Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxides on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides (abbreviated NMC, Li-NMC, LNMC, or NCM) are mixed metal oxides of  There is a particular interest in optimizing NMC for electric vehicle applications because of the material's high
There is a particular interest in optimizing NMC for electric vehicle applications because of the material's high
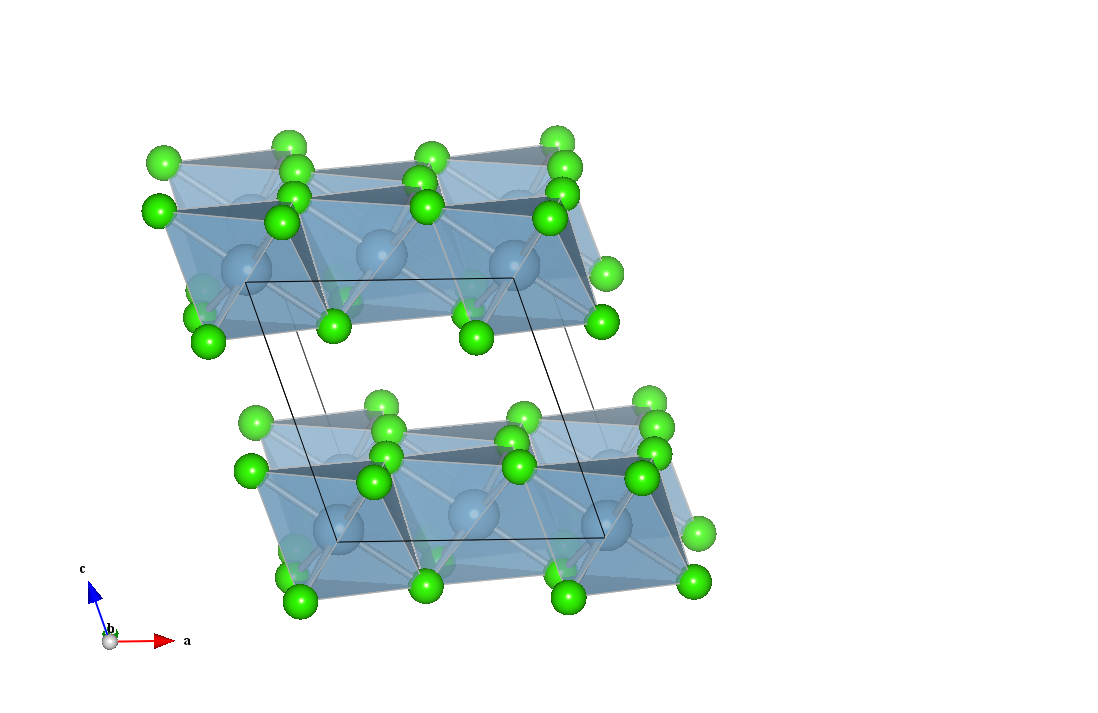 NMC materials have layered structures similar to the individual metal oxide compound
NMC materials have layered structures similar to the individual metal oxide compound
{{Lithium compounds
Manganese compounds
Lithium compounds
Nickel compounds
Cobalt compounds
Oxygen compounds
lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
and cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
with the general formula LiNi''x''Mn''y''Co''1-x-y''O2. These materials are commonly used in lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy ...
for mobile devices and electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a motor vehicle whose propulsion is powered fully or mostly by electricity. EVs encompass a wide range of transportation modes, including road vehicle, road and rail vehicles, electric boats and Submersible, submer ...
s, acting as the positively charged cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional curren ...
.
 There is a particular interest in optimizing NMC for electric vehicle applications because of the material's high
There is a particular interest in optimizing NMC for electric vehicle applications because of the material's high energy density
In physics, energy density is the quotient between the amount of energy stored in a given system or contained in a given region of space and the volume of the system or region considered. Often only the ''useful'' or extractable energy is measure ...
and operating voltage. Reducing the cobalt content in NMC is also a current target, due to metal's high cost. Furthermore, an increased nickel content provides more capacity within the stable operation window.
Structure
 NMC materials have layered structures similar to the individual metal oxide compound
NMC materials have layered structures similar to the individual metal oxide compound lithium cobalt oxide
Lithium cobalt oxide, sometimes called lithium cobaltateA. L. Emelina, M. A. Bykov, M. L. Kovba, B. M. Senyavin, E. V. Golubina (2011), "Thermochemical properties of lithium cobaltate". ''Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry'', volume 85, issue ...
(LiCoO2). Lithium ions intercalate between the layers upon discharging, remaining between the lattice planes until the battery gets charged, at which point the lithium de-intercalates and moves to the anode.
Points in a solid solution phase diagram between the end members LiCoO2, LiMnO2, and LiNiO2 represent stoichiometric
Stoichiometry () is the relationships between the masses of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of mass; the total mass of reactants must equal the total m ...
NMC cathodes. Three numbers immediately following the NMC abbreviation indicate the relative stoichiometry of the three defining metals. For example, an NMC molar composition of 33% nickel, 33% manganese, and 33% cobalt would abbreviate to NMC111 (also NMC333 or NCM333) and have a chemical formula of LiNi 0.33Mn0.33Co 0.33O2. A composition of 50% nickel, 30% manganese, and 20% cobalt would be called NMC532 (or NCM523) and have the formula LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2. Other newer common compositions are NMC622 and NMC811. The general lithium content typically remains around 1:1 with the total transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinid ...
content, with commercial NMC samples usually containing less than 5% excess lithium.
Performance
In NMC cathodes, the reversible insertion (lithiation) and extraction (delithiation) of lithium ions during battery discharge and charge are facilitated by redox reactions involving changes in the oxidation states of atoms within the oxide structure . * ''Traditional View (Cationic Redox)'': Historically, this capacity was attributed primarily to changes in the oxidation states of the transition metal cations (Ni, Mn, Co) – termed cationic redox. Transition metals have been chosen for their ability to adopt multiple stable oxidation states. * ''Measurement Challenge'': Directly probing the oxidation states of these cations during battery operation is difficult. Techniques like X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) provide indirect evidence but are typically performed ex-situ . * ''Emerging Understanding (Anionic Redox)'': Recent research has revealed a significant role for oxygen anion redox (anionic redox) in the charge compensation mechanism, particularly in manganese-rich NMC compositions. Oxygen can participate in redox reactions, exhibiting oxidation states other than -2 during delithiation. This contrasts with the simplistic view of oxygen as a spectator anion . * ''Impact on Design'': The computational design of advanced cathode materials now explicitly considers anionic redox mechanisms alongside cationic redox. This approach has been crucial for improving the performance particularly of manganese-based oxides like NMC. For NMC111, the idealoxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
s for charge distribution are Mn4+, Co3+, and Ni2+. Cobalt and nickel oxidize
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
partially to Co4+ and Ni4+ during charging, while Mn4+ remains inactive and maintains structural stability. Modifying the transition metal stoichiometry changes the material's properties, providing a way to adjust cathode performance. Most notably, increasing the nickel content in NMC increases its initial discharge capacity, but lowers its thermal stability and capacity retention. Increasing cobalt content comes at the cost of replacing either higher-energy nickel or chemically stable manganese while also being expensive. Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
can generate from the metal oxide at 300 °C when fully discharged, degrading the lattice. Higher nickel content decreases the oxygen generation temperature while also increasing the heat generation during battery operation. Cation mixing, a process in which Li+ substitutes Ni2+ ions in the lattice, increases as nickel concentration increases as well. The similar size of Ni2+ (0.69 Å) and Li+ (0.76 Å) facilitates cation mixing. Displacing nickel from the layered structure can alter the material's bonding characteristics, forming undesirable phases and lowering its capacity.
Synthesis
Thecrystallinity
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal, the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a large influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusi ...
, particle size distribution
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscle in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from s ...
, morphology, and composition all affect the performance of NMC materials, and these parameters can be tuned by using different synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
**Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organi ...
methods. The first report of nickel manganese cobalt oxide used a coprecipitation method, which is still commonly used today. This method involves dissolving the desired amount of metal precursors together and then drying them to remove the solvent. This material is then blended with a lithium source and heated to temperatures up to 900 °C under oxygen in a process called calcination
Calcination is thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), generally f ...
. Hydroxides, oxalic acid, and carbonates are the most common coprecipitation agents.
Sol–gel methods are another common NMC synthesis method. In this method, transition metal precursors are dissolved in a nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
or acetate
An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. alkaline, earthy, metallic, nonmetallic, or radical base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called ...
solution, then combined with a lithium nitrate or lithium acetate and citric acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a Transparency and translucency, colorless Weak acid, weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in Citrus, citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, ...
solution. This mixture is stirred and heated to about 80 °C under basic
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
conditions until a viscous gel forms. The gel is dried at around 120 °C and calcined twice, once at 450 °C and again at 800–900 °C, to obtain NMC material.
Hydrothermal treatment can be paired with either the coprecipitation or sol–gel routes. It involves heating the coprecipitate or gel precursors in an autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform steriliza ...
. The treated precursors are then filtered off and calcined normally. Hydrothermal treatments before calcination improves the crystallinity of NMC, which increases the material's performance in cells. However, this comes at the cost of longer material processing times.
History
NMC cathode materials are historically related toJohn B. Goodenough
John Bannister Goodenough ( ; July 25, 1922 – June 25, 2023) was an American materials scientist, a solid-state physicist, and a Nobel laureate in chemistry. From 1986 he was a professor of Materials Science, Electrical Engineering and Mechani ...
's 1980s work on lithium cobalt oxide
Lithium cobalt oxide, sometimes called lithium cobaltateA. L. Emelina, M. A. Bykov, M. L. Kovba, B. M. Senyavin, E. V. Golubina (2011), "Thermochemical properties of lithium cobaltate". ''Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry'', volume 85, issue ...
(LiCoO2), and can be represented as an intergrowth between a layered NaFeO2-type oxide and a closely related lithium rich Li2MnO3 oxide whose amount is related to the initial lithium excess. The first report of Li-rich NMCs was by Zhaolin Liu et. al. from the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering in Singapore in 1999. Further reports of the work of Li-rich NCM cathode material(s) were reported ca. 2000–2001 independently by four research teams:
# At Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center in Lemont, Illinois, Lemont, Illinois, United States. Founded in 1946, the laboratory is owned by the United Sta ...
in the USA a group led by Michael M. Thackeray reported these lithium-rich cathodes with the intergrowth structure.
# At Pacific Lithium in New Zealand a team led by Brett Amundsen reported a series of Li(LixCryMnz)O2 layered electrochemically active compounds.
# At Dalhousie University
Dalhousie University (commonly known as Dal) is a large public research university in Nova Scotia, Canada, with three campuses in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, a fourth in Bible Hill, Nova Scotia, Bible Hill, and a second medical school campus ...
in Canada a team led by Jeff Dahn reported a series of layered cathode materials based on a solid solution formulation of Li(LixMyMnz)O2, where metal M is not chromium.
# A group at Osaka City University led by Tsutomu Ohzuku, who also developed lithium nickel cobalt aluminium oxides
The lithium nickel cobalt aluminium oxides (abbreviated as Li-NCA, LNCA, or NCA) are a group of mixed metal oxides. Some of them are important due to their application in lithium-ion batteries. NCAs are used as active material in the positive elec ...
.
As of 2023, the biggest producers of NMC materials include EcoPro, Ronbay Technology, Easpring and Umicore.
Properties
The cell voltage of lithium-ion batteries with NMC cathodes is 3.6–3.7 V. Arumugam Manthiram has reported that the relative positioning of the metals' 3d bands to the oxygen 2p band leads to each metal's role within NMC cathode materials. The manganese 3d band is above the oxygen 2p band, resulting in manganese's high chemical stability. The cobalt and nickel 3d bands overlap the oxygen 2p band, allowing them to charge to their 4+ oxidation states without the oxygen ions losing electron density.Usage
Manyelectric car
An electric car or electric vehicle (EV) is a passenger car, passenger automobile that is propelled by an electric motor, electric traction motor, using electrical energy as the primary source of propulsion. The term normally refers to a p ...
s use NMC cathode batteries. NMC batteries were installed in the BMW ActiveE in 2011, and in the BMW i8 starting from 2013. Other electric cars with NMC batteries include, as of 2020: Audi e-tron GE, BAIC EU5 R550, BMW i3
The BMW i3 is an electric car that was manufactured by German marque BMW from 2013 to 2022. The i3 was BMW's first mass-produced zero-emissions vehicle, zero emissions vehicle and was launched as part of BMW's electric vehicle ''BMW i'' sub-bra ...
, BMW i4, BYD Yuan EV535, Chevrolet Bolt, Hyundai Kona Electric, Jaguar I-Pace, Jiangling Motors JMC E200L, NIO ES6, Nissan Leaf S Plus, Renault ZOE, Roewe Ei5, VW e-Golf and VW ID.3. Only a few electric car manufacturers do not use NMC cathodes in their traction batteries. Tesla is a significant exception, as they use nickel cobalt aluminium oxide and lithium iron phosphate
Lithium iron phosphate or lithium ferro-phosphate (LFP) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a component of lithium iron phosp ...
batteries for their vehicles. In 2015, Elon Musk
Elon Reeve Musk ( ; born June 28, 1971) is a businessman. He is known for his leadership of Tesla, SpaceX, X (formerly Twitter), and the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE). Musk has been considered the wealthiest person in th ...
reported that the home storage Tesla Powerwall
The Tesla Powerwall is a rechargeable lithium-ion battery stationary home energy storage product manufactured by Tesla Energy. The Powerwall stores electricity for solar self-consumption, time of use load shifting, and backup power.
The ...
is based on NMC in order to increase the number of charge/discharge cycles over the life of the units.
Mobile electronics such as mobile phones/smartphones, laptops, and pedelec
A Pedelec (from pedal electric cycle) or EPAC (''electronically power assisted cycle''), is a type of low-powered electric bicycle where the rider's pedalling is assisted by a small electric motor. However, unlike some other types of e-bikes, p ...
s can also use NMC-based batteries. These applications almost exclusively used lithium cobalt oxide batteries previously. Another application of NMC batteries is battery storage power station
A battery energy storage system (BESS), battery storage power station, battery energy grid storage (BEGS) or battery grid storage is a type of energy storage technology that uses a group of batteries in the grid to store electrical energy. Batte ...
s. Two such storage systems were installed in Korea in 2016 with a combined capacity of 15 MWh. In 2017, a 35 MW NMC battery with a capacity of 11 MWh was installed and commissioned in Newman in the Australian state of Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
.
See also
*Lithium-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energ ...
* Lithium cobalt oxide
Lithium cobalt oxide, sometimes called lithium cobaltateA. L. Emelina, M. A. Bykov, M. L. Kovba, B. M. Senyavin, E. V. Golubina (2011), "Thermochemical properties of lithium cobaltate". ''Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry'', volume 85, issue ...
* Lithium iron phosphate
Lithium iron phosphate or lithium ferro-phosphate (LFP) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a component of lithium iron phosp ...
* Karim Zaghib
References