List of nearest stars on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This list covers all known
This list covers all known

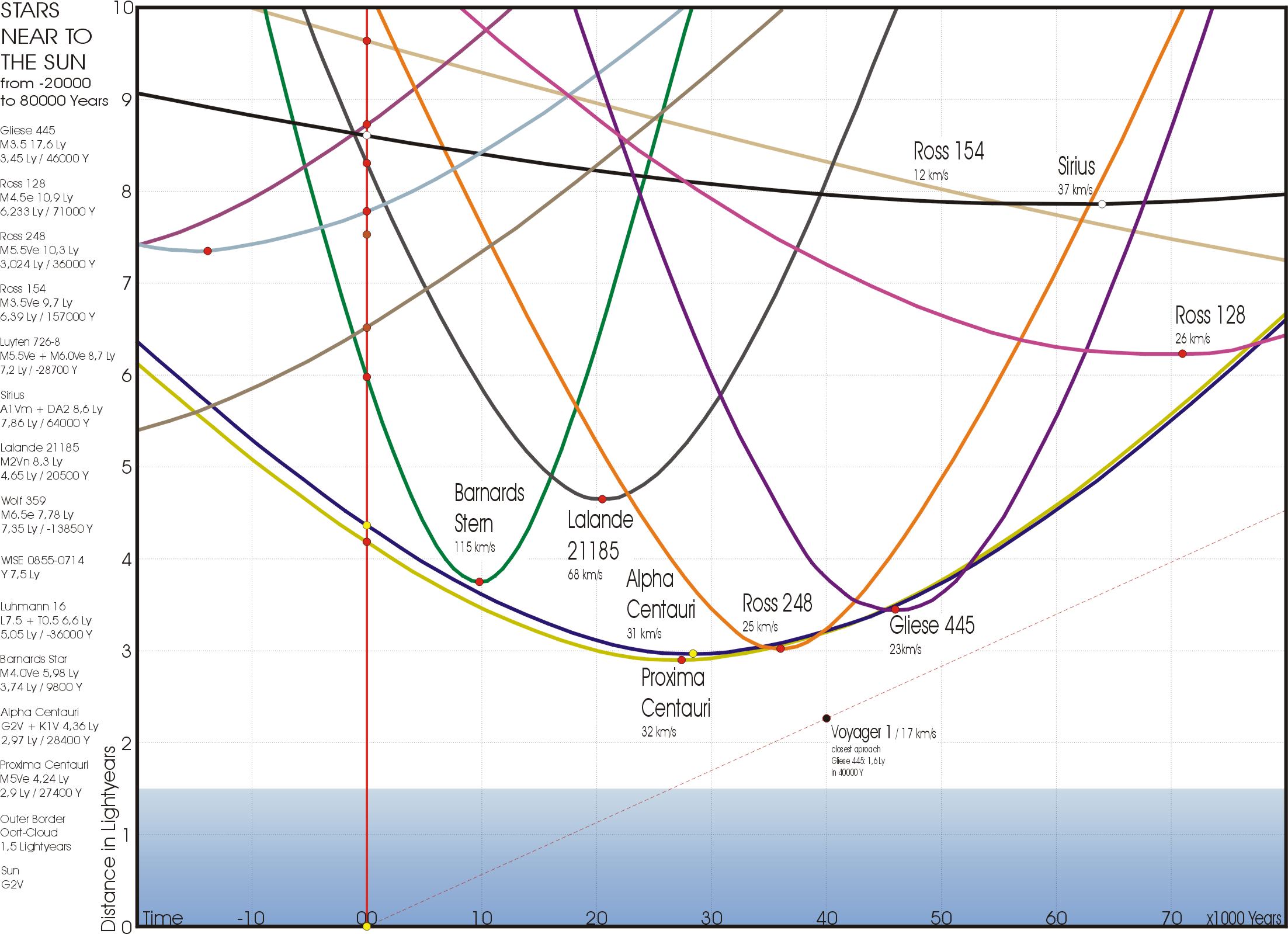 Over long periods of time, the slow independent motion of stars change in both relative position and in their distance from the observer. This can cause other currently distant stars to fall within a stated range, which may be readily calculated and predicted using accurate
Over long periods of time, the slow independent motion of stars change in both relative position and in their distance from the observer. This can cause other currently distant stars to fall within a stated range, which may be readily calculated and predicted using accurate
"The 100 nearest star systems"
'' Research Consortium on Nearby Stars'' * * * *
The dynamics of the closest stars
*
Nearest Stars 3D View
*Table 4 "The Census of Stars and Brown Dwarfs within 8 Parsecs of the Sun" in {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System nearest stars and brown dwarfs Local Bubble nearest stars and brown dwarfs Articles containing video clips nearest stars and brown dwarfs
 This list covers all known
This list covers all known star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s, white dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place i ...
s, brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big en ...
s, and sub-brown dwarfs within of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
. So far, 131 such objects have been found. Only 22 are bright enough to be visible without a telescope, for which the star's visible light needs to reach or exceed the dimmest brightness visible to the naked eye
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnification, magnifying, Optical telescope#Light-gathering power, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microsc ...
from Earth, which is typically around 6.5 apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), ...
.
The known 131 objects are bound in 94 stellar systems. Of those, 103 are main sequence stars: 80 red dwarf
A red dwarf is the smallest kind of star on the main sequence. Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of fusing star in the Milky Way, at least in the neighborhood of the Sun. However, due to their low luminosity, individual red dwarfs are ...
s and 23 "typical" stars having greater mass. Additionally, astronomers have found 6 white dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place i ...
s (stars that have exhausted all fusible hydrogen), 21 brown dwarfs, as well as 1 sub-brown dwarf, WISE 0855−0714
WISE 0855−0714 (full designation WISE J085510.83−071442.5, or W0855 for short) is a sub-brown dwarf of Y dwarf, spectral class Y4, located from the Sun in the constellation Hydra (constellation), Hydra. It is the fourth-List of ne ...
(possibly a rogue planet). The closest system is Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri (, α Cen, or Alpha Cen) is a star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus (constellation), Centaurus. It consists of three stars: Rigil Kentaurus (), Toliman (), and Proxima Centauri (). Proxima Centauri ...
, with Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri is the nearest star to Earth after the Sun, located 4.25 light-years away in the southern constellation of Centaurus. This object was discovered in 1915 by Robert T. A. Innes, Robert Innes. It is a small, low-mass st ...
as the closest star in that system, at 4.2465 light-years from Earth. The brightest, most massive and most luminous object among those 131 is Sirius A, which is also the brightest star in Earth's night sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon.
Natural light sources in a night sky include moonlig ...
; its white dwarf companion Sirius B is the hottest object among them. The largest object within the 20 light-years is Procyon
Procyon () is the brightest star in the constellation of Canis Minor and usually the list of brightest stars, eighth-brightest star in the night sky, with an apparent visual magnitude of 0.34. It has the Bayer designation α Canis Min ...
.
The Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
, and the other stars/dwarfs listed here, are currently moving within (or near) the Local Interstellar Cloud, roughly across. The Local Interstellar Cloud is, in turn, contained inside the Local Bubble
The Local Bubble, or Local Cavity, is a relative superbubble, cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest stars and brown dwarfs and, among others, the ...
, a cavity in the interstellar medium about across. It contains Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa M ...
and the Hyades star cluster
A star cluster is a group of stars held together by self-gravitation. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters, tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound; and open cluster ...
, among others. The Local Bubble also contains the neighboring G-Cloud, which contains the stars Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri (, α Cen, or Alpha Cen) is a star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus (constellation), Centaurus. It consists of three stars: Rigil Kentaurus (), Toliman (), and Proxima Centauri (). Proxima Centauri ...
and Altair
Altair is the brightest star in the constellation of Aquila (constellation), Aquila and the list of brightest stars, twelfth-brightest star in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Aquilae, which is Latinisation of name ...
. In the galactic context, the Local Bubble is a small part of the Orion Arm, which contains most stars that we can see without a telescope. The Orion Arm is one of the spiral arms of our Milky Way galaxy
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are ...
.
Astrometrics
The easiest way to determine stellar distance to the Sun for objects at these distances isparallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
, which measures how much stars appear to move against background objects over the course of Earth's orbit around the Sun. As a parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (AU), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and ...
(parallax-second) is defined by the distance of an object that would appear to move exactly one second of arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
against background objects, stars less than 5 parsecs away will have measured parallaxes of over 0.2 arcseconds, or 200 milliarcseconds. Determining past and future positions relies on accurate astrometric
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, the Milky Way.
History ...
measurements of their parallax and total proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable referenc ...
s (how far they move across the sky due to their actual velocity relative to the Sun), along with spectroscopically determined radial velocities (their speed directly towards or away from us, which combined with proper motion defines their true movement through the sky relative to the Sun). Both of these measurements are subject to increasing and significant errors over very long time spans, especially over the several thousand-year time spans it takes for stars to noticeably move relative to each other.
Based on results from the Gaia
In Greek mythology, Gaia (; , a poetic form of ('), meaning 'land' or 'earth'),, , . also spelled Gaea (), is the personification of Earth. Gaia is the ancestral mother—sometimes parthenogenic—of all life. She is the mother of Uranus (S ...
telescope's second data release from April 2018, an estimated 694 stars will approach the Solar System to less than 5 parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (AU), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and ...
s in the next 15 million years. Of these, 26 have a good probability to come within and another 7 within . This number is likely much higher, due to the sheer number of stars needed to be surveyed; a star approaching the Solar System 10 million years ago, moving at a typical Sun-relative 20–200 kilometers per second, would be 600–6,000 light-years from the Sun at present day, with millions of stars closer to the Sun. The closest encounter to the Sun so far predicted is the low-mass orange dwarf star Gliese 710 / HIP 89825 with roughly 60% the mass of the Sun. It is currently predicted to pass ( au) from the Sun in million years from the present, close enough to significantly disturb the Solar System's Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (pronounced or ), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, is scientific theory, theorized to be a cloud of billions of Volatile (astrogeology), icy planetesimals surrounding the Sun at distances ranging from 2,000 to 200,000 A ...
.

List
The classes of the stars and brown dwarfs are shown in the color of their spectral types (these colors are derived from conventional names for the spectral types and do not necessarily represent the star's observed color). Many brown dwarfs are not listed byvisual magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction of the object's light ca ...
but are listed by near-infrared J band apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), ...
due to how dim (and often invisible) they are in visible color bands (U, B or V). Absolute magnitude (with electromagnetic wave, 'light' band denoted in subscript) is a measurement at a 10-parsec distance across imaginary empty space devoid of all its sparse dust and gas. Some of the parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
es and resultant distances are rough measurements.
Distant future and past encounters
 Over long periods of time, the slow independent motion of stars change in both relative position and in their distance from the observer. This can cause other currently distant stars to fall within a stated range, which may be readily calculated and predicted using accurate
Over long periods of time, the slow independent motion of stars change in both relative position and in their distance from the observer. This can cause other currently distant stars to fall within a stated range, which may be readily calculated and predicted using accurate astrometric
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, the Milky Way.
History ...
measurements of parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
and total proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable referenc ...
s, along with spectroscopically determined radial velocities. Although extrapolations can be made into the past or future, they are subject to increasingly significant cumulative errors over very long periods. Inaccuracies of these measured parameters make determining the true minimum distances of any encountering stars or brown dwarfs fairly difficult.
One of the first stars known to approach the Sun particularly close is Gliese 710. The star, whose mass is roughly half that of the Sun, is currently 62 light-years from the Solar System. It was first noticed in 1999 using data from the Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions and distances of ...
satellite, and was estimated to pass less than from the Sun in 1.4 million years. With the release of ''Gaia'''s observations of the star, it has since been refined to a much closer , close enough to significantly disturb objects in the Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (pronounced or ), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, is scientific theory, theorized to be a cloud of billions of Volatile (astrogeology), icy planetesimals surrounding the Sun at distances ranging from 2,000 to 200,000 A ...
, which extends from the Sun.
''Gaia'' third data release has provided updated values for many of the candidates in the table below.
See also
*Interstellar travel
Interstellar travel is the hypothetical travel of spacecraft between star systems. Due to the vast distances between the Solar System and nearby stars, interstellar travel is not practicable with current propulsion technologies.
To travel between ...
* Location of Earth
* The Magnificent Seven
* Nearby Stars Database
* Solar System#Galactic context
* Stars in fiction
Related lists
* List of stars with resolved images *List of brightest stars
This is a list of stars arranged by their apparent magnitude – their brightness as observed from Earth. It includes all stars brighter than magnitude +2.50 in visible light, measured using a ''V''-band filter in the UBV photometric system. St ...
* List of star systems within 20–25 light-years
* List of star systems within 25–30 light-years
This is a list of star systems within 25–30 light-years of Earth. List
See also
* List of nearest stars
* List of star systems within 20–25 light-years
* List of star systems within 30–35 light-years
* Lists of stars
* List of nearest ...
* List of star systems within 30–35 light-years
* List of star systems within 35–40 light-years
* List of star systems within 40–45 light-years
* List of star systems within 45–50 light-years
* List of star systems within 50–55 light-years
* List of star systems within 55–60 light-years
* List of star systems within 60–65 light-years
* List of star systems within 65–70 light-years
* List of star systems within 70–75 light-years
* List of star systems within 75–80 light-years
* List of star systems within 80–85 light-years
* List of star systems within 85–90 light-years
* List of star systems within 90–95 light-years
* List of star systems within 95–100 light-years
* List of nearest giant stars
* List of nearest supergiants
* List of nearest bright stars
The following nearest bright stars are found within of the closest star, the Sun, and have an absolute magnitude of +8.5 or brighter, which is approximately comparable to a listing of stars more luminous than a red dwarf. Right ascension and ...
** Historical brightest stars
* List of nearest exoplanets
* List of nearest terrestrial exoplanet candidates
* List of nearest stars by spectral type
Below there are lists the nearest stars separated by spectral type. The scope of the list is still restricted to the main sequence spectral types: M-type star, M, K-type star, K, F-type star, F, G-type star, G, A-type star, A, B-type star, B and O- ...
* List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups
* List of star-forming regions in the Local Group
* Lists of stars
* List of Solar System objects by greatest aphelion
* List of trans-Neptunian objects
* List of nearest known black holes
Notes
References
External links
"The 100 nearest star systems"
'' Research Consortium on Nearby Stars'' * * * *
The dynamics of the closest stars
*
Nearest Stars 3D View
*Table 4 "The Census of Stars and Brown Dwarfs within 8 Parsecs of the Sun" in {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System nearest stars and brown dwarfs Local Bubble nearest stars and brown dwarfs Articles containing video clips nearest stars and brown dwarfs