Mariner 8 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mariner-H (Mariner Mars '71), also commonly known as Mariner 8, was (along with
 Spacecraft power was provided by a total of 14,742
Spacecraft power was provided by a total of 14,742
Mariner 8 Mission Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
{{Orbital launches in 1971 Mariner program Missions to Mars Satellite launch failures Spacecraft launched by Atlas-Centaur rockets Spacecraft which reentered in 1971 Spacecraft launched in 1971 de:Mariner#Mariner 8 und 9 fr:Programme Mariner#Mariner 8
Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971, from Spaceport Florida Launch Comp ...
) part of the Mariner Mars '71 project. It was intended to go into Mars orbit and return images and data, but a launch vehicle failure prevented Mariner 8 from achieving Earth orbit and the spacecraft reentered into the Atlantic Ocean shortly after launch.
Mission
Mariner 8 was launched on anAtlas-Centaur
The Atlas-Centaur was a United States expendable launch vehicle derived from the SM-65 Atlas D missile. The vehicle featured a Centaur (rocket stage), Centaur upper stage, the first such stage to use high-performance liquid hydrogen as fuel. La ...
SLV-3C booster (AC-24). The main Centaur engine was ignited 265 seconds after launch, but the upper stage began to oscillate in pitch and tumbled out of control. The Centaur stage shut down 365 seconds after launch due to starvation caused by the tumbling. The Centaur and spacecraft payload separated and re-entered the Earth's atmosphere approximately downrange and fell into the Atlantic Ocean about north of Puerto Rico.
A guidance system failure was suspected as the culprit, but JPL navigation chief Bill O'Neil dismissed the idea that the entire guidance system had failed. He argued that an autopilot malfunction had occurred since the event had occurred at the exact moment when the system was supposed to activate. Investigation proceeded quickly and the problem was soon discovered to be the result of a malfunction in the pitch rate gyro amplifier. A diode intended to protect the system from transient voltages was thought to have been damaged during repairs/installation of the pitch amplifier's printed circuit board, something that would not have been detected through bench tests.
, Mariner 8 is the most recent US planetary probe to be lost in a launch vehicle malfunction.
Mariner Mars 71 Project
The Mariner Mars 71 project consisted of two spacecraft (Mariners H and I), each of which would be inserted into a Martian orbit, and each of which would perform a separate but complementary mission. Either spacecraft could perform either of the two missions. The two spacecraft would have orbited the planet Mars a minimum of 90 days, during which time data would be gathered on the composition, density, pressure, and temperature of the atmosphere, and the composition, temperature, and topography of the surface. Approximately 70 percent of the planetary surface was to be covered, and temporal as well as spatial variations would be observed. Some of the objectives of the Mariner-H mission were successfully added to the Mariner-I (Mariner 9) mission profile. Total research, development, launch, and support costs for the Mariner series of spacecraft (Mariners 1 through 10) was approximately $554 million.Spacecraft and subsystems
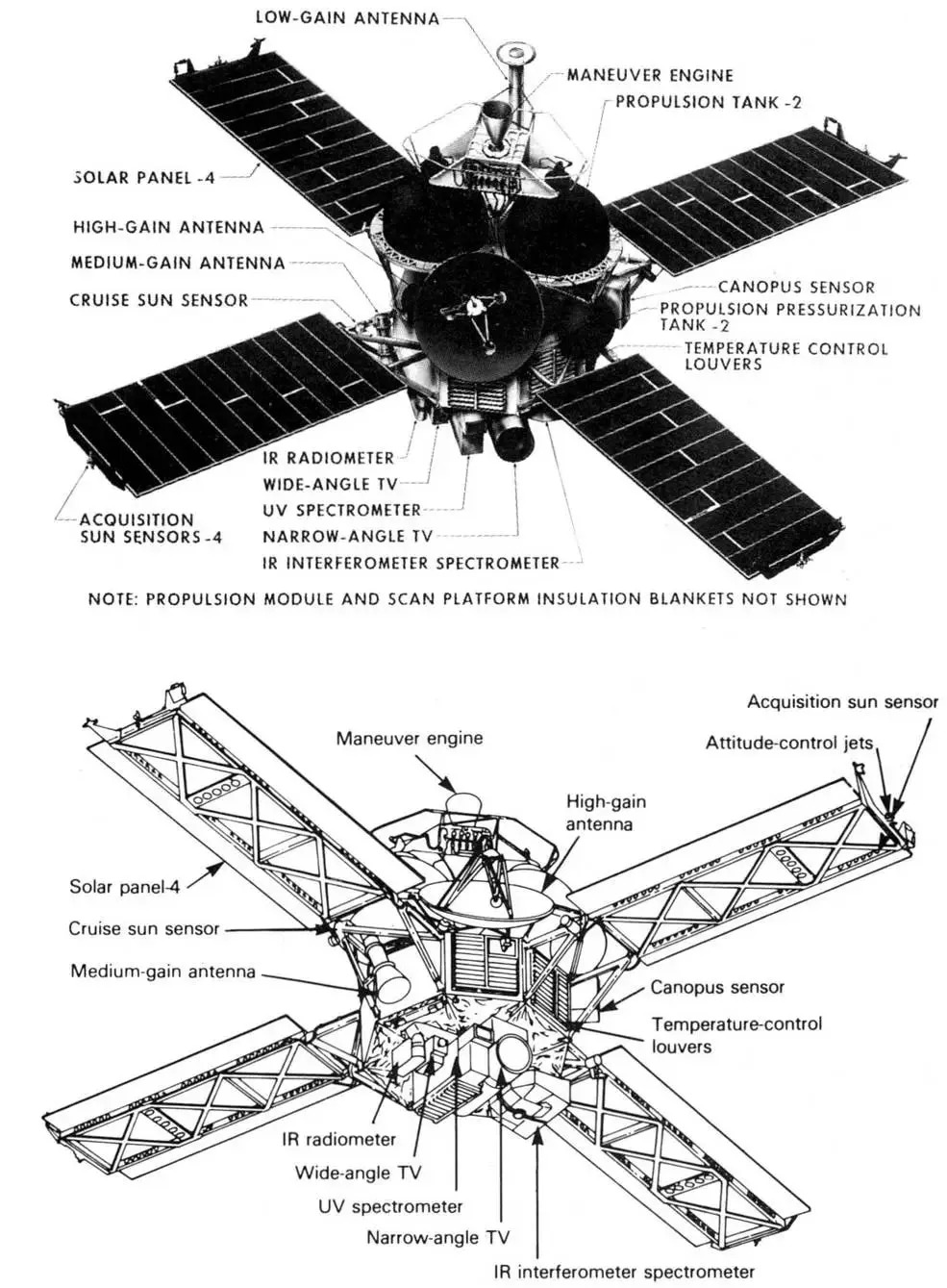
The Mariner 8 spacecraft was built on an octagonalmagnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
frame, deep and across a diagonal. Four solar panels
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. These electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct ...
, each , extended out from the top of the frame. Each set of two solar panels spanned from tip to tip. Also mounted on the top of the frame were two propulsion tanks, the maneuver engine, a long low gain antenna mast and a parabolic high gain antenna. A scan platform was mounted on the bottom of the frame, on which were attached the mutually bore-sighted science instruments (wide- and narrow-angle TV cameras, infrared radiometer, ultraviolet spectrometer, and infrared interferometer spectrometer). The overall height of the spacecraft was . The launch mass was , of which were expendables. The science instrumentation had a total mass of . The electronics for communications and command and control were housed within the frame.
 Spacecraft power was provided by a total of 14,742
Spacecraft power was provided by a total of 14,742 solar cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect.
s which made up the 4 solar panels with a total area of area. The solar panels could produce 800 W at Earth and 500 W at Mars. Power was stored in a 20 ampere hour
An ampere-hour or amp-hour (symbol: A⋅h or A h; often simplified as Ah) is a unit of electric charge, having dimensions of electric current multiplied by time, equal to the charge transferred by a steady current of one ampere flowing for ...
nickel-cadmium battery. Propulsion was provided by a gimbaled engine capable of 1340 N thrust and up to 5 restarts. The propellant was monomethyl hydrazine and nitrogen tetroxide. Two sets of 6 attitude control nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
jets were mounted on the ends of the solar panels. Attitude knowledge was provided by a Sun sensor, a Canopus star tracker, gyroscopes, an inertial reference unit, and an accelerometer. Passive thermal control was achieved through the use of louvres on the eight sides of the frame and thermal blankets.
Spacecraft control was through the central computer and sequencer which had an onboard memory of 512 words. The command system was programmed with 86 direct commands, 4 quantitative commands, and 5 control commands. Data was stored on a digital reel-to-reel tape recorder. The 8-track tape could store 180 million bits recorded at 132 kbit/s. Playback could be done at 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1 kbit/s using two tracks at a time. Telecommunications were via dual S-band 10 W/20 W transmitters and a single receiver through the high gain parabolic antenna, the medium gain horn antenna, or the low gain omnidirectional antenna.
See also
*Exploration of Mars
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Uncrewed spacecraft, Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding G ...
* List of missions to Mars
This is a list of spacecraft missions (including unsuccessful ones) to the planet Mars, such as orbiters, landers, and rovers.
Missions
;Mission Type Legend:
Landing locations
In 1999, Mars Climate Orbiter accidentally entered Mars ...
* Space exploration
Space exploration is the process of utilizing astronomy and space technology to investigate outer space. While the exploration of space is currently carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration is conducted bo ...
* Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes
This timeline of artificial satellites and space probes includes uncrewed spacecraft including technology demonstrators, observatories, lunar probes, and interplanetary probes. First satellites from each country are included. Not included are most ...
* Unmanned space missions
References
External links
Mariner 8 Mission Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
{{Orbital launches in 1971 Mariner program Missions to Mars Satellite launch failures Spacecraft launched by Atlas-Centaur rockets Spacecraft which reentered in 1971 Spacecraft launched in 1971 de:Mariner#Mariner 8 und 9 fr:Programme Mariner#Mariner 8