Luhman 16 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Luhman 16 (also designated WISE 1049−5319 or WISE J104915.57−531906.1) is a binary brown-dwarf system in the southern
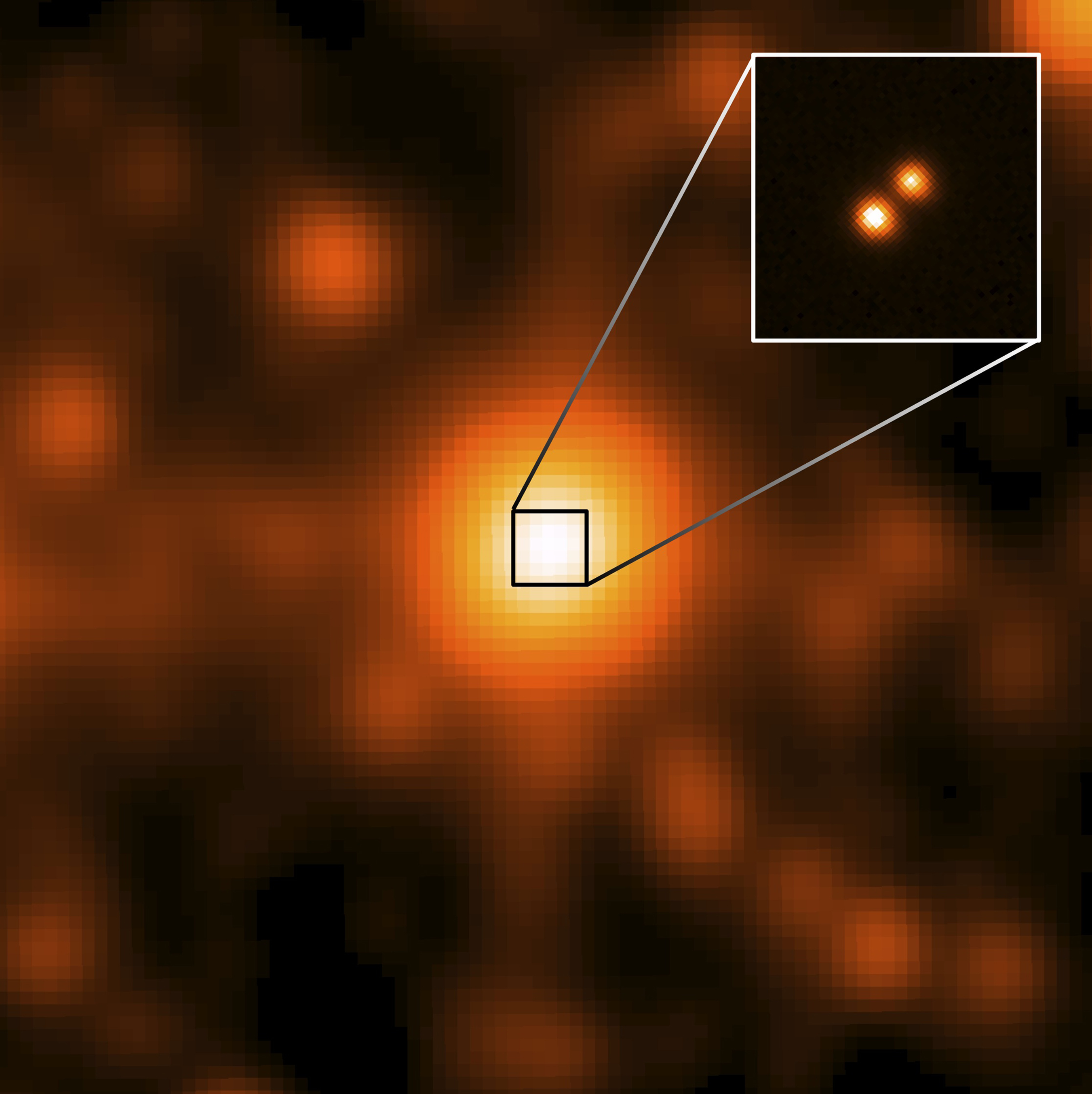 This system was discovered by Kevin Luhman, astronomer from
This system was discovered by Kevin Luhman, astronomer from
 The trigonometric
The trigonometric
File:Surface map of Luhman 16B recreated from VLT observations (Vid).ogg, Surface map of Luhman 16B recreated from VLT observations
File:Artist's impression of Luhman 16B recreated from VLT observations.ogg, Artist's impression of Luhman 16B based on the VLT observations
File:Luhman 16 visible light MUSE.jpg, Luhman 16 with VLT's
slideshow
. * *
at Solstation.com
"WISE Nabs the Closest Brown Dwarfs Yet Discovered"
at ''Universe Today''
"Checking Out Our New Neighbors"
at Astrobites.org
Nearest Brown Dwarf Might Remind You Of Jupiter
AstroBob, 5/13/20 {{DEFAULTSORT:Luhman 16 20130323 Binary stars Local Bubble L-type brown dwarfs T-type brown dwarfs Vela (constellation) J104915.57-531906.1 Articles containing video clips J10491891-5319100 119862115
constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
Vela at a distance of from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
. These are the closest-known brown dwarfs and the closest system found since the measurement of the proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable referenc ...
of Barnard's Star in 1916, and the third-closest-known system to the Sun (after the Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri (, α Cen, or Alpha Cen) is a star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus (constellation), Centaurus. It consists of three stars: Rigil Kentaurus (), Toliman (), and Proxima Centauri (). Proxima Centauri ...
system and Barnard's Star). The primary is of spectral type
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the ...
L7.5 and the secondary of type (and is hence near the L–T transition). The masses of Luhman 16 A and B are 35.4 and 29.4 Jupiter masses, respectively, and their ages are estimated to be 400–800 million years. Luhman 16 A and B orbit each other at a distance of about 3.5 astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its m ...
s with an orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
of approximately 26.6 years.
Discovery
 This system was discovered by Kevin Luhman, astronomer from
This system was discovered by Kevin Luhman, astronomer from Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsyl ...
and a researcher at Penn State's Center for Exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
s and Habitable Worlds, from images made by the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE, List of observatory codes, observatory code C51, Explorer 92 and MIDEX-6) was a NASA infrared astronomy Space observatory, space telescope in the Explorers Program launched in December 2009.. . WISE L ...
(WISE) Earth-orbiting satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
—NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
infrared-wavelength space telescope
A space telescope (also known as space observatory) is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO ...
, a mission that lasted from December 2009 to February 2011; the discovery images were taken from January 2010 to January 2011, and the discovery was announced in 2013 (the pair are the only two objects announced in the discovery paper). The system was found by comparing WISE images at different epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided b ...
s to reveal objects that have high proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable referenc ...
s.
Luhman 16 appears in the sky close to the galactic plane
The galactic plane is the plane (geometry), plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms ''galactic plane'' and ''galac ...
, which is densely populated by stars; the abundance of light sources makes it difficult to spot faint objects. This explains why an object so near to the Sun was not discovered in earlier searches.
Discovery of companion
The second component of the system was also discovered by Luhman in 2013, and was announced in the same article as the primary. Its discovery image in the ''i''-band was taken on the night of 23 February 2013 with the Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS) at the Gemini South telescope,Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
. The components of the system were resolved with an angular distance of 1.5 arcseconds, corresponding to a projected separation of 3 AU, and a magnitude difference of 0.45 mag.
Precovery
Although the system was first found on images taken by WISE in 2010–2011, afterwards it was precovered from theDigitized Sky Survey
The Digitized Sky Survey (DSS) is a digital data, digitized version of several photography, photographic astronomical surveys of the night sky, produced by the Space Telescope Science Institute between 1983 and 2006.
Versions and source materia ...
(DSS, 1978 ( IR) & 1992 (red)), Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS
The Infrared Astronomical Satellite (Dutch language, Dutch: ''Infrarood Astronomische Satelliet'') (IRAS) was the first space telescope to perform a astronomical survey, survey of the entire night sky at infrared wavelengths. Launched on 25 Janu ...
, 1983), ESO Schmidt telescope (1984 (red)), Guide Star Catalog (GSC, 1995), Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern Sky
The Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern Sky (DENIS) was a deep astronomical survey of the southern sky in the near-infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than t ...
(DENIS, 1999), Two Micron All-Sky Survey ( 2MASS, 1999), and the AKARI satellite (2007).
On the ESO Schmidt telescope image, taken in 1984, the source looks elongated with a position angle
In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the Celestial pole, north celestial pole (NCP), turning pos ...
of 138 °. The similarity of this position angle with that of the resolved pair in the GMOS image (epoch 2013) in Fig. 1 of Luhman (2013) suggests that the time period between 1984 and 2013 may be close to the orbital period of the system (not far from original orbital period estimate by Luhman (2013)).
Name
Eric E. Mamajek proposed the name Luhman 16 for the system, with the components called Luhman 16A and Luhman 16B. The name originates from the frequently updated Washington Double Star Catalog (WDS). Kevin Luhman had already published several new discoveries of binary stars that have been compiled in the WDS with discovery identifier "LUH". The WDS catalog now lists this system with the identifier 10493−5319 and discoverer designation LUH 16. The rationale given by Mamajek is that Luhman 16 is easier to remember than WISE J104915.57−531906.1 and "it seems silly to call this object by a 24-character name (space included)". The "phone number names" also include WISE J1049−5319 and WISE 1049−5319. Luhman–WISE 1 was proposed as another alternative. As a binary object it is also called Luhman 16AB.Astrometry
Position in the sky
Luhman 16 is located in the southern celestial hemisphere in the constellation Vela. As of July 2015, its components are the nearest-known celestial objects in this constellation outside the Solar System. Its celestial coordinates: RA = , Dec = .Distance
 The trigonometric
The trigonometric parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
of Luhman 16 as published by Sahlmann & Lazorenko (2015) is arcsec, corresponding to a distance of . Subsequent observations with Hubble and Gaia improved the parallax to , corresponding to a distance of , which is accurate to about 50 astronomical units.
Proximity to the Solar System
Currently Luhman 16 is the third-closest-known star/brown-dwarf system to the Sun after the tripleAlpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri (, α Cen, or Alpha Cen) is a star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus (constellation), Centaurus. It consists of three stars: Rigil Kentaurus (), Toliman (), and Proxima Centauri (). Proxima Centauri ...
system (4.344 ly) and Barnard's Star (5.98 ly), pushing Wolf 359 (7.78 ly) to the fifth place, along with the discovery of WISE 0855−0714
WISE 0855−0714 (full designation WISE J085510.83−071442.5, or W0855 for short) is a sub-brown dwarf of Y dwarf, spectral class Y4, located from the Sun in the constellation Hydra (constellation), Hydra. It is the fourth-List of ne ...
. It also holds several records: the nearest brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big en ...
, the nearest L-type dwarf, and possibly the nearest T-type dwarf (if component B is of T-type).
Proximity to Alpha Centauri
Luhman 16 is the nearest-known star/brown-dwarf system toAlpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri (, α Cen, or Alpha Cen) is a star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus (constellation), Centaurus. It consists of three stars: Rigil Kentaurus (), Toliman (), and Proxima Centauri (). Proxima Centauri ...
, located from Alpha Centauri AB, and from Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri is the nearest star to Earth after the Sun, located 4.25 light-years away in the southern constellation of Centaurus. This object was discovered in 1915 by Robert T. A. Innes, Robert Innes. It is a small, low-mass st ...
. Both systems are located in neighboring constellations, in the same part of the sky as seen from Earth, but Luhman 16 is a bit farther away. Before the discovery of Luhman 16, the Solar System was the nearest-known system to Alpha Centauri.
Luhman 16 is closer to Proxima Centauri than to Alpha Centauri AB, just like Earth, even though Luhman 16 is farther from Earth than is the Alpha Centauri system. Therefore Luhman 16 has smaller angular distance to Proxima Centauri than to Alpha Centauri AB in Earth's sky, and this makes more contribution to the distance difference from Luhman 16 to Alpha Centauri than to the distance difference between them and Earth.
Proper motion
Theproper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable referenc ...
of Luhman 16 as published by Garcia ''et al.'' (2017), is about 2.79″/year, which is relatively large due to the proximity of Luhman 16.
Radial velocity
Theradial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity of a target with respect to an observer is the rate of change of the vector displacement between the two points. It is formulated as the vector projection of the target-observer relative velocity ...
of is , and the radial velocity of is . Since values of the radial velocity are positive, the system currently is moving away from the Solar System.
Assuming these values for the components, and a mass ratio of from Sahlmann & Lazorenko (2015) of 0.78, the system's barycentre radial velocity is about . This implies that passed by the Solar System around 36,000 years ago at a minimal distance of about .
Orbit and masses
In Luhman 16's original discovery paper, Luhman ''et al.'' (2013) estimated theorbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
of its components to be about 25 years.
Garcia ''et al.'' (2017), using archival observations extending over 31 years, found an orbital period of 27.4 years with a semi-major axis of 3.54 AU. This orbit has an eccentricity of 0.35 and an inclination of 79.5°. The masses of the components were found to be and , respectively, with their mass ratio being about 0.82.
With the data from ''Gaia'' DR2 in 2018, their orbit was refined to a period of years, with a semi-major axis of , an eccentricity of , and an inclination of (facing the opposite direction as the 2017 study found). Their masses were additionally refined to and . In 2024 the distance and orbit was further refined, resulting in a semi-major axis of 3.52 AU (assuming a parallax of 500.993 mas), an eccentricity of and an inclination of , bringing the inclination in line with previous measurements. The secondary has a mass which is that of the primary. The individual masses were measured to be and .
These results are consistent with all previous estimates of the orbit and component masses.
By comparing the rotation periods of the brown dwarfs with the projected rotational velocities, it appears that both brown dwarfs are viewed roughly equator-on, and they are aligned well to their orbits.
Age
A 2013 paper, published shortly after Luhman 16 was discovered, concluded that the brown dwarf belongs to the thin disk of theMilky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
with 96% probability, and therefore does not belong to a young moving group. Based on lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ...
absorption lines the system has a maximum age of about 3–4.5 Gyr. Observations with the VLT showed that the system is older than 120 Myr.
However, in 2022, Luhman 16 was found to be a member of the newly discovered Oceanus moving group, which has an age of Myr. Age estimates of 400–800 Myr in 2024 is in line with the membership with this group. The age estimates are mismatched for both components, which could be due to different cloud coverage resulting in different cooling efficiency. Alternatively this could be due to inaccurate luminosities or errors in the evolutionary models.
Search for planets
In December 2013, perturbations of the orbital motions in the system were reported, suggesting a third body in the system. The period of this possible companion was a few months, suggesting an orbit around one of the brown dwarfs. Any companion would necessarily be below the brown-dwarf mass limit, as otherwise it would have been detected through direct imaging. Researchers estimated the odds of a false positive as 0.002%, assuming the measurements had not been made in error. If confirmed, this would have been the first exoplanet discovered astrometrically. They estimate the planet to likely have a mass between "a few" and , although they mention that a more massive planet would be brighter and therefore would affect the "photocenter" or measured position of the star. This would make it difficult to measure the astrometric movement of an exoplanet around it. Subsequent astrometric monitoring of Luhman 16 with theVery Large Telescope
The Very Large Telescope (VLT) is an astronomical facility operated since 1998 by the European Southern Observatory, located on Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. It consists of four individual telescopes, each equipped with ...
has excluded the presence of any third object with a mass greater than orbiting around either brown dwarf with a period between 20 and 300 days. Luhman 16 does not contain any close-in giant planets.
Observations with the ''Hubble Space Telescope'' in 2014–2016 confirmed the nonexistence of any additional brown dwarfs in the system. It additionally ruled out any Neptune mass () objects with an orbital period of one to two years. This makes the existence of the previously found exoplanet candidate highly unlikely.
Additional observations with Hubble rules out the existence of a planet with >1.5 Neptune masses at an orbit of 400 to 5000 days. This study did however not rule out planets with a mass of less than 3 Neptune masses and a shorter period of 2 to 400 days.
A 70 day radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity of a target with respect to an observer is the rate of change of the vector displacement between the two points. It is formulated as the vector projection of the target-observer relative velocity ...
campaign with Gemini South did not detect any planets for both brown dwarfs. For Luhman 16A, the researchers exclude planets with orbital periods smaller than 1 day and a mass of M sin i >0.2 , as well as planets in orbits smaller than 10 days and a mass of >0.4 . For Luhman 16B, the researchers exclude M sin i >0.3 in <1 day orbital periods, as well as >0.7 in <10-d periods.
Atmosphere
A study by Gillon ''et al.'' (2013) found that Luhman 16B exhibited uneven surface illumination during its rotation. On 5 May 2013, Crossfield ''et al.'' (2014) used theEuropean Southern Observatory
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 m ...
Very Large Telescope
The Very Large Telescope (VLT) is an astronomical facility operated since 1998 by the European Southern Observatory, located on Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. It consists of four individual telescopes, each equipped with ...
(VLT) to directly observe the Luhman 16 system for five hours, the equivalent of a full rotation of Luhman 16B. Their research confirmed the observation of Gillon ''et al.'', finding a large, dark region at the middle latitudes, a bright area near its upper pole, and mottled illumination elsewhere. They suggest this variant illumination indicates "patchy global clouds", where darker areas represent thick clouds and brighter areas are holes in the cloud layer permitting light from the interior. Luhman 16B's illumination patterns change rapidly, on a day-to-day basis. Luhman 16B is one of the most photometrically variable brown dwarfs known, sometimes varying with an amplitude of over 20%. Only 2MASS J21392676+0220226 is known to be more variable.
Heinze ''et al.'' (2021) observed variability in spectral lines of alkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
s such as potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
and sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
; they suggested that the variations were caused by changes in cloud cover, which changed the local chemical equilibrium with chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pr ...
s. Lightning or aurorae were deemed possible, but less likely.
Luhman 16B's lightcurve shows evidence of differential rotation
Differential rotation is seen when different parts of a rotating object move with different angular velocities (or rates of rotation) at different latitudes and/or depths of the body and/or in time. This indicates that the object is not rigi ...
. There is evidence of equatorial regions and mid-latitude regions with different rotation periods. The main period is 5.28 hours, corresponding to the rotation period of the equatorial region. Meanwhile, the rotation period of Luhman 16A is likely 6.94 hours.
Biller et al. 2024 observed both components with JWST for 8 hours with MIRI
Miri () is a coastal city in north-eastern Sarawak, Malaysia, located near the border of Brunei, on the island of Borneo. The city covers an area of , located northeast of Kuching and southwest of Kota Kinabalu. Miri is the second largest ...
LRS and directly followed by an 7 hour observation with NIRSpec. The observations found water vapor
Water vapor, water vapour, or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of Properties of water, water. It is one Phase (matter), state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from th ...
, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
absorption in both brown dwarfs, which is typical for L/T dwarfs. Luhman 16A shows a flat plateau beyond 8.5 μm, which is indicative of small grain silicates
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for an ...
. The lightcurves produced from the observations show that both components are variable, with Luhman 16B being considerable more variable than Luhman 16A. The variability has a complex wavelength dependent trend. The researchers identified changes in behaviour at 2.3 μm and 4.2 μm coincident with the CO band and changes in behaviour at 8.3–8.5 μm coincident with silicate absorption. These changes in behaviour were interpreted as changes of average pressure at three different depths of the atmosphere. The observations also tested if patchy clouds could produce the variability. While small silicate grains corresponding to high-altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometr ...
silicate clouds were found in Luhman 16A, it is unlikely to be a patchy cloud layer. Luhman 16B does not have this small grained silicate feature, but larger grained silicate clouds deeper in the atmosphere are possible. The researchers also tested general circulation models (GCM) and hotspots, but the lightcurves are more complex than these models predict. A second epoch of JWST observations showed continued variability. The study found that patchy clouds likely shape the variability of deepest layer detected between 1-2.5 μm. CO and CH4 hot spots are located at high-altitude levels and detected between 2.5-3.6 μm and 4.3-8.5 μm. These hot spots are caused by vertical mixing and indicate temperature and/or chemical variation. Additionally WISE 1049A shows potential contribution by small-grained silicates detected at 8.5-11 μm and located at an intermediate layer.
Ishikawa et al. 2025 used 70 days of Gemini South H- and K-band spectroscopic observations to determine the composition of the brown dwarfs. The researchers detected ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
(NH3) in both brown dwarfs, making Luhman 16A the warmest brown dwarf with this detection. Both brown dwarfs also show water vapor
Water vapor, water vapour, or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of Properties of water, water. It is one Phase (matter), state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from th ...
(H2O), carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
(CO), hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
(H2), hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
(H2S) and hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluori ...
(HF). The molecule methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
(CH4) shows a small contribution. Iron hydride
An iron hydride is a chemical system which contains iron and hydrogen in some associated form.
Because of the common occurrence of those two element (chemistry), elements in the universe, possible compounds of hydrogen and iron have attracted at ...
(FeH) is not detected, meaning iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
rain-out is more efficient than the models predict.
Using data collected by TESS,the research team, Dániel Apai, Domenico Nardiello and Luigi R. Bedin, found that the brown dwarf, between star and gas giant, is more similar to Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
in that its high-speed winds form stripes parallel to the equators of Luhman 16 AB.
MUSE
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, the Muses (, ) were the Artistic inspiration, inspirational goddesses of literature, science, and the arts. They were considered the source of the knowledge embodied in the poetry, lyric p ...
instrument in visible light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm ...
.
File:Luhman16.png, High-speed winds form bands parallel to the equators of Luhman 16 AB.
Radio and X-ray activity
In a study by Osten ''et al.'' (2015), Luhman 16 was observed with the Australia Telescope Compact Array inradio wave
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths g ...
s and with the Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources ...
in X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s. No radio or X-ray activity was found at Luhman 16 AB, and constraints on radio and X-ray activity were presented, which are "the strongest constraints obtained so far for the radio and X-ray luminosity of any ultracool dwarf".
See also
*Substellar object
A substellar object, sometimes called a substar, is an astronomical object, the mass of which is smaller than the smallest mass at which hydrogen fusion can be sustained (approximately 0.08 solar masses). This definition includes brown dwarfs and f ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * See relateslideshow
. * *
External links
at Solstation.com
"WISE Nabs the Closest Brown Dwarfs Yet Discovered"
at ''Universe Today''
"Checking Out Our New Neighbors"
at Astrobites.org
Nearest Brown Dwarf Might Remind You Of Jupiter
AstroBob, 5/13/20 {{DEFAULTSORT:Luhman 16 20130323 Binary stars Local Bubble L-type brown dwarfs T-type brown dwarfs Vela (constellation) J104915.57-531906.1 Articles containing video clips J10491891-5319100 119862115