Mantoux Test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening for tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis diagnosis. It is one of the major

British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for biologic therapy for psoriasis 2017*
''www.bad.org.uk'', accessed 11 October 2020
T-SPOT.TB is another IGRA; it uses the ELISPOT method.
tuberculin
Tuberculin, also known as purified protein derivative, is a combination of proteins that are used in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. This use is referred to as the tuberculin skin test and is recommended only for those at high risk. Reliable adm ...
skin tests used around the world, largely replacing multiple-puncture tests such as the tine test. The Heaf test
The Heaf test, a diagnostic skin test, was long performed to determine whether or not children had been exposed to tuberculosis infection. The test was named after F. R. G. Heaf. Also known as the Sterneedle test, it was administered by a Heaf ...
, a form of tine test, was used until 2005 in the UK, when it was replaced by the Mantoux test. The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society The American Thoracic Society (ATS) is a nonprofit organization focused on improving care for pulmonary diseases, critical illnesses and sleep-related breathing disorders. It was established in 1905 as the
American Sanatorium Association, and ...
and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
. It was also used in the USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they ...
, although Soviet mantoux produced many false positives due to children's allergic reaction.
History


Tuberculin
Tuberculin, also known as purified protein derivative, is a combination of proteins that are used in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. This use is referred to as the tuberculin skin test and is recommended only for those at high risk. Reliable adm ...
is a glycerol
Glycerol () is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pha ...
extract of the tubercle bacillus
''Bacillus'', from Latin "bacillus", meaning "little staff, wand", is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum ''Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-sh ...
. Purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin is a precipitate of species-nonspecific molecules obtained from filtrates of sterilized, concentrated cultures. The tuberculin reaction was first described by Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch ( ; ; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera and anthrax, he i ...
in 1890. The test was first developed and described by the German physician Felix Mendel in 1908. It is named after Charles Mantoux
Charles Mantoux (; May 14, 1877, Paris – May 3, 1947, Le Cannet) was a French physician and the developer of the eponymous serological test for tuberculosis.
Biography
Mantoux graduated from the University of Paris, where he studied under B ...
, a French physician who built on the work of Koch and Clemens von Pirquet
Clemens Peter Freiherr von Pirquet (12 May 187428 February 1929) was an Austrian scientist and pediatrician best known for his contributions to the fields of bacteriology and immunology.
Career
Born in Vienna, he studied theology at the Universit ...
to create his test in 1907. However, the test was unreliable due to impurities in tuberculin which tended to cause false results.
Esmond R. Long and Florence B. Seibert identified the active agent in tuberculin as a protein. Seibert then spent a number of years developing methods for separating and purifying the protein from ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', obtaining purified protein derivative (PPD) and enabling the creation of a reliable test for tuberculosis. Her first publication on the purification of tuberculin appeared in 1934. By the 1940s, Seibert's PPD was the international standard for tuberculin tests. In 1939, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
n M.A. Linnikova created a modified version of PPD. In 1954, the Soviet Union started mass production of PPD-L, named after Linnikova.
Procedure
In the Mantoux test, a standard dose of 5 tuberculin units (TU – 0.1 ml), according to theCDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
, or 2 TU of Statens Serum Institute (SSI) tuberculin RT23 in 0.1 ml solution, according to the National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern ...
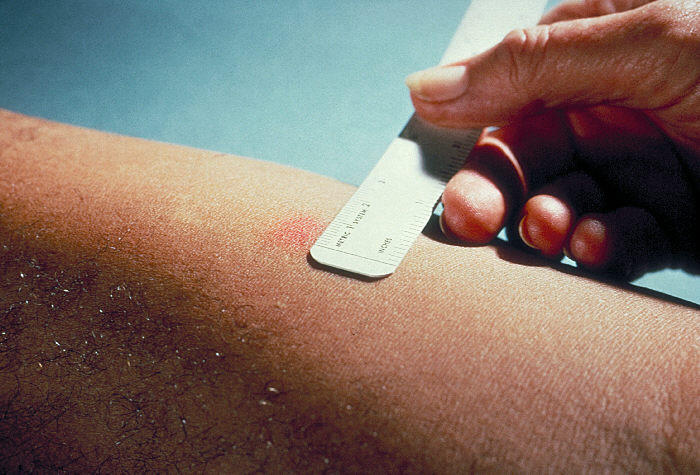
, is injected intradermally (between the layers of dermis) on the flexor surface of the left forearm, mid-way between elbow and wrist. The injection should be made with a tuberculin syringe, with the needle bevel facing upward. When placed correctly, injection should produce a pale wheal of the skin, 6 to 10 mm in diameter. The result of the test is read after 48–96 hours, ideally after 72 hours/3rd day. This procedure is termed the 'Mantoux technique'. A person who has been exposed to the bacteria would be expected to mount an immune response in the area of skin containing the bacterial proteins. This response is a classic example of 'delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction' ( DTH), a type IV of hypersensitivities. T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s and myeloid cells are attracted to the site of reaction in 1–3 days and generate local inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
. The reaction is read by measuring the diameter of induration
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this sys ...
(palpable raised, hardened area) across the forearm (perpendicular to the long axis) in millimeters. If there is no induration, the result should be recorded as "0 mm". Erythema
Erythema (, ) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology inc ...
(redness) should not be measured. In the Pirquet version of the test tuberculin is applied to the skin via scarification
Scarification involves scratching, etching, burning/ branding, or superficially cutting designs, pictures, or words into the skin as a permanent body modification or body art. The body modification can take roughly 6–12 months to heal. In t ...
.
Classification of tuberculin reaction
The results of this test must be interpreted carefully. The person's medical risk factors determine at which increment (5 mm, 10 mm, or 15 mm) of induration the result is considered positive. A positive result indicates TB exposure. * 5 mm or more is positive in ** An HIV-positive person ** Persons with recent contacts with a TB patient ** Persons with nodular or fibrotic changes on chest X-ray consistent with old healed TB ** Patients with organ transplants, and other immunosuppressed patients * 10 mm or more is positive in ** Recent arrivals (less than five years) from high-prevalence countries ** Injection drug users ** Residents and employees of high-risk congregate settings (e.g., prisons, nursing homes, hospitals, homeless shelters, etc.) ** Mycobacteriology lab personnel ** Persons with clinical conditions that place them at high risk (e.g.,diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, prolonged corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
therapy, leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' ...
, end-stage renal disease, chronic malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a varie ...
syndromes, low body weight, etc.)
** Children less than four years of age, or children and adolescents exposed to adults in high-risk categories
* 15 mm or more is positive in
** Persons with no known risk factors for TB
A tuberculin test conversion is defined as an increase of 10 mm or more within a two-year period, regardless of age. Alternative criteria include increases of 6, 12, 15 or 18 mm.
False positive result
TST (tuberculin skin test) positive is measured by size of induration. The size of the induration considered to be a positive result depends on risk factors. For example, a low-risk patient must have a larger induration for a positive result than a high-risk patient. High-risk groups include recent contacts, those with HIV, those with chestradiograph
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiography and "therapeu ...
with fibrotic changes, organ transplant recipients, and those with immunosuppression.
A meta-analysis in 2014 found that the Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine reduced infections by 19–27% and reduced progression to active tuberculosis by 71%. The Ohio Department of Health states that it give 80% of children protection against tuberculous meningitis
Tuberculous meningitis, also known as TB meningitis or tubercular meningitis, is a specific type of bacterial meningitis caused by the ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' infection of the meninges—the system of membranes which envelop the central ner ...
and miliary tuberculosis
Miliary tuberculosis is a form of tuberculosis that is characterized by a wide dissemination into the human body and by the tiny size of the lesions (1–5 mm). Its name comes from a distinctive pattern seen on a chest radiograph of many tiny ...
. Therefore, a positive TST/PPD in a person who has received BCG vaccine is interpreted as latent TB infection (LTBI).
Due to the test's low specificity, most positive reactions in low-risk individuals are false positives. A false positive result may be caused by nontuberculous mycobacteria or previous administration of BCG vaccine. Vaccination with BCG may result in a false-positive result for many years after vaccination.
False positives can also occur when the injected area is touched, causing swelling and itching. If the swelling is less than 5 mm, it is possibly due to error by the healthcare personnel causing inflammation to the area.
Another source of false positive results can be allergic reaction or hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to an antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes Imm ...
. Although rare (about 0.08 reported reactions per million doses of tuberculin), these reactions can be dangerous and precautions should be taken by having epinephrin available.
False negative result
Reaction to the PPD or tuberculin test is suppressed by the following conditions: * Recent TB infection (less than 8–10 weeks) *Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM, mono), also known as glandular fever, is an infection usually caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces few or no symptoms. In young adu ...
* Live virus vaccine – The test should not be carried out within 3 weeks of live virus vaccination (e. g. MMR vaccine
The MMR vaccine is a vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella (German measles), abbreviated as ''MMR''. The first dose is generally given to children around 9 months to 15 months of age, with a second dose at 15 months to 6 years of age, w ...
or Sabin vaccine).
* Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph n ...
* Hodgkin's disease
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the lymph nodes. The condition was named a ...
* Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
therapy/steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
use
* Malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
* Immunological compromise – Those on immuno-suppressive treatment or those with HIV and low CD4 T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
counts, frequently show negative results from the PPD test.
This is because the immune system needs to be functional to mount a response to the protein derivative injected under the skin. A false negative result may occur in a person who has been recently infected with TB, but whose immune system hasn't yet reacted to the bacteria.
* Upper respiratory virus infection
In case a second tuberculin test is necessary it should be carried out in the other arm to avoid hypersensitising the skin.
BCG vaccine and the Mantoux test
The role of Mantoux testing in people who have been vaccinated is disputed. The US recommends that tuberculin skin testing is not contraindicated for BCG-vaccinated persons, and prior BCG vaccination should not influence the interpretation of the test. The UK recommends that interferon-γ testing should be used to help interpret positive Mantoux tests of over 5 mm, and repeated tuberculin skin testing must not be done in people who have had BCG vaccinations. In general, the US recommendation may result in a larger number of people being falsely diagnosed with latent tuberculosis, while the UK approach has an increased chance of missing patients with latent tuberculosis who should be treated. According to the US guidelines,latent tuberculosis
Latent tuberculosis (LTB), also called latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI), is when a person is infected with ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', but does not have active tuberculosis (TB). Active tuberculosis can be contagious while latent tubercul ...
infection diagnosis and treatment is considered for any BCG-vaccinated person whose skin test is 10 mm or greater, if any of these circumstances are present:
* Was in contact with another person with infectious TB
* Was born or has lived in a high TB prevalence country
* Is continually exposed to populations where TB prevalence is high
Anergy testing
In cases ofanergy
In immunology, anergy characterizes the absence of a response from the body's defense mechanisms when confronted with foreign substances. This phenomenon involves the direct induction of peripheral lymphocyte tolerance. When an individual is i ...
, a lack of reaction by the body's defence mechanisms when it comes into contact with foreign substances, the tuberculin reaction will occur weakly, thus compromising the value of Mantoux testing. For example, anergy is present in AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
, a disease which strongly depresses the immune system. Therefore, anergy testing is advised in cases where there is suspicion that anergy is present. However, routine anergy skin testing is not recommended.
Two-step testing
Some people who have been infected with TB may have a negative reaction when tested years after infection, as the immune system response may gradually wane. This initial skin test, though negative, may stimulate (boost) the body's ability to react to tuberculin in future tests. Thus, a positive reaction to a subsequent test may be misinterpreted as a new infection, when in fact it is the result of the boosted reaction to an old infection. Use of two-step testing is recommended for initial skin testing of adults who will be retested periodically (e.g., health care workers). This ensures any future positive tests can be interpreted as being caused by a new infection, rather than simply a reaction to an old infection. * The first test is read 48–72 hours after injection. ** If the first test is positive, consider the person infected. ** If the first test is negative, give a second test one to three weeks after the first injection. * The second test is read 48–72 hours after injection. ** If the second test is positive, consider the person infected in the distant past. ** If the second test is negative, consider the person uninfected. A person who is diagnosed as "infected in the distant past" on two-step testing is called a "tuberculin reactor". The US recommendation that prior BCG vaccination be ignored results in almost universal false diagnosis of tuberculosis infection in people who have had BCG (mostly foreign nationals).The latest interpretation for Mantoux test results
According to the guidelines published by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2005, the results are re-categorized into 3 parts based on their previous or baseline outcomes: * Baseline test: ≥10 mm is positive (either first or second step); 0 to 9 mm is negative * Serial testing without known exposure: Increase of ≥10 mm is positive * Known exposure: ** ≥5 mm is positive in patients with baseline of 0 mm ** ≥10 mm is positive in patients with negative baseline or previous screening result of >0 mmRecent developments
In addition to tuberculin skin tests such as (principally) the Mantoux test,interferon gamma release assay Interferon-γ release assays (IGRA) are medical tests used in the diagnosis of some infectious diseases, especially tuberculosis. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) release assays rely on the fact that T-lymphocytes will release IFN-γ when exposed to specifi ...
s (IGRAs) have become common in clinical use in the 2010s. In some contexts they are used instead of TSTs, whereas in other contexts TSTs and IGRAs both continue to be useful.
The QuantiFERON-TB Gold blood test measures the patient's immune reactivity to the TB bacterium, and is useful for initial and serial testing of persons with an increased risk of latent or active tuberculosis infection. Guidelines for its use were released by the CDC in December 2005. QuantiFERON-TB Gold is FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
-approved in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, has CE Mark
The presence of the logo on Product (business), commercial products indicates that the Manufacturing, manufacturer or importer affirms the goods' conformity with European Environment, health and safety, health, safety, and environmental prote ...
approval in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and has been approved by the MHLW in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. The interferon gamma release assay is the preferred method for patients who have had immunosuppression and are about to start biological therapies.''www.bad.org.uk'', accessed 11 October 2020
Heaf test
The Heaf tuberculin skin test was used in the United Kingdom, but discontinued in 2005. The equivalent Mantoux test positive levels done with 10 TU (0.1 ml at 100 TU/ml, 1:1000) are * <5 mm induration (Heaf 0–1) * 5–15 mm induration (Heaf 2) * >15 mm induration (Heaf 3–4)See also
*Latent tuberculosis
Latent tuberculosis (LTB), also called latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI), is when a person is infected with ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', but does not have active tuberculosis (TB). Active tuberculosis can be contagious while latent tubercul ...
* QuantiFERON
* Geronimo (alpaca)
* Shambo
References
{{Tuberculosis Immunologic tests Tuberculosis Dermatologic procedures