosomes are distributed between the polar bodies and the egg cell
The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is ...
. Every individual organism contains two alleles for each trait. They segregate (separate) during meiosis such that each gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce ...
contains only one of the alleles. When the gametes unite in the zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
the alleles—one from the mother one from the father—get passed on to the offspring. An offspring thus receives a pair of alleles for a trait by inheriting homologous chromosome
A couple of homologous chromosomes, or homologs, are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during fertilization. Homologs have the same genes in the same loci where they provide points along ...
s from the parent organisms: one allele for each trait from each parent. Heterozygous individuals with the dominant trait in the phenotype are genetic carriers of the recessive trait.
Law of Independent Assortment
 The Law of Independent Assortment states that alleles for separate traits are passed independently of one another. That is, the biological selection of an allele for one trait has nothing to do with the selection of an allele for any other trait. Mendel found support for this law in his dihybrid cross experiments. In his monohybrid crosses, an idealized 3:1 ratio between dominant and recessive phenotypes resulted. In dihybrid crosses, however, he found a 9:3:3:1 ratios. This shows that each of the two alleles is inherited independently from the other, with a 3:1 phenotypic ratio for each.
Independent assortment occurs in
The Law of Independent Assortment states that alleles for separate traits are passed independently of one another. That is, the biological selection of an allele for one trait has nothing to do with the selection of an allele for any other trait. Mendel found support for this law in his dihybrid cross experiments. In his monohybrid crosses, an idealized 3:1 ratio between dominant and recessive phenotypes resulted. In dihybrid crosses, however, he found a 9:3:3:1 ratios. This shows that each of the two alleles is inherited independently from the other, with a 3:1 phenotypic ratio for each.
Independent assortment occurs in eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
organisms during meiotic metaphase I, and produces a gamete with a mixture of the organism's chromosomes. The physical basis of the independent assortment of chromosomes is the random orientation of each bivalent chromosome along the metaphase plate with respect to the other bivalent chromosomes. Along with crossing over, independent assortment increases genetic diversity by producing novel genetic combinations.
There are many deviations from the principle of independent assortment due to genetic linkage
Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separ ...
.
Of the 46 chromosomes in a normal diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respecti ...
human cell, half are maternally derived (from the mother's egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
) and half are paternally derived (from the father's sperm). This occurs as sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote th ...
involves the fusion of two haploid gametes (the egg and sperm) to produce a zygote and a new organism, in which every cell has two sets of chromosomes (diploid). During gametogenesis
Gametogenesis is a biological process by which diploid or haploid precursor cells undergo cell division and differentiation to form mature haploid gametes. Depending on the biological life cycle of the organism, gametogenesis occurs by meiotic d ...
the normal complement of 46 chromosomes needs to be halved to 23 to ensure that the resulting haploid gamete can join with another haploid gamete to produce a diploid organism.
In independent assortment, the chromosomes that result are randomly sorted from all possible maternal and paternal chromosomes. Because zygotes end up with a mix instead of a pre-defined "set" from either parent, chromosomes are therefore considered assorted independently. As such, the zygote can end up with any combination of paternal or maternal chromosomes. For human gametes, with 23 chromosomes, the number of possibilities is 223 or 8,388,608 possible combinations. This contributes to the genetic variability of progeny. Generally, the recombination of genes has important implications for many evolutionary processes.
Mendelian trait
A Mendelian trait is one whose inheritance follows Mendel’s principles—namely, the trait depends only on a single locus, whosealleles
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
are either dominant or recessive.
Many traits are inherited in a non-Mendelian
Non-Mendelian inheritance is any pattern in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendel's laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. In Mendelian inheritance, each parent ...
fashion.
Non-Mendelian inheritance
Mendel himself warned that care was needed in extrapolating his patterns to other organisms or traits. Indeed, many organisms have traits whose inheritance works differently from the principles he described; these traits are called non-Mendelian.Khan AcademyVariations on Mendel's laws (overview)
/ref> For example, Mendel focused on traits whose genes have only two alleles, such as "A" and "a". However, many genes have more than two alleles. He also focused on traits determined by a single gene. But some traits, such as height, depend on many genes rather than just one. Traits dependent on multiple genes are called
polygenic traits
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus (section of DNA) that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers (such as SNPs or AFLPs) ...
.See also
* List of Mendelian traits in humans *Mendelian disease
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
s (monogenic disease)
* Mendelian error
* Particulate inheritance
* Punnett square
The Punnett square is a square diagram that is used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It is named after Reginald C. Punnett, who devised the approach in 1905. The diagram is used by biologists to determine ...
References
Notes
* * *External links
Khan Academy, video lecture
Mendel's principles of Inheritance
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mendelian Inheritance Classical genetics
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar worki ...
it:Gregor Mendel#Le leggi di Mendel