Litmus Paper on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Litmus is a
Litmus is a
 Litmus can be found in many different species of
Litmus can be found in many different species of
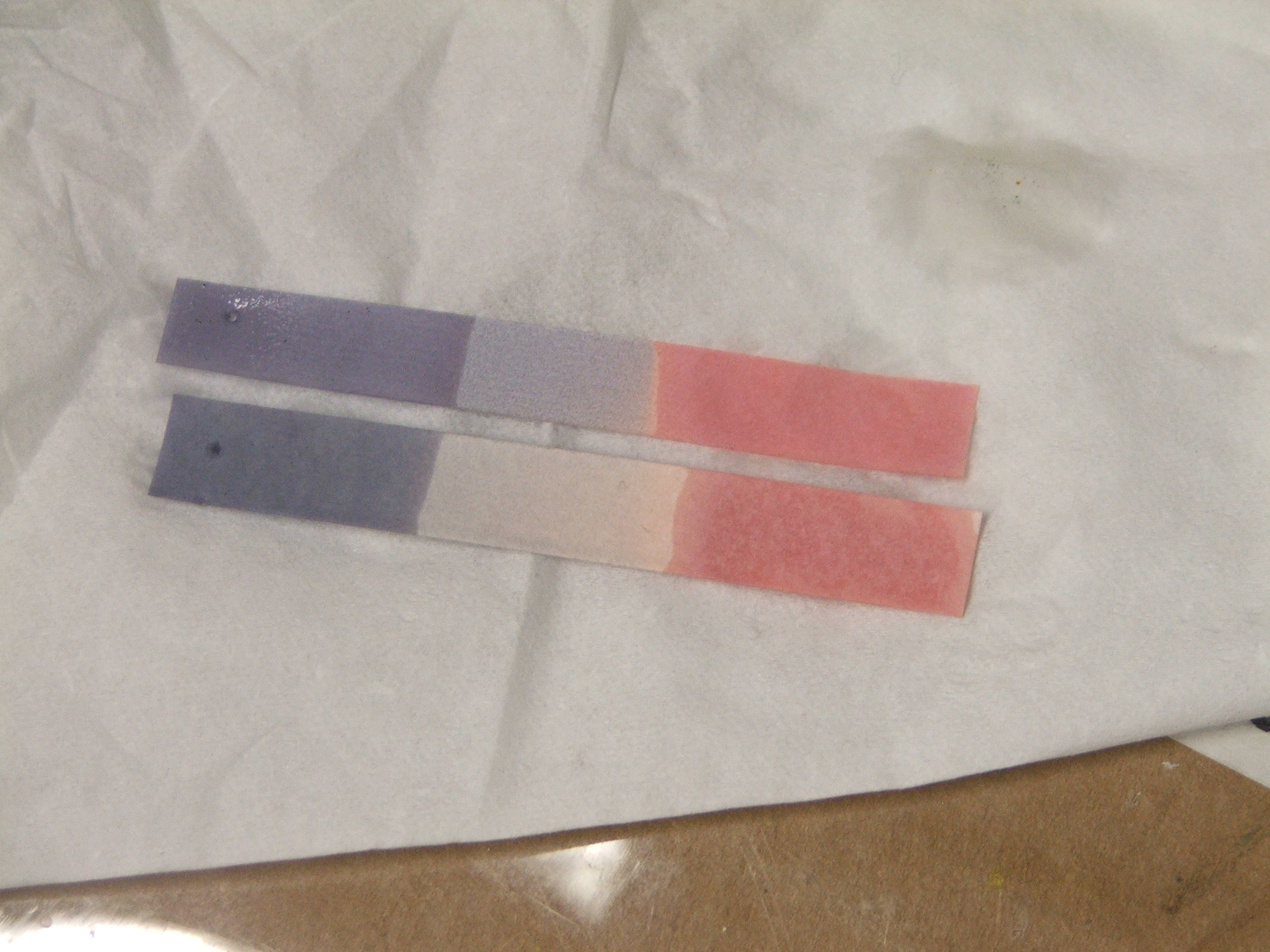 The main use of litmus is to test whether a solution is acidic or
The main use of litmus is to test whether a solution is acidic or

water-soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solub ...
mixture of different dyes extract
An extract (essence) is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may be sold as tinctures or absolutes or dried and powdered.
The aromatic principles of ma ...
ed from lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...
s. It is often absorbed onto filter paper to produce one of the oldest forms of pH indicator
A pH indicator is a halochromism, halochromic chemical compound added in small amounts to a Solution (chemistry), solution so the pH (acidity or Base (chemistry), basicity) of the solution can be determined visually or spectroscopically by chang ...
, used to test materials for acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
ity. In an acidic medium, blue litmus paper turns red, while in a basic or alkaline medium, red litmus paper turns blue. In short, it is a dye and indicator which is used to place substances on a pH scale.
History
The word "litmus" comes from theOld Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
word "litmosi" meaning "colour moss" or "colouring moss". The word is attested only in one Mediaeval source, a Norwegian law codex from 1316 in a chapter on customs and excise duties on pelts and furs. About 1300, the Spanish physician Arnaldus de Villa Nova began using litmus to study acids and bases.
From the 16th century onwards, the blue dye was extracted from some lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...
s, especially in the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
.
Natural sources
 Litmus can be found in many different species of
Litmus can be found in many different species of lichens
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...
. The dyes are extracted from such species as '' Roccella tinctoria'' (South American), '' Roccella fuciformis'' (Angola and Madagascar), '' Roccella pygmaea'' (Algeria), '' Roccella phycopsis'', '' Lecanora tartarea'' (Norway, Sweden), ''Variolaria dealbata'', '' Ochrolechia parella'', '' Parmotrema tinctorum'', and '' Parmelia''. Currently, the main sources are '' Roccella montagnei'' (Mozambique) and '' Dendrographa leucophoea'' (California).
Uses
basic
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
, as blue litmus paper turns red under acidic conditions, and red litmus paper turns blue under basic
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
or alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The ...
conditions, with the color change occurring over the pH range 4.5–8.3 at . Neutral litmus paper is purple. Wet litmus paper can also be used to test for water-soluble gases that affect acidity or basicity
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": ''Arrhenius bases'', ''Brønsted bases'', and ''Lewis bases''. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by Guilla ...
; the gas dissolves in the water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
and the resulting solution colors the litmus paper. For instance, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
gas, which is alkaline, turns red litmus paper blue. While all litmus paper acts as pH paper, the opposite is not true.
Litmus can also be prepared as an aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water ...
that functions similarly. Under acidic conditions, the solution is red, and under alkaline conditions, the solution is blue.
Chemical reactions other than acid–base can also cause a color change to litmus paper. For instance, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
gas turns blue litmus paper white; the litmus dye is bleached because hypochlorite ions are present. This reaction is irreversible, so the litmus is not acting as an indicator in this situation.
Chemistry
The litmus mixture has the CAS number 1393-92-6 and contains 10 to around 15 different dyes. All of the chemical components of litmus are likely to be the same as those of the related mixture known as orcein but in different proportions. In contrast with orcein, the principal constituent of litmus has an average molecular mass of 3300. Acid-base indicators on litmus owe their properties to a 7-hydroxyphenoxazonechromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The word is derived .
The color that is seen by our eyes is that of the light not Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavele ...
. Some fractions of litmus were given specific names including erythrolitmin (or erythrolein), azolitmin, spaniolitmin, leucoorcein, and leucazolitmin. Azolitmin shows nearly the same effect as litmus.
A recipe to make litmus out of the lichens, as outlined on a UC Santa Barbara website says:
Mechanism
Red litmus contains a weak diprotic acid. When it is exposed to a basic compound, thehydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
ions react with the added base. The conjugate base formed from the litmus acid has a blue color, so the wet red litmus paper turns blue in an alkaline solution.
References
{{reflist PH indicators Paper products