Local Government In Japan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Government of Japan is the
 The emperor of Japan is the head of the
The emperor of Japan is the head of the
 The is designated by the
The is designated by the
 The consists of the
The consists of the

 The consist of eleven executive ministries and the
The consist of eleven executive ministries and the
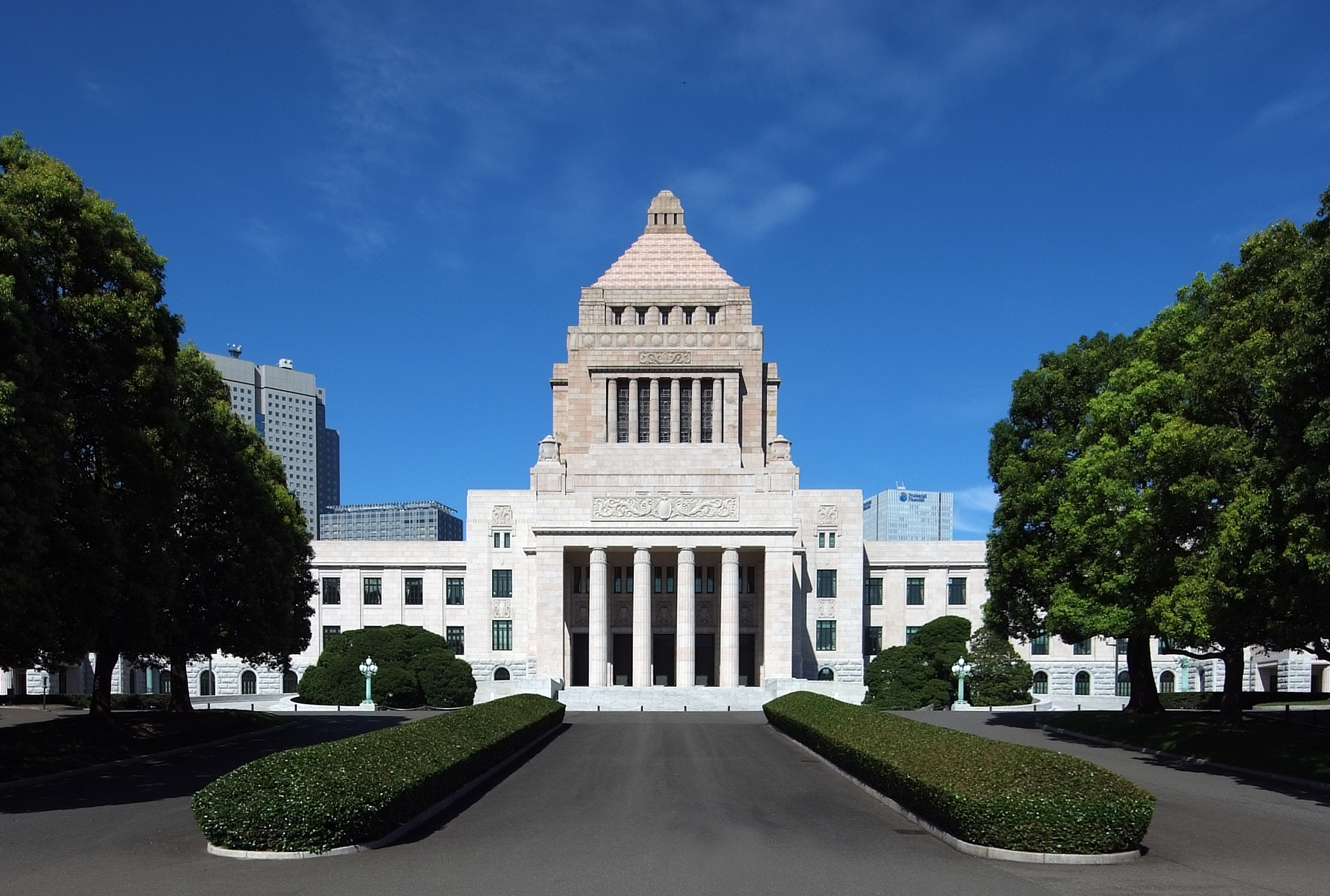 The legislative branch organ of
The legislative branch organ of
 The is the
The is the
 The is the
The is the
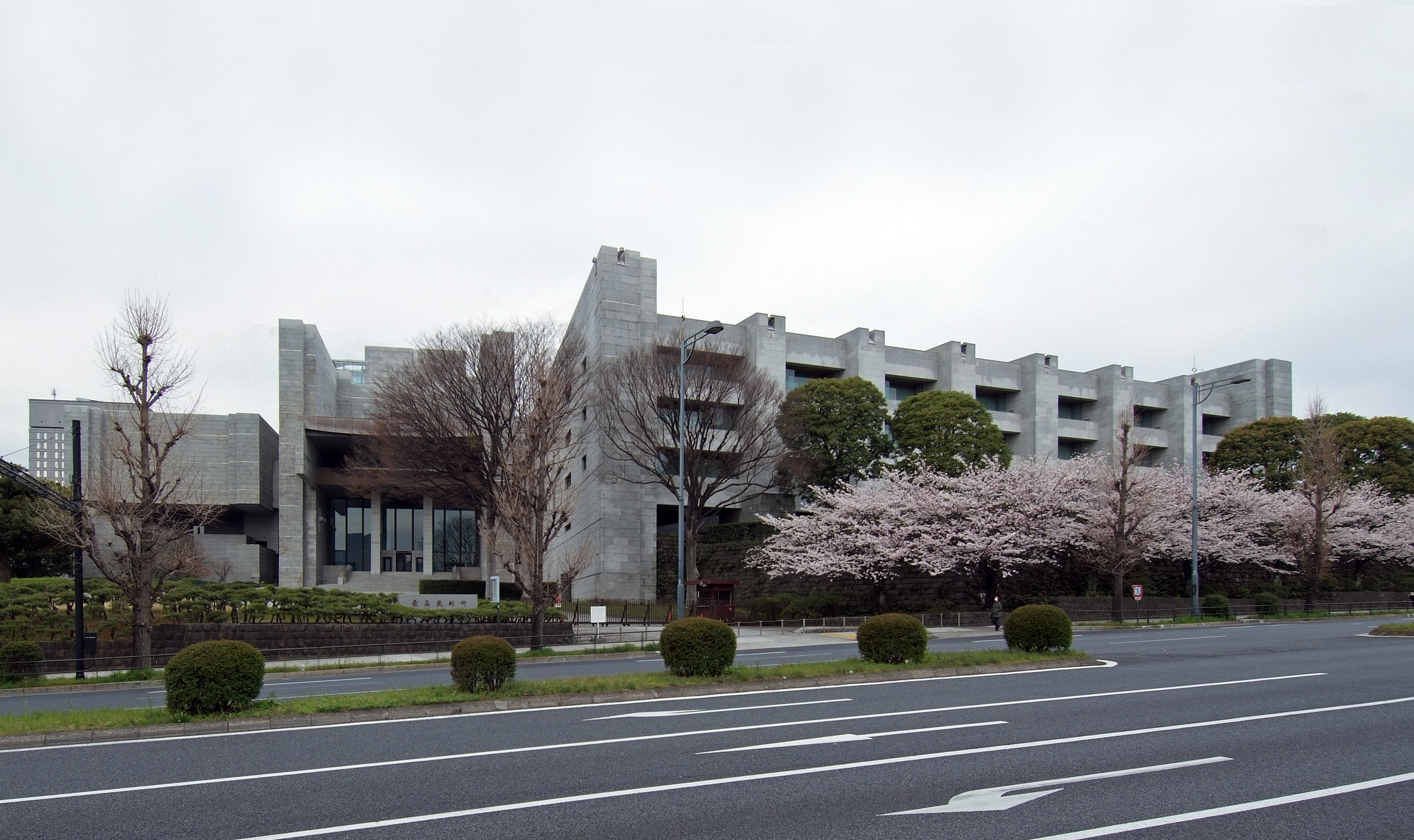
 The judicial branch of
The judicial branch of
 The is the court of last resort and has the power of
The is the court of last resort and has the power of
 According to Article 92 of the Constitution, the are local public entities whose body and functions are defined by law in accordance with the principle of local autonomy. The main law that defines them is the
According to Article 92 of the Constitution, the are local public entities whose body and functions are defined by law in accordance with the principle of local autonomy. The main law that defines them is the
JapanGov – The Government of Japan
– official site of the Imperial House of Japan (archived November 20, 2016)
* ttp://www.digital.archives.go.jp/index_e.html Search official Japanese Government documents and records
Facts about Japan by CIA's The World Factbook
Video of the Enthronement Ceremony of the Emperor
Video of the National Diet Convocation Ceremony
Video of the House of Representatives Dissolution Ceremony
* {{Asia topic, Government of, title=Governments of Asia, TW=Government of the Republic of China Asian governments
central government
A central government is the government that is a controlling power over a unitary state. Another distinct but sovereign political entity is a federal government, which may have distinct powers at various levels of government, authorized or deleg ...
of Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. It consists of legislative
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers ...
, executive
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive dir ...
and judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
branches and functions under the framework established by the Constitution of Japan
The Constitution of Japan is the supreme law of Japan. Written primarily by American civilian officials during the occupation of Japan after World War II, it was adopted on 3 November 1946 and came into effect on 3 May 1947, succeeding the Meij ...
. Japan is a unitary state
A unitary state is a (Sovereign state, sovereign) State (polity), state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create or abolish administrative divisions (sub-national or ...
, containing forty-seven administrative divisions
Administrative divisions (also administrative units, administrative regions, subnational entities, or constituent states, as well as many similar generic terms) are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divi ...
, with the emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
as its head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 "
. His role is ceremonial and he has no powers related to the Government. Instead, it is the Cabinet, comprising the he head of state
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (letter), the fifth letter of the Semitic abjads
* He (pronoun), a pronoun in Modern English
* He (kana), one of the Japanese kana (へ in hiragana and ヘ in katakana)
* Ge (Cyrillic), a Cyrillic letter cal ...
being an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
and the ministers of state
Minister of state is a designation for a government minister, with varying meanings in different jurisdictions. In a number of European countries, the title is given as an honorific conferring a higher rank, often bestowed upon senior ministers ...
, that directs and controls the government and the civil service
The civil service is a collective term for a sector of government composed mainly of career civil service personnel hired rather than elected, whose institutional tenure typically survives transitions of political leadership. A civil service offic ...
. The Cabinet has the executive power
The executive branch is the part of government which executes or enforces the law.
Function
The scope of executive power varies greatly depending on the political context in which it emerges, and it can change over time in a given country. In ...
and is formed by the prime minister, who is the head of government
In the Executive (government), executive branch, the head of government is the highest or the second-highest official of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presid ...
. The Prime Minister is nominated by the National Diet
, transcription_name = ''Kokkai''
, legislature = 215th Session of the National Diet
, coa_pic = Flag of Japan.svg
, house_type = Bicameral
, houses =
, foundation=29 November 1890(), leader1_type ...
and appointed to office by the Emperor. The current cabinet is the Second Ishiba Cabinet
The Second Ishiba Cabinet is the 103rd Cabinet of Japan, formed by Shigeru Ishiba on 11 November 2024, following the 2024 Japanese general election, general election on 27 October 2024. Members of the First Ishiba Cabinet were reappointed excep ...
, which was formed on 11 November 2024 and is led by prime minister Shigeru Ishiba
Shigeru Ishiba (born 4 February 1957) is a Japanese politician who has served as Prime Minister of Japan and President of the Liberal Democratic Party (Japan), President of the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) since 2024. He has been a member of ...
who assumed office on 1 October 2024. The country has had a Liberal Democratic
Liberal democracy, also called Western-style democracy, or substantive democracy, is a form of government that combines the organization of a democracy with ideas of liberal political philosophy. Common elements within a liberal democracy are: ...
–Komeito
, formerly New Komeito (NKP) and commonly referred to as simply Komei, is a political party in Japan founded by the leader of Soka Gakkai, Daisaku Ikeda, in 1964. It is generally considered centrist and socially conservative. Since 2012, i ...
coalition
A coalition is formed when two or more people or groups temporarily work together to achieve a common goal. The term is most frequently used to denote a formation of power in political, military, or economic spaces.
Formation
According to ''A G ...
minority government
A minority government, minority cabinet, minority administration, or a minority parliament is a government and cabinet formed in a parliamentary system when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in ...
since 2024
The year saw the list of ongoing armed conflicts, continuation of major armed conflicts, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Myanmar civil war (2021–present), Myanmar civil war, the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudane ...
.
The National Diet is the legislature
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial power ...
, the organ of the Legislative branch. The Diet is bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature that is divided into two separate Deliberative assembly, assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate ...
, consisting of two houses with the House of Councilors
The is the upper house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Representatives is the lower house. The House of Councillors is the successor to the pre-war House of Peers. If the two houses disagree on matters of the budget, treaties, or ...
being the upper house
An upper house is one of two Legislative chamber, chambers of a bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house. The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restricted p ...
, and the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
being the lower house
A lower house is the lower chamber of a bicameral legislature, where the other chamber is the upper house. Although styled as "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has come to wield more power or otherwise e ...
. The members of both houses of the Diet are directly elected by the people
The term "the people" refers to the public or Common people, common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. I ...
, who are the source of sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
. The Diet is defined as the supreme organ of sovereignty in the Constitution. The Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
and other lower courts make up the Judicial branch and have all the judicial powers in the state. The Supreme Court has ultimate judicial authority to interpret the constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
and the power of judicial review
Judicial review is a process under which a government's executive, legislative, or administrative actions are subject to review by the judiciary. In a judicial review, a court may invalidate laws, acts, or governmental actions that are in ...
. The judicial branch is independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in Pennsylvania, United States
* Independentes (English: Independents), a Portuguese artist ...
from the executive and the legislative branches. Judge
A judge is a person who wiktionary:preside, presides over court proceedings, either alone or as a part of a judicial panel. In an adversarial system, the judge hears all the witnesses and any other Evidence (law), evidence presented by the barris ...
s are nominated or appointed by the Cabinet and never removed by the executive or the legislature except during impeachment
Impeachment is a process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
In Eur ...
.
The Government of Japan is based in the capital of Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
, where the National Diet Building
The is the building where both houses of the National Diet, National Diet of Japan meet. It is located at Nagatachō, Tokyo, Nagatachō 1-chome 7–1, Chiyoda, Tokyo.
Sessions of the House of Representatives (Japan), House of Representatives ta ...
, the Imperial Palace, the Supreme Court, the Prime Minister's Office and the ministries are all located.
History
Before theMeiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored Imperial House of Japan, imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Althoug ...
, Japan was ruled by the government of successive military shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military rulers of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, except during parts of the Kamak ...
. During this period, effective power of the government resided in the Shōgun, who officially ruled the country in the name of the Emperor. The Shōgun were the hereditary military governors, with their modern rank equivalent to a generalissimo
''Generalissimo'' ( ), also generalissimus, is a military rank of the highest degree, superior to field marshal and other five-star ranks in the states where they are used.
Usage
The word (), an Italian term, is the absolute superlative ...
. Although the Emperor was the sovereign who appointed the Shōgun, his roles were ceremonial and he took no part in governing the country. This is often compared to the present role of the Emperor, whose official role is to appoint the Prime Minister.
The return of political power to the Emperor (to the Imperial Court) at the end of 1867 meant the resignation of Shōgun Tokugawa Yoshinobu
Kazoku, Prince was the 15th and last ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan. He was part of a movement which aimed to reform the aging shogunate, but was ultimately unsuccessful. He resigned his position as shogun in late 1867, while ai ...
, agreeing to "be the instrument for carrying out" the Emperor's orders. This event restored the country to Imperial rule and the proclamation of the Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
. In 1889, the Meiji Constitution
The Constitution of the Empire of Japan ( Kyūjitai: ; Shinjitai: , ), known informally as the Meiji Constitution (, ''Meiji Kenpō''), was the constitution of the Empire of Japan which was proclaimed on February 11, 1889, and remained in ...
was adopted in a move to strengthen Japan to the level of western nations, resulting in the first parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their Election, democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of t ...
in Asia. It provided a form of mixed constitutional
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
- absolute monarchy (a semi-constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
), with an independent judiciary, based on the Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
n model of the time.
A new aristocracy known as the ''kazoku
The was the hereditary peerage of the Empire of Japan, which existed between 1869 and 1947. It was formed by merging the feudal lords (''Daimyo, daimyō'') and court nobles (''kuge'') into one system modelled after the British peerage. Distin ...
'' was established. It merged the ancient court nobility of the Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kammu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means in Japanese. It is a ...
, the ''kuge
The was a Japanese Aristocracy (class), aristocratic Social class, class that dominated the Japanese Imperial Court in Kyoto. The ''kuge'' were important from the establishment of Kyoto as the capital during the Heian period in the late 8th ce ...
'', and the former ''daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and no ...
'', feudal lords subordinate to the ''shōgun''. It also established the Imperial Diet, consisting of the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
and the House of Peers. Members of the House of Peers were made up of the Imperial Family
A royal family is the immediate family of monarch, monarchs and sometimes their extended family.
The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or emperor, empress, and the term papal family describes the family of ...
, the Kazoku, and those nominated by the Emperor, while members of the House of Representatives were elected by direct male suffrage. Despite clear distinctions between powers of the executive branch and the Emperor in the Meiji Constitution, ambiguity and contradictions in the Constitution eventually led to a political crisis
A cabinet crisis, government crisis or political crisis refers to a situation where an incumbent government is unable to form or function, is toppled through an uprising, or collapses. Political crises may correspond with, cause or be caused by an ...
. It also devalued the notion of civilian control over the military, which meant that the military could develop and exercise a great influence on politics.
Following the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the present Constitution of Japan
The Constitution of Japan is the supreme law of Japan. Written primarily by American civilian officials during the occupation of Japan after World War II, it was adopted on 3 November 1946 and came into effect on 3 May 1947, succeeding the Meij ...
was adopted. It replaced the previous Imperial rule with a form of Western-style liberal democracy
Liberal democracy, also called Western-style democracy, or substantive democracy, is a form of government that combines the organization of a democracy with ideas of liberalism, liberal political philosophy. Common elements within a liberal dem ...
.
As of 2020, the Japan Research Institute found the national government is mostly analog, because only 7.5% (4,000 of the 55,000) administrative procedures can be completed entirely online. The rate is 7.8% at the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, 8% at the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, and only 1.3% at the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries.
On 12 February 2021, Tetsushi Sakamoto
is a Japanese politician who served as the minister of loneliness from 12 February 2021 to 4 October 2021 and as the Minister of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (Japan), Minister of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries from 14 December 2023 to ...
was appointed as the Minister of Loneliness to alleviate social isolation and loneliness across different age groups and genders.
The Emperor
 The emperor of Japan is the head of the
The emperor of Japan is the head of the Imperial Family
A royal family is the immediate family of monarch, monarchs and sometimes their extended family.
The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or emperor, empress, and the term papal family describes the family of ...
and the ceremonial head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 "
. He is defined by the he head of state
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (letter), the fifth letter of the Semitic abjads
* He (pronoun), a pronoun in Modern English
* He (kana), one of the Japanese kana (へ in hiragana and ヘ in katakana)
* Ge (Cyrillic), a Cyrillic letter cal ...
being an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
to be "the symbol of the State and of the unity of the people". However, his role is entirely ceremonial and representative in nature. As explicitly stated in article 4 of the Constitution, he has no powers related to government.
Article 6 of the Constitution of Japan
The Constitution of Japan is the supreme law of Japan. Written primarily by American civilian officials during the occupation of Japan after World War II, it was adopted on 3 November 1946 and came into effect on 3 May 1947, succeeding the Meij ...
delegates the Emperor the following ceremonial roles:
# Appointment of the prime minister as designated by the Diet.
# Appointment of the chief justice of the Supreme Court as designated by the Cabinet.
While the Cabinet is the source of executive power and most of its power is exercised directly by the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
, several of its powers are exercised through the Emperor. The powers exercised via the Emperor, as stipulated by Article 7 of the Constitution, are:
# Promulgation of amendments of the constitution, laws, cabinet orders and treaties.
# Dissolution of the House of Representatives.
# Proclamation of general election of members of the Diet.
# Attestation of the appointment and dismissal of Ministers of State and other officials as provided for by law, and of full powers and credentials of Ambassadors and Ministers.
# Attestation of general and special amnesty, commutation of punishment, reprieve, and restoration of rights.
# Awarding of honors.
# Attestation of instruments of ratification and other diplomatic documents as provided for by law.
# Receiving foreign ambassadors and ministers.
# Performance of ceremonial functions.
These powers are exercised in accordance with the binding advice of the Cabinet.
The emperor is known to hold the nominal ceremonial authority. For example, he is the only person that has the authority to appoint the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
, even though the Diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
has the power to designate the person fitted for the position. One such example can be prominently seen in the 2009 Dissolution of the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
. The House was expected to be dissolved on the advice of the prime minister, but was temporarily unable to do so for the next general election, as both the Emperor and Empress were visiting Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
.
In this manner, the emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
's modern role is often compared to those of the Shogunate
, officially , was the title of the military rulers of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, except during parts of the Kamak ...
period and much of Japan's history, whereby the emperor held great symbolic authority
Authority is commonly understood as the legitimate power of a person or group of other people.
In a civil state, ''authority'' may be practiced by legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government,''The New Fontana Dictionary of M ...
but had little political power
In political science, power is the ability to influence or direct the actions, beliefs, or conduct of actors. Power does not exclusively refer to the threat or use of force (coercion) by one actor against another, but may also be exerted thro ...
; which is often held by others nominally appointed by the emperor himself. Today, a legacy has somewhat continued for a retired prime minister who still wields considerable power, to be called a ''Shadow Shogun''.
Unlike his European counterparts, the emperor is not the source of sovereign power and the government does not act under his name. Instead, the emperor represents the state and appoints other high officials in the name of the state, in which the Japanese people
are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago. Japanese people constitute 97.4% of the population of the country of Japan. Worldwide, approximately 125 million people are of Japanese descent, making them list of contempora ...
hold sovereignty. Article 5 of the Constitution, in accordance with the Imperial Household Law, allows a regency
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
to be established in the emperor's name, should the emperor be unable to perform his duties.
On November 20, 1989, the Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
ruled it doesn't have judicial power over the emperor.
The Imperial House of Japan
The is the reigning dynasty of Japan, consisting of those members of the extended family of the reigning emperor of Japan who undertake official and public duties. Under the present constitution of Japan, the emperor is "the symbol of the State ...
is said to be the oldest continuing hereditary monarchy in the world. According to the Kojiki
The , also sometimes read as or , is an early Japanese chronicle of myths, legends, hymns, genealogies, oral traditions, and semi-historical accounts down to 641 concerning the origin of the Japanese archipelago, the , and the Japanese imperia ...
and Nihon Shoki
The or , sometimes translated as ''The Chronicles of Japan'', is the second-oldest book of classical Japanese history. It is more elaborate and detailed than the , the oldest, and has proven to be an important tool for historians and archaeol ...
, Japan was founded by the Imperial House in 660 BC by Emperor Jimmu. Emperor Jimmu was the first Emperor of Japan and the ancestor of all of the Emperors that followed. He is, according to Japanese mythology
Japanese mythology is a collection of traditional stories, folktales, and beliefs that emerged in the islands of the Japanese archipelago. Shinto traditions are the cornerstones of Japanese mythology. The history of thousands of years of contac ...
, the direct descendant of Amaterasu, the sun goddess of the native Shinto
, also called Shintoism, is a religion originating in Japan. Classified as an East Asian religions, East Asian religion by Religious studies, scholars of religion, it is often regarded by its practitioners as Japan's indigenous religion and as ...
religion, through Ninigi
is a deity in Japanese mythology. (-no-Mikoto here is an honorific title applied to the names of Japanese gods; Ninigi is the specific god's name.) Grandson of the sun goddess Amaterasu, Ninigi is regarded according to Japanese mythology as the ...
, his great-grandfather.
The current emperor of Japan is Naruhito
Naruhito (born 23 February 1960) is Emperor of Japan. He acceded to the Chrysanthemum Throne following 2019 Japanese imperial transition, the abdication of his father, Akihito, on 1 May 2019, beginning the Reiwa era. He is the 126th monarch, ...
. He was officially enthroned on May 1, 2019, following the abdication of his father. He is styled as His Imperial Majesty, and his reign bears the era name of Reiwa. Fumihito
is the heir presumptive to the Japanese throne. He is the younger brother of Emperor Naruhito, and the younger son of Emperor Akihito and Empress Michiko. Since his marriage in June 1990, he has had the title and has headed the Akishino br ...
is the heir presumptive to the Chrysanthemum Throne
The is the throne of the Emperor of Japan. The term also can refer to very specific seating, such as the throne in the Shishin-den at Kyoto Imperial Palace.
Various other thrones or seats that are used by the Emperor during official functions ...
.
Executive
The executive branch ofJapan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
is headed by the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
. The prime minister is the head of the Cabinet, and is designated by the legislative organ, the National Diet
, transcription_name = ''Kokkai''
, legislature = 215th Session of the National Diet
, coa_pic = Flag of Japan.svg
, house_type = Bicameral
, houses =
, foundation=29 November 1890(), leader1_type ...
. The Cabinet consists of the Ministers of State
Minister of state is a designation for a government minister, with varying meanings in different jurisdictions. In a number of European countries, the title is given as an honorific conferring a higher rank, often bestowed upon senior ministers ...
and may be appointed or dismissed by the Prime Minister at any time. Explicitly defined to be the source of executive power
Power may refer to:
Common meanings
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power, a type of energy
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
Math ...
, it is in practice, however, mainly exercised by the prime minister. The practice of its powers is responsible to the Diet, and as a whole, should the Cabinet lose confidence
Confidence is the feeling of belief or trust that a person or thing is reliable.
*
*
* Self-confidence is trust in oneself. Self-confidence involves a positive belief that one can generally accomplish what one wishes to do in the future. Sel ...
and support to be in office by the Diet, the Diet may dismiss the Cabinet ''en masse'' with a motion of no confidence
A motion or vote of no confidence (or the inverse, a motion or vote of confidence) is a motion and corresponding vote thereon in a deliberative assembly (usually a legislative body) as to whether an officer (typically an executive) is deemed fi ...
.
Prime minister
National Diet
, transcription_name = ''Kokkai''
, legislature = 215th Session of the National Diet
, coa_pic = Flag of Japan.svg
, house_type = Bicameral
, houses =
, foundation=29 November 1890(), leader1_type ...
and serves a term of four years or less; with no limits imposed on the number of terms the Prime Minister may hold. The Prime Minister heads the Cabinet and exercises "control and supervision" of the executive branch, and is the head of government
In the Executive (government), executive branch, the head of government is the highest or the second-highest official of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presid ...
and commander-in-chief of the Japan Self-Defense Forces
The are the military forces of Japan. Established in 1954, the JSDF comprises the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force, the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force, and the Japan Air Self-Defense Force. They are controlled by the Ministry of Defense ...
. The prime minister is vested with the power to present bills to the Diet, to sign laws, to declare a state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state before, during, o ...
, and may also dissolve the Diet's House of Representatives at will. The prime minister presides over the Cabinet and appoints, or dismisses, the other Cabinet ministers.
Both houses of the National Diet designates the Prime Minister with a ballot cast under the run-off system. Under the Constitution, should both houses not agree on a common candidate, then a joint committee is allowed to be established to agree on the matter; specifically within a period of ten days, exclusive of the period of recess. However, if both houses still do not agree to each other, the decision made by the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
is deemed to be that of the National Diet. Upon designation, the Prime Minister is presented with their commission, and then formally appointed to office by the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
.
As a candidate designated by the Diet, the prime minister is required to report to the Diet whenever demanded. The prime minister must also be both a civilian
A civilian is a person who is not a member of an armed force. It is war crime, illegal under the law of armed conflict to target civilians with military attacks, along with numerous other considerations for civilians during times of war. If a civi ...
and a member of either house of the Diet.
The Cabinet

 The consists of the
The consists of the Ministers of State
Minister of state is a designation for a government minister, with varying meanings in different jurisdictions. In a number of European countries, the title is given as an honorific conferring a higher rank, often bestowed upon senior ministers ...
and the Prime Minister. The members of the Cabinet are appointed by the Prime Minister, and under the Cabinet Law, the number of members of the Cabinet appointed, excluding the Prime Minister, must be fourteen or less, but may only be increased to nineteen should a special need arise. Article 68 of the Constitution states that all members of the Cabinet must be civilian
A civilian is a person who is not a member of an armed force. It is war crime, illegal under the law of armed conflict to target civilians with military attacks, along with numerous other considerations for civilians during times of war. If a civi ...
s and the majority of them must be chosen from among the members of either house of the National Diet
, transcription_name = ''Kokkai''
, legislature = 215th Session of the National Diet
, coa_pic = Flag of Japan.svg
, house_type = Bicameral
, houses =
, foundation=29 November 1890(), leader1_type ...
. The precise wording leaves an opportunity for the Prime Minister to appoint some non-elected Diet officials. The Cabinet is required to resign ''en masse'' while still continuing its functions, till the appointment of a new Prime Minister, when the following situation arises:
# The Diet's House of Representatives passes a non-confidence resolution, or rejects a confidence resolution, unless the House of Representatives is dissolved within the next ten days.
# When there is a vacancy in the post of the Prime Minister, or upon the first convocation of the Diet after a general election of the members of the House of Representatives.
Conceptually deriving legitimacy from the Diet, whom it is responsible to, the Cabinet exercises its power in two different ways. In practice, much of its power is exercised by the Prime Minister, while others are exercised nominally by the Emperor.
Article 73 of the Constitution of Japan
The Constitution of Japan is the supreme law of Japan. Written primarily by American civilian officials during the occupation of Japan after World War II, it was adopted on 3 November 1946 and came into effect on 3 May 1947, succeeding the Meij ...
expects the Cabinet to perform the following functions, in addition to general administration:
# Administer the law faithfully; conduct affairs of state.
# Manage foreign affairs.
# Conclude treaties. However, it shall obtain prior or, depending on circumstances, subsequent approval of the Diet.
# Administer the civil service
The civil service is a collective term for a sector of government composed mainly of career civil service personnel hired rather than elected, whose institutional tenure typically survives transitions of political leadership. A civil service offic ...
, in accordance with standards established by law.
# Prepare the budget, and present it to the Diet.
# Enact cabinet orders in order to execute the provisions of this Constitution and of the law. However, it cannot include penal provisions in such cabinet orders unless authorized by such law.
# Decide on general amnesty, special amnesty, commutation of punishment, reprieve, and restoration of rights.
Under the Constitution, all laws and cabinet orders must be signed by the competent Minister and countersigned by the Prime Minister, before being formally promulgated by the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
. Also, all members of the Cabinet cannot be subject to legal action without the consent of the Prime Minister; however, without impairing the right to take legal action.
Ministries and agencies

Cabinet Office
The Cabinet Office is a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, ministerial department of the Government of the United Kingdom. It is responsible for supporting the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime minister and Cabinet ...
. Each ministry is headed by a Minister of State
Minister of state is a designation for a government minister, with varying meanings in different jurisdictions. In a number of European countries, the title is given as an honorific conferring a higher rank, often bestowed upon senior minister ...
, which are mainly senior legislators, and are appointed from among the members of the Cabinet by the Prime Minister. The Cabinet Office, formally headed by the Prime Minister, is an agency that handles the day-to-day affairs of the Cabinet. The ministries are the most influential part of the daily-exercised executive power, and since few ministers serve for more than a year or so necessary to grab hold of the organisation, most of its power lies within the senior bureaucrat
A bureaucrat is a member of a bureaucracy and can compose the administration of any organization of any size, although the term usually connotes someone within an institution of government.
The term ''bureaucrat'' derives from "bureaucracy", wh ...
s.
Below is a series of ministry-affiliated government agencies and bureaus responsible for government procedures and activities as of 23 August 2022.
* Cabinet Office
The Cabinet Office is a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, ministerial department of the Government of the United Kingdom. It is responsible for supporting the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime minister and Cabinet ...
** National Public Safety Commission
** National Police Agency National Police may refer to the national police forces of several countries:
*Afghanistan: Afghan National Police
*Haiti: Haitian National Police
*Canada: Royal Canadian Mounted Police
*Colombia: National Police of Colombia
*Cuba: National Revolut ...
** Consumer Affairs Agency
The is an administrative agency of the Cabinet Office of Japan responsible for consumer protection established on September 1, 2009.
Under the law passed on December 10, 2022, the Consumer Affairs Agency now also has jurisdiction over the issue ...
** Financial Services Agency
The is a Japanese government agency and an integrated financial regulator responsible for overseeing banking, securities and exchange, and insurance sectors in order to ensure the stability of the financial system of Japan. The agency operates ...
** Fair Trade Commission
** Food Safety Commission
** Personal Information Protection Commission
** Imperial Household Agency
The (IHA) is an agency of the government of Japan in charge of state matters concerning the Imperial House of Japan, Imperial Family, and the keeping of the Privy Seal of Japan, Privy Seal and State Seal of Japan. From around the 8th century ...
** Gender Equality Bureau
** Council on Economic and Fiscal Policy
** Atomic Energy Commission
** International Peace Cooperation
** Council for Science, Technology and Innovation
** Headquarters for Ocean Policy
** Northern Territories Affairs Administration
** Public Relations Office of the Government of Japan
* Cabinet Secretariat
** National Information Security Centre
** National Personnel Authority
** Coordination Office of Measures on Emerging Infectious Diseases
** Headquarters for the Abduction Issue
** Cabinet Legislation Bureau
** Office of Policy Planning and Coordination on Territory and Sovereignty
* Reconstruction Agency
The is an agency of the Government of Japan, Japanese government established on February 10, 2012 to coordinate reconstruction activities related to the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.
Mission
Accordi ...
* Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
The is a Cabinet (government), cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. Its English name was Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications (MPHPT) prior to 2004. It is housed in the 2nd Building of the Centr ...
** Environmental Dispute Coordination Commission
** Fire and Disaster Management Agency
The (FDMA) is an external agency attached to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications in Japan.
Background
The Fire and Disaster Management Agency was established through article 3 paragraph 2 of the 1948 National Government Organizat ...
* Ministry of Justice
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice, is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a ...
** Public Security Examination Commission
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichkei ...
** Public Security Intelligence Agency
The is the Security agency, domestic intelligence agency of Japan. It is administered by the Ministry of Justice (Japan), Ministry of Justice and is tasked with internal security and espionage against threats to Japanese national security based o ...
** Public Prosecutors Office
** Immigration Services Agency
* Ministry of Foreign Affairs
In many countries, the ministry of foreign affairs (abbreviated as MFA or MOFA) is the highest government department exclusively or primarily responsible for the state's foreign policy and relations, diplomacy, bilateral, and multilateral r ...
* Ministry of Finance
A ministry of finance is a ministry or other government agency in charge of government finance, fiscal policy, and financial regulation. It is headed by a finance minister, an executive or cabinet position .
A ministry of finance's portfoli ...
** National Tax Agency
The is the official tax collecting agency of Japan. As of October 2018, the Commissioner of NTA is Takeshi Fujii.
Mission
Mission: To enable taxpayers to properly and smoothly fulfill their tax responsibility.
To achieve the mission stated abo ...
** Japan Customs
* Ministry of Defense
** Acquisition, Technology and Logistics Agency
** Japan Self-Defence Forces
The are the military forces of Japan. Established in 1954, the JSDF comprises the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force, the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force, and the Japan Air Self-Defense Force. They are controlled by the Ministry of Defense ...
( Ground / Maritime / Air
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
)
** Joint Staff
* Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
The , also known as MEXT, is one of the eleven ministries of Japan that compose part of the executive branch of the government of Japan.
History
The Meiji period, Meiji government created the first Ministry of Education in 1871. In January 2001 ...
(MEXT)
** Education Policy Bureau
** Elementary and Secondary Education Bureau
** Higher Education Bureau
** Science and Technology Policy Bureau
** Research Promotion Bureau
** Agency for Cultural Affairs
The is a special body of the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). It was set up in 1968 to promote Japanese arts and culture.
The agency's budget for FY 2018 rose to ¥107.7 billion.
Overview
The age ...
** Japan Sports Agency
** The Japan Art Academy
** National Institute for Educational Policy Research
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ce ...
** National Institute of Science and Technology Policy
** The Japan Academy
** Headquarters for Earthquake Research Promotion
** Japanese National Commission for UNESCO
* Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare
** Pension Service
** Central Labour Relations Commission
* Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries may refer to:
* Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (Cambodia)
* Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (Japan)
* Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (Niue)
* Depar ...
** Fisheries Agency
** Forestry Agency
* Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry
The , METI for short, is a ministry of the Government of Japan. It was created by the 2001 Central Government Reform when the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI) merged with agencies from other ministries related to economic acti ...
(METI)
** Agency for Natural Resources and Energy
** Small and Medium Enterprise Agency
** Japan Patent Office
The is a Japanese governmental agency in charge of industrial property right affairs, under the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. The Japan Patent Office is located in Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda, Tokyo and is one of the world's largest pa ...
* Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
The , abbreviated MLIT, is a ministry of the Japanese government.国土交通省設置法
(MLIT)
** Japan Transport Safety Board
The is Japan's authority for establishing transportation safety (excluding related United States Forces Japan). It is a division of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT).
The agency formed on October 1, 2008 as a ...
** Japan Tourism Agency
The , JTA, is an organization which was set up on October 1, 2008 as an agency of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism.
** Japan Meteorological Agency
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA; ''気象庁, Kishō-chō'') is a division of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism dedicated to the Scientific, scientific observation and research of natural phenomena. Headquartered ...
** Japan Coast Guard
The is the coast guard responsible for the protection of the Geography of Japan#Composition, topography and geography, coastline of Japan under the oversight of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. It consists of about ...
* Ministry of the Environment
** Nuclear Regulation Authority
The is an administrative body of the Cabinet of Japan established to ensure nuclear safety in Japan as part of the Ministry of the Environment. Established on September 19, 2012, its first head was Shunichi Tanaka.
Background
The NRA was forme ...
* Board of Audit
Legislative
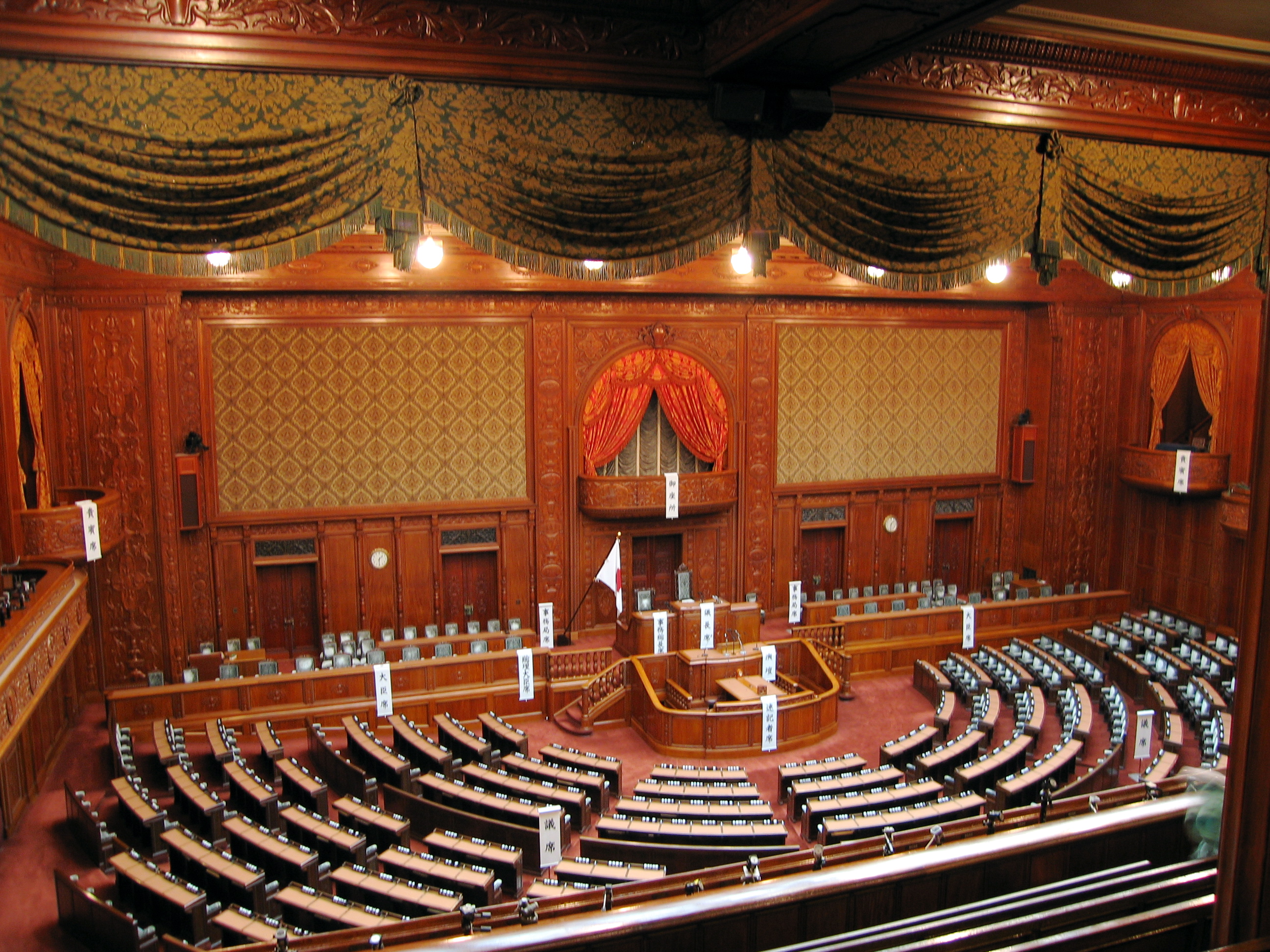
 The legislative branch organ of
The legislative branch organ of Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
is the . It is a bicameral legislature, composing of a lower house, the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
, and an upper house, the House of Councillors
The is the upper house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Representatives (Japan), House of Representatives is the lower house. The House of Councillors is the successor to the pre-war House of Peers (Japan), House of Peers. If the t ...
. Empowered by the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
to be "the highest organ of State power" and the only "sole law-making organ of the State", its houses are both directly elected under a parallel voting system and is ensured by the Constitution to have no discrimination on the qualifications of each members; whether be it based on "race, creed, sex, social status, family origin, education, property or income". The National Diet, therefore, reflects the sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
of the people; a principle of popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the leaders of a state and its government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associativ ...
whereby the supreme power lies within, in this case, the Japanese people
are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago. Japanese people constitute 97.4% of the population of the country of Japan. Worldwide, approximately 125 million people are of Japanese descent, making them list of contempora ...
.
The Diet responsibilities includes the making of laws, the approval of the annual national budget, the approval of the conclusion of treaties and the selection of the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
. In addition, it has the power to initiate draft constitutional amendments, which, if approved, are to be presented to the people for ratification in a referendum
A referendum, plebiscite, or ballot measure is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate (rather than their Representative democracy, representatives) on a proposal, law, or political issue. A referendum may be either bin ...
before being promulgated by the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
, in the name of the people
The term "the people" refers to the public or Common people, common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. I ...
. The Constitution also enables both houses to conduct investigations in relation to government, demand the presence and testimony of witnesses, and the production of records, as well as allowing either house of the Diet to demand the presence of the Prime Minister or the other Minister of State, in order to give answers or explanations whenever so required. The Diet is also able to impeach
Impeachment is a process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
In Euro ...
Court judges convicted of criminal or irregular conduct. The Constitution, however, does not specify the voting methods, the number of members of each house, and all other matters pertaining to the method of election of the each members, and are thus, allowed to be determined for by law.
Under the provisions of the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
and by law, all adults aged over 18 are eligible to vote, with a secret ballot
The secret ballot, also known as the Australian ballot, is a voting method in which a voter's identity in an election or a referendum is anonymous. This forestalls attempts to influence the voter by intimidation, blackmailing, and potential vote ...
and a universal suffrage
Universal suffrage or universal franchise ensures the right to vote for as many people bound by a government's laws as possible, as supported by the " one person, one vote" principle. For many, the term universal suffrage assumes the exclusion ...
, and those elected have certain protections from apprehension while the Diet is in session. Speeches, debates, and votes cast in the Diet also enjoy parliamentary privilege
Parliamentary privilege is a legal immunity enjoyed by members of certain legislatures, in which legislators are granted protection against civil or criminal liability for actions done or statements made in the course of their legislative duties ...
s. Each house is responsible for disciplining its own members, and all deliberations are public unless two-thirds or more of those members present passes a resolution agreeing it otherwise. The Diet also requires the presence of at least one-third of the membership of either house in order to constitute a quorum. All decisions are decided by a majority of those present, unless otherwise stated by the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
, and in the case of a tie, the presiding officer has the right to decide the issue. A member cannot be expelled, however, unless a majority of two-thirds or more of those members present passes a resolution.
Under the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
, at least one session of the Diet must be convened each year. The Cabinet can also, at will, convoke extraordinary sessions of the Diet and is required to, when a quarter or more of the total members of either house demands it. During an election, only the House of Representatives is dissolved. The House of Councillors is however, not dissolved but only closed, and may, in times of national emergency, be convoked for an emergency session. The Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
both convokes the Diet and dissolves the House of Representatives, but only does so on the advice of the Cabinet.
For bills to become law, they are to be first passed by both houses of the National Diet
, transcription_name = ''Kokkai''
, legislature = 215th Session of the National Diet
, coa_pic = Flag of Japan.svg
, house_type = Bicameral
, houses =
, foundation=29 November 1890(), leader1_type ...
, signed by the Ministers of State
Minister of state is a designation for a government minister, with varying meanings in different jurisdictions. In a number of European countries, the title is given as an honorific conferring a higher rank, often bestowed upon senior ministers ...
, countersigned by the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
, and then finally promulgated by the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
; however, without specifically giving the Emperor the power to oppose legislation.
House of Representatives
 The is the
The is the Lower house
A lower house is the lower chamber of a bicameral legislature, where the other chamber is the upper house. Although styled as "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has come to wield more power or otherwise e ...
, with the members of the house being elected once every four years, or when dissolved, for a four-year term. As of November 18, 2017, it has 465 members. Of these, 176 members are elected from 11 multi-member constituencies by a party-list system of proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions (Political party, political parties) amon ...
, and 289 are elected from single-member constituencies. 233 seats are required for majority. The House of Representatives is the more powerful house out of the two, it is able to override veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president (government title), president or monarch vetoes a bill (law), bill to stop it from becoming statutory law, law. In many countries, veto powe ...
es on bills imposed by the House of Councillors
The is the upper house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Representatives (Japan), House of Representatives is the lower house. The House of Councillors is the successor to the pre-war House of Peers (Japan), House of Peers. If the t ...
with a two-thirds majority. It can, however, be dissolved by the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
at will. Members of the house must be of Japanese nationality; those aged 18 years and older may vote, while those aged 25 years and older may run for office in the lower house.
The legislative powers of the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
is considered to be more powerful than that of the House of Councillors
The is the upper house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Representatives (Japan), House of Representatives is the lower house. The House of Councillors is the successor to the pre-war House of Peers (Japan), House of Peers. If the t ...
. While the House of Councillors has the ability to veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president (government title), president or monarch vetoes a bill (law), bill to stop it from becoming statutory law, law. In many countries, veto powe ...
most decisions made by the House of Representatives, some however, can only be delayed. This includes the legislation of treaties, the budget, and the selection of the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
. The Prime Minister, and collectively his Cabinet, can in turn, however, dissolve the House of Representatives whenever intended. While the House of Representatives is considered to be officially dissolved upon the preparation of the document, the House is only formally dissolved by the dissolution ceremony. The dissolution ceremony of the House is as follows:
# The document is rubber stamped by the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
, and wrapped in a purple silk cloth; an indication of a document of state act, done on behalf of the people.
# The document is passed on to the Chief Cabinet Secretary at the House of Representatives President's reception room.
# The document is taken to the Chamber for preparation by the General-Secretary.
# The General-Secretary prepares the document for reading by the Speaker.
# The Speaker of the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
promptly declares the dissolution of the House.
# The House of Representatives is formally dissolved.
It is customary that, upon the dissolution of the House, members will shout the Three Cheers of Banzai (萬歲).
House of Councillors
 The is the
The is the Upper house
An upper house is one of two Legislative chamber, chambers of a bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house. The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restricted p ...
, with half the members of the house being elected once every three years, for a six-year term. As of November 18, 2017, it has 242 members. Of these, 73 are elected from the 47 prefectural districts, by single non-transferable vote
Single non-transferable vote or SNTV is a multi-winner electoral system in which each voter casts a single vote. Being a semi-proportional variant of first-past-the-post voting, under SNTV small parties, as well as large parties, have a chance t ...
s, and 48 are elected from a nationwide list by proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions (Political party, political parties) amon ...
with open lists. The House of Councillors cannot be dissolved by the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
. Members of the house must be of Japanese nationality; those aged 18 years and older may vote, while those aged 30 years and older may run for office in the upper house.
As the House of Councillors can veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president (government title), president or monarch vetoes a bill (law), bill to stop it from becoming statutory law, law. In many countries, veto powe ...
a decision made by the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
, the House of Councillors can cause the House of Representatives to reconsider its decision. The House of Representatives however, can still insist on its decision by overriding the veto
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president (government title), president or monarch vetoes a bill (law), bill to stop it from becoming statutory law, law. In many countries, veto powe ...
by the House of Councillors with a two-thirds majority of its members present. Each year, and when required, the National Diet
, transcription_name = ''Kokkai''
, legislature = 215th Session of the National Diet
, coa_pic = Flag of Japan.svg
, house_type = Bicameral
, houses =
, foundation=29 November 1890(), leader1_type ...
is convoked at the House of Councillors, on the advice of the Cabinet, for an extra or an ordinary session, by the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
. A short speech is, however, usually first made by the Speaker of the House of Representatives before the Emperor proceeds to convoke the Diet with his Speech from the throne
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or their representative, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a Legislative session, session is opened. ...
.
Judicial

 The judicial branch of
The judicial branch of Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
consists of the Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
, and four other lower courts; the High Courts, District Courts, Family Courts and Summary Courts. Divided into four basic tiers, the Court's independence from the executive and legislative branches are guaranteed by the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
, and is stated as: "no extraordinary tribunal shall be established, nor shall any organ or agency of the Executive be given final judicial power"; a feature known as the Separation of Powers
The separation of powers principle functionally differentiates several types of state (polity), state power (usually Legislature#Legislation, law-making, adjudication, and Executive (government)#Function, execution) and requires these operat ...
. Article 76 of the Constitution states that all the Court judges are independent in the exercise of their own conscience and that they are only bounded by the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
and the laws. Court judges are removable only by public impeachment
Impeachment is a process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
In Eur ...
, and can only be removed, without impeachment, when they are judicially declared mentally or physically incompetent to perform their duties. The Constitution also explicitly denies any power for executive organs or agencies to administer disciplinary actions against judges. However, a Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
judge may be dismissed by a majority in a referendum; of which, must occur during the first general election of the National Diet's House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entities. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often ...
following the judge's appointment, and also the first general election for every ten years lapse thereafter. Trials must be conducted, with judgment declared, publicly, unless the Court "unanimously determines publicity to be dangerous to public order or morals"; with the exception for trials of political offenses, offenses involving the press, and cases wherein the rights of people as guaranteed by the Constitution, which cannot be deemed and conducted privately. Court judges are appointed by the Cabinet, in attestation of the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
, while the Chief Justice is appointed by the Emperor, after being nominated by the Cabinet; which in practice, known to be under the recommendation of the former Chief Justice.
The Legal system
A legal system is a set of legal norms and institutions and processes by which those norms are applied, often within a particular jurisdiction or community. It may also be referred to as a legal order. The comparative study of legal systems is th ...
in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
has been historically influenced by Chinese law
Chinese law is one of the oldest legal traditions in the world. The core of modern Chinese law is based on Germanic-style civil law, socialist law, and traditional Chinese approaches. For most of the history of China, its legal system has ...
; developing independently during the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
through texts such as '' Kujikata Osadamegaki''. It has, however, changed during the Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored Imperial House of Japan, imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Althoug ...
, and is now largely based on the Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an civil law; notably, the civil code
A civil code is a codification of private law relating to property law, property, family law, family, and law of obligations, obligations.
A jurisdiction that has a civil code generally also has a code of civil procedure. In some jurisdiction ...
based on the German model still remains in effect. A quasi-jury system has recently came into use, and the legal system also includes a bill of rights since May 3, 1947. The collection of Six Codes
Six Codes (; Kana: ろっぽう; Hangul: 육법) refers to the six main legal codes that make up the main body of law in Japan, Korea, and Republic of China (Taiwan). Sometimes, the term is also used to describe the six major areas of law. Furth ...
makes up the main body of the Japanese statutory law.
All Statutory Law
A statute is a law or formal written enactment of a legislature. Statutes typically declare, command or prohibit something. Statutes are distinguished from court law and unwritten law (also known as common law) in that they are the expressed wi ...
s in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
are required to be rubber stamped by the Emperor with the , and no Law can take effect without the Cabinet's signature, the prime minister's countersignature and the Emperor's promulgation.
Supreme Court
 The is the court of last resort and has the power of
The is the court of last resort and has the power of Judicial review
Judicial review is a process under which a government's executive, legislative, or administrative actions are subject to review by the judiciary. In a judicial review, a court may invalidate laws, acts, or governmental actions that are in ...
; as defined by the Constitution to be "the court of last resort with power to determine the constitutionality of any law, order, regulation or official act". The Supreme Court is also responsible for nominating judges to lower courts and determining judicial procedures. It also oversees the judicial system, overseeing activities of public prosecutors, and disciplining judges and other judicial personnel.
High Courts
The has the jurisdiction to hear appeals to judgments rendered by District Courts and Family Courts, excluding cases under the jurisdiction of theSupreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
. Criminal appeals are directly handled by the High Courts, but Civil cases are first handled by District Courts. There are eight High Courts in Japan: the Tokyo, Osaka, Nagoya, Hiroshima, Fukuoka, Sendai, Sapporo, and Takamatsu High Courts.
Penal system
The is operated by theMinistry of Justice
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice, is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a ...
. It is part of the criminal justice system
Criminal justice is the delivery of justice to those who have been accused of committing crimes. The criminal justice system is a series of government agencies and institutions. Goals include the rehabilitation of offenders, preventing other ...
, and is intended to resocialize, reform
Reform refers to the improvement or amendment of what is wrong, corrupt, unsatisfactory, etc. The modern usage of the word emerged in the late 18th century and is believed to have originated from Christopher Wyvill's Association movement, which ...
, and rehabilitate offenders. The ministry's Correctional Bureau administers the adult prison system, the juvenile correctional system, and three of the women's guidance homes, while the Rehabilitation Bureau operates the probation
Probation in criminal law is a period of supervision over an offence (law), offender, ordered by the court often in lieu of incarceration. In some jurisdictions, the term ''probation'' applies only to community sentences (alternatives to incar ...
and the parole
Parole, also known as provisional release, supervised release, or being on paper, is a form of early release of a prisoner, prison inmate where the prisoner agrees to abide by behavioral conditions, including checking-in with their designated ...
systems.
Other government agencies
The Cabinet Public Affairs Office's Government Directory also listed a number of government agencies that are more independent from executive ministries. The list for these types of agencies can be seen below. * Japan National Tourism Organisation (JNTO) *Japan International Cooperation Agency
The Japan International Cooperation Agency (), also known as JICA'','' is a governmental agency that delivers the bulk of Official Development Assistance (ODA) for the government of Japan. It is chartered with assisting economic and social gr ...
(JICA)
* Japan External Trade Organisation (JETRO)
* The Japan Foundation
* Bank of Japan
The is the central bank of Japan.Louis Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis Frédéric. (2005). "Nihon Ginkō" in The bank is often called for short. It is headquartered in Nihonbashi, Chūō, Tokyo, Chūō, Tokyo.
The said bank is a corporate entity ...
* Japan Mint
* National Research Bureau of Brewing (NRIB)
* State Guest Houses (Akasaka Palace
is a of the government of Japan. Other state guesthouses of the government include the Kyoto State Guest House.
The palace was originally built as the in 1909. Today the palace is designated by the government of Japan as an official accommod ...
, Kyoto State Guest House)
* National Archives of Japan
The preserve Japanese government documents and historical records and make them available to the public. Although Japan's reverence for its unique history and art is well documented and illustrated by collections of art and documents, there is a ...
* National Women's Education Centre
* Japan Broadcasting Corporation
, also known by its romanized initialism NHK, is a Japanese public broadcaster. It is a statutory corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television license fee.
NHK operates two terrestrial television channels (NHK General TV and NHK ...
(NHK)
* National Institutes for Cultural Heritage
* Japan Arts Council
* Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
The is an Independent Administrative Institution in Japan, established for the purpose of contributing to the advancement of science in all fields of the natural and social sciences and the humanities.JSPSweb page
History
The Japan Society f ...
(JSPS)
* Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The is the Japanese national Aeronautics, air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satell ...
(JAXA)
* Japan Science and Technology Agency
The Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST; Japanese: 科学技術振興機構) is a Japanese government agency which aims to build infrastructure that supports knowledge creation and dissemination in Japan. It is one of the National Research an ...
(JST)
* Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC)
* National Institute for Materials Science
is an Independent Administrative Institution and one of the largest scientific research centers in Japan.
History
The growth and development of today's scientific research center has passed through several phases in a number of locations:
In ...
(JIMS)
* Japan Atomic Energy Agency
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is a Japanese atomic energy company. While it inherited the activities of both Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute, JNC and Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, JAERI, it also inherited the nickname of J ...
(JAEA)
* New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation (NEDO)
* National Institute of Infectious Diseases (NIID)
* The Japan Institute for Labour Policy and Training
Local government
Local Autonomy Law
The , passed by the House of Representatives and the House of Peers on March 28, 1947 and promulgated as Law No. 67 of 1947 on April 17,Ministry of Justice, Japanese Law Translation Database SystemLocal Autonomy Act/ref> is an Act of devolution t ...
. They are given limited executive and legislative powers by the Constitution. Governors, mayors and members of assemblies are constitutionally elected by the residents.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
The is a Cabinet (government), cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. Its English name was Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications (MPHPT) prior to 2004. It is housed in the 2nd Building of the Centr ...
intervenes significantly in local government, as do other ministries. This is done chiefly financially because many local government jobs need funding initiated by national ministries. This is dubbed as the "thirty-percent autonomy".三割自治
The result of this power is a high level of organizational and policy standardization among the different local jurisdictions allowing them to preserve the uniqueness of their prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin word, "''praefectura"'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain inter ...
, city, or town. Some of the more collectivist jurisdictions, such as Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
and Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it t ...
, have experimented with policies in such areas as social welfare that later were adopted by the national government.
Local authorities
Japan is divided into forty-sevenadministrative divisions
Administrative divisions (also administrative units, administrative regions, subnational entities, or constituent states, as well as many similar generic terms) are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divi ...
, the prefectures
A prefecture (from the Latin word, "''praefectura"'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain inter ...
are: one metropolitan district (Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
), two urban prefectures (Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it t ...
and Osaka
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ...
), forty-three rural prefectures, and one "district", Hokkaidō
is the second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by railway via the Seikan Tunnel.
The ...
. Large cities are subdivided into wards, and further split into towns, or precincts, or subprefectures and counties.
Cities are self-governing units administered independently of the larger jurisdictions within which they are located. In order to attain city status, a jurisdiction must have at least 500,000 inhabitants, 60 percent of whom are engaged in urban occupations. There are self-governing
Self-governance, self-government, self-sovereignty or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any ...
towns outside the cities as well as precincts of urban wards. Like the cities, each has its own elected mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a Municipal corporation, municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilitie ...
and assembly. Villages are the smallest self-governing entities in rural areas. They often consist of a number of rural hamlets containing several thousand people connected to one another through the formally imposed framework of village administration. Villages have mayors and councils elected to four-year terms.
Structure
Each jurisdiction has a chief executive, called a in prefectures and a in municipalities. Most jurisdictions also have a unicameral , although towns and villages may opt for direct governance by citizens in a . Both the executive and assembly are elected by popular vote every four years. Local governments follow a modified version of theseparation of powers
The separation of powers principle functionally differentiates several types of state (polity), state power (usually Legislature#Legislation, law-making, adjudication, and Executive (government)#Function, execution) and requires these operat ...
used in the national government. An assembly may pass a vote of no confidence
A motion or vote of no confidence (or the inverse, a motion or vote of confidence) is a motion and corresponding vote thereon in a deliberative assembly (usually a legislative body) as to whether an officer (typically an executive) is deemed fi ...
in the executive, in which case the executive must either dissolve the assembly within ten days or automatically lose their office. Following the next election, however, the executive remains in office unless the new assembly again passes a no confidence resolution.
The primary methods of local lawmaking are and . Ordinances, similar to statutes in the national system, are passed by the assembly and may impose limited criminal penalties for violations (up to 2 years in prison and/or 1 million yen in fines). Regulations, similar to cabinet orders in the national system, are passed by the executive unilaterally, are superseded by any conflicting ordinances, and may only impose a fine of up to 50,000 yen.
Local governments also generally have multiple committee
A committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to a deliberative assembly or other form of organization. A committee may not itself be considered to be a form of assembly or a decision-making body. Usually, an assembly o ...
s such as school boards, public safety committees (responsible for overseeing the police
The police are Law enforcement organization, a constituted body of Law enforcement officer, people empowered by a State (polity), state with the aim of Law enforcement, enforcing the law and protecting the Public order policing, public order ...
), personnel committees, election committees and auditing committees. These may be directly elected or chosen by the assembly, executive or both.
Scholars have noted that political contestations at the local level tend not to be marked by strong party affiliation or political ideologies when compared to the national level. Moreover, in many local communities candidates from different parties tend to share similar concerns, e.g., regarding depopulation and how to attract new residents. Analyzing the political discourse among local politicians, Hijino suggests that local politics in depopulated areas is marked by two overarching ideas: "populationism" and "listenism." He writes, "“Populationism” assumes the necessity of maintaining and increasing the number of residents for the future and vitality of the municipality. “Listenism” assumes that no decision can be made unless all parties are consulted adequately, preventing majority decisions taken by elected officials over issues contested by residents. These two ideas, though not fully-fledged ideologies, are assumptions guiding the behavior of political actors in municipalities in Japan when dealing with depopulation."
All prefectures
A prefecture (from the Latin word, "''praefectura"'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain inter ...
are required to maintain departments of general affairs, finance, welfare, health, and labor. Departments of agriculture, fisheries, forestry, commerce, and industry are optional, depending on local needs. The Governor is responsible for all activities supported through local taxation
A comparison of tax rates by countries is difficult and somewhat subjective, as tax laws in most countries are extremely complex and the Tax incidence, tax burden falls differently on different groups in each country and sub-national unit. The l ...
or the national government.
See also
* Japanese honours system *Politics of Japan
The politics of Japan are conducted in a framework of a dominant-party bicameral parliamentary representative democratic constitutional monarchy. A hereditary monarch, currently Emperor Naruhito, serves as head of state while the Prime Min ...
* Administrative structure of the Imperial Japanese Government
* List of Japanese government and military commanders of World War II
This article provides a comprehensive overview of key leaders who played pivotal roles in Japan’s political and military governance during the Second World War. Covering influential figures from heads of state to high-ranking military officers. ...
References
External links
JapanGov – The Government of Japan
– official site of the Imperial House of Japan (archived November 20, 2016)
* ttp://www.digital.archives.go.jp/index_e.html Search official Japanese Government documents and records
Facts about Japan by CIA's The World Factbook
Video of the Enthronement Ceremony of the Emperor
Video of the National Diet Convocation Ceremony
Video of the House of Representatives Dissolution Ceremony
* {{Asia topic, Government of, title=Governments of Asia, TW=Government of the Republic of China Asian governments