Local Sheet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Local Sheet in 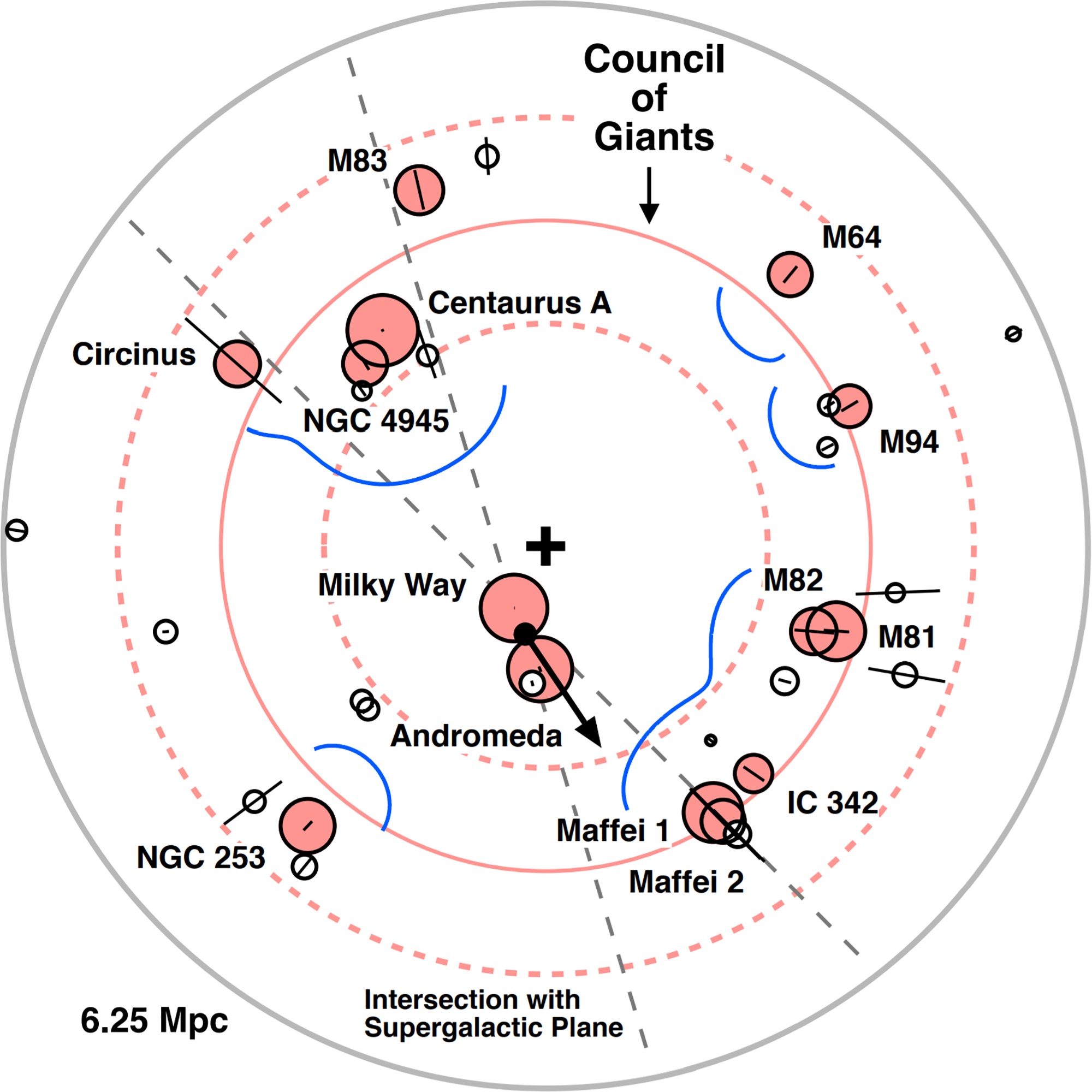
* The mass is given as the logarithm (base unspecified) of the mass in
astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
is a nearby extragalactic region of space where the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
, the members of the Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way, where Earth is located. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of .
It consists of two collections of galaxies in a " dumbbell" shape; the Milky Way ...
and other galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar Sys ...
share a similar peculiar velocity. This region lies within a radius of about , thick, and galaxies beyond that distance show markedly different velocities. The Local Group has only a relatively small peculiar velocity of with respect to the Local Sheet. Typical velocity dispersion of galaxies is only in the radial direction. Nearly all nearby bright galaxies belong to the Local Sheet. The Local Sheet is part of the Local Volume and is in the Virgo Supercluster
The Local Supercluster (LSC or LS), or Virgo Supercluster is a formerly defined supercluster containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least 100 galaxy group ...
(Local Supercluster). The Local Sheet forms a wall of galaxies delineating one boundary of the Local Void.
A significant component of the mean velocity of the galaxies in the Local Sheet appears as the result of the gravitational attraction of the Virgo Cluster
The Virgo Cluster is a cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly (16.5 ± 0.1 Mpc) away in the Virgo constellation. Comprising approximately 1,300 (and possibly up to 2,000) member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger ...
of galaxies, resulting in a peculiar motion ~ toward the cluster. A second component is directed away from the center of the Local Void; an expanding region of space spanning an estimated that is only sparsely populated with galaxies. This component has a velocity of . The Local Sheet is inclined 8° from the Local Supercluster (Virgo Supercluster).
The so-called Council of Giants is a ring of twelve large galaxies surrounding the Local Group in the Local Sheet, with a radius of . Ten of these are spirals
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving further away as it revolves around the point. It is a subtype of whorled patterns, a broad group that also includes concentric objects.
Two-dimensional
A two-dimension ...
, while the remaining two are ellipticals. The two ellipticals ( Maffei 1 and Centaurus A) lie on opposite sides of the Local Group.
solar mass
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxie ...
es.
See also
* Local Void, the Local Sheet defining the wall of galaxies at one end of the void * Supergalactic coordinate system, the coordinate system taking the Local Sheet, the Supergalactic Plane, as its X–Y basesReferences
{{Portal bar, Stars, Astronomy, Science Galaxy superclusters Large-scale structure of the cosmos