Load Duration Curve on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
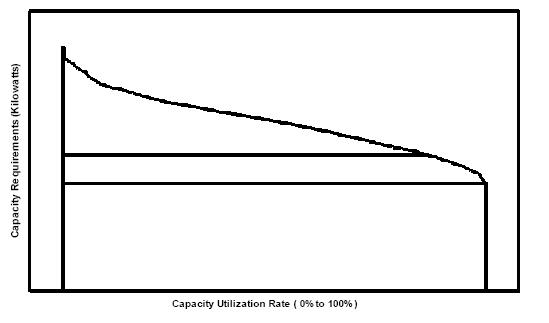 A load duration curve (LDC) is used in
A load duration curve (LDC) is used in
electric power generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its stor ...
to illustrate the relationship between generating capacity requirements and capacity utilization.
A LDC is similar to a load curve but the demand data is ordered in descending order of magnitude, rather than chronologically. The LDC curve shows the capacity utilization requirements for each increment of load. The height of each slice is a measure of capacity, and the width of each slice is a measure of the utilization rate or capacity factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is def ...
. The product of the two is a measure of electrical energy (e.g. kilowatthours).
A price duration curve shows the proportion of time for which the price exceeded a certain value.
Together, the price duration curve and load duration curve enable the analyst to understand the behaviour of the electricity market
An electricity market is a system that enables the exchange of electrical energy, through an electrical grid. Historically, electricity has been primarily sold by companies that operate electric generators, and purchased by consumers or electr ...
, for example, the likelihood of peaking power plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the powe ...
being required for service, and the impact that this might have on price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation expected, required, or given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, especially when the product is a service rather than a ph ...
.
Mathematically, it is a complementary cumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x.
Ever ...
.
References
{{reflist Electric power