Mandibular Canal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In human anatomy, the mandibular canal is a
In human anatomy, the mandibular canal is a
File:Slide2cec.JPG, Mandibular nerve and bone. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
File:Slide7cece.JPG, Infratemporal fossa. Lingual and inferior alveolar nerve. Deep dissection. Anterolateral view
 In human anatomy, the mandibular canal is a
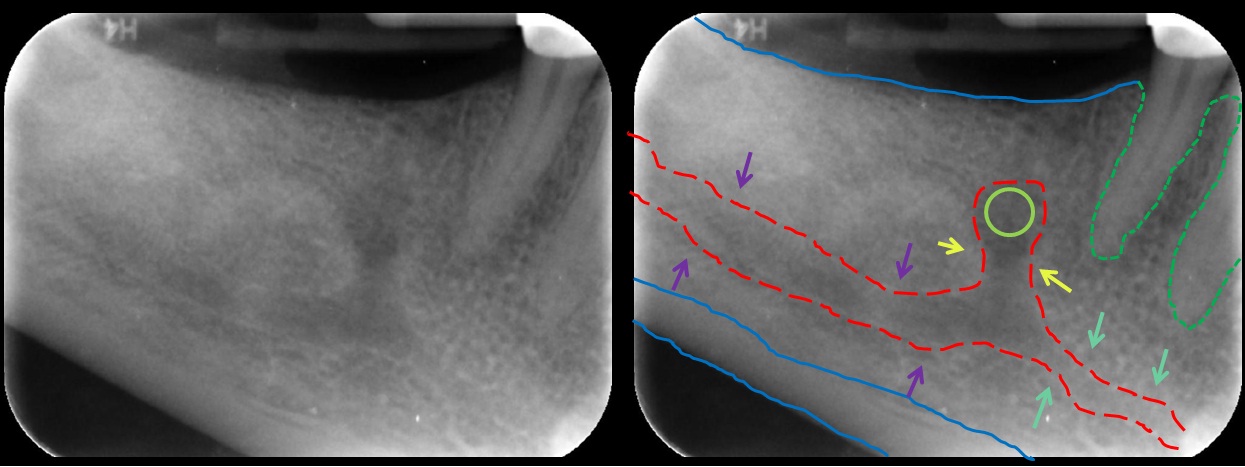
In human anatomy, the mandibular canal is a canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
within the mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
that contains the inferior alveolar nerve
The inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) (also the inferior dental nerve) is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) (which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). The nerve provides sensory innervation to the lower/mandibu ...
, inferior alveolar artery, and inferior alveolar vein. It runs obliquely downward and forward in the ramus, and then horizontally forward in the body, where it is placed under the alveoli and communicates with them by small openings.
On arriving at the incisor teeth
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...
, it turns back to communicate with the mental foramen
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It is part of the mandibular canal. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and the mental vessels.
Structure
Th ...
, giving off a small canal known as the mandibular incisive canal
The mandibular incisive canal is a bilaterally paired bony canal within the anterior portion of the mandible that extends from the mental foramen (usually) to near the ipsilateral lateral incisor teeth.
The inferior alveolar nerve splits into ...
, which run to the cavities containing the incisor teeth
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...
. It carries branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and artery.
The mandibular canal is continuous with two foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; : foramina, or foramens ; ) is an opening or enclosed gap within the dense connective tissue (bones and deep fasciae) of extant and extinct amniote animals, typically to allow passage of nerves, arter ...
: the mental foramen which opens in the mental region of the mandible and carried the distal fibres of the inferior alveolar nerve as the mental nerve
The mental nerve is a sensory nerve of the face. It is a branch of the posterior trunk of the inferior alveolar nerve, itself a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensation to the f ...
; and the mandibular foramen
The mandibular foramen is an opening on the internal surface of the ramus of the mandible. It allows for divisions of the mandibular nerve and blood vessels to pass through.
Structure
The mandibular foramen is an opening on the internal surfac ...
on medial aspect of ramus, into which the mandibular nerve
In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth Cranial nerves, cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which ...
enters to become the inferior alveolar nerve. The mandibular canal often runs close to the apices of the third molar tooth, and the inferior alveolar nerve can become damaged during removal of this tooth, causing sensory disturbance in the distribution of the nerve. This is sometimes the case for the second or first molar teeth, and care must be taken during removal or root canal treatment in such cases to prevent nerve injury or extrusion of root canal filling materials.
Variations
Several variations of the mandibular canal exist with varying frequency. The most common variant is the retromolar canal (~10 % of canals), whereby a branch is given off in the mandibular ramus which terminates in the retromolar region of the mandible. The retromolar canal may cause bleeding during surgery in the retromolar region such as removal of mandibular third molar teeth. Other variants include a bifid canal with a branch (~41%): following the course of the main mandibular canal before re-joining it (forward or buccolingual type); terminating at the apex of a tooth, usually themolar teeth
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone toot ...
(dental type); opening as an accessory mental foramen
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It is part of the mandibular canal. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and the mental vessels.
Structure
Th ...
. A trifid mandibular canal variation has also been described.
Additional Images
See also
*Human mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbon ...
* Inferior alveolar artery
References
External links
* {{Authority control Foramina of the skull