Mahmud Ghazan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mahmud Ghazan (5 November 1271 – 11 May 1304) (, Ghazan Khan, sometimes westernized as Casanus was the seventh ruler of the
 Ghazan's parents were
Ghazan's parents were


Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
's Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate or Il-khanate was a Mongol khanate founded in the southwestern territories of the Mongol Empire. It was ruled by the Il-Khans or Ilkhanids (), and known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (). The Ilkhanid realm was officially known ...
division in modern-day Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
from 1295 to 1304. He was the son of Arghun
Arghun Khan ( Mongolian Cyrillic: Аргун; Traditional Mongolian: ; c. 1258 – 10 March 1291) was the fourth ruler of the Mongol empire's Ilkhanate division, from 1284 to 1291. He was the son of Abaqa Khan, and like his father, was a de ...
, grandson of Abaqa Khan
Abaqa Khan (27 February 1234 – 4 April 1282, , "paternal uncle", also transliterated Abaġa), was the second Mongol ruler ('' Ilkhan'') of the Ilkhanate. The son of Hulagu Khan and Lady Yesünčin and the grandson of Tolui, he reigned from 1265 ...
and great-grandson of Hulegu Khan
Hulegu Khan, also known as Hülegü or Hulagu; ; ; ; ( 8 February 1265), was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of Western Asia. As a son of Tolui and the Keraite princess Sorghaghtani Beki, he was a grandson of Genghis Khan and brother of Ar ...
, continuing a long line of rulers who were direct descendants of Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
. Considered the most prominent of the Ilkhan
Il Khan (also ''il-khan'', ''ilkhan'', ''elkhan'', etc.), in Turkic languages and Mongolian, is a title of leadership. It combines the title ''khan'' with the prefix ''el/il'', from the word ''ulus'' – 'tribe, clan', 'the people', 'nation', ' ...
s, he is perhaps best known for converting to Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
and meeting Imam
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Salah, Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, ...
Ibn Taymiyya
Ibn Taymiyya (; 22 January 1263 – 26 September 1328)Ibn Taymiyya, Taqi al-Din Ahmad, The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-959 was a Sunni Muslim schola ...
in 1295 when he took the throne, marking a turning point for the dominant religion of the Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
in West Asia: Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
, Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, and the South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
.
One of his many principal wives was Kököchin
Kököchin, also Kökejin, Kūkājīn, Cocacin or Cozotine ( Mongolian: ; ), was a 13th-century princess of the Mongol-led Chinese Yuan dynasty, belonging to the Mongol Bayaut tribe. In 1291, she was betrothed to the Ilkhanate khan Arghun by t ...
, a Mongol princess (originally betrothed to Ghazan's father Arghun before his death) sent by his great-uncle Kublai Khan
Kublai Khan (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder and first emperor of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China. He proclaimed the ...
.
Military conflicts during Ghazan's reign included war with the Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate (), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz from the mid-13th to early 16th centuries, with Cairo as its capital. It was ruled by a military caste of mamluks ...
for control of Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
and battles with the Turko-Mongol Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, also known as the Chagatai Ulus, was a Mongol and later Turkification, Turkicized khanate that comprised the lands ruled by Chagatai Khan, second son of Genghis Khan, and his descendants and successors. At its height in the l ...
. Ghazan also pursued diplomatic contacts with Europe, continuing his predecessors' unsuccessful attempts at forming a Franco-Mongol alliance
Several attempts at a military alliance between the Franks#Crusaders and other Western Europeans as "Franks", Frankish Crusaders and the Mongol Empire against the Islamic caliphates, their common enemy, were made by various leaders among them dur ...
. A man of high culture, Ghazan spoke multiple languages, had many hobbies, and reformed many elements of the Ilkhanate, especially in the matter of standardizing currency and fiscal policy.
Childhood
 Ghazan's parents were
Ghazan's parents were Arghun
Arghun Khan ( Mongolian Cyrillic: Аргун; Traditional Mongolian: ; c. 1258 – 10 March 1291) was the fourth ruler of the Mongol empire's Ilkhanate division, from 1284 to 1291. He was the son of Abaqa Khan, and like his father, was a de ...
and his concubine Kultak Egechi of the Dörböd. At the time of their marriage, Arghun was 12. Kultak's elder sister Ashlun was the wife of Tübshin, son of Hulagu and the previous viceroy in Greater Khorasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...
. According to Rashid al-Din Hamadani
Rashīd al-Dīn Ṭabīb (; 1247–1318; also known as Rashīd al-Dīn Faḍlullāh Hamadānī, ) was a statesman, historian, and physician in Ilkhanate Iran.Mazandaran
Mazandaran Province (; ) is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Its capital is the city of Sari, Iran, Sari. Located along the southern coast of the Caspian Sea and in the adjacent Central Alborz mountain range and Hyrcanian forests, it is border ...
, where Arghun was viceroy.
Ghazan was born on 5 November 1271 in Abaskun (now near Bandar Torkaman
Bandar Torkaman () is a city in the Central District of Torkaman County, Golestan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
Demographics Population
At the time of the 2006 National Census, the city's populati ...
), although he was raised in the nomadic palace of the orda of his grandfather Abaqa's favorite wife, Buluqhan Khatun
Buluqhan Khatun (; Mongolian: , lit. 'Sable'), also Bulughan, Bulukhan, Bolgana, Bulugan, Zibeline or ''Bolghara'' for Marco Polo, was a 13th-century Mongol princess, and the principal wife of the Mongol Ilkhanid ruler Abaqa (1234–1282).
...
, who herself was childless. Ghazan and Arghun didn't see each other until Abaqa's attack on Qara'unas
The Qara'unas or Negüderi were the Mongols who settled in Afghanistan after moving from Turkestan and Mongolia.
Foundation
The word Qarauna derived from the Turkic word ''Qara'' meaning black in Mongolian. At first they were subjects of the ...
in 1279, when they briefly met.
Ghazan was raised an Eastern Christian
Eastern Christianity comprises Christianity, Christian traditions and Christian denomination, church families that originally developed during Classical antiquity, classical and late antiquity in the Eastern Mediterranean region or locations fu ...
, as was his brother Öljaitü
Öljaitü, also known as Mohammad-e Khodabandeh (24 March 1282 – 16 December 1316), was the eighth Ilkhanid dynasty ruler from 1304 to 1316 in Tabriz, Iran. His name 'Öjaitü' means 'blessed' in the Mongolian language and his last name 'Khod ...
. The Mongols were traditionally tolerant of multiple religions, and during Ghazan's youth, he was educated by a Chinese Buddhist monk, who taught him Old Mandarin
Old Mandarin or Early Mandarin was the speech of northern China during the Jurchen-ruled Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasty and the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty (12th to 14th centuries). New genres of vernacular literature were based on this langu ...
and Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, as well as the Mongolian
Mongolian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Mongolia, a country in Asia
* Mongolian people, or Mongols
* Bogd Khanate of Mongolia, the government of Mongolia, 1911–1919 and 1921–1924
* Mongolian language
* Mongolian alphabet
* ...
and Uighur scripts.
Under Tekuder
He lived together with Gaykhatu inBuluqhan Khatun
Buluqhan Khatun (; Mongolian: , lit. 'Sable'), also Bulughan, Bulukhan, Bolgana, Bulugan, Zibeline or ''Bolghara'' for Marco Polo, was a 13th-century Mongol princess, and the principal wife of the Mongol Ilkhanid ruler Abaqa (1234–1282).
...
's encampment in Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
after Abaqa's death. He reunited again with his father when Buluqhan Khatun was wed to Arghun and became Ghazan's step-mother.
Rule in Khorasan
Under Arghun
After the overthrow ofTekuder
Ahmed Tekuder (; ; 10 August 1284), also known as Sultan Ahmad, was the sultan of the Ilkhanate from 1282 to 1284. He was a son of Hulegu and brother of Abaqa. He was eventually succeeded by his nephew Arghun Khan.
Early life
Tekuder was bor ...
in 1284, Ghazan's father Arghun was enthroned as Ilkhan, the 11-year-old Ghazan became viceroy, and he moved to the capital of Khorasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West and Central Asia that encompasses western and no ...
, never to see Arghun again. Emir Tegene was appointed as his deputy, who he didn't like very much. In 1289, conflict with other Mongols ensued when a revolt was led against Arghun by Nawruz, a young emir of the Oirat clan, whose father had been civil governor of Persia before the arrival of Hulegu. Ghazan's deputy Tegene was among the victims of Nawruz's raid on 20 April 1289 in which he was captured and imprisoned. Nawruz's protege, Prince Hulachu was arrested by Ghazan's commander Mulay
Mulay, Mûlay, Bulay ( or Molay for the Franks, ) was a general under the Mongol Ilkhanate ruler Ghazan at the end of the 13th century. Mulay was part of the 1299–1300 Mongol offensive in Syria and Palestine, and remained with a small force t ...
ten days later. When Nawruz was defeated by Arghun's reinforcements in 1290, he fled the Ilkhanate and joined the alliance of Kaidu
Kaidu (; Middle Mongol: , Modern Mongol: , ''Khaidu'' ; c. 1235 – 1301) was a grandson of the Mongol khagan Ögedei (1185–1241) and thus leader of the House of Ögedei and the '' de facto'' khan of the Chagatai Khanate, a division of t ...
, another descendant of Genghis Khan who was the ruler of both the House of Ögedei
The House of Ögedei, sometimes called the Ögedeids, was an influential Mongol family and a branch of the Borjigin clan from the 12th to 14th centuries. They were descended from Ögedei (c. 1186–1241), a son of Genghis Khan who succeeded his ...
and the neighboring Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, also known as the Chagatai Ulus, was a Mongol and later Turkification, Turkicized khanate that comprised the lands ruled by Chagatai Khan, second son of Genghis Khan, and his descendants and successors. At its height in the l ...
. Ghazan spent the next ten years defending the frontier of the Ilkhanate against incursions by the Chagatai Khanate of Central Asia.
Under Gaykhatu
When his father, Arghun, died in 1291, Ghazan was prevented from pursuing his claim of leadership in the capital because he was engaged both with Nawruz's raids, and dealing with rebellion and famine in Khorasan andNishapur
Nishapur or Neyshabur (, also ) is a city in the Central District (Nishapur County), Central District of Nishapur County, Razavi Khorasan province, Razavi Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
Ni ...
. Taghachar
Taghachar, also spelled Tajir, Ta'achar (, ; died c. 1296) was a commander in the Mongol Empire's army. He was one of the conspirators involved in the overthrow of three Ilkhanate khans, and placed the short-lived Baydu on the throne in 1295.
Ba ...
, an army commander who had served the previous three generations of Ilkhans, was probably behind the death of Arghun, and supported Ghazan's uncle Gaykhatu
Gaykhatu (Mongolian script:; ) was the fifth Ilkhanate ruler in Iran. He reigned from 1291 to 1295. His Buddhist baghshi gave him the Tibetan name Rinchindorj () which appeared on his paper money.
Early life
He was born to Abaqa and Nukdan K ...
as the new Ilkhan. Despite being boyhood rivals, Gaykhatu sent aid to Ghazan's fight against Nawruz in Khorasan under the leadership of Prince Anbarchi (son of Möngke Temür Mongke Temur may refer to:
*Mengu-Timur
Mengu-Timur ( ) or Möngke Temür (; died 1280) was a son of Toqoqan Khan (himself the son of Batu) and Köchu Khatun of Oirat, the daughter of Toralchi Küregen and granddaughter of Qutuqa Beki. Men ...
) and emirs Tuladai, Quncuqbal and El Temür; himself going to Anatolia to quell Turcoman uprisings. However, famine reached his court too in spring and Anbarchi, unable to feed his soldiers, had to leave soon for Azerbaijan again. He again tried to visit Gaykhatu, but after his refusal, he had to go back. Ghazan received Kököchin
Kököchin, also Kökejin, Kūkājīn, Cocacin or Cozotine ( Mongolian: ; ), was a 13th-century princess of the Mongol-led Chinese Yuan dynasty, belonging to the Mongol Bayaut tribe. In 1291, she was betrothed to the Ilkhanate khan Arghun by t ...
, a Mongol princess from the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
in China, on his way back from Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
to Khorasan. She had been brought from the east in a caravan which included Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
among hundreds of other travellers. She had originally been betrothed to Ghazan's father, IlKhan Arghun, but since he had died during her months-long journey, she instead married his son Ghazan.
In 1294, Ghazan forced Nawruz to surrender at Nishapur
Nishapur or Neyshabur (, also ) is a city in the Central District (Nishapur County), Central District of Nishapur County, Razavi Khorasan province, Razavi Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
Ni ...
and Nawruz then became one of Ghazan's lieutenants. Ghazan was loyal to his uncle, though he refused to follow Gaykhatu's lead in introducing paper currency
Paper money, often referred to as a note or a bill (North American English), is a type of negotiable promissory note that is payable to the bearer on demand, making it a form of currency. The main types of paper money are government notes, which ...
to his province, explaining that the weather of Khorasan was too humid to handle paper.
Against Baydu
In 1295,Taghachar
Taghachar, also spelled Tajir, Ta'achar (, ; died c. 1296) was a commander in the Mongol Empire's army. He was one of the conspirators involved in the overthrow of three Ilkhanate khans, and placed the short-lived Baydu on the throne in 1295.
Ba ...
and his conspirators, who probably had been behind the death of Arghun, had his successor Gaykhatu killed as well. They then placed the pliable Baydu Baydu (Mongolian script:; ) (died 1295) was the sixth ruler of the Mongol empire's Ilkhanate division in Iran. He was the son of Taraqai, who was in turn the fifth son of Hulagu Khan.Stevens, John. ''The history of Persia. Containing, the lives and ...
, a cousin of Ghazan, on the throne. Baydu was primarily a figurehead, allowing the conspirators to divide the Ilkhanate among themselves. Hearing of Gaykhatu's murder, Ghazan marched on Baydu. Baydu explained that Ghazan was away during the events leading to Gaykhatu's fall, therefore nobles had no choice but to raise him to throne. Nevertheless, Amir Nowruz encouraged Ghazan to take steps against Baydu, because he was nothing but a figurehead under grips of nobles. Baydu's forces commanded by Ildar (his cousin and Prince Ajay's son), Eljidei and Chichak met him near Qazvin
Qazvin (; ; ) is a city in the Central District (Qazvin County), Central District of Qazvin County, Qazvin province, Qazvin province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is the largest city in the provi ...
. Ghazan's army were commanded by Prince Sogai (son of Yoshmut
Yoshmut () was an Ilkhanate prince and one of the eldest sons of Hulagu. According to Dai Matsui and Daniel King, his name was of Christian Uyghur origin and ultimately derived from the Sogdian word "''ʿywšmbt''" (cognate with ).
Life
He was ...
), Buralghi, Nowruz, Qutluqshah and Nurin Aqa. The first battle was won by Ghazan but he had to fall back after realising that Ildar's contingent was just a fraction of the whole army he faced, leaving Nowruz behind. Nevertheless, he captured Arslan, a descendant of Jochi Qasar.
After a short truce, Baydu offered Ghazan co-rulership of the Ilkhanate and offered Nowruz the post of ''sahib-i divan'' to which as a counter-condition Ghazan demanded the revenues of his father's hereditary lands in Fars, Persian Iraq
Persian Iraq, also uncommonly spelled Persian Irak ( ''Erāq-e Ajam'' or ''Erāq-e Ajami''; ''ʿIrāq al-ʿAjam'' or ''al-ʿIrāq al-ʿAjamī'', literally, "Iraq of the Ajam"), is a historical region of the western parts of Iran.
The region, ...
and Kerman
Kerman (; ) is a city in the Central District (Kerman County), Central District of Kerman County, Kerman province, Kerman province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district.
History
Kerman was founded as a def ...
. Nowruz refused these conditions, which led to his arrest. According to an anecdote, he promised to bring Ghazan back tied up on condition of his release. Once he reached Ghazan, he sent back a cauldron
A cauldron (or caldron) is a large cookware and bakeware, pot (kettle) for cooking or boiling over an open fire, with a lid and frequently with an arc-shaped hanger and/or integral handles or feet. There is a rich history of cauldron lore in r ...
to Baydu; a word play on the Turkish word kazan
Kazan; , IPA: Help:IPA/Tatar, ɑzanis the largest city and capital city, capital of Tatarstan, Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka (river), Kazanka Rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1. ...
. Nowruz promised him the throne and his help on condition of Ghazan's conversion to Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. Ghazan converted to Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any Succession to Muhammad, successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr ...
, on June 16, 1295, at the hands of Ibrahim ibn Muhammad ibn al-Mu'ayyid ibn Hamaweyh al-Khurasani al-Juwayni as a condition for Nawruz's military support. Nowruz entered Qazvin
Qazvin (; ; ) is a city in the Central District (Qazvin County), Central District of Qazvin County, Qazvin province, Qazvin province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is the largest city in the provi ...
with 4,000 soldiers and claimed an additional number of 120,000 soldiers commanded by Ebügen (in other sources, 30,000) – descendant of Jochi Qasar – on his way towards Azerbaijan which caused panic among masses which was followed by defections of Taghachar's subordinates (thanks to Taghachar's vizier Sadr ul-Din Zanjani) and other powerful emirs like Qurumishi and Chupan
Amir Chūpān (; died October/November 1327), also spelt Choban or Coban, was a Chupanids, Chupanid noble of the Ilkhanate, and nominal general of the Mongol Empire. He was ennobled by Yesün Temür (Yuan dynasty), Emperor Taiding of Yuan as Duke ...
on 28 August 1295.
Seeing imminent defeat, Baydu asked for Taghachar's support, ignorant of his defection. After realising Taghachar's withdrawal, he fled to Emir Tukal in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
on 26 September 1295. Ghazan's commanders found him near Nakhchivan and arrested him, taking back to Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
, having him executed on October 4, 1295.Early reign
Ghazan declared his victory after the execution of Baydu on the outskirts ofTabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
on 4 October 1295, he entered the city. After this declaration, several appointments, orders and executions came as usual – Gaykhatu's son Alafrang's son-in-law Eljidai Qushchi was executed, Nawrūz was rewarded with of state and was given extreme power, akin to Buqa
Buqa (or Bugha) (died January 16, 1289) was a Mongol lord and chancellor who was instrumental in sweeping Arghun to power as the fourth Il-Khan of Iran in 1284 and became his chief minister (vizier) and advisor, succeeding Shams ad-Din Juvayni ...
's back in the day of Arghun. Nawrūz, on his part, issued a formal edict in opposition to other religions in the Ilkhanate. Nawruz loyalists persecuted Buddhists and Christians to such an extent that Buddhism in Iran
Buddhism in Iran dates back to the 2nd century, when Parthian Buddhist missionaries, such as An Shigao and An Xuan, were active in spreading Buddhism in China. Many of the earliest translators of Buddhist literature into Chinese were from Parthi ...
never recovered, the Church of the East cathedral in the Mongol capital of Maragheh
Maragheh () is a city in the Central District (Maragheh County), Central District of Maragheh County, East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Maragheh is on the bank of ...
was looted, and churches in Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
and Hamadan
Hamadan ( ; , ) is a mountainous city in western Iran. It is located in the Central District of Hamadan County in Hamadan province, serving as the capital of the province, county, and district. As of the 2016 Iranian census, it had a po ...
were destroyed.
Baydu loyalists too were purged – emirs Jirghadai and Qonchuqbal were executed on 10 and 15 October respectively. Qonchuqbal was specifically hated for his murder of Aq Buqa Jalair, his executioner was Nawrūz's brother Hajji, who was also Aq Buqa's son-in-law. Taghachar's protege, Sadr al-Din Zanjani was granted the office of vizier following deposition of Baydu's vizier, Jamal al-Din. He reappointed Taghachar
Taghachar, also spelled Tajir, Ta'achar (, ; died c. 1296) was a commander in the Mongol Empire's army. He was one of the conspirators involved in the overthrow of three Ilkhanate khans, and placed the short-lived Baydu on the throne in 1295.
Ba ...
to the Anatolian viceroyalty on 10 November 1295. Another series of executions came after 1296: Prince Ajai's son Ildar fled to Anatolia on 6 February but was captured and executed; Yesütai, an Oirat commander who supported Hulegu's son-in-law Taraghai, in his migration to Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate (), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz from the mid-13th to early 16th centuries, with Cairo as its capital. It was ruled by a military caste of mamluks ...
Syria, was executed on 24 May and Buralghi Qiyatai, a commander who was rebellious against Arghun was executed on 12 February.
Meanwhile, Nogai Khan
Nogai, or Noğay ( Kypchak and Turki: نوغای; also spelled Nogay, Nogaj, Nohai, Nokhai, Noqai, Ngoche, Noche, Kara Nokhai, and Isa Nogai; died 1299/1300) was a general and kingmaker of the Golden Horde. His great grandfather was Jochi, son o ...
, kingmaker in the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
, was murdered and his wife Chubei fled to Ghazan with his son Torai (or Büri) who was Abaqa
Abaqa Khan (27 February 1234 – 4 April 1282, , "paternal uncle", also transliterated Abaġa), was the second Mongol ruler ('' Ilkhan'') of the Ilkhanate. The son of Hulagu Khan and Lady Yesünčin and the grandson of Tolui, he reigned from 1265 ...
's son-in-law in 1296.
Purge of nobles
Ghazan eased the troubles with theGolden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
, but the House of Ögedei
The House of Ögedei, sometimes called the Ögedeids, was an influential Mongol family and a branch of the Borjigin clan from the 12th to 14th centuries. They were descended from Ögedei (c. 1186–1241), a son of Genghis Khan who succeeded his ...
and Chagatais of Central Asia continued to pose a serious threat to both the Ilkhanate and his overlord and ally to the Great Khan in China. When Ghazan was crowned, the Chagatai khan
Chagatai Khan (; – 1242) was a son of Genghis Khan and a prominent figure in the early Mongol Empire. The second son of Genghis's wife Börte, Chagatai was renowned for his masterful knowledge of Mongol custom and law, which he scrupulously ...
Duwa
Duwa (; died 1307), also known as Du'a, was Khan of the Chagatai Khanate (1282–1307). He was the second son of Baraq. He was the longest reigning monarch of the Chagatayid Khanate and accepted the nominal supremacy of the Yuan dynasty as ...
invaded Khorasan on 9 December 1295. Ghazan sent two of his relatives, Prince Sogai (son of Yoshmut
Yoshmut () was an Ilkhanate prince and one of the eldest sons of Hulagu. According to Dai Matsui and Daniel King, his name was of Christian Uyghur origin and ultimately derived from the Sogdian word "''ʿywšmbt''" (cognate with ).
Life
He was ...
) and Esen Temür (son of Qonqurtai Qonqurtai () was a Mongol prince and viceroy of Anatolia for the Ilkhanate khanate.
Life
Qonqurtai was born to Hulagu Khan and Ajuja Aguchi, his Khitan people, Khitan Concubinage, concubine wife. Qonqurtai was Hulagu's ninth son and was the seni ...
), against the army of Chagatai Khanate, but they deserted, believing this was Nawrūz's plot to further deprive the nobility of their possessions. Nawrū informed Ghazan of this plot, subsequently executing them in 1296. Another Borjigid prince, Arslan who was captured by Ghazan previously and pardoned, revolted in Bilasuvar. After a series of battles near Baylaqan he too was captured and executed, along with the rebellious emirs on 29 March.
Following the purge of princes, Taghachar was thought to have been implicated in the rebellion of Prince Sogai and was declared a rebel. Taghachar strengthened himself in Tokat
Tokat is a city of Turkey in the mid-Black Sea region of Anatolia. It is the seat of Tokat Province and Tokat District.
and resisted against Ghazan's commanders Harmanji, Baltu and Arap (son of Samagar
Samagar, also Cemakar, was a Mongol general of the Il-Khan ruler Abaqa Khan (1234–1282), mentioned as leading a Mongol invasion force in 1271, in attempted coordination with the Ninth Crusade.
Background
Little is known about Samagar, but he ...
). He was soon arrested by Baltu near Delice
Delice is a town in Kırıkkale Province in the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. It is the seat of Delice District
Delice District is a district of the Kırıkkale Province of Turkey. Its seat is the town of Delice.Chormaqan
Chormaqan (also Chormagan or Chormaqan Noyan) (; Chagatai: جورماقان; Khalkha Mongolian: ; died was one of the most famous generals of the Mongol Empire under Genghis Khan and Ögedei Khan. He was also a member of the keshik.
Career
A ...
's grandson Baighut on 7 September 1296, Hazaraspid ruler Afrasiab I in October 1296, Baydu's vizier Jamal ud-Din Dastgerdani on 27 October 1296.
Revolt of Baltu
Taghachar's death triggered the revolt of Baltu of theJalayir
Jalair (; ; ), also Djalair, Yyalair, Jalayir, is one of the Darliqin Mongol tribes according to Rashid-al-Din Hamadani's ''Jami' al-tawarikh''.They lived along the Orkhon River in modern day Central Mongolia.History of Mongolia, Volume II, 2003 ...
, in Anatolia, where he was stationed since Abaqa's reign. He was supported by Ildar (son of Qonqurtai Qonqurtai () was a Mongol prince and viceroy of Anatolia for the Ilkhanate khanate.
Life
Qonqurtai was born to Hulagu Khan and Ajuja Aguchi, his Khitan people, Khitan Concubinage, concubine wife. Qonqurtai was Hulagu's ninth son and was the seni ...
), who was arrested and executed in September 1296. Two months later, Qutluqshah invaded Anatolia with 30,000 men and crushed Baltu's revolt, arresting him in June. He was brought to Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
and jailed there until 14 September 1297, when he was executed along with his son. Seljuk Sultan of Rum Mesud II
Ghiyath al-Dīn Me’sud ibn Kaykaus or Mesud II (, ''Ghiyāth ad-Dīn Mas'ūd bin Kaykāwūs''; , ) bore the title of Sultan of Rûm at various times between 1284 and 1308. He was a vassal of the Mongols under Mahmud Ghazan and exercised no re ...
on the other hand was arrested and jailed in Hamadan
Hamadan ( ; , ) is a mountainous city in western Iran. It is located in the Central District of Hamadan County in Hamadan province, serving as the capital of the province, county, and district. As of the 2016 Iranian census, it had a po ...
.
Fall of Nawrūz
Nawrūz soon embroiled himself in an argument with Nurin Aqa, who was more popular with the military and then leftKhorasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West and Central Asia that encompasses western and no ...
. After returning to the west, he survived an assassination attempt by a soldier named Tuqtay, who claimed that Nawrūz murdered his father, Arghun Aqa
Arghun Agha, also Arghun Aqa or Arghun the Elder (; ; - 1275) was a Mongol noble of the Oirat clan in the 13th century. He was a governor in the Mongol-controlled area of Persia from 1243 to 1255, before the Ilkhanate was created by Hulagu. Ar ...
. Soon he was accused of treason by Sadr al-Din Khaladi, ''sahib-divan'' of Ghazan by a secret alliance with the Mamlukes. Indeed, according to Mamluk sources, Nawrūz corresponded with Sultan Lajin. Using the opportunity, Ghazan started a purge against Nawrūz and his followers in May 1297. His brother Hajji Narin and his follower Satalmish were executed, along with Nawrūz's children in Hamadan
Hamadan ( ; , ) is a mountainous city in western Iran. It is located in the Central District of Hamadan County in Hamadan province, serving as the capital of the province, county, and district. As of the 2016 Iranian census, it had a po ...
, his other brother Lagzi Güregen was also put to death in Iraq on 2 April 1297. His 12-year-old son Toghai was spared due to efforts of Bulughan Khatun Khurasani, Ghazan's wife Arghun Aqa
Arghun Agha, also Arghun Aqa or Arghun the Elder (; ; - 1275) was a Mongol noble of the Oirat clan in the 13th century. He was a governor in the Mongol-controlled area of Persia from 1243 to 1255, before the Ilkhanate was created by Hulagu. Ar ...
's granddaughter and given to the household of Amir Husayn. Others who were spared, were his brother Yol Qutluq and his nephew Kuchluk. Later that year Ghazan marched against Nawrūz himself, who at the time was the commander of the army of Khorasan. Ghazan's forces were victorious at a battle near Nishapur. Nawrūz took refuge at the court of the king of Herat
Herāt (; Dari/Pashto: هرات) is an oasis city and the third-largest city in Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Se ...
in northern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, but the Malik betrayed him and delivered Nawrūz to Kutlushah
Kutlushah, Kutlusha or Qutlughshah (, , or Cotlesse in Frank sources), was a general under the Mongol Ilkhanate ruler Ghazan at the end the 13th century. He was particularly active in the Christian country of Georgia and especially during the M ...
, who had Nawrūz executed immediately on August 13.Roux, p. 432
Relationship with other Mongol khanates
Ghazan maintained strong ties with the Great Khan of the Yuan and the Golden Horde. In 1296Temür Khan
Öljeyitü Khan ( Mongolian: Өлзийт; Mongolian script: '; zh, t=完澤篤汗), born Temür ( ; zh , t = 鐵穆耳 ; 15 October 1265 – 10 February 1307), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzong of Yuan ( zh , c = 元成� ...
, the successor of Kublai Khan, dispatched a military commander, Baiju, to Mongol Persia. Five years later Ghazan sent his Mongolian and Persian retainers to collect income from Hulegu's holdings in China. While there, they presented tribute to Temür and were involved in cultural exchanges across Mongol Eurasia. Ghazan also called upon other Mongol Khans to unite their will under Temür Khan, in which he was supported by Kaidu's enemy, Bayan Khan of the White Horde
The White Horde (, ; ), or more appropriately, the left wing of the Jochid ulus, was one of the uluses within the Mongol Empire formed around 1225, after the death of Jochi when his son, Orda, inherited his father's appanage by the Jaxartes. It ...
. Ghazan's court had Chinese physicians present.
Later reign
In order to stabilize the country Ghazan attempted to control the situation and continued the executions – Taiju (son ofMöngke Temür Mongke Temur may refer to:
*Mengu-Timur
Mengu-Timur ( ) or Möngke Temür (; died 1280) was a son of Toqoqan Khan (himself the son of Batu) and Köchu Khatun of Oirat, the daughter of Toralchi Küregen and granddaughter of Qutuqa Beki. Men ...
) on 15 April 1298 on charges of sedition
Sedition is overt conduct, such as speech or organization, that tends toward rebellion against the established order. Sedition often includes subversion of a constitution and incitement of discontent toward, or insurrection against, establ ...
, vizier Sadr ul-Din Zanjani on 4 May and his brother Qutb ul-Din and with cousin Qawam ul-Mulk on 3 June on charges of embezzlement
Embezzlement (from Anglo-Norman, from Old French ''besillier'' ("to torment, etc."), of unknown origin) is a type of financial crime, usually involving theft of money from a business or employer. It often involves a trusted individual taking ...
, Abu Bakr Dadqabadi on 10 October. Ghazan appointed a Jewish convert to Islam – Rashid-al-Din Hamadani
Rashīd al-Dīn Ṭabīb (; 1247–1318; also known as Rashīd al-Dīn Faḍlullāh Hamadānī, ) was a statesman, historian, and physician in Ilkhanate Iran. Ghazan also commissioned Rashid-al-Din to produce a history of the Mongols and their dynasty, the ''
 Ghazan was one of a long line of Mongol leaders who engaged in diplomatic communications with the Europeans and
Ghazan was one of a long line of Mongol leaders who engaged in diplomatic communications with the Europeans and  In February 1301, the Mongols advanced again with a force of 60,000, but could do little else than engage in some raids around Syria. Ghazan's general
In February 1301, the Mongols advanced again with a force of 60,000, but could do little else than engage in some raids around Syria. Ghazan's general
 As part of his conversion to Islam, Ghazan changed his first name to the Islamic ''Mahmud'', and Islam gained popularity within Mongol territories. He showed tolerance for multiple religions, encouraged the original archaic Mongol culture to flourish, tolerated the shias, and respected the religions of his Georgian and
As part of his conversion to Islam, Ghazan changed his first name to the Islamic ''Mahmud'', and Islam gained popularity within Mongol territories. He showed tolerance for multiple religions, encouraged the original archaic Mongol culture to flourish, tolerated the shias, and respected the religions of his Georgian and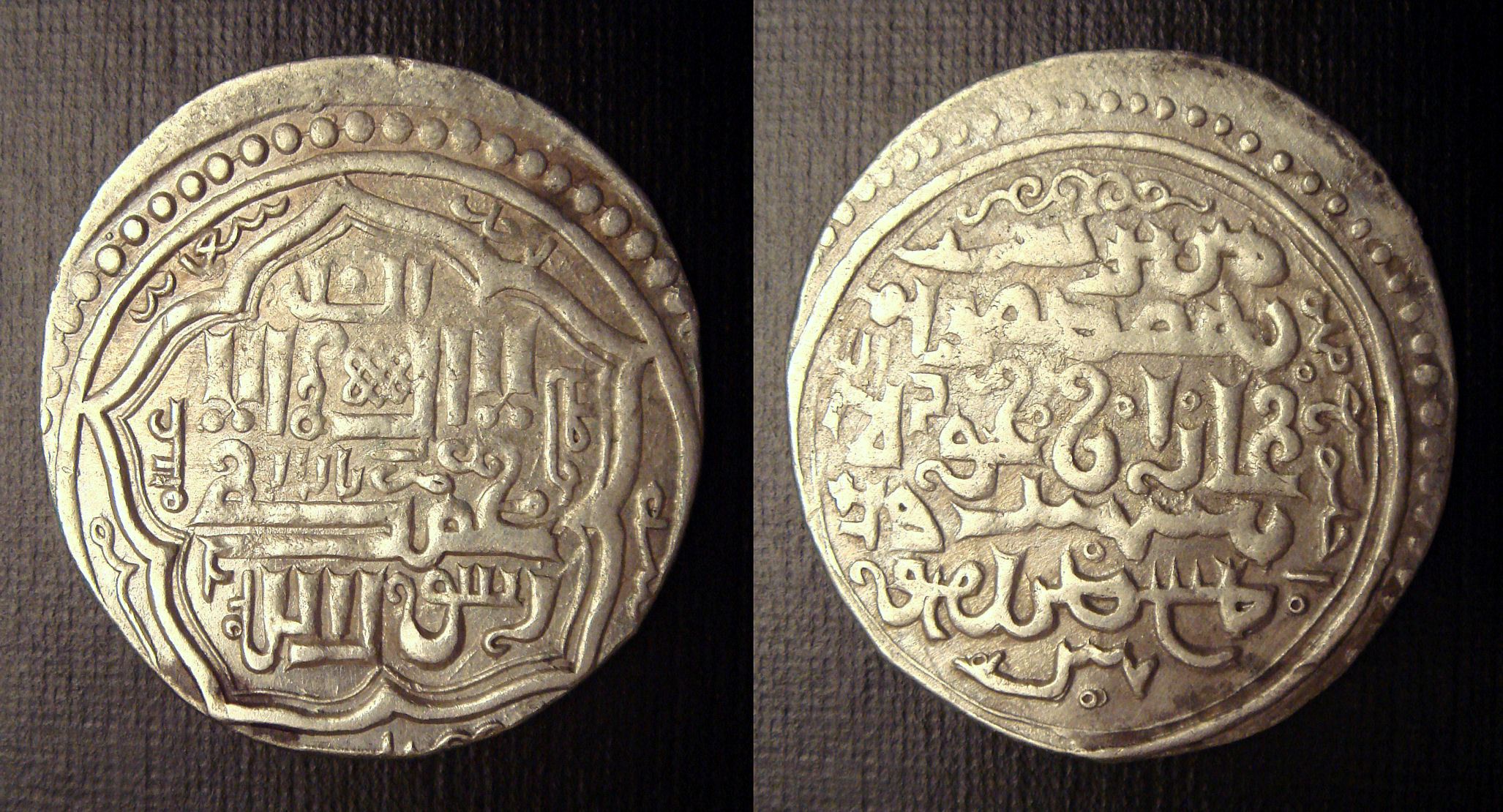 
 Ghazan had nine wives, 6 of them being principal wives and one being concubine:
*Yedi Kurtka Khatun – daughter of Möngke Temür Güregen (from
Ghazan had nine wives, 6 of them being principal wives and one being concubine:
*Yedi Kurtka Khatun – daughter of Möngke Temür Güregen (from
Online
(English translation). * * *Encyclopædia Iranica
* * Foltz, Richard, ''Religions of the Silk Road'', Palgrave Macmillan, 2nd edition, 2010 * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control 1271 births 1304 deaths Il-Khan emperors Mongol Empire Muslims 13th-century monarchs in Asia 14th-century monarchs in Asia 14th-century crusades Converts to Islam from Christianity
Jami' al-Tawarikh
''Jāmiʿ al-Tawārīkh'' () is a work of literature and history, produced in the Mongol Ilkhanate. Written by Rashid al-Din Hamadani (1247–1318 AD) at the start of the 14th century, the breadth of coverage of the work has caused it to be call ...
'' "Compendium of Chronicles" or ''Universal History''. Over several years of expansion, the work grew to cover the entire history of the world since the time of Adam
Adam is the name given in Genesis 1–5 to the first human. Adam is the first human-being aware of God, and features as such in various belief systems (including Judaism, Christianity, Gnosticism and Islam).
According to Christianity, Adam ...
, and was completed during the reign of Ghazan's successor, Öljaitü. Many copies were made, a few of which survive to the modern day.
After Taiju's execution, he appointed Nurin Aqa as viceroy of Arran on 11 September 1298.
Revolt of Sulemish
Sulemish, who Qutlughshah appointed as viceroy inAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
after Baltu's revolt, rebelled himself in 1299. He assembled a 20,000 strong force, which postponed Ghazan's plan to invade Mamluk-controlled Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
. Qutlughshah was forced to come back from Arran and won a victory against him, on 27 April 1299 near Erzincan
Erzincan (; ), historically Yerznka (), is the capital of Erzincan Province in eastern Turkey. Nearby cities include Erzurum, Sivas, Tunceli, Bingöl, Elazığ, Malatya, Gümüşhane, Bayburt, and Giresun. The city is majority Turkish Sunni w ...
, causing the rebels to flee to Mamluk Egypt
The Mamluk Sultanate (), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz from the mid-13th to early 16th centuries, with Cairo as its capital. It was ruled by a military caste of mamluks ...
. He returned with Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
reinforcements to Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
but was defeated again. He was brought to Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
and executed by burning on 27 September 1299.
Mamluk-Ilkhanid War
Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding ...
in attempts to form a Franco-Mongol alliance
Several attempts at a military alliance between the Franks#Crusaders and other Western Europeans as "Franks", Frankish Crusaders and the Mongol Empire against the Islamic caliphates, their common enemy, were made by various leaders among them dur ...
against their common enemy, primarily the Egyptian Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate (), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz from the mid-13th to early 16th centuries, with Cairo as its capital. It was ruled by a military caste of mamluks ...
. He already had the use of forces from Christian vassal countries such as Cilician Armenia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, also known as Cilician Armenia, Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia, was an Armenians, Armenian state formed during the High Middle Ages b ...
and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
. The plan was to coordinate actions between Ghazan's forces, the Christian military orders, and the aristocracy of Cyprus to defeat the Egyptian Mamluks, after which Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
would be returned to the European Crusaders. Many Europeans are known to have worked for Ghazan, such as Isol the Pisan or Buscarello de Ghizolfi, often in high positions. Hundreds of such Western adventurers entered into the service of Mongol rulers. According to historian Peter Jackson
Sir Peter Robert Jackson (born 31 October 1961) is a New Zealand filmmaker. He is best known as the director, writer, and producer of the ''Lord of the Rings'' trilogy (2001–2003) and the ''Hobbit'' trilogy (2012–2014), both of which ar ...
, the 14th century saw such a vogue of Mongol things in the West that many new-born children in Italy were named after Mongol rulers, including Ghazan: names such as ''Can Grande'' ("Great Khan"), ''Alaone'' (Hulegu
Hulegu Khan, also known as Hülegü or Hulagu; ; ; ; ( 8 February 1265), was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of Western Asia. As a son of Tolui and the Keraite princess Sorghaghtani Beki, he was a grandson of Genghis Khan and brother of Ari ...
, Ghazan's great-grandfather), ''Argone'' (Arghun
Arghun Khan ( Mongolian Cyrillic: Аргун; Traditional Mongolian: ; c. 1258 – 10 March 1291) was the fourth ruler of the Mongol empire's Ilkhanate division, from 1284 to 1291. He was the son of Abaqa Khan, and like his father, was a de ...
, Ghazan's father) or ''Cassano'' (Ghazan) were recorded with a high frequency.
In October 1299, Ghazan marched with his forces towards Syria and invited the Christians to join him. His army took the city of Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
, and was there joined by his vassal King Hethum II
Hethum II, OFM (; 1266– 17 November 1307) was king of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia from 1289 to 1293, 1295 to 1296 and 1299 to 1303, while Armenia was a subject state of the Mongol Empire. He abdicated twice to take vows with the Franciscan ...
of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, also known as Cilician Armenia, Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia, was an Armenian state formed during the High Middle Ages by Armenian ...
, whose forces included some Templars
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a military order of the Catholic faith, and one of the most important military orders in Western Christianity. They were founded in 11 ...
and Hospitallers
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), is a Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there ...
, and who participated in the rest of the offensive. The Mongols and their allies defeated the Mamluks in the Battle of Wadi al-Khazandar
The Battle of Wadi al-Khaznadar, also known as the Third Battle of Homs, was a Mongol victory over the Mamluks in 1299.''Wadi 'L-Khaznadar'', R. Amitai, The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Vol XI, ed. P.J.Bearman, T.Bianquis, C.E.Bosworth, E. van Don ...
, on December 23 or 24, 1299. One group of Mongols then split off from Ghazan's army and pursued the retreating Mamluk troops as far as Gaza, pushing them back to Egypt. The bulk of Ghazan's forces proceeded to Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
, which surrendered somewhere between December 30, 1299, and January 6, 1300, though its Citadel
A citadel is the most fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of ''city'', meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
...
resisted.Demurger, p. 142. Most of Ghazan's forces then retreated in February, probably because their horses needed fodder. He promised to return in the winter of 1300–1301 to attack Egypt.Schein, 1979, p. 810 About 10,000 horsemen under the Mongol general Mulay
Mulay, Mûlay, Bulay ( or Molay for the Franks, ) was a general under the Mongol Ilkhanate ruler Ghazan at the end of the 13th century. Mulay was part of the 1299–1300 Mongol offensive in Syria and Palestine, and remained with a small force t ...
were left to briefly rule Syria, before they too retreated due to Mamluk raids.
Ghazan was indeed feared and despised by the Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
s, who sent a delegation of leading scholars and imam
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Salah, Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, ...
s including Ibn Taymiyya
Ibn Taymiyya (; 22 January 1263 – 26 September 1328)Ibn Taymiyya, Taqi al-Din Ahmad, The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-959 was a Sunni Muslim schola ...
, north from Damascus to al-Nabk
An-Nabek or Al-Nabek () is a Syrian city administratively belonging to Rif Dimashq and the capital of the Qalamoun. It is located north of Damascus and south of Homs and has an altitude of . According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics ...
, where Ghazan was encamped, in January 1300, in order to persuade Ghazan to stop his attack on Damascus. Ibn Taymiyya also may have met the envoys of Ghazan, including the qadi Diya' al-Din Muhammad, in Damascus in August 1301. On one of these occasions, it is reported that not one of the scholars dared to say anything to Ghazan except Ibn Taymiyyah
Ibn Taymiyya (; 22 January 1263 – 26 September 1328)Ibn Taymiyya, Taqi al-Din Ahmad, The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-959 was a Sunni Muslim ulama, ...
who said:
''"You claim that you are a Muslim and you have with you Mu'adhdhins, Mufti
A mufti (; , ) is an Islamic jurist qualified to issue a nonbinding opinion ('' fatwa'') on a point of Islamic law (''sharia''). The act of issuing fatwas is called ''iftāʾ''. Muftis and their ''fatāwa'' have played an important role thro ...
s, Imam
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Salah, Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, ...
s and Shaykh
Sheikh ( , , , , ''shuyūkh'' ) is an honorific title in the Arabic language, literally meaning "elder (administrative title), elder". It commonly designates a tribal chief or a Muslim ulama, scholar. Though this title generally refers to me ...
s but you invaded us and reached our country for what? Although your father and your grandfather, Hulegu
Hulegu Khan, also known as Hülegü or Hulagu; ; ; ; ( 8 February 1265), was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of Western Asia. As a son of Tolui and the Keraite princess Sorghaghtani Beki, he was a grandson of Genghis Khan and brother of Ari ...
were non-believers, they did not attack us and they kept their promise. But you promised and broke your promise."''
In July 1300, the Crusaders formed a small fleet of sixteen galleys with some smaller vessels to raid the coast, and Ghazan's ambassador traveled with them.Demurger, p. 147.Schein, 1979, p. 811. The Crusader forces also attempted to establish a base at the small island of Ruad, from which raids were launched on Tartus
Tartus ( / ALA-LC: ''Ṭarṭūs''; known in the County of Tripoli as Tortosa and also transliterated from French language, French Tartous) is a major port city on the Mediterranean coast of Syria. It is the second largest port city in Syria (af ...
while awaiting Ghazan's forces. However, the Mongol army was delayed, and the Crusader forces retreated to Cyprus, leaving a garrison on Ruad which was besieged and captured by Mamluks by 1303 (see Siege of Ruad
The fall of Ruad in 1302 was one of the culminating events of the Crusades in the Eastern Mediterranean. In 1291, the Crusaders had lost their main power base at the coastal city of Acre, and the Muslim Mamluks had been systematically destroying ...
).
Kutlushah
Kutlushah, Kutlusha or Qutlughshah (, , or Cotlesse in Frank sources), was a general under the Mongol Ilkhanate ruler Ghazan at the end the 13th century. He was particularly active in the Christian country of Georgia and especially during the M ...
stationed 20,000 horsemen in the Jordan Valley to protect Damascus, where a Mongol governor was stationed.Jean Richard, p. 481. But again, they were soon forced to withdraw.
Plans for combined operations with the Crusaders were again made for the following winter offensive, and in late 1301, Ghazan asked Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII (; born Benedetto Caetani; – 11 October 1303) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 December 1294 until his death in 1303. The Caetani family was of baronial origin with connections to the p ...
to send troops, priests, and peasants, in order to make the Holy Land a Frank state again. But again, Ghazan did not appear with his own troops. He wrote again to the Pope in 1302, and his ambassadors also visited the court of Charles II of Anjou
Charles II, also known as Charles the Lame (; ; 1254 – 5 May 1309), was King of Naples, Count of Provence and Forcalquier (1285–1309), Prince of Achaea (1285–1289), and Count of Anjou and Maine (1285–1290); he also was King of Albania (12 ...
, who on April 27, 1303, sent Gualterius de Lavendel as his own ambassador back to Ghazan's court.
In 1303, Ghazan sent another letter to Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
via Buscarello de Ghizolfi, reiterating his great-grandfather Hulegu Khan's promise that the Mongols would give Jerusalem to the Franks in exchange for help against the Mamluks. The Mongols, along with their Armenian vassals, had mustered a force of about 80,000 to repel the raiders of the Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, also known as the Chagatai Ulus, was a Mongol and later Turkification, Turkicized khanate that comprised the lands ruled by Chagatai Khan, second son of Genghis Khan, and his descendants and successors. At its height in the l ...
, which was under the leadership of Qutlugh Khwaja
Qutlugh Khwaja ( Chagatai and Persian: قتلغ خواجه; d. 1299/1300) was a son of Duwa, the Mongol khan of Chagatai Khanate, a division of the Mongol Empire. He became a chief of the Qara'unas in Afghanistan after Abdullah was recalled by th ...
. After their success there, they advanced again towards Syria. However, Ghazan's forces were utterly defeated by the Mamluks just south of Damascus at the decisive Battle of Marj al-Saffar in April 1303.Demurger, p. 158. It was to be the last major Mongol invasion of Syria.
End of reign
After military campaigns, Ghazan returned to his capital Ujan in July 1302 and made several appointments: Nirun Aqa andÖljaitü
Öljaitü, also known as Mohammad-e Khodabandeh (24 March 1282 – 16 December 1316), was the eighth Ilkhanid dynasty ruler from 1304 to 1316 in Tabriz, Iran. His name 'Öjaitü' means 'blessed' in the Mongolian language and his last name 'Khod ...
were reconfirmed in Arran and Khorasan as viceroys respectively, while Mulay
Mulay, Mûlay, Bulay ( or Molay for the Franks, ) was a general under the Mongol Ilkhanate ruler Ghazan at the end of the 13th century. Mulay was part of the 1299–1300 Mongol offensive in Syria and Palestine, and remained with a small force t ...
was sent to Diyarbakir and Qutluqshah was assigned to Georgia. He received a concubine from Andronikos II Palaiologos
Andronikos II Palaiologos (; 25 March 1259 – 13 February 1332), Latinization of names, Latinized as Andronicus II Palaeologus, reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1282 to 1328. His reign marked the beginning of the recently restored em ...
in 1302, who may be the Despina Khatun that later married to Öljaitü. On 17 September 1303, Ghazan betrothed his daughter Öljei Qutlugh to Bistam, son of his brother Öljaitü
Öljaitü, also known as Mohammad-e Khodabandeh (24 March 1282 – 16 December 1316), was the eighth Ilkhanid dynasty ruler from 1304 to 1316 in Tabriz, Iran. His name 'Öjaitü' means 'blessed' in the Mongolian language and his last name 'Khod ...
.
According to Rashid al-Din, Ghazan became depressed after his wife Karamun's death on 21 January. He once told his amirs that "life was a prison... and is not a benefit". Later in March/April, he nominated his brother Öljaitü as his successor, as he had no son his own. Eventually, he died on 11 May 1304 near Qazvin
Qazvin (; ; ) is a city in the Central District (Qazvin County), Central District of Qazvin County, Qazvin province, Qazvin province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is the largest city in the provi ...
. He was bathed in the water of Lar Damavand
Mount Damavand ( ) is a dormant stratovolcano and is the highest peak in Iran and Western Asia, the highest volcano in Asia, and the 3rd highest volcano in the Eastern Hemisphere (after Mount Kilimanjaro and Mount Elbrus), at an elevation o ...
valley of Mazandaran
Mazandaran Province (; ) is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Its capital is the city of Sari, Iran, Sari. Located along the southern coast of the Caspian Sea and in the adjacent Central Alborz mountain range and Hyrcanian forests, it is border ...
.
Ghazan himself appears to have dabbled in Sufism. According to the testimony of Shaykh Sadr al-Din Ibrahim Hammuiya, recorded in several Mamluk sources, Ghazan was given a woolen coat by him, indicating that perhaps the Ilkhan was initiated as a Sufi. This is not to say that Ghazan's relations with Sufis were trouble-free. In 703/1303, word came to him of a conspiracy of Sufi shaykhs and others to depose and replace him with his cousin, Ala Fireng, son of the Ilkhan Gaykhatu (r. 1291–95).
Legacy
Religious policy
 As part of his conversion to Islam, Ghazan changed his first name to the Islamic ''Mahmud'', and Islam gained popularity within Mongol territories. He showed tolerance for multiple religions, encouraged the original archaic Mongol culture to flourish, tolerated the shias, and respected the religions of his Georgian and
As part of his conversion to Islam, Ghazan changed his first name to the Islamic ''Mahmud'', and Islam gained popularity within Mongol territories. He showed tolerance for multiple religions, encouraged the original archaic Mongol culture to flourish, tolerated the shias, and respected the religions of his Georgian and Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
vassals. Ghazan therefore continued his forefather's approach toward religious tolerance
Religious tolerance or religious toleration may signify "no more than forbearance and the permission given by the adherents of a dominant religion for other religions to exist, even though the latter are looked on with disapproval as inferior, ...
. When Ghazan learned that some Buddhist monks feigned conversion to Islam due to their temples being earlier destroyed, he granted permission to all who wished to return to Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
or Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
and other regions in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
where they could freely follow their faith and be among other Buddhists. The Mongol Yassa
The Yassa (alternatively ''Yasa'', ''Yasaq'', ''Jazag'' or ''Zasag''; ) was the oral law code of the Mongols, gradually built up through the reign of Genghis Khan. It was the '' de facto'' law of the Mongol Empire, even though the "law" was kep ...
code remained in place and Mongol shamans remained politically influential throughout the reign of both Ghazan and his brother and successor Öljaitü
Öljaitü, also known as Mohammad-e Khodabandeh (24 March 1282 – 16 December 1316), was the eighth Ilkhanid dynasty ruler from 1304 to 1316 in Tabriz, Iran. His name 'Öjaitü' means 'blessed' in the Mongolian language and his last name 'Khod ...
, but ancient Mongol traditions eventually went into decline after Öljaitü's demise. Other religious upheaval in the Ilkhanate during Ghazan's reign was instigated by Nawruz, Ghazan put a stop to these exactions by issuing an edict exempting the Christians from the ''jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
'' (tax on non-Muslims), and re-established the Christian Patriarch Mar Yaballaha III
Yahballaha III ( 1245–13 November 1317), known in earlier years as Rabban Marcos (or Markos) was Patriarch of the East from 1281 to 1317. As patriarch, Yahballaha headed the Church of the East during the severe Persecution of Christians, ...
in 1296. Ghazan reportedly punished religious fanatics who destroyed churches and synagogues in Tabriz on 21 July 1298.

Reforms
Ghazan was a man of high culture, with many hobbies including linguistics, agro-techniques, painting, and chemistry. According to theByzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
historian Pachymeres (1242–1310): "No one surpassed him, in making saddles, bridles, spurs, greaves and helmets; he could hammer, stitch and polish, and in such occupations employed the hours of his leisure from war." Ghazan spoke numerous languages, including Chinese, Arabic, and "Frank" (probably Latin), as well as his own native language Mongolian.
In addition to his religious deep impact on Persia, Ghazan had unified measures, coinage
Coinage may refer to:
* Coins, standardized as currency
* Coining (mint), the process of manufacturing coins
* '' COINage'', a numismatics magazine
* Tin coinage, a tax on refined tin
* Coinage, a protologism or neologism
In linguistics, a neolo ...
and weights in the Ilkhanate. He ordered a new census in Persia to define the Dynasty's fiscal policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection ( taxes or tax cuts) and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variab ...
. He began to reuse wilderness, non-producing and abandoned lands to raise crops, strongly supporting the use and introduction of Eastern Asian crops in Persia, and improved the Yam system. He constructed hostels, hospitals, schools, and posts. Envoys from the court received a per diem stipend
A stipend is a regular fixed sum of money paid for services or to defray expenses, such as for scholarship, internship, or apprenticeship. It is often distinct from an income or a salary because it does not necessarily represent payment for work pe ...
, and those of the nobility traveled at their own expense. Ghazan ordered only envoys bearing urgent military intelligence to use the staffed postal relay service. Mongol soldiers were given by the Ilkhanid court, where they were allowed to gather revenue provided by a piece of land. Ghazan also banned lending at interest.
Ghazan reformed the issuance of '' jarliqs'' (edicts), creating set forms and graded seals, ordering that all jarliqs be kept on file at court. Jarliqs older than 30 years were to be cancelled, along with old paiza
A paiza or paizi or gerege (, , ''pāiza'', ''páizi'') was a tablet carried by Mongol officials and envoys to signify certain privileges and authority. They enabled Mongol nobles and officials to demand goods and services from civilian populatio ...
s (Mongol seals of authority). He fashioned new paizas into two ranks, which contained the names of the bearers on them to prevent them from being transferred. Old paizas were also to be turned in at the end of the official's term.
In fiscal policy, Ghazan introduced a unified bi-metallic currency including Ghazani dananeer ( plural of dinar ), and reformed purchasing procedures, replacing the traditional Mongol policy on craftsmen in the Ilkhanate, such as organizing purchases of raw materials and payment to artisans
An artisan (from , ) is a skilled worker, skilled craft worker who makes or creates material objects partly or entirely by handicraft, hand. These objects may be wikt:functional, functional or strictly beauty, decorative, for example furnit ...
. He also opted to purchase most weapons on the open market.
On coins, Ghazan omitted the name of the Great Khan
Khagan or Qaghan ( Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=大汗, p=Dàhán; ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of imperial ...
, instead inscribing his own name upon his coins in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
. But he continued to diplomatic and economic relations with the Great Khan at Dadu. In Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, he minted coins with the traditional Mongolian formula "Struck by the Ilkhan Ghazan in the name of Khagan" because he wanted to secure his claim on the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
with the help of the Great Khans of the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
. He also continued to use the Great Khan's Chinese seal which declared him to be a wang (prince) below the Great Khan.Mostaert and Cleaves ''Trois documents'', p. 483.
His reforms also extended to the military, as several new guard units, mostly Mongols, were created by Ghazan for his army center. However, he restricted new guards' political significance. Seeing Mongol commoners selling their children into slavery as damaging to both the manpower and the prestige of the Mongol army, Ghazan budgeted funds to redeem Mongol slave boys, and made his minister Bolad
Bolad ( Mongolian: , , , d.1313), was an ethnic Mongol minister of the Yuan dynasty of China, and later served in the Ilkhanate as the representative of the Great Khan of the Mongol Empire and cultural adviser to the Ilkhans. He also provided val ...
(the ambassador of the Great Khan Kublai) commander of a military unit of redeemed Mongol slaves.
Family
 Ghazan had nine wives, 6 of them being principal wives and one being concubine:
*Yedi Kurtka Khatun – daughter of Möngke Temür Güregen (from
Ghazan had nine wives, 6 of them being principal wives and one being concubine:
*Yedi Kurtka Khatun – daughter of Möngke Temür Güregen (from Suldus
The Taichuud (; ) was one of the three core tribes of the Khamag Mongol confederation in the Mongolian Plateau during the 12th century, its first recorded with Ambaghai Khan in 1148 AD, however this Clan founded by Ambaghais grandfather Chirhya L ...
tribe) and Tuglughshah Khatun (daughter of Qara Hülegü
Qara Hülegü (died 1252) was head of the ''ulus'' of the Chagatai Khanate (1242–1246, 1252).
He was the son of Mutukan (killed during the siege of Bamyan), who was the favored son of Chagatai Khan. He was nominated by Chagatai Khan, as well ...
)
*Bulughan Khatun Khurasani – daughter of Amir Tasu (from Eljigin
The Eljigin people are a Khalkha Mongolian sub-ethnic group. They live in Uvs province. The name sounds similar to Mongolian word "el" for "this" and to Turkic word " tegin" for "lord"
References
{{Mongol Yastan, state=uncollapsed
Mongol pe ...
clan of Khongirad
The Khongirad (; ; ; ) was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Their homeland was located in the vicinity of Hulun Lake, Lake Hulun in Inner Mongolia and Khalkha River in Mongolia,M. Sanjdorj, History of the Mongolian People's Repub ...
) and Menglitegin, daughter of Arghun Aqa
Arghun Agha, also Arghun Aqa or Arghun the Elder (; ; - 1275) was a Mongol noble of the Oirat clan in the 13th century. He was a governor in the Mongol-controlled area of Persia from 1243 to 1255, before the Ilkhanate was created by Hulagu. Ar ...
*#A stillborn son (born 1291 in Damavand
Mount Damavand ( ) is a dormant stratovolcano and is the highest peak in Iran and Western Asia, the highest volcano in Asia, and the 3rd highest volcano in the Eastern Hemisphere (after Mount Kilimanjaro and Mount Elbrus), at an elevation o ...
)
*Kököchin
Kököchin, also Kökejin, Kūkājīn, Cocacin or Cozotine ( Mongolian: ; ), was a 13th-century princess of the Mongol-led Chinese Yuan dynasty, belonging to the Mongol Bayaut tribe. In 1291, she was betrothed to the Ilkhanate khan Arghun by t ...
Khatun (b. 1269, m. 1293 at Abhar
Abhar () is a city in the Central District of Abhar County, Zanjan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Abhar has historically served as a place of importance due to lying right between the cities of Qazvin ...
, d. 1296) – relative of Buluqhan Khatun
Buluqhan Khatun (; Mongolian: , lit. 'Sable'), also Bulughan, Bulukhan, Bolgana, Bulugan, Zibeline or ''Bolghara'' for Marco Polo, was a 13th-century Mongol princess, and the principal wife of the Mongol Ilkhanid ruler Abaqa (1234–1282).
...
*Bulughan Khatun Muazzama (m. 17 October 1295 at Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
, d. 5 January 1310) – daughter of Otman Noyan (from Khongirad
The Khongirad (; ; ; ) was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Their homeland was located in the vicinity of Hulun Lake, Lake Hulun in Inner Mongolia and Khalkha River in Mongolia,M. Sanjdorj, History of the Mongolian People's Repub ...
tribe), widow of Gaykhatu
Gaykhatu (Mongolian script:; ) was the fifth Ilkhanate ruler in Iran. He reigned from 1291 to 1295. His Buddhist baghshi gave him the Tibetan name Rinchindorj () which appeared on his paper money.
Early life
He was born to Abaqa and Nukdan K ...
and Arghun
Arghun Khan ( Mongolian Cyrillic: Аргун; Traditional Mongolian: ; c. 1258 – 10 March 1291) was the fourth ruler of the Mongol empire's Ilkhanate division, from 1284 to 1291. He was the son of Abaqa Khan, and like his father, was a de ...
*# Uljay Qutlugh Khatun – married firstly to Bistam, son of Öljaitü
Öljaitü, also known as Mohammad-e Khodabandeh (24 March 1282 – 16 December 1316), was the eighth Ilkhanid dynasty ruler from 1304 to 1316 in Tabriz, Iran. His name 'Öjaitü' means 'blessed' in the Mongolian language and his last name 'Khod ...
, married secondly to his brother Abu Sa'id
*#Alju (b. 22 February 1298 in Arran – 20 August 1300 in Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
)
*Eshil Khatun (betrothed in 1293, married on 2 July 1296 at Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the distric ...
, d. 5 August 1309, bur. Shanb Ghazan) – daughter of Tugh Timur Amir-Tüman (son of Noqai Yarghuchi of Bayauts)
*Dondi Khatun (d. 9 February 1298) – daughter of Aq Buqa (from Jalayir
Jalair (; ; ), also Djalair, Yyalair, Jalayir, is one of the Darliqin Mongol tribes according to Rashid-al-Din Hamadani's ''Jami' al-tawarikh''.They lived along the Orkhon River in modern day Central Mongolia.History of Mongolia, Volume II, 2003 ...
tribe), widow of Gaykhatu
*Karamün Khatun (m. 17 July 1299, d. 21 January 1304) – daughter of Qutlugh Temür (cousin of Bulughan Khatun Muazzama, from Khongirad
The Khongirad (; ; ; ) was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Their homeland was located in the vicinity of Hulun Lake, Lake Hulun in Inner Mongolia and Khalkha River in Mongolia,M. Sanjdorj, History of the Mongolian People's Repub ...
tribe)
*Günjishkab Khatun – daughter of Shadai Güregen (great-grandson of Chilaun) and Orghudaq Khatun (daughter of Jumghur
Jumghur () was the second son of Genghis Khan's grandson Hulagu. Although according to some researchers, he may have been the eldest one.
Life
He was born to Hulagu and his Oirat wife Guyuk Khatun in 1234. He was descended from Genghis Khan on ...
)
*Eirene Palaiologina, daughter of Andronikos II (married in 1302)
Notes
References
*Adh-Dhababi, ''Record of the Destruction of Damascus by the Mongols in 1299–1301'' Translated by Joseph Somogyi. From: Ignace Goldziher Memorial Volume, Part 1Online
(English translation). * * *Encyclopædia Iranica
* * Foltz, Richard, ''Religions of the Silk Road'', Palgrave Macmillan, 2nd edition, 2010 * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control 1271 births 1304 deaths Il-Khan emperors Mongol Empire Muslims 13th-century monarchs in Asia 14th-century monarchs in Asia 14th-century crusades Converts to Islam from Christianity