Logic Signal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A digital signal is a
A digital signal is a 
 In
In
 In
In
 In
In
: "A digital signal is a complex waveform and can be defined as a discrete waveform having a finite set of levels" representing a
Computer Networking and the Internet
"In order to transmit a digital signal over an analog subscriber line, modulated transmission must be used; that is the electrical signal that represents the binary bit stream of the source (digital) output must first be converted to an analog signal that is compatible with a (telephony) speech signal." In communications, sources of interference are usually present, and noise is frequently a significant problem. The effects of interference are typically minimized by filtering off interfering signals as much as possible and by using
 A
A
 Digital signals may be ''sampled'' by a clock signal at regular intervals by passing the signal through a flip-flop. When this is done, the input is measured at the clock edge and the signal from that time. The signal is then held steady until the next clock. This process is the basis of synchronous logic.
Asynchronous logic also exists, which uses no single clock, and generally operates more quickly, and may use less power, but is significantly harder to design.
Digital signals may be ''sampled'' by a clock signal at regular intervals by passing the signal through a flip-flop. When this is done, the input is measured at the clock edge and the signal from that time. The signal is then held steady until the next clock. This process is the basis of synchronous logic.
Asynchronous logic also exists, which uses no single clock, and generally operates more quickly, and may use less power, but is significantly harder to design.
CodSim 2.0: Open source Virtual Laboratory for Digital Data Communications Model
Department of Computer Architecture, University of Malaga. Simulates Digital line encodings and Digital Modulations. Written in HTML for any web browser. {{Authority control Telecommunications
 A digital signal is a
A digital signal is a signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
that represents data as a sequence of discrete
Discrete may refer to:
*Discrete particle or quantum in physics, for example in quantum theory
* Discrete device, an electronic component with just one circuit element, either passive or active, other than an integrated circuit
* Discrete group, ...
values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal
An analog signal (American English) or analogue signal (British and Commonwealth English) is any continuous-time signal representing some other quantity, i.e., ''analogous'' to another quantity. For example, in an analog audio signal, the ins ...
, which represents continuous
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
Mathematics
* Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include
** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics
** Continuous ...
values; at any given time it represents a real number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every re ...
within a continuous range of values.
Simple digital signals represent information in discrete bands of levels. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state. In most digital circuits
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. It deals with the relationship between binary inputs and outputs by passing electrical signals through ...
, the signal can have two possible valid values; this is called a binary signal or logic signal. They are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ''ground'' or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the two values ''zero'' and ''one'' (or ''false'' and ''true'') of the Boolean domain
In mathematics and abstract algebra, a Boolean domain is a set consisting of exactly two elements whose interpretations include ''false'' and ''true''. In logic, mathematics and theoretical computer science, a Boolean domain is usually written ...
, so at any given time a binary signal represents one binary digit
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical o ...
(bit). Because of this discretization
In applied mathematics, discretization is the process of transferring continuous functions, models, variables, and equations into discrete counterparts. This process is usually carried out as a first step toward making them suitable for numeri ...
, relatively small changes to the signal levels do not leave the discrete envelope, and as a result are ignored by signal state sensing circuitry. As a result, digital signals have noise immunity
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibratio ...
; electronic noise
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal.
Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects.
In particular, noise is inherent in physics and central to thermod ...
, provided it is not too great, will not affect digital circuits, whereas noise always degrades the operation of analog signals to some degree.
Digital signals having more than two states are occasionally used; circuitry using such signals is called multivalued logic. For example, signals that can assume three possible states are called three-valued logic
In logic, a three-valued logic (also trinary logic, trivalent, ternary, or trilean, sometimes abbreviated 3VL) is any of several many-valued logic systems in which there are three truth values indicating ''true'', ''false'', and some third value ...
.
In a digital signal, the physical quantity representing the information may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or polarization of an optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
or other electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field) is a physical field, varying in space and time, that represents the electric and magnetic influences generated by and acting upon electric charges. The field at any point in space and time can be regarde ...
, acoustic pressure, the magnetization
In classical electromagnetism, magnetization is the vector field that expresses the density of permanent or induced magnetic dipole moments in a magnetic material. Accordingly, physicists and engineers usually define magnetization as the quanti ...
of a magnetic storage
Magnetic storage or magnetic recording is the storage of data on a magnetized medium. Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetisation in a magnetizable material to store data and is a form of non-volatile memory. The information is acc ...
media, etcetera. Digital signals are used in all digital electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. It deals with the relationship between Binary number, binary inputs and outputs by passing electrical s ...
, notably computing equipment and data transmission
Data communication, including data transmission and data reception, is the transfer of data, signal transmission, transmitted and received over a Point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication chann ...
.
Definitions
The term ''digital signal'' has related definitions in different contexts.In digital electronics
 In
In digital electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. It deals with the relationship between Binary number, binary inputs and outputs by passing electrical s ...
, a digital signal is a pulse amplitude modulated
Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) is a form of signal modulation in which the message information is encoded in the amplitude of a pulse train interrupting the carrier frequency. Demodulation is performed by detecting the amplitude level of th ...
signal, i.e. a sequence of fixed-width electrical pulses or light pulses, each occupying one of a discrete number of levels of amplitude. A special case is a ''logic signal'' or a ''binary signal'', which varies between a low and a high signal level.
The pulse trains in digital circuits
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. It deals with the relationship between binary inputs and outputs by passing electrical signals through ...
are typically generated by metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
(MOSFET) devices, due to their rapid on–off electronic switch
In electronics, an electronic switch is a switch controlled by an Passivity (engineering), active electronic component or device. Without using moving parts, they are called solid state switches, which distinguishes them from mechanical switches. ...
ing speed and large-scale integration
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
(LSI) capability. In contrast, bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A ...
s more slowly generate signals resembling sine waves
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is '' simple harmonic motion''; as rotation, it correspond ...
.
In signal processing
digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a ...
, a digital signal is a representation of a physical signal that is sampled and quantized. A digital signal is an abstraction that is discrete in time and amplitude. The signal's value only exists at regular time intervals, since only the values of the corresponding physical signal at those sampled moments are significant for further digital processing. The digital signal is a sequence of codes drawn from a finite set of values. The digital signal may be stored, processed or transmitted physically as a pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the amplitud ...
(PCM) signal.
In communications
 In
In digital communications
Data communication, including data transmission and data reception, is the transfer of data, signal transmission, transmitted and received over a Point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication chann ...
, a digital signal is a continuous-time physical signal, alternating between a discrete number of waveforms, Analogue and Digital Communication Techniques: "A digital signal is a complex waveform and can be defined as a discrete waveform having a finite set of levels" representing a
bitstream
A bitstream (or bit stream), also known as binary sequence, is a sequence of bits.
A bytestream is a sequence of bytes. Typically, each byte is an 8-bit quantity, and so the term octet stream is sometimes used interchangeably. An octet may ...
. The shape of the waveform depends on the transmission scheme, which may be either a line coding
In telecommunications, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained ...
scheme allowing baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into ...
transmission; or a digital modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
scheme, allowing passband
A passband is the range of frequency, frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a Filter (signal processing), filter. For example, a radio receiver contains a bandpass filter to select the frequency of the desired radio signal out of all t ...
transmission over long wires or over a limited radio frequency band. Such a carrier-modulated sine wave is considered a digital signal in literature on digital communications and data transmission, but considered as a bit stream converted to an analog signal in specific cases where the signal will be carried over a system meant for analog communication, such as an analog telephone line.Fred HalsallComputer Networking and the Internet
"In order to transmit a digital signal over an analog subscriber line, modulated transmission must be used; that is the electrical signal that represents the binary bit stream of the source (digital) output must first be converted to an analog signal that is compatible with a (telephony) speech signal." In communications, sources of interference are usually present, and noise is frequently a significant problem. The effects of interference are typically minimized by filtering off interfering signals as much as possible and by using
data redundancy
In computer main memory, auxiliary storage and computer buses, data redundancy is the existence of data that is additional to the actual data and permits correction of errors in stored or transmitted data. The additional data can simply be a com ...
. The main advantages of digital signals for communications are often considered to be noise immunity, and the ability, in many cases such as with audio and video data, to use data compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compressi ...
to greatly decrease the bandwidth that is required on the communication media.
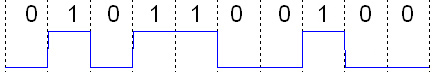
Logic voltage levels
waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its Graph of a function, graph as a function of time, independent of its time and Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude Scale (ratio), scales and of any dis ...
that switches representing the two states of a Boolean value (0 and 1, or low and high, or false and true) is referred to as a ''digital signal'' or ''logic signal'' or ''binary signal'' when it is interpreted in terms of only two possible digits.
The two states are usually represented by some measurement of an electrical property: Voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
is the most common, but current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (hydr ...
is used in some logic families. Two ranges of voltages are typically defined for each logic family, which are frequently not directly adjacent. The signal is low when in the low range and high when in the high range, and in between the two ranges the behavior can vary between different types of gates.
The clock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and ...
is a special digital signal that is used to synchronize
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchrono ...
many digital circuits. The image shown can be considered the waveform of a clock signal. Logic changes are triggered either by the rising edge or the falling edge. The rising edge is the transition from a low voltage (level 1 in the diagram) to a high voltage (level 2). The falling edge is the transition from a high voltage to a low one.
Although in a highly simplified and idealized model of a digital circuit, we may wish for these transitions to occur instantaneously, no real-world circuit is purely resistive and therefore no circuit can instantly change voltage levels. This means that during a short, finite transition time
Transition or transitional may refer to:
Mathematics, science, and technology
Biology
* Transition (genetics), a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (A ↔ G) or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (C ↔ ...
the output may not properly reflect the input, and will not correspond to either a logically high or low voltage.
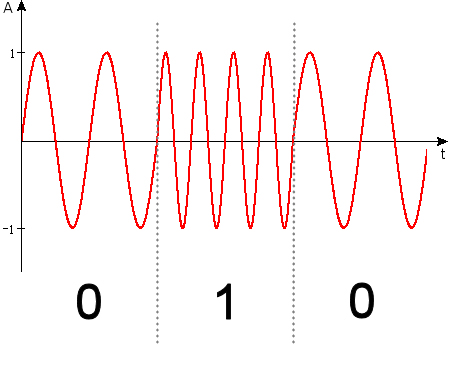
Modulation
To create a digital signal, a signal must be modulated with a control signal to produce it. The simplest modulation, a type of unipolar encoding, is simply to switch on and off a DC signal so that high voltages represent a '1' and low voltages are '0'. Indigital radio
Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services. This should not be confused with In ...
schemes one or more carrier waves are amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
, frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
or phase modulated by the control signal to produce a digital signal suitable for transmission.
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a type of digital subscriber line (DSL) technology, a data communications technology that enables faster data transmission over copper telephone lines than a conventional voiceband modem can provide ...
(ADSL) over telephone wire
A telephone line or telephone circuit (or just line or circuit industrywide) is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system. It is designed to reproduce speech of a quality that is understandable. It is the physical wire or oth ...
s, does not primarily use binary logic; the digital signals for individual carriers are modulated with different valued logics, depending on the Shannon capacity of the individual channel.
Clocking
See also
*Intersymbol interference
In telecommunications, intersymbol interference (ISI) is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have a similar effect as noise, thus making ...
References
External links
*CodSim 2.0: Open source Virtual Laboratory for Digital Data Communications Model
Department of Computer Architecture, University of Malaga. Simulates Digital line encodings and Digital Modulations. Written in HTML for any web browser. {{Authority control Telecommunications