Manifest Destiny on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Manifest destiny was the belief in the 19th-century United States that American settlers were destined to expand westward across
 The phrase "manifest destiny" is most associated with the territorial expansion of the United States from 1803 to 1900. However, the
The phrase "manifest destiny" is most associated with the territorial expansion of the United States from 1803 to 1900. However, the
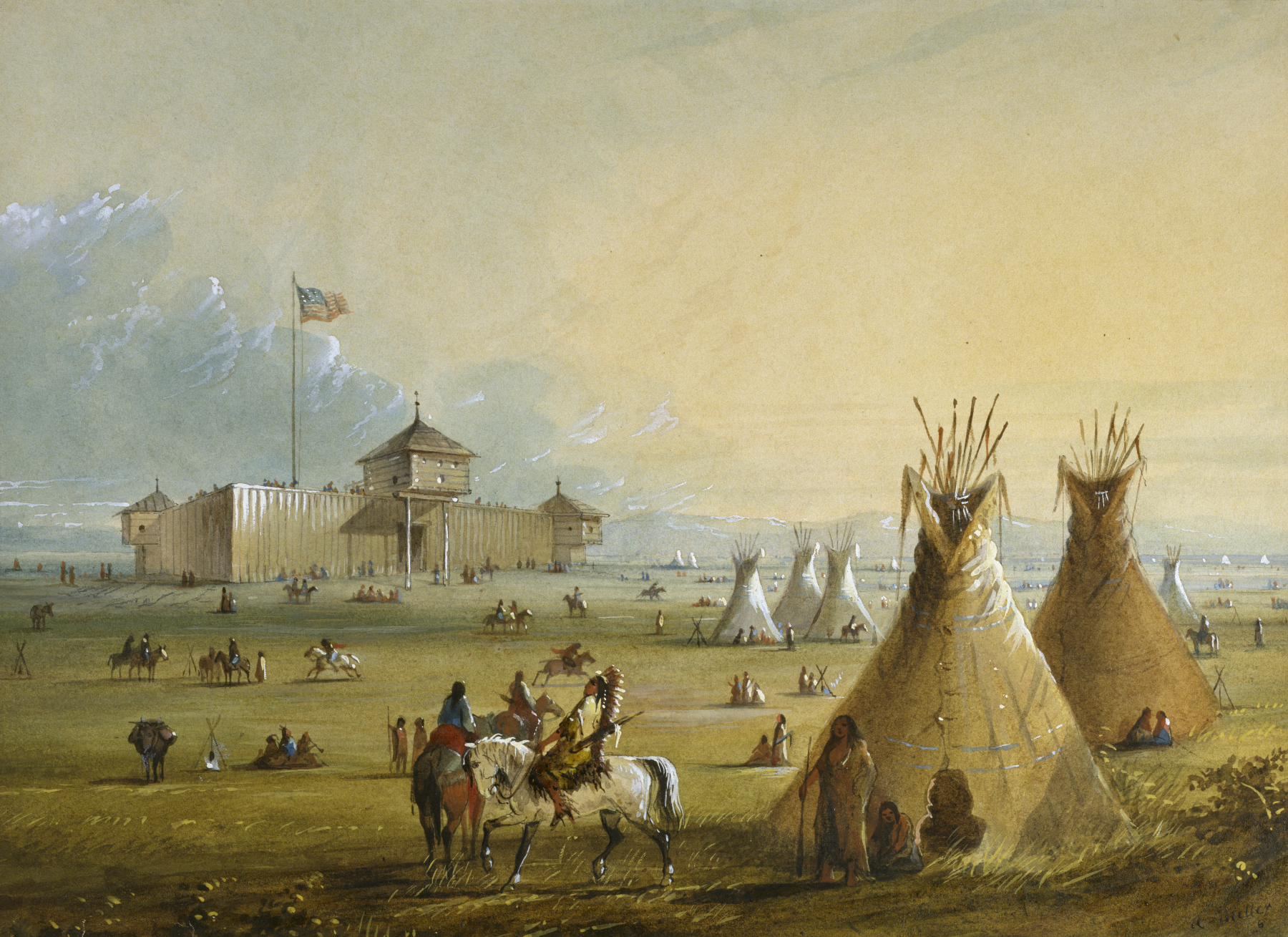 Adams did much to further this idea. He orchestrated the Treaty of 1818, which established the border between British North America and the United States as far west as the Rocky Mountains, and provided for the joint occupation of the region known in American history as the
Adams did much to further this idea. He orchestrated the Treaty of 1818, which established the border between British North America and the United States as far west as the Rocky Mountains, and provided for the joint occupation of the region known in American history as the
 As president, Polk sought compromise and renewed the earlier offer to divide the territory in half along the 49th parallel, to the dismay of the most ardent advocates of manifest destiny. When the British refused the offer, American expansionists responded with slogans such as "The whole of Oregon or none" and "Fifty-four forty or fight", referring to the northern border of the region. (The latter slogan is often mistakenly described as having been a part of the 1844 presidential campaign.) When Polk moved to terminate the joint occupation agreement, the British finally agreed in early 1846 to divide the region along the 49th parallel, leaving the lower Columbia basin as part of the United States. The
As president, Polk sought compromise and renewed the earlier offer to divide the territory in half along the 49th parallel, to the dismay of the most ardent advocates of manifest destiny. When the British refused the offer, American expansionists responded with slogans such as "The whole of Oregon or none" and "Fifty-four forty or fight", referring to the northern border of the region. (The latter slogan is often mistakenly described as having been a part of the 1844 presidential campaign.) When Polk moved to terminate the joint occupation agreement, the British finally agreed in early 1846 to divide the region along the 49th parallel, leaving the lower Columbia basin as part of the United States. The
 The controversy was eventually ended by the
The controversy was eventually ended by the
 Although they were illegal, filibustering operations in the late 1840s and early 1850s were romanticized in the United States. The Democratic Party's national platform included a plank that specifically endorsed William Walker's filibustering in
Although they were illegal, filibustering operations in the late 1840s and early 1850s were romanticized in the United States. The Democratic Party's national platform included a plank that specifically endorsed William Walker's filibustering in
 The Homestead Act of 1862 encouraged 600,000 families to settle the West by giving them land (usually 160 acres) almost free. Over the course of 123 years, 200 million claims were made and over 270 million acres were settled, accounting for 10% of the land in the U.S. They had to live on and improve the land for five years. Before the
The Homestead Act of 1862 encouraged 600,000 families to settle the West by giving them land (usually 160 acres) almost free. Over the course of 123 years, 200 million claims were made and over 270 million acres were settled, accounting for 10% of the land in the U.S. They had to live on and improve the land for five years. Before the
 In 1859, Reuben Davis, a member of the House of Representatives from Mississippi, articulated one of the most expansive visions of manifest destiny on record:
In 1859, Reuben Davis, a member of the House of Representatives from Mississippi, articulated one of the most expansive visions of manifest destiny on record:
Americans, Almost and Forgotten
, 107 California Law Review (2019) After the
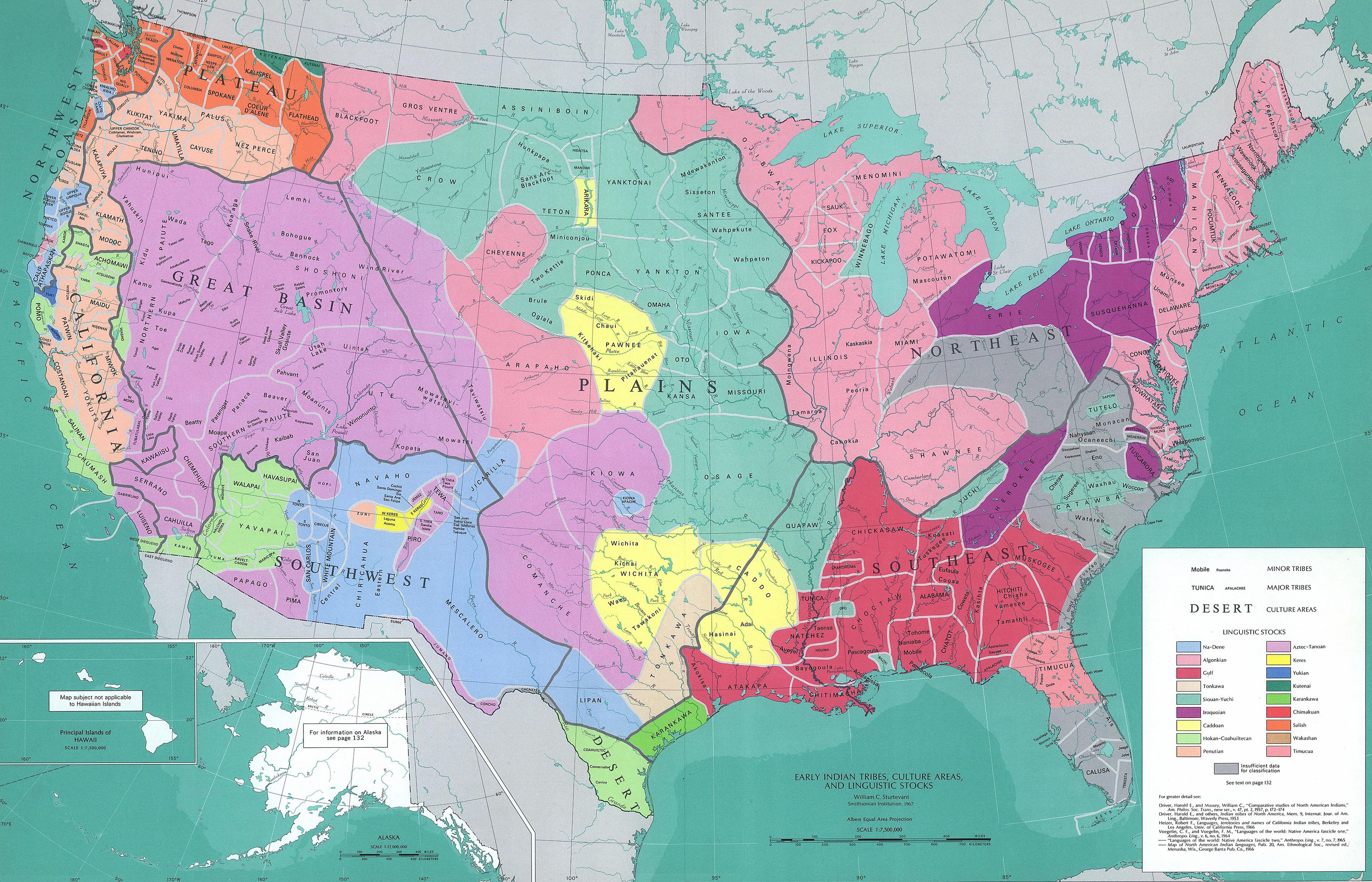 Manifest destiny had serious consequences for Native Americans, since continental expansion implicitly meant the occupation and annexation of Native American land, sometimes to expand slavery. This ultimately led to confrontations and wars with several groups of native peoples via Indian removal. The United States continued the European practice of recognizing only limited land rights of
Manifest destiny had serious consequences for Native Americans, since continental expansion implicitly meant the occupation and annexation of Native American land, sometimes to expand slavery. This ultimately led to confrontations and wars with several groups of native peoples via Indian removal. The United States continued the European practice of recognizing only limited land rights of
 After the turn of the 19th century to the 20th century, the phrase ''manifest destiny'' declined in usage, as territorial expansion ceased to be promoted as being a part of America's "destiny". Under President
After the turn of the 19th century to the 20th century, the phrase ''manifest destiny'' declined in usage, as territorial expansion ceased to be promoted as being a part of America's "destiny". Under President
President Polk's Inaugural Address
Collection: "Manifest Destiny and the American West"
from the University of Michigan Museum of Art {{Authority control 1845 establishments in the United States American exceptionalism American imperialism American nationalism American political catchphrases Geopolitical terminology History of North America History of United States expansionism International relations theory 19th century in the United States Political terminology of the United States Politics of the United States Territorial evolution of the United States United States federal Indian policy 1840s neologisms 1840s quotations Internal migrations in the United States
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, and that this belief was both obvious ("''manifest''") and certain ("''destiny''"). The belief is rooted in American exceptionalism
American exceptionalism is the belief that the United States is either distinctive, unique, or exemplary compared to other nations. Proponents argue that the Culture of the United States, values, Politics of the United States, political system ...
, Romantic nationalism
Romantic nationalism (also national romanticism, organic nationalism, identity nationalism) is the form of nationalism in which the state claims its political legitimacy as an organic consequence of the unity of those it governs. This includes ...
, and white nationalism
White nationalism is a type of racial nationalism or pan-nationalism which espouses the belief that white people are a Race (human categorization), raceHeidi Beirich and Kevin Hicks. "Chapter 7: White nationalism in America". In Perry, Barbara ...
, implying the inevitable spread of republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology that encompasses a range of ideas from civic virtue, political participation, harms of corruption, positives of mixed constitution, rule of law, and others. Historically, it emphasizes the idea of self ...
and the American way. It is one of the earliest expressions of American imperialism in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
.
According to historian William Earl Weeks, there were three basic tenets behind the concept:
* The assumption of the unique moral virtue of the United States.
* The assertion of its mission to redeem the world by the spread of republican government and more generally the "American way of life".
* The faith in the nation's divinely ordained destiny to succeed in this mission.
Manifest destiny remained heavily divisive in politics, causing constant conflict with regards to slavery in these new states and territories. It is also associated with the settler-colonial displacement of Indigenous Americans and the annexation of lands to the west of the United States borders at the time on the continent. The concept became one of several major campaign issues during the 1844 presidential election, where the Democratic Party won and the phrase "Manifest Destiny" was coined within a year.
The concept of manifest destiny was used by Democrats to justify the 1846 Oregon boundary dispute
The Oregon boundary dispute or the Oregon Question was a 19th-century territorial dispute over the political division of the Pacific Northwest of North America between several nations that had competing territorial and commercial aspirations in ...
and the 1845 annexation
Annexation, in international law, is the forcible acquisition and assertion of legal title over one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. In current international law, it is generally held t ...
of Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
as a slave state, culminating in the 1846 Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
. In contrast, the large majority of Whigs and prominent Republicans (such as Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
and Ulysses S. Grant) rejected the concept and campaigned against these actions. By 1843, former U.S. President John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was the sixth president of the United States, serving from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States secretary of state from 1817 to 1825. During his long diploma ...
, originally a major supporter of the concept underlying manifest destiny, had changed his mind and repudiated expansionism
Expansionism refers to states obtaining greater territory through military Imperialism, empire-building or colonialism.
In the classical age of conquest moral justification for territorial expansion at the direct expense of another established p ...
because it meant the expansion of slavery in Texas. Ulysses S. Grant served in and condemned the Mexican–American War, declaring it "one of the most unjust ever waged by a stronger against a weaker nation".
After the United States Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by states that had seceded ...
, the U.S. acquired Alaska in 1867. In the 1890s, Republican president William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until Assassination of William McKinley, his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Repub ...
annexed Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
, Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
, and American Samoa
American Samoa is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated and unorganized territory of the United States located in the Polynesia region of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. Centered on , it is southeast of the island count ...
. The 1898 Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
was controversial and imperialism became a major issue in the 1900 United States presidential election. Historian Daniel Walker Howe summarizes that "American imperialism did not represent an American consensus; it provoked bitter dissent within the national polity".
Context
There was never a set of principles defining manifest destiny; it was always a general idea rather than a specific policy made with a motto. Ill-defined but keenly felt, manifest destiny was an expression of conviction in the morality and value of expansionism that complemented other popular ideas of the era, includingAmerican exceptionalism
American exceptionalism is the belief that the United States is either distinctive, unique, or exemplary compared to other nations. Proponents argue that the Culture of the United States, values, Politics of the United States, political system ...
and Romantic nationalism
Romantic nationalism (also national romanticism, organic nationalism, identity nationalism) is the form of nationalism in which the state claims its political legitimacy as an organic consequence of the unity of those it governs. This includes ...
. Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
, who spoke of "extending the area of freedom", typified the conflation of America's potential greatness, the nation's budding sense of Romantic self-identity, and its expansion.
Yet Jackson was not the only president to elaborate on the principles underlying manifest destiny. Owing in part to the lack of a definitive narrative outlining its rationale, proponents offered divergent or seemingly conflicting viewpoints. While many writers focused primarily upon American expansionism, be it into Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
or across the Pacific, others saw the term as a call to example. Without an agreed-upon interpretation, much less an elaborated political philosophy, these conflicting views of America's destiny were never resolved. This variety of possible meanings was summed up by Ernest Lee Tuveson: "A vast complex of ideas, policies, and actions is comprehended under the phrase 'Manifest Destiny'. They are not, as we should expect, all compatible, nor do they come from any one source."
Etymology
Most historians credit the conservative newspaper editor and future propagandist for the Confederacy, John O'Sullivan, with coining the term ''manifest destiny'' in 1845. However, other historians suggest the unsigned editorial titled "Annexation" in which it first appeared was written by journalist and annexation advocate Jane Cazneau. O'Sullivan was an influential advocate forJacksonian democracy
Jacksonian democracy, also known as Jacksonianism, was a 19th-century political ideology in the United States that restructured a number of federal institutions. Originating with the seventh U.S. president, Andrew Jackson and his supporters, i ...
, described by Julian Hawthorne as "always full of grand and world-embracing schemes". O'Sullivan wrote an article in 1839 that, while not using the term "manifest destiny", did predict a "divine destiny" for the United States based upon values such as equality, rights of conscience, and personal enfranchisement "to establish on earth the moral dignity and salvation of man". This destiny was not explicitly territorial, but O'Sullivan predicted that the United States would be one of a "Union of many Republics" sharing those values.
Six years later, in 1845, O'Sullivan wrote another essay titled "Annexation" in the ''Democratic Review'', in which he first used the phrase ''manifest destiny''. In this article he urged the U.S. to annex the Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas (), or simply Texas, was a country in North America that existed for close to 10 years, from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846. Texas shared borders with Centralist Republic of Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande, an ...
, not only because Texas desired this, but because it was "our manifest destiny to overspread the continent allotted by Providence for the free development of our yearly multiplying millions". Overcoming Whig opposition, Democrats annexed Texas in 1845. O'Sullivan's first usage of the phrase "manifest destiny" attracted little attention.
O'Sullivan's second use of the phrase became extremely influential. On December 27, 1845, in his newspaper the ''New York Morning News'', O'Sullivan addressed the ongoing boundary dispute with Britain. O'Sullivan argued that the United States had the right to claim "the whole of Oregon":
And that claim is by the right of our manifest destiny to overspread and to possess the whole of the continent which Providence has given us for the development of the great experiment of liberty and federated self-government entrusted to us.McCrisken, Trevor B.That is, O'Sullivan believed that Providence had given the United States a mission to spread republican democracy ("the great experiment of liberty"). Because the
"Exceptionalism: Manifest Destiny"
in ''Encyclopedia of American Foreign Policy'' (2002), Vol. 2, p. 68
British government
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
would not spread democracy, thought O'Sullivan, British claims to the territory should be overruled. O'Sullivan believed that manifest destiny was a moral ideal (a "higher law") that superseded other considerations.
O'Sullivan's original conception of manifest destiny was not a call for territorial expansion by force. He believed that the expansion of the United States would happen without the direction of the U.S. government or the involvement of the military. After Americans immigrated to new regions, they would set up new democratic governments, and then seek admission to the United States, as Texas had done. In 1845, O'Sullivan predicted that California would follow this pattern next, and that even Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
would eventually request annexation as well. He was critical of the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
in 1846, although he came to believe that the outcome would be beneficial to both countries.
Ironically, O'Sullivan's term became popular only after it was criticized by Whig opponents of the Polk administration. Whigs denounced manifest destiny, arguing, "that the designers and supporters of schemes of conquest, to be carried on by this government, are engaged in treason to our Constitution and Declaration of Rights, giving aid and comfort to the enemies of republicanism, in that they are advocating and preaching the doctrine of the right of conquest
The right of conquest was historically a right of ownership to land after immediate possession via force of arms. It was recognized as a principle of international law that gradually deteriorated in significance until its proscription in the af ...
". On January 3, 1846, in a speech Representative Robert Winthrop used the term for the first time in Congress stating:There is one element in our title o Oregon however, which I confess that I have not named, and to which I may not have done entire justice. I mean that new revelation of right which has been designated as the right of our manifest destiny to spread over this whole continent. It has been openly avowed in a leading Administration journal that this, after all, is our best and strongest title-one so clear, so pre-eminent, and so indisputable, that if Great Britain had all our other titles in addition to her own, they would weigh nothing against it. The right of our manifest destiny! There is a right for a new chapter in the law of nations; or rather, in the special laws of our own country; for I suppose the right of a manifest destiny to spread will not be admitted to exist in any nation except the universal Yankee nation!" Winthrop was the first in a long line of critics who suggested that advocates of manifest destiny were citing "Divine Providence" for justification of actions that were motivated by chauvinism and self-interest. Despite this criticism, expansionists embraced the phrase, which caught on so quickly that its origin was soon forgotten.
Themes and influences
Historian Frederick Merk wrote in 1963 that the concept of manifest destiny was born out of "a sense of mission to redeem the Old World by high example ... generated by the potentialities of a new earth for building a new heaven". Merk also states that manifest destiny was a heavily contested concept within the nation:From the outset Manifest Destiny—vast in program, in its sense of continentalism—was slight in support. It lacked national, sectional, or party following commensurate with its magnitude. The reason was it did not reflect the national spirit. The thesis that it embodied nationalism, found in much historical writing, is backed by little real supporting evidence.A possible influence is racial predominance, namely the idea that the American Anglo-Saxon race was "separate, innately superior" and "destined to bring good government, commercial prosperity and Christianity to the American continents and the world". Author Reginald Horsman wrote in 1981, this view also held that "inferior races were doomed to subordinate status or extinction." and that this was used to justify "the enslavement of the blacks and the expulsion and possible extermination of the Indians". The origin of the first theme, later known as
American exceptionalism
American exceptionalism is the belief that the United States is either distinctive, unique, or exemplary compared to other nations. Proponents argue that the Culture of the United States, values, Politics of the United States, political system ...
, was often traced to America's Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
heritage, particularly John Winthrop's famous " City upon a Hill" sermon of 1630, in which he called for the establishment of a virtuous community that would be a shining example to the Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
. In his influential 1776 pamphlet ''Common Sense
Common sense () is "knowledge, judgement, and taste which is more or less universal and which is held more or less without reflection or argument". As such, it is often considered to represent the basic level of sound practical judgement or know ...
'', Thomas Paine
Thomas Paine (born Thomas Pain; – In the contemporary record as noted by Conway, Paine's birth date is given as January 29, 1736–37. Common practice was to use a dash or a slash to separate the old-style year from the new-style year. In ...
echoed this notion, arguing that the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
provided an opportunity to create a new, better society:
We have it in our power to begin the world over again. A situation, similar to the present, hath not happened since the days of Noah until now. The birthday of a new world is at hand...Many Americans agreed with Paine, and came to believe that the United States' virtue was a result of its special experiment in freedom and democracy.
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
, in a letter to James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American Founding Father of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. He was the last Founding Father to serve as presiden ...
, wrote, "it is impossible not to look forward to distant times when our rapid multiplication will expand itself beyond those limits, and cover the whole northern, if not the southern continent." To Americans in the decades that followed their proclaimed freedom for mankind, embodied in the Declaration of Independence, could only be described as the inauguration of "a new time scale" because the world would look back and define history as events that took place before, and after, the Declaration of Independence. It followed that Americans owed to the world an obligation to expand and preserve these beliefs.
The second theme's origination is less precise. A popular expression of America's mission was elaborated by President Abraham Lincoln's description in his December 1, 1862, message to Congress. He described the United States as "the last, best hope of Earth". The "mission" of the United States was further elaborated during Lincoln's Gettysburg Address, in which he interpreted the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
as a struggle to determine if any nation with democratic ideals could survive; this has been called by historian Robert Johannsen "the most enduring statement of America's Manifest Destiny and mission".
The third theme can be viewed as a natural outgrowth of the belief that God had a direct influence in the foundation and further actions of the United States. Political scientist and historian Clinton Rossiter described this view as summing "that God, at the proper stage in the march of history, called forth certain hardy souls from the old and privilege-ridden nations ... and that in bestowing his grace He also bestowed a peculiar responsibility". Americans presupposed that they were not only divinely elected to maintain the North American continent, but also to "spread abroad the fundamental principles stated in the Bill of Rights". In many cases this meant neighboring colonial holdings and countries were seen as obstacles rather than the destiny God had provided the United States.
Faragher's 1997 analysis of the political polarization between the Democratic Party and the Whig Party is that:
Two Native American writers have recently tried to link some of the themes of manifest destiny to the original ideology of the 15th-century decree of the Doctrine of Christian Discovery. Nick Estes (a Lakota) links the 15th-century Catholic doctrine of distinguishing Christians from non-Christians in the expansion of European nations. Estes and international jurist Tonya Gonnella Frichner (of the Onondaga Nation) further link the doctrine of discovery to '' Johnson v. McIntosh'' and frame their arguments on the correlation between manifest destiny and Doctrine of Christian Discovery by using the statement made by Chief Justice John Marshall
John Marshall (September 24, 1755July 6, 1835) was an American statesman, jurist, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fourth chief justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835. He remai ...
during the case, as he "spelled out the rights of the United states to Indigenous lands" and drew upon the Doctrine of Christian Discovery for his statement. Marshall ruled that "indigenous peoples possess 'occupancy' rights, meaning their lands could be taken by the powers of 'discovery'". Frichner explains that "The newly formed United States needed to manufacture an American Indian political identity and concept of Indian land that would open the way for united states and westward colonial expansion." In this way, manifest destiny was inspired by the original European colonization of the Americas, and it excuses U.S. violence against Indigenous Nations.
According to historian Dorceta Taylor: "Minorities are not usually chronicled as explorers or environmental activists, yet the historical records show that they were a part of expeditions, resided and worked on the frontier, founded towns, and were educators and entrepreneurs. In short, people of color were very important actors in westward expansion."
The desire for trade with China and other Asian countries was another ground for expansionism, with Americans seeing prospects of westward contact with Asia as fulfilling long-held Western hopes of finding new routes to Asia, and perceiving the Pacific as less unruly and dominated by Old World conflicts than the Atlantic and therefore a more inviting area for the new nation to expand its influence in.
Debate over Manifest destiny
With theLouisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
in 1803, which doubled the size of the United States, Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
set the stage for the continental expansion of the United States. Many began to see this as the beginning of a new providential mission: If the United States was successful as a " shining city upon a hill", people in other countries would seek to establish their own democratic republics. Not all Americans or their political leaders believed that the United States was a divinely favored nation, or thought that it ought to expand. For example, many Whigs opposed territorial expansion based on the Democratic claim that the United States was destined to serve as a virtuous example to the rest of the world, and also had a divine obligation to spread its superordinate political system and a way of life throughout North American continent. Many in the Whig party "were fearful of spreading out too widely", and they "adhered to the concentration of national authority in a limited area". In July 1848, Alexander Stephens denounced President Polk's expansionist interpretation of America's future as "mendacious".
In the mid‑19th century, expansionism, especially southward toward Cuba, also faced opposition from those Americans who were trying to abolish slavery. As more territory was added to the United States in the following decades, "extending the area of freedom" in the minds of southerners also meant extending the institution of slavery. That is why slavery became one of the central issues in the continental expansion of the United States before the Civil War.
Before and during the Civil War both sides claimed that America's destiny was rightfully their own. Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
opposed anti-immigrant nativism, and the imperialism of manifest destiny as both unjust and unreasonable. He objected to the Mexican war and believed each of these disordered forms of patriotism threatened the inseparable moral and fraternal bonds of liberty and union that he sought to perpetuate through a patriotic love of country guided by wisdom and critical self-awareness. Lincoln's " Eulogy to Henry Clay", June 6, 1852, provides the most cogent expression of his reflective patriotism.
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
served in the war with Mexico and later wrote:
I was bitterly opposed to the measure o annex Texas and to this day regard the war ith Mexicowhich resulted as one of the most unjust ever waged by a stronger against a weaker nation. It was an instance of a republic following the bad example of European monarchies, in not considering justice in their desire to acquire additional territory... The Southern rebellion was largely the outgrowth of the Mexican war. Nations, like individuals, are punished for their transgressions. We got our punishment in the most sanguinary and expensive war of modern times.
Era of expansion
 The phrase "manifest destiny" is most associated with the territorial expansion of the United States from 1803 to 1900. However, the
The phrase "manifest destiny" is most associated with the territorial expansion of the United States from 1803 to 1900. However, the Vermont Republic
The Vermont Republic, officially known at the time as the State of Vermont, was an independent state in New England that existed from January 15, 1777, to March 4, 1791. The state was founded in January 1777, when delegates from 28 towns met ...
joined the United States in 1791, the territory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected to a particular country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, ...
of American Samoa
American Samoa is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated and unorganized territory of the United States located in the Polynesia region of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. Centered on , it is southeast of the island count ...
grew larger in 1904 and 1925, and the U.S. acquired what is now the United States Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands, officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and a territory of the United States. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located ...
in 1917 and what was the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994. The Imperial Japanese South Seas Mandate had been seized by the U.S. during the Pacifi ...
in 1947. Of that Trust Territory, the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory and Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States consistin ...
joined the United States in 1986, while the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (, abbreviated FSM), or simply Micronesia, is an island country in Micronesia, a region of Oceania. The federation encompasses the majority of the Caroline Islands (excluding Palau) and consists of four Admin ...
, Republic of the Marshall Islands, and Palau
Palau, officially the Republic of Palau, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the western Pacific Ocean. The Republic of Palau consists of approximately 340 islands and is the western part of the Caroline Islands ...
became independent states in a Compact of Free Association with the U.S.AmericanSamoa
Some scholars limit the "manifest destiny" period to solely North American continental expansion from the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
to the acquisition of Alaska in 1867, sometimes called the "age of manifest destiny". During this time, the United States expanded to the Pacific Ocean—"from sea to shining sea"—largely defining the borders of the continental United States as they are today. In the 1890s, the United States expanded into Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
and Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
with the annexation of the Republic of Hawaii
The Republic of Hawaii (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Lepupalika o Hawaii'' epupəˈlikə o həˈvɐjʔi was a short-lived one-party state in Hawaii, Hawaii between July 4, 1894, when the Provisional Government of Hawaii had Black Week (H ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
, and American Samoa
American Samoa is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated and unorganized territory of the United States located in the Polynesia region of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. Centered on , it is southeast of the island count ...
.
War of 1812
One of the goals of the War of 1812 was to threaten to annex the British colony ofLower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada () was a British colonization of the Americas, British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence established in 1791 and abolished in 1841. It covered the southern portion o ...
as a bargaining chip to force the British to abandon their fortifications in the Northwestern United States and support for the various Native American tribes residing there. The result of this overoptimism was a series of defeats in 1812 in part due to the wide use of poorly-trained state militias rather than regular troops. The American victories at the Battle of Lake Erie and the Battle of the Thames in 1813 ended the Indian raids and removed the main reason for threatening annexation. To end the War of 1812 John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was the sixth president of the United States, serving from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States secretary of state from 1817 to 1825. During his long diploma ...
, Henry Clay
Henry Clay (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seventh Spea ...
and Albert Gallatin (former treasury secretary and a leading expert on Indians) and the other American diplomats negotiated the Treaty of Ghent in 1814 with Britain. They rejected the British plan to set up an Indian state in U.S. territory south of the Great Lakes. They explained the American policy toward acquisition of Indian lands:
A shocked Henry Goulburn, one of the British negotiators at Ghent, remarked, after coming to understand the American position on taking the Indians' land:
Continentalism
The 19th-century belief that the United States would eventually encompass all of North America is known as "continentalism". An early proponent of this idea, John Quincy Adams became a leading figure in U.S. expansion between theLouisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
in 1803 and the Polk administration in the 1840s. In 1811, Adams wrote to his father:
The whole continent of North America appears to be destined by Divine Providence to be peopled by one ''nation'', speaking one language, professing one general system of religious and political principles, and accustomed to one general tenor of social usages and customs. For the common happiness of them all, for their peace and prosperity, I believe it is indispensable that they should be associated in one federal Union.
 Adams did much to further this idea. He orchestrated the Treaty of 1818, which established the border between British North America and the United States as far west as the Rocky Mountains, and provided for the joint occupation of the region known in American history as the
Adams did much to further this idea. He orchestrated the Treaty of 1818, which established the border between British North America and the United States as far west as the Rocky Mountains, and provided for the joint occupation of the region known in American history as the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long Oregon boundary dispute, dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcat ...
and in British and Canadian history as the New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
and Columbia District
The Columbia District was a fur-trading district in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, in both the United States and British North America in the 19th century. Much of its territory overlapped with the temporarily jointly occupi ...
s. He negotiated the Transcontinental Treaty in 1819, transferring Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
from Spain to the United States and extending the U.S. border with Spanish Mexico all the way to the Pacific Ocean. And he formulated the Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine is a foreign policy of the United States, United States foreign policy position that opposes European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It holds that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign ...
of 1823, which warned Europe that the Western Hemisphere was no longer open for European colonization.
The Monroe Doctrine and "manifest destiny" formed a closely related nexus of principles: historian Walter McDougall calls manifest destiny a corollary of the Monroe Doctrine, because while the Monroe Doctrine did not specify expansion, expansion was necessary in order to enforce the doctrine. Concerns in the United States that European powers were seeking to acquire colonies or greater influence in North America led to calls for expansion in order to prevent this. In his influential 1935 study of manifest destiny, done in conjunction with the Walter Hines Page School of International Relations, Albert Weinberg wrote: "the expansionism of the 830sarose as a defensive effort to forestall the encroachment of Europe in North America".
Transcontinental railroad
Manifest destiny played an important role in the development of thetranscontinental railroad
A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous rail transport, railroad trackage that crosses a continent, continental land mass and has terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks may be via the Ra ...
. The transcontinental railroad system is often used in manifest destiny imagery like John Gast's painting, American Progress where multiple locomotives are seen traveling west. According to academic Dina Gilio-Whitaker, "the transcontinental railroads not only enabled .S. control over the continentbut also accelerated it exponentially." Historian Boyd Cothran says that "modern transportation development and abundant resource exploitation gave rise to an appropriation of indigenous land, ndresources."
All Oregon
Manifest destiny played its most important role in theOregon boundary dispute
The Oregon boundary dispute or the Oregon Question was a 19th-century territorial dispute over the political division of the Pacific Northwest of North America between several nations that had competing territorial and commercial aspirations in ...
between the United States and Britain, when the phrase "manifest destiny" originated. The Anglo-American Convention of 1818 had provided for the joint occupation of the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long Oregon boundary dispute, dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcat ...
, and thousands of Americans migrated there in the 1840s over the Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and Westward Expansion Trails, emigrant trail in North America that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon Territory. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail crossed what ...
. The British rejected a proposal by U.S. President John Tyler
John Tyler (March 29, 1790 – January 18, 1862) was the tenth president of the United States, serving from 1841 to 1845, after briefly holding office as the tenth vice president of the United States, vice president in 1841. He was elected ...
(in office 1841–1845) to divide the region along the 49th parallel, and instead proposed a boundary line farther south, along the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook language, Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin language, Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river headwater ...
, which would have made most of what later became the state of Washington part of their colonies in North America. Advocates of manifest destiny protested and called for the annexation of the entire Oregon Country up to the Alaska line ( 54°40ʹ N). Presidential candidate Polk used this popular outcry to his advantage, and the Democrats called for the annexation of "All Oregon" in the 1844 U.S. presidential election.
 As president, Polk sought compromise and renewed the earlier offer to divide the territory in half along the 49th parallel, to the dismay of the most ardent advocates of manifest destiny. When the British refused the offer, American expansionists responded with slogans such as "The whole of Oregon or none" and "Fifty-four forty or fight", referring to the northern border of the region. (The latter slogan is often mistakenly described as having been a part of the 1844 presidential campaign.) When Polk moved to terminate the joint occupation agreement, the British finally agreed in early 1846 to divide the region along the 49th parallel, leaving the lower Columbia basin as part of the United States. The
As president, Polk sought compromise and renewed the earlier offer to divide the territory in half along the 49th parallel, to the dismay of the most ardent advocates of manifest destiny. When the British refused the offer, American expansionists responded with slogans such as "The whole of Oregon or none" and "Fifty-four forty or fight", referring to the northern border of the region. (The latter slogan is often mistakenly described as having been a part of the 1844 presidential campaign.) When Polk moved to terminate the joint occupation agreement, the British finally agreed in early 1846 to divide the region along the 49th parallel, leaving the lower Columbia basin as part of the United States. The Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty was a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to ...
of 1846 formally settled the dispute; Polk's administration succeeded in selling the treaty to Congress because the United States was about to begin the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
, and the president and others argued it would be foolish to also fight the British Empire.
Despite the earlier clamor for "All Oregon", the Oregon Treaty was popular in the United States and was easily ratified by the Senate. The most fervent advocates of manifest destiny had not prevailed along the northern border because, according to Reginald Stuart, "the compass of manifest destiny pointed west and southwest, not north, despite the use of the term 'continentalism.
In 1869, American historian Frances Fuller Victor published '' Manifest Destiny in the West'' in the ''Overland Monthly
The ''Overland Monthly'' was a monthly literary magazine, literary and cultural magazine, based in California, United States. It was founded in 1868 and published between the second half of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th centu ...
'', arguing that the efforts of early American fur traders and missionaries presaged American control of Oregon. She concluded the article as follows:
Mexico and Texas
Manifest destiny played an important role in the expansion of Texas and American relationship withMexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
. In 1836, the Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas (), or simply Texas, was a country in North America that existed for close to 10 years, from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846. Texas shared borders with Centralist Republic of Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande, an ...
declared independence from Mexico and, after the Texas Revolution
The Texas Revolution (October 2, 1835 – April 21, 1836) was a rebellion of colonists from the United States and Tejanos (Hispanic Texans) against the Centralist Republic of Mexico, centralist government of Mexico in the Mexican state of ...
, sought to join the United States as a new state. This was an idealized process of expansion that had been advocated from Jefferson to O'Sullivan: newly democratic and independent states would request entry into the United States, rather than the United States extending its government over people who did not want it. The annexation of Texas was attacked by anti-slavery spokesmen because it would add another slave state to the Union. Presidents Andrew Jackson and Martin Van Buren declined Texas's offer to join the United States in part because the slavery issue threatened to divide the Democratic Party.
Before the election of 1844, Whig candidate Henry Clay and the presumed Democratic candidate, former president, Van Buren, both declared themselves opposed to the annexation of Texas, each hoping to keep the troublesome topic from becoming a campaign issue. This unexpectedly led to Van Buren being dropped by the Democrats in favor of Polk, who favored annexation. Polk tied the Texas annexation question with the Oregon dispute, thus providing a sort of regional compromise on expansion. (Expansionists in the North were more inclined to promote the occupation of Oregon, while Southern expansionists focused primarily on the annexation of Texas.) Although elected by a very slim margin, Polk proceeded as if his victory had been a mandate for expansion.
All of Mexico
After the election of Polk, but before he took office, Congress approved the annexation of Texas. Polk moved to occupy a portion of Texas that had declared independence from Mexico in 1836, but was still claimed by Mexico. This paved the way for the outbreak of the Mexican–American War on April 24, 1846. With American successes on the battlefield, by the summer of 1847 there were calls for the annexation of "All Mexico", particularly among Eastern Democrats, who argued that bringing Mexico into the Union was the best way to ensure future peace in the region. This was a controversial proposition for two reasons. First, idealistic advocates of manifest destiny like O'Sullivan had always maintained that the laws of the United States should not be imposed on people against their will. The annexation of "All Mexico" would be a violation of this principle. And secondly, the annexation of Mexico was controversial because it would mean extending U.S. citizenship to millions of Mexicans, who were of dark skin and majority Catholic. Senator John C. Calhoun of South Carolina, who had approved of the annexation of Texas, was opposed to the annexation of Mexico, as well as the "mission" aspect of manifest destiny, for racial reasons. He made these views clear in a speech to Congress on January 4, 1848:We have never dreamt of incorporating into our Union any but the Caucasian race—the free white race. To incorporate Mexico, would be the very first instance of the kind, of incorporating an Indian race; for more than half of the Mexicans are Indians, and the other is composed chiefly of mixed tribes. I protest against such a union as that! Ours, sir, is the Government of a white race.... We are anxious to force free government on all; and I see that it has been urged ... that it is the mission of this country to spread civil and religious liberty over all the world, and especially over this continent. It is a great mistake.This debate brought to the forefront one of the contradictions of manifest destiny: on the one hand, while identitarian ideas inherent in manifest destiny suggested that Mexicans, as non-whites, would present a threat to white racial integrity and thus were not qualified to become Americans, the "mission" component of manifest destiny suggested that Mexicans would be improved (or "regenerated", as it was then described) by bringing them into American democracy. Identitarianism was used to promote manifest destiny, but, as in the case of Calhoun and the resistance to the "All Mexico" movement, identitarianism was also used to oppose manifest destiny. Conversely, proponents of annexation of "All Mexico" regarded it as an anti-slavery measure.
 The controversy was eventually ended by the
The controversy was eventually ended by the Mexican Cession
The Mexican Cession () is the region in the modern-day Western United States that Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United S ...
, which added the territories of Alta California
Alta California (, ), also known as Nueva California () among other names, was a province of New Spain formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but was made a separat ...
and Nuevo México to the United States, both more sparsely populated than the rest of Mexico. Like the "All Oregon" movement, the "All Mexico" movement quickly abated.
Historian Frederick Merk, in ''Manifest Destiny and Mission in American History: A Reinterpretation'' (1963), argued that the failure of the "All Oregon" and "All Mexico" movements indicates that manifest destiny had not been as popular as historians have traditionally portrayed it to have been. Merk wrote that, while belief in the beneficent mission of democracy was central to American history, aggressive "continentalism" were aberrations supported by only a minority of Americans, all of them Democrats. Some Democrats were also opposed; the Democrats of Louisiana opposed annexation of Mexico, while those in Mississippi supported it.
These events related to the Mexican–American War and had an effect on the American people living in the Southern Plains at the time. A case study by David Beyreis depicts these effects through the operations of a fur trading and Indian trading business named Bent, St. Vrain and Company during the period. The telling of this company shows that the idea of Manifest Destiny was not unanimously loved by all Americans and did not always benefit Americans. The case study goes on to show that this company could have ceased to exist in the name of territorial expansion.
Filibusterism
After the Mexican–American War ended in 1848, disagreements over the expansion of slavery made further annexation by conquest too divisive to be official government policy. Some, such as John Quitman, Governor of Mississippi, offered what public support they could. In one memorable case, Quitman simply explained that the state of Mississippi had "lost" its state arsenal, which began showing up in the hands of filibusters. Yet these isolated cases only solidified opposition in the North as many Northerners were increasingly opposed to what they believed to be efforts by Southern slave owners—and their friends in the North—to expand slavery through filibustering. Sarah P. Remond on January 24, 1859, delivered an impassioned speech at Warrington, England, that the connection between filibustering and slave power was clear proof of "the mass of corruption that underlay the whole system of American government". The Wilmot Proviso and the continued " Slave Power" narratives thereafter, indicated the degree to which manifest destiny had become part of the sectional controversy. Without official government support the most radical advocates of manifest destiny increasingly turned to military filibustering. Originally filibuster had come from the Dutch ''vrijbuiter'' and referred to buccaneers in the West Indies that preyed on Spanish commerce. While there had been some filibustering expeditions into Canada in the late 1830s, it was only by mid-century did filibuster become a definitive term. By then, declared the '' New-York Daily Times'' "the fever of Fillibusterism is on our country. Her pulse beats like a hammer at the wrist, and there's a very high color on her face." Millard Fillmore's second annual message to Congress, submitted in December 1851, gave double the amount of space to filibustering activities than the brewing sectional conflict. The eagerness of the filibusters, and the public to support them, had an international hue. Clay's son, a diplomat in Portugal, reported that the invasion created a sensation in Lisbon. Although they were illegal, filibustering operations in the late 1840s and early 1850s were romanticized in the United States. The Democratic Party's national platform included a plank that specifically endorsed William Walker's filibustering in
Although they were illegal, filibustering operations in the late 1840s and early 1850s were romanticized in the United States. The Democratic Party's national platform included a plank that specifically endorsed William Walker's filibustering in Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America aft ...
. Wealthy American expansionists financed dozens of expeditions, usually based out of New Orleans, New York, and San Francisco. The primary target of manifest destiny's filibusters was Latin America but there were isolated incidents elsewhere. Mexico was a favorite target of organizations devoted to filibustering, like the Knights of the Golden Circle
The Knights of the Golden Circle (KGC) was a secret society founded in 1854 by American George W. L. Bickley, the objective of which was to create a new country known as the Golden Circle (), where slavery would be legal. The country would have ...
. William Walker got his start as a filibuster in an ill-advised attempt to separate the Mexican states Sonora and Baja California. Narciso López, a near second in fame and success, spent his efforts trying to secure Cuba from the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
.
The United States had long been interested in acquiring Cuba from the declining Spanish Empire. As with Texas, Oregon, and California, American policy makers were concerned that Cuba would fall into British hands, which, according to the thinking of the Monroe Doctrine, would constitute a threat to the interests of the United States. Prompted by O'Sullivan, in 1848 President Polk offered to buy Cuba from Spain for $100 million. Polk feared that filibustering would hurt his effort to buy the island, and so he informed the Spanish of an attempt by the Cuban filibuster López to seize Cuba by force and annex it to the United States, foiling the plot. Spain declined to sell the island, which ended Polk's efforts to acquire Cuba. O'Sullivan eventually landed in legal trouble..
Filibustering continued to be a major concern for presidents after Polk. Whigs presidents Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor (November 24, 1784 – July 9, 1850) was an American military officer and politician who was the 12th president of the United States, serving from 1849 until his death in 1850. Taylor was a career officer in the United States ...
and Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800 – March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853. He was the last president to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House, and the last to be neither a De ...
tried to suppress the expeditions. When the Democrats recaptured the White House in 1852 with the election of Franklin Pierce
Franklin Pierce (November 23, 1804October 8, 1869) was the 14th president of the United States, serving from 1853 to 1857. A northern Democratic Party (United States), Democrat who believed that the Abolitionism in the United States, abolitio ...
, a filibustering effort by John A. Quitman to acquire Cuba received the tentative support of the president. Pierce backed off and instead renewed the offer to buy the island, this time for $130 million. When the public learned of the Ostend Manifesto in 1854, which argued that the United States could seize Cuba by force if Spain refused to sell, this effectively killed the effort to acquire the island. The public now linked expansion with slavery; if manifest destiny had once enjoyed widespread popular approval, this was no longer true.
Filibusters like William Walker continued to garner headlines in the late 1850s, but to little effect. Expansionism was among the various issues that played a role in the coming of the war. With the divisive question of the expansion of slavery, Northerners and Southerners, in effect, were coming to define manifest destiny in different ways, undermining nationalism as a unifying force. According to Frederick Merk, "The doctrine of Manifest Destiny, which in the 1840s had seemed Heaven-sent, proved to have been a bomb wrapped up in idealism."
The filibusterism of the era even opened itself up to some mockery among the headlines. In 1854, a San Francisco Newspaper published a satirical poem called "Filibustering Ethics". This poem features two characters, Captain Robb and Farmer Cobb. Captain Robb makes claim to Farmer Cobb's land arguing that Robb deserves the land because he is Anglo-Saxon, has weapons to "blow out" Cobb's brains, and nobody has heard of Cobb so what right does Cobb have to claim the land. Cobb argues that Robb doesn't need his land because Robb already has more land than he knows what to do with. Due to threats of violence, Cobb surrenders his land and leaves grumbling that "''might'' should be the rule of ''right'' among ''enlightened'' nations."
Homestead Act
 The Homestead Act of 1862 encouraged 600,000 families to settle the West by giving them land (usually 160 acres) almost free. Over the course of 123 years, 200 million claims were made and over 270 million acres were settled, accounting for 10% of the land in the U.S. They had to live on and improve the land for five years. Before the
The Homestead Act of 1862 encouraged 600,000 families to settle the West by giving them land (usually 160 acres) almost free. Over the course of 123 years, 200 million claims were made and over 270 million acres were settled, accounting for 10% of the land in the U.S. They had to live on and improve the land for five years. Before the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, Southern leaders opposed the Homestead Acts because they feared it would lead to more free states and free territories. After the mass resignation of Southern senators and representatives at the beginning of the war, Congress was subsequently able to pass the Homestead Act.
In some areas, the Homestead Act resulted in the direct removal of Indigenous communities. According to American historian Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz, all five nations of the "Five Civilized Tribes" signed treaties with the Confederacy and initially supported them in hopes of dividing and weakening the U.S. so that they could remain on their land. The United States Army, led by prominent Civil War generals such as William Tecumseh Sherman, Philip Sheridan, and George Armstrong Custer, waged wars on "non-treaty Indians" who continued to live on land that had already been ceded to the U.S. through treaty. Homesteaders and other settlers soon followed and took possession of the land for farms and mining. Occasionally, white settlers would move ahead of the U.S. Army, into land that had not yet been settled by the United States, causing conflict with the Native people who still resided there. According to Anglo-American historian Julius Wilm, while the U.S. government did not approve of settlers moving ahead of the army, Indian Affairs officials did believe "the move of frontier whites into the proximity of contested territory—be they homesteaders or parties interested in other pursuits—necessitated the removal of Indigenous nations."
According to historian Hannah Anderson, the Homestead Act also led to environmental degradation
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, referring respectively to all living and non-living things occurring naturally and the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism ...
. While it succeeded in settling and farming the land, the Act failed to preserve the land. Continuous plowing of the top soil made the soil vulnerable to erosion and wind, as well as stripping the nutrients from the ground. This deforestation and erosion would play a key role in the Dust Bowl in the 1930s. Intense logging caused a decrease in much of the forests and hunting harmed many of the native animal populations, including the bison, whose population was reduced to a few hundreds.
Beyond North America: Annexation of Hawaii
 In 1859, Reuben Davis, a member of the House of Representatives from Mississippi, articulated one of the most expansive visions of manifest destiny on record:
In 1859, Reuben Davis, a member of the House of Representatives from Mississippi, articulated one of the most expansive visions of manifest destiny on record:
We may expand so as to include the whole world. Mexico, Central America, South America, Cuba, the West India Islands, and even England and France emight annex without inconvenience... allowing them with their local Legislatures to regulate their local affairs in their own way. And this, Sir, is the mission of this Republic and its ultimate destiny.As the Civil War faded into history, the term ''manifest destiny'' experienced a brief revival. Protestant missionary Josiah Strong, in his best-seller of 1885, ''Our Country'', argued that the future was devolved upon America since it had perfected the ideals of civil liberty, "a pure spiritual Christianity", and concluded, "My plea is not, Save America for America's sake, but, Save America for the world's sake." In the 1892 U.S. presidential election, the Republican Party platform proclaimed: "We reaffirm our approval of the
Monroe doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine is a foreign policy of the United States, United States foreign policy position that opposes European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It holds that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign ...
and believe in the achievement of the manifest destiny of the Republic in its broadest sense." What was meant by "manifest destiny" in this context was not clearly defined, particularly since the Republicans lost the election.
In the 1896 election, the Republicans recaptured the White House and held on to it for the next 16 years. During that time, manifest destiny was cited to promote overseas expansion. Whether or not this version of manifest destiny was consistent with the continental expansionism of the 1840s was debated at the time, and long afterwards.
For example, when President William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until Assassination of William McKinley, his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Repub ...
advocated annexation of the Republic of Hawaii
The Republic of Hawaii (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Lepupalika o Hawaii'' epupəˈlikə o həˈvɐjʔi was a short-lived one-party state in Hawaii, Hawaii between July 4, 1894, when the Provisional Government of Hawaii had Black Week (H ...
in 1898, he said that "We need Hawaii just as much and a good deal more than we did California. It is manifest destiny." On the other hand, former President Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States, serving from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. He was the first U.S. president to serve nonconsecutive terms and the first Hist ...
, a Democrat who had blocked the annexation of Hawaii during his administration, wrote that McKinley's annexation of the territory was a "perversion of our national destiny". Historians continued that debate; some have interpreted American acquisition of other Pacific island groups in the 1890s as an extension of manifest destiny across the Pacific Ocean. Others have regarded it as the antithesis of manifest destiny and merely imperialism
Imperialism is the maintaining and extending of Power (international relations), power over foreign nations, particularly through expansionism, employing both hard power (military and economic power) and soft power (diplomatic power and cultura ...
.
Spanish–American War
In 1898, the United States intervened in the Cuban insurrection and launched theSpanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
to force Spain out. According to the terms of the Treaty of Paris, Spain relinquished sovereignty over Cuba and ceded the Philippine Islands
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
, and Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
to the United States. The terms of cession for the Philippines involved a payment of the sum of $20 million by the United States to Spain. The treaty was highly contentious and denounced by William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan (March 19, 1860 – July 26, 1925) was an American lawyer, orator, and politician. He was a dominant force in the History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, running three times as the party' ...
, who tried to make it a central issue in the 1900 election, which he lost to McKinley.
The Teller Amendment, passed unanimously by the U.S. Senate before the war, which proclaimed Cuba "free and independent", forestalled annexation of the island. The Platt Amendment (1902) then established Cuba as a virtual protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over ...
of the United States.
American Samoa
The United States,German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
, and United Kingdom participted in the Tripartite Convention of 1899 at the end of the Second Samoan Civil War, resulting in the formal partition of the Samoan archipelago into a German colony and the U.S. territory of what is now called American Samoa
American Samoa is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated and unorganized territory of the United States located in the Polynesia region of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. Centered on , it is southeast of the island count ...
. The United States annexed Tutuila in 1900, Manu'a in 1904, and Swains Island in 1925.
The eastern Samoan islands became a territory of the United States. The western islands, by far the greater landmass, became known as German Samoa, after Britain gave up all claims to Samoa and in return accepted the termination of German rights in Tonga and certain areas in the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, t ...
and West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
. Forerunners to the Tripartite Convention of 1899 were the Washington Conference of 1887, the Treaty of Berlin of 1889, and the Anglo-German Agreement on Samoa of 1899.
The following year, the U.S. formally annexed its portion, a smaller group of eastern islands, one of which contains the noted harbor of Pago Pago
Pago Pago ( or ; Samoan language, Samoan: )Harris, Ann G. and Esther Tuttle (2004). ''Geology of National Parks''. Kendall Hunt. Page 604. . is the capital of American Samoa. It is in Maoputasi County, American Samoa, Maoputasi County on Tutuila ...
.Lin, Tom C.W.Americans, Almost and Forgotten
, 107 California Law Review (2019) After the
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
took possession of eastern Samoa for the United States government
The Federal Government of the United States of America (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the Federation#Federal governments, national government of the United States.
The U.S. federal government is composed of three distinct ...
, the existing coaling station at Pago Pago Bay was expanded into a full naval station, known as United States Naval Station Tutuila and commanded by a commandant. The Navy secured a Deed of Cession of Tutuila in 1900 and a Deed of Cession of Manua in 1904 on behalf of the U.S. government. The last sovereign of Manua, the Tui Manua Elisala, signed a Deed of Cession of Manua following a series of U.S. naval trials, known as the "Trial of the Ipu", in Pago Pago, Tau, and aboard a Pacific Squadron gunboat. The territory became known as the U.S. Naval Station Tutuila.
On July 17, 1911, the U.S. Naval Station Tutuila, which was composed of Tutuila, Aunuu and Manua, was officially renamed American Samoa. People of Manua had been unhappy since they were left out of the name "Naval Station Tutuila". In May 1911, Governor William Michael Crose authored a letter to the Secretary of the Navy conveying the sentiments of Manua. The department responded that the people should choose a name for their new territory. The traditional leaders chose "American Samoa", and, on July 7, 1911, the solicitor general of the Navy authorized the governor to proclaim it as the name for the new territory.Sunia, Fofo I.F. (2009). ''A History of American Samoa''. Amerika Samoa Humanities Council. .
Insular cases
The acquisition ofHawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
, Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
, and American Samoa
American Samoa is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated and unorganized territory of the United States located in the Polynesia region of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. Centered on , it is southeast of the island count ...
marked a new chapter in U.S. history. Traditionally, territories were acquired by the United States for the purpose of becoming new states on equal footing with already existing states. These islands were acquired as colonies rather than prospective states. The process was validated by the Insular Cases. The Supreme Court ruled that full constitutional rights did not automatically extend to all areas under American control. The Philippines became independent in 1946 and Hawaii became a state in 1959, but Puerto Rico, Guam, and American Samoa remain territories.
According to Frederick Merk, these colonial acquisitions marked a break from the original intention of manifest destiny. Previously, "Manifest Destiny had contained a principle so fundamental that a Calhoun and an O'Sullivan could agree on it—that a people not capable of rising to statehood should never be annexed. That was the principle thrown overboard by the imperialism of 1899." Albert J. Beveridge maintained the contrary at his September 25, 1900, speech in the Auditorium, at Chicago. He declared that the current desire for Cuba and the other acquired territories was identical to the views expressed by Washington, Jefferson and Marshall. Moreover, "the sovereignty of the Stars and Stripes can be nothing but a blessing to any people and to any land." The nascent revolutionary government, desirous of independence, resisted the United States in the Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War, known alternatively as the Philippine Insurrection, Filipino–American War, or Tagalog Insurgency, emerged following the conclusion of the Spanish–American War in December 1898 when the United States annexed th ...
in 1899; it won no support from any government anywhere and collapsed when its leader was captured. William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan (March 19, 1860 – July 26, 1925) was an American lawyer, orator, and politician. He was a dominant force in the History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, running three times as the party' ...
denounced the war and any form of future overseas expansion, writing, Destiny' is not as manifest as it was a few weeks ago."
20th-century reforms
In 1917, all Puerto Ricans were made full American citizens via the Jones Act, which also provided for a popularly elected legislature and a bill of rights, and authorized the election of a Resident Commissioner who has a voice (but no vote) in Congress. In 1934, the Tydings–McDuffie Act put the Philippines on a path to independence, which was realized in 1946 with the Treaty of Manila. The Guam Organic Act of 1950 established Guam alongside Puerto Rico as an unincorporated unorganized territory of the United States, provided for the structure of the island's civilian government, and granted the people U.S. citizenship.21st century
In 2025,Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
became the first president to use the phrase "manifest destiny" during an inaugural address, declaring an extension of American influence "into the stars" with ambitions to plant the U.S. flag on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
. Since being elected, Trump has suggested at various points to annex Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
, and the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal () is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean. It cuts across the narrowest point of the Isthmus of Panama, and is a Channel (geography), conduit for maritime trade between th ...
, to invade Venezuela and Mexico, and to take over the Gaza Strip.
Impact on Native Americans
 Manifest destiny had serious consequences for Native Americans, since continental expansion implicitly meant the occupation and annexation of Native American land, sometimes to expand slavery. This ultimately led to confrontations and wars with several groups of native peoples via Indian removal. The United States continued the European practice of recognizing only limited land rights of
Manifest destiny had serious consequences for Native Americans, since continental expansion implicitly meant the occupation and annexation of Native American land, sometimes to expand slavery. This ultimately led to confrontations and wars with several groups of native peoples via Indian removal. The United States continued the European practice of recognizing only limited land rights of Indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
. In a policy formulated largely by Henry Knox
Henry Knox (July 25, 1750 – October 25, 1806) was an American military officer, politician, bookseller, and a Founding Father of the United States. Knox, born in Boston, became a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionar ...
, Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
in the Washington Administration, the U.S. government sought to expand into the west through the purchase of Native American land in treaties. Only the Federal Government could purchase Indian lands, and this was done through treaties with tribal leaders. Whether a tribe actually had a decision-making structure capable of making a treaty was a controversial issue. The national policy was for the Indians to join American society and become "civilized", which meant no more wars with neighboring tribes or raids on white settlers or travelers, and a shift from hunting to farming and ranching. Advocates of civilization programs believed that the process of settling native tribes would greatly reduce the amount of land needed by the Native Americans, making more land available for homesteading by white Americans. Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
believed that, while the Indigenous people of America were intellectual equals to whites, they had to assimilate to and live like the whites or inevitably be pushed aside by them.
According to historian Jeffrey Ostler, Jefferson advocated for the extermination of Indigenous people once he believed assimilation was no longer possible.
On February 27, 1803, Jefferson wrote in a letter to William Henry Harrison:"but this letter being unofficial, & private, I may with safety give you a more extensive view of our policy respecting the Indians... Our system is to live in perpetual peace with the Indians, to cultivate an affectionate attachment from them, by everything just & liberal which we can do for them within the bounds of reason, and by giving them effectual protection against wrongs from our own people. The decrease of game rendering their subsistence by hunting insufficient, we wish to draw them to agriculture, to spinning & weaving... when they withdraw themselves to the culture of a small piece of land, they will perceive how useless to them are their extensive forests, and will be willing to pare them off from time to time in exchange for necessaries for their farms & families. At our trading houses too we mean to sell so low as merely to repay us cost and charges so as neither to lessen or enlarge our capital. this is what private traders cannot do, for they must gain; they will consequently retire from the competition, & we shall thus get clear of this pest without giving offence or umbrage to the Indians. in this way our settlements will gradually circumbscribe & approach the Indians, & they will in time either incorporate with us as citizens of the U.S. or remove beyond the Mississippi."Noted by Law Scholar and professor Robert J. Miller, Thomas Jefferson "Understood and utilized the Doctrine of Discovery ka Manifest destinythrough his political careers and was heavily involved in using the Doctrine against Indian tribes." Jefferson was "often immersed in Indian affairs through his legal and political careers" and "was also well acquainted with the process Virginia governments had historically used to extinguish Indian andtitles". Jefferson used this knowledge to make the Louisiana purchase in 1803, aided in the construction of the Indian Removal Policy, and laid the ground work for removing Native American tribes further and further into eventual small reservation territories. The idea of "Indian removal" gained traction in the context of manifest destiny and, with Jefferson as one of the main political voices on the subject, accumulated advocates who believed that American Indians would be better off moving away from white settlers. The removal effort was further solidified through policy by Andrew Jackson when he signed the Indian Removal Act in 1830. In his First Annual Message to Congress in 1829, Jackson stated with regards to removal:
I suggest for your consideration the propriety of setting apart an ample district west of the Mississippi, and without the limits of any state or territory now formed, to be guaranteed to the Indian tribes as long as they shall occupy it, each tribe having a distinct control over the portion designated for its use. There they may be secured in the enjoyment of governments of their own choice, subject to no other control from the United States than such as may be necessary to preserve peace on the frontier and between the several tribes. There the benevolent may endeavor to teach them the arts of civilization, and, by promoting union and harmony among them, to raise up an interesting commonwealth, destined to perpetuate the race and to attest the humanity and justice of this government."Following the forced removal of many Indigenous Peoples, Americans increasingly believed that Native American ways of life would eventually disappear as the United States expanded. Humanitarian advocates of removal believed that American Indians would be better off moving away from whites. As historian Reginald Horsman argued in his influential study ''Race and Manifest Destiny'', racial rhetoric increased during the era of manifest destiny. Americans increasingly believed that Native American ways of life would "fade away" as the United States expanded. As an example, this idea was reflected in the work of one of America's first great historians, Francis Parkman, whose landmark book '' The Conspiracy of Pontiac'' was published in 1851. Parkman wrote that after the French defeat in the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
, Indians were "destined to melt and vanish before the advancing waves of Anglo-American power, which now rolled westward unchecked and unopposed". Parkman emphasized that the collapse of Indian power in the late 18th century had been swift and was a past event.
Legacy and consequences
The belief in an American mission to promote and defend democracy throughout the world, as expounded by Jefferson and his " Empire of Liberty", and continued by Lincoln, Wilson and George W. Bush, continues to have an influence on American political ideology. UnderDouglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American general who served as a top commander during World War II and the Korean War, achieving the rank of General of the Army (United States), General of the Army. He served with dis ...
, the Americans "were imbued with a sense of manifest destiny," says historian John Dower.
 After the turn of the 19th century to the 20th century, the phrase ''manifest destiny'' declined in usage, as territorial expansion ceased to be promoted as being a part of America's "destiny". Under President
After the turn of the 19th century to the 20th century, the phrase ''manifest destiny'' declined in usage, as territorial expansion ceased to be promoted as being a part of America's "destiny". Under President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
the role of the United States in the New World was defined, in the 1904 Roosevelt Corollary
In the history of United States foreign policy, the Roosevelt Corollary was an addition to the Monroe Doctrine articulated by President Theodore Roosevelt in his 1904 State of the Union Address, largely as a consequence of the Venezuelan cri ...
to the Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine is a foreign policy of the United States, United States foreign policy position that opposes European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It holds that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign ...
, as being an "international police power" to secure American interests in the Western Hemisphere. Roosevelt's corollary contained an explicit rejection of territorial expansion. In the past, manifest destiny had been seen as necessary to enforce the Monroe Doctrine in the Western Hemisphere, but now expansionism had been replaced by interventionism as a core value associated with the doctrine.
President Wilson continued the policy of interventionism in the Americas, and attempted to redefine both manifest destiny and America's "mission" on a broader, worldwide scale. Wilson led the United States into World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
with the argument that "The world must be made safe for democracy." In his 1920 message to Congress after the war, Wilson stated:
... I think we all realize that the day has come when Democracy is being put upon its final test. The Old World is just now suffering from a wanton rejection of the principle of democracy and a substitution of the principle of autocracy as asserted in the name, but without the authority and sanction, of the multitude. This is the time of all others when Democracy should prove its purity and its spiritual power to prevail. It is surely the manifest destiny of the United States to lead in the attempt to make this spirit prevail.This was the only time a president had used the phrase "manifest destiny" in his annual address. Wilson's version of manifest destiny was a rejection of expansionism and an endorsement (in principle) of
self-determination
Self-determination refers to a people's right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage.
Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international la ...
, emphasizing that the United States had a mission to be a world leader for the cause of democracy. This U.S. vision of itself as the leader of the " Free World" would grow stronger in the 20th century after the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, although rarely would it be described as "manifest destiny", as Wilson had done.
"Manifest destiny" is sometimes used by critics of U.S. foreign policy to characterize interventions in the Middle East and elsewhere. In this usage, "manifest destiny" is interpreted as the underlying cause of what is denounced by some as " American imperialism". A more positive-sounding phrase devised by scholars at the end of the 20th century is "nation building", and State Department official Karin Von Hippel notes that the U.S. has "been involved in nation-building and promoting democracy since the middle of the 19th century and 'Manifest Destiny.
Criticisms
Critics have condemned manifest destiny as an ideology used to justify dispossession and genocide against indigenous peoples. Critics argue it resulted in the forceful settler-colonial displacement of Indigenous Americans in order to carry out colonial expansion. Critics at the time of the country's growing desire for expansion doubted the country's ability to rule such an extensive empire.See also
*American frontier
The American frontier, also known as the Old West, and popularly known as the Wild West, encompasses the Geography of the United States, geography, History of the United States, history, Folklore of the United States, folklore, and Cultur ...
** Frontier Thesis
* Christian mission
A Christian mission is an organized effort to carry on evangelism, in the name of the Christian faith. Missions involve sending individuals and groups across boundaries, most commonly geographical boundaries. Sometimes individuals are sent and a ...
* Civilizing mission
The civilizing mission (; ; ) is a political rationale for military intervention and for colonization purporting to facilitate the cultural assimilation of indigenous peoples, especially in the period from the 15th to the 20th centuries. As ...
* Greater United States
* " The White Man's Burden" (1899)
* Young America movement
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * Previously published as * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
Journal articles
* * * *Books
* * Burge, Daniel J. (2022). ''A Failed Vision of Empire: The Collapse of Manifest Destiny, (1845–1872)''. University of Nebraska Press. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
President Polk's Inaugural Address
Collection: "Manifest Destiny and the American West"
from the University of Michigan Museum of Art {{Authority control 1845 establishments in the United States American exceptionalism American imperialism American nationalism American political catchphrases Geopolitical terminology History of North America History of United States expansionism International relations theory 19th century in the United States Political terminology of the United States Politics of the United States Territorial evolution of the United States United States federal Indian policy 1840s neologisms 1840s quotations Internal migrations in the United States