low-temperature polycrystalline silicon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) is
 Amorphous silicon TFTs have been widely used in
Amorphous silicon TFTs have been widely used in
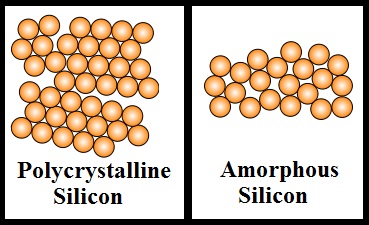 XeCl Excimer-Laser Annealing (ELA) is the first key method to produce p-Si by melting a-Si material through laser irradiation. The counterpart of a-Si, polycrystalline silicon, which can be synthesized from amorphous silicon by certain procedures, has several advantages over widely used a-Si TFT:
# High
XeCl Excimer-Laser Annealing (ELA) is the first key method to produce p-Si by melting a-Si material through laser irradiation. The counterpart of a-Si, polycrystalline silicon, which can be synthesized from amorphous silicon by certain procedures, has several advantages over widely used a-Si TFT:
# High
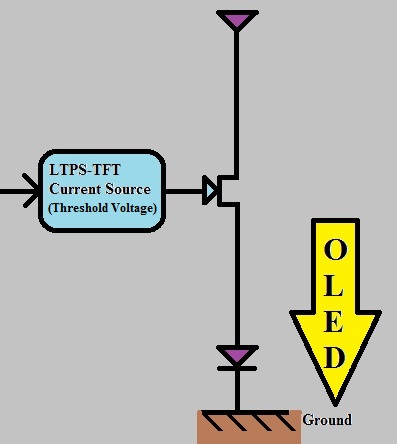 Apart from the improvement of the TFTs themselves, the successful application of LTPS to graphic display also depends on innovative circuits. One recent technique involves a pixel circuit in which the outgoing current from the transistor is independent of the threshold voltage, thus producing uniform brightness.Banger, K. K., Y. Yamashita, K. Mori, R. L. Peterson, T. Leedham, J. Rickard, and H. Sirringhaus. "Low-temperature, High-performance Solution-processed Metal Oxide Thin-film Transistors Formed by a ‘sol–gel on Chip’ Process." Nature Materials (2010): 45–50. Nature Materials. Web. 2 Mar. 2015.'' Tai, Y.-H., B.-T. Chen, Y.-J. Kuo, C.-C. Tsai, K.-Y. Chiang, Y.-J. Wei, and H.-C. Cheng. "A New Pixel Circuit for Driving Organic Light-Emitting Diode With Low Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon Thin-Film Transistors." Journal of Display Technology 01.01 (2015): 100-104. IEEE Xplore. Web. 2 Mar. 2015. LTPS-TFT is commonly used to drive organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays because it has high resolution and accommodation for large panels. However, variations in LTPS structure would result in non-uniform threshold voltage for signals and non-uniform brightness using traditional circuits. The new pixel circuit includes four n-type TFTs, one p-type TFT, a capacitor, and a control element to control the image resolution. Enhancing the performance and microlithography for TFTs is important for advancing LTPS active-matrix OLEDs.
These many important techniques have allowed the mobility of crystalline film to reach up to 13 cm2/Vs, and they have helped to mass-produce LEDs and LCDs over 500 ppi in resolution.
Apart from the improvement of the TFTs themselves, the successful application of LTPS to graphic display also depends on innovative circuits. One recent technique involves a pixel circuit in which the outgoing current from the transistor is independent of the threshold voltage, thus producing uniform brightness.Banger, K. K., Y. Yamashita, K. Mori, R. L. Peterson, T. Leedham, J. Rickard, and H. Sirringhaus. "Low-temperature, High-performance Solution-processed Metal Oxide Thin-film Transistors Formed by a ‘sol–gel on Chip’ Process." Nature Materials (2010): 45–50. Nature Materials. Web. 2 Mar. 2015.'' Tai, Y.-H., B.-T. Chen, Y.-J. Kuo, C.-C. Tsai, K.-Y. Chiang, Y.-J. Wei, and H.-C. Cheng. "A New Pixel Circuit for Driving Organic Light-Emitting Diode With Low Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon Thin-Film Transistors." Journal of Display Technology 01.01 (2015): 100-104. IEEE Xplore. Web. 2 Mar. 2015. LTPS-TFT is commonly used to drive organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays because it has high resolution and accommodation for large panels. However, variations in LTPS structure would result in non-uniform threshold voltage for signals and non-uniform brightness using traditional circuits. The new pixel circuit includes four n-type TFTs, one p-type TFT, a capacitor, and a control element to control the image resolution. Enhancing the performance and microlithography for TFTs is important for advancing LTPS active-matrix OLEDs.
These many important techniques have allowed the mobility of crystalline film to reach up to 13 cm2/Vs, and they have helped to mass-produce LEDs and LCDs over 500 ppi in resolution.
polycrystalline silicon
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry.
Polysilicon is produ ...
that has been synthesized at relatively low temperatures (~650 °C and lower) compared to in traditional methods (above 900 °C). LTPS is important for display industries, since the use of large glass panels prohibits exposure to deformative high temperatures. More specifically, the use of polycrystalline silicon in thin-film transistors (LTPS-TFT) has high potential for large-scale production of electronic devices like flat panel LCD
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but in ...
displays or image sensors.
Development of polycrystalline silicon
Polycrystalline silicon (p-Si) is a pure and conductive form of the element composed of many crystallites, or grains of highly orderedcrystal lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by
: \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n ...
. In 1984, studies showed that amorphous silicon (a-Si) is an excellent precursor for forming p-Si films with stable structures and low surface roughness. Silicon film is synthesized by low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD) to minimize surface roughness. First, amorphous silicon is deposited at 560–640 °C. Then it is thermally annealed (recrystallized) at 950–1000 °C. Starting with the amorphous film, rather than directly depositing crystals, produces a product with a superior structure and a desired smoothness. In 1988, researchers discovered that further lowering temperature during annealing, together with advanced plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD), could facilitate even higher degrees of conductivity. These techniques have profoundly impacted the microelectronics, photovoltaic, and display enhancement industries.
Use in liquid-crystal display
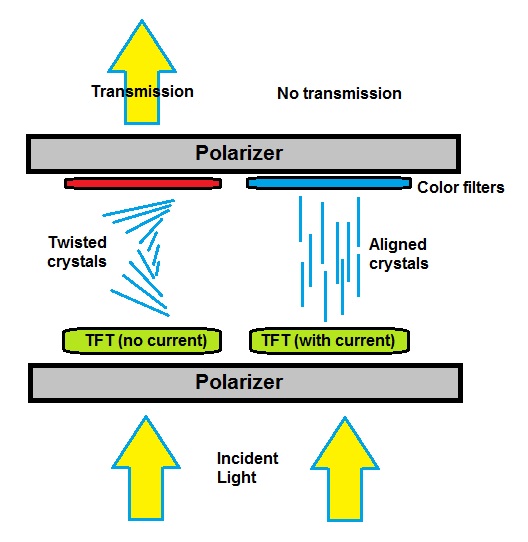
 Amorphous silicon TFTs have been widely used in
Amorphous silicon TFTs have been widely used in liquid-crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display
A flat-panel display (FPD) is an electronic display used to display visual content such as text or images. It is present in consumer, medical, transportation, and industrial equipmen ...
(LCD) flat panels because they can be assembled into complex high-current driver circuits. Amorphous Si-TFT electrodes drive the alignment of crystals in LCDs. The evolution to LTPS-TFTs can have many benefits such as higher device resolution, lower synthesis temperature, and reduced price of essential substrates. However, LTPS-TFTs also have several drawbacks. For example, the area of TFTs in traditional a-Si devices is large, resulting in a small aperture ratio (the amount of area which is not blocked by the opaque TFT and thus admits light). The incompatibility of different aperture ratios prevents LTPS-based complex circuits and drivers from being integrated into a-Si material. Additionally, the quality of LTPS decreases over time due to an increase in temperature upon turning on the transistor, which degrades the film by breaking the Si-H bonds in the material. This would cause the device to suffer from drain breakdown and current leakage, most notably in small and thin transistors, which dissipate heat poorly.
Processing by laser annealing
electron mobility
In solid-state physics, the electron mobility characterises how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor when pulled by an electric field. There is an analogous quantity for holes, called hole mobility. The term carrier mobili ...
rate;
# High resolution and aperture ratio;
# Available for high integration of circuits.
XeCl-ELA succeeds in crystallizing a-Si (thickness ranges from 500-10000A) into p-Si without heating the substrates.'' Sameshima, T., S. Usui, and M. Sekiya. "XeClExcimer Laser Annealing Used in the Fabrication of Poly-Si TFT's." IEEE Electron Device Letters 07.05 (1986): 276-78. IEEE Xplore. Web. 2 Mar. 2015. The polycrystalline form has larger grains that yield better mobility for TFTs due to reduced scattering from grain boundaries. This technique leads to the successful integration of complicated circuits in LCD displays.
Development of LTPS-TFT devices
 Apart from the improvement of the TFTs themselves, the successful application of LTPS to graphic display also depends on innovative circuits. One recent technique involves a pixel circuit in which the outgoing current from the transistor is independent of the threshold voltage, thus producing uniform brightness.Banger, K. K., Y. Yamashita, K. Mori, R. L. Peterson, T. Leedham, J. Rickard, and H. Sirringhaus. "Low-temperature, High-performance Solution-processed Metal Oxide Thin-film Transistors Formed by a ‘sol–gel on Chip’ Process." Nature Materials (2010): 45–50. Nature Materials. Web. 2 Mar. 2015.'' Tai, Y.-H., B.-T. Chen, Y.-J. Kuo, C.-C. Tsai, K.-Y. Chiang, Y.-J. Wei, and H.-C. Cheng. "A New Pixel Circuit for Driving Organic Light-Emitting Diode With Low Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon Thin-Film Transistors." Journal of Display Technology 01.01 (2015): 100-104. IEEE Xplore. Web. 2 Mar. 2015. LTPS-TFT is commonly used to drive organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays because it has high resolution and accommodation for large panels. However, variations in LTPS structure would result in non-uniform threshold voltage for signals and non-uniform brightness using traditional circuits. The new pixel circuit includes four n-type TFTs, one p-type TFT, a capacitor, and a control element to control the image resolution. Enhancing the performance and microlithography for TFTs is important for advancing LTPS active-matrix OLEDs.
These many important techniques have allowed the mobility of crystalline film to reach up to 13 cm2/Vs, and they have helped to mass-produce LEDs and LCDs over 500 ppi in resolution.
Apart from the improvement of the TFTs themselves, the successful application of LTPS to graphic display also depends on innovative circuits. One recent technique involves a pixel circuit in which the outgoing current from the transistor is independent of the threshold voltage, thus producing uniform brightness.Banger, K. K., Y. Yamashita, K. Mori, R. L. Peterson, T. Leedham, J. Rickard, and H. Sirringhaus. "Low-temperature, High-performance Solution-processed Metal Oxide Thin-film Transistors Formed by a ‘sol–gel on Chip’ Process." Nature Materials (2010): 45–50. Nature Materials. Web. 2 Mar. 2015.'' Tai, Y.-H., B.-T. Chen, Y.-J. Kuo, C.-C. Tsai, K.-Y. Chiang, Y.-J. Wei, and H.-C. Cheng. "A New Pixel Circuit for Driving Organic Light-Emitting Diode With Low Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon Thin-Film Transistors." Journal of Display Technology 01.01 (2015): 100-104. IEEE Xplore. Web. 2 Mar. 2015. LTPS-TFT is commonly used to drive organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays because it has high resolution and accommodation for large panels. However, variations in LTPS structure would result in non-uniform threshold voltage for signals and non-uniform brightness using traditional circuits. The new pixel circuit includes four n-type TFTs, one p-type TFT, a capacitor, and a control element to control the image resolution. Enhancing the performance and microlithography for TFTs is important for advancing LTPS active-matrix OLEDs.
These many important techniques have allowed the mobility of crystalline film to reach up to 13 cm2/Vs, and they have helped to mass-produce LEDs and LCDs over 500 ppi in resolution.
See also
* Amorphous silicon *Polycrystalline silicon
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry.
Polysilicon is produ ...
*Monocrystalline silicon
Monocrystalline silicon, more often called single-crystal silicon, in short mono c-Si or mono-Si, is the base material for silicon-based discrete components and integrated circuits used in virtually all modern electronic equipment. Mono-Si also ...
* Wafer (electronics)
* Photovoltaics
* Light-emitting diode
*Liquid-crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display
A flat-panel display (FPD) is an electronic display used to display visual content such as text or images. It is present in consumer, medical, transportation, and industrial equipmen ...
References
{{Reflist Electronics manufacturing Liquid crystal displays Silicon, Polycrystalline Crystals Silicon solar cells Silicon forms