Lipofuscin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
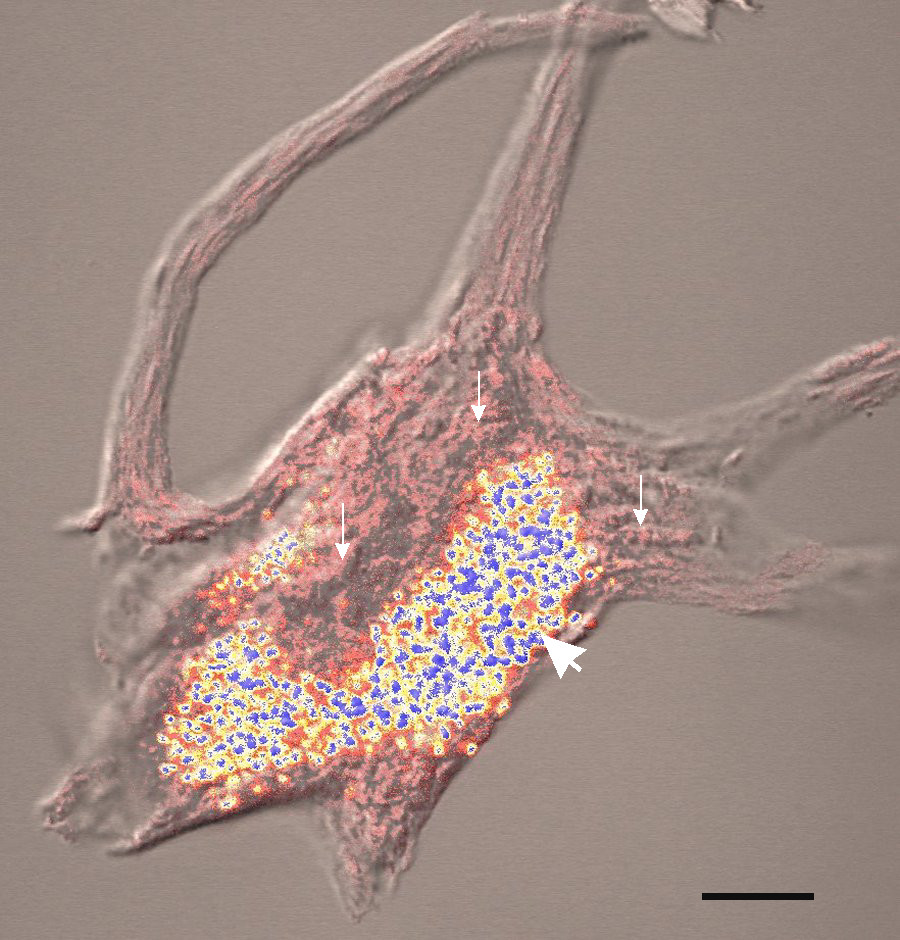 Lipofuscin is the name given to fine yellow-brown
Lipofuscin is the name given to fine yellow-brown
Lipofuscin
", ''Stanislaus Journal of Biochemical Reviews'' May 1997 Lipofuscin is also accepted as consisting of oxidized proteins (30–70%) as well as lipids (20–50%). It is a type of lipochrome and is specifically arranged around the nucleus. The accumulation of lipofuscin-like material may be the result of an imbalance between formation and disposal mechanisms. Such accumulation can be induced in rats by administering a
 Lipofuscin accumulation in the eye is a major risk factor implicated in
Lipofuscin accumulation in the eye is a major risk factor implicated in
Histology at neuro.wustl.edu
*
Destroying Lipofuscin and Destroying Cancer, FightAging.org
Unfocused Pulsed Lasers Selectively Destroy Lipofuscin, AcceleratingFuture.com
Lipofuscin
{{Pathology Biomolecules Senescence
 Lipofuscin is the name given to fine yellow-brown
Lipofuscin is the name given to fine yellow-brown pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
granules composed of lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
-containing residues of lysosomal
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
digestion. It is considered to be one of the aging or "wear-and-tear" pigments, found in the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
, heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
muscle, retina, adrenal
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
s, nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
cells, and ganglion
A ganglion (: ganglia) is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there are ...
cells.
Formation and turnover
Lipofuscin appears to be the product of theoxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
of unsaturated fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
s and may be symptomatic of membrane damage, or damage to mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
and lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
s. Aside from a large lipid content, lipofuscin is known to contain sugars and metals, including mercury, aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
.Chris Gaugler,Lipofuscin
", ''Stanislaus Journal of Biochemical Reviews'' May 1997 Lipofuscin is also accepted as consisting of oxidized proteins (30–70%) as well as lipids (20–50%). It is a type of lipochrome and is specifically arranged around the nucleus. The accumulation of lipofuscin-like material may be the result of an imbalance between formation and disposal mechanisms. Such accumulation can be induced in rats by administering a
protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
inhibitor ( leupeptin); after a period of three months, the levels of the lipofuscin-like material return to normal, indicating the action of a significant disposal mechanism. However, this result is controversial, as it is questionable if the leupeptin-induced material is true lipofuscin. There exists evidence that "true lipofuscin" is not degradable ''in vitro''; whether this holds ''in vivo'' over longer time periods is not clear.
The ''ABCR -/-'' knockout mouse has delayed dark adaptation but normal final rod threshold relative to controls. Bleaching the retina with strong light leads to formation of toxic cationic ''bis''-pyridinium salt, ''N''-retinylidene-''N''-retinyl-ethanolamine (''A2E''), which causes dry and wet age-related macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Some people experien ...
. From this experiment, it was concluded that ABCR has a significant role in preventing formation of A2E in extracellular photoreceptor surfaces during bleach recovery.
Relation to diseases
 Lipofuscin accumulation in the eye is a major risk factor implicated in
Lipofuscin accumulation in the eye is a major risk factor implicated in macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no sym ...
, a degenerative disease, and Stargardt disease
Stargardt disease is the most common inherited single-gene retinal disease. In terms of the first description of the disease, it follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which has been later linked to bi-allelic ABCA4 gene variants ...
, an inherited juvenile form of macular degeneration.
In the peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of Bilateria, bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside t ...
, abnormal accumulation of lipofuscin known as ''lipofuscinosis'' is associated with a family of neurodegenerative disorder
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Neuronal damage may also ultimately result in their death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, mul ...
s – neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses, the most common of these is Batten disease.
Also, pathological accumulation of lipofuscin is implicated in Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results i ...
, certain lysosomal diseases, acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disorder that results in excess growth of certain parts of the human body. It is caused by excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There ...
, denervation atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
, lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
myopathy
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. ''Myopathy'' means muscle disease ( Greek : myo- ''muscle'' + patheia '' -pathy'' : ''suffering''). This meaning implies that the primary defec ...
, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD defines COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory s ...
, and centronuclear myopathy. Accumulation of lipofuscin in the colon is the cause of the condition melanosis coli.
On the other hand, myocardial lipofuscin accumulation more directly reflects chronological ageing rather than human cardiac pathology.
Possible therapies
Calorie restriction
Calorie restriction (CR, also known as caloric restriction or energy restriction) is a dietary regimen that reduces the energy intake from foods and beverages without incurring malnutrition. The possible effect of calorie restriction on body w ...
, vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight compounds related in molecular structure that includes four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. The tocopherols function as fat-soluble antioxidants which may help protect cell membranes from reactive oxygen speci ...
, and increased glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources ...
appear to reduce or halt the production of lipofuscin.
The nootropic drug piracetam
Piracetam is a drug that has efficacy in cognitive disorders, vertigo, cortical myoclonus, dyslexia, and sickle cell anemia; sources differ on its usefulness for dementia. Piracetam is sold as a medication in many European countries. Piracetam ...
appears to significantly reduce accumulation of lipofuscin in the brain tissue of rats.
Other possible treatments:
* Centrophenoxine
* Acetyl-L-carnitine
* ''Ginkgo biloba
''Ginkgo biloba'', commonly known as ginkgo or gingko ( ), also known as the maidenhair tree, is a species of gymnosperm tree native to East Asia. It is the last living species in the order Ginkgoales, which first appeared over 290 million year ...
''
* Dimethylethanolamine
Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE or DMEA) is an organic compound with the formula . It is bifunctional, containing both a tertiary amine and primary alcohol functional groups. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is used in skin care products for improv ...
* Curcumin
Curcumin is a bright yellow chemical produced by plants of the ''Curcuma longa'' species. It is the principal curcuminoid of turmeric (''Curcuma longa''), a member of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is sold as a herbal supplement, cosmetic ...
Wet macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no sym ...
can be treated using selective photothermolysis
Laser hair removal is the process of hair removal by means of exposure to pulses of laser light that destroy the hair follicle. It had been performed experimentally for about twenty years before becoming commercially available in 1995–1996. One ...
where a pulsed unfocused laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
predominantly heats and kills lipofuscin-rich cells, leaving untouched healthy cells to multiply and fill in the gaps. The technique is also used as a skin treatment to remove tattoos
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the Human skin, skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several Process of ...
, liverspots, and in general make skin appear younger. This ability to selectively target lipofuscin has opened up research opportunities in the field of anti-aging medicine.
Soraprazan (remofuscin) has been found to remove lipofuscin from retinal pigment epithelial cells in animals. This opens up a new therapy option for the treatment of dry age-related macular degeneration and Stargardt disease
Stargardt disease is the most common inherited single-gene retinal disease. In terms of the first description of the disease, it follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which has been later linked to bi-allelic ABCA4 gene variants ...
, for which there is currently no treatment. The drug has now been granted orphan drug
An orphan drug is a medication, pharmaceutical agent that is developed to treat certain rare medical conditions. An orphan drug would not be profitable to produce without government assistance, due to the small population of patients affected by th ...
designation for the treatment of Stargardt disease by the European Medicines Agency.
Other uses
Lipofuscin quantification is used for age determination in variouscrustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s such as lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
s and spiny lobsters. Since these animals lack bony parts, they cannot be aged in the same way as bony fish, in which annual increments in the ear-bones or otolith
An otolith (, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called otoconium, statolith, or statoconium, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule ...
s are commonly used. Age determination of fish and shellfish is a fundamental step in generating basic biological data such as growth curves, and is needed for many stock assessment methods. Several studies have indicated that quantifying the amount of lipofuscin present in the eye-stalks of various crustaceans can give an index of their age. This method has not yet been widely applied in fisheries management mainly due to problems in relating lipofuscin levels in wild-caught animals with accumulation curves derived from aquarium-reared animals.
See also
* Residual body *Advanced glycation end-product
Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) are proteins or lipids that become Glycation, glycated as a result of exposure to sugars. They are a bio-marker implicated in aging and the development, or worsening, of many degenerative diseases, such as dia ...
s (AGEs)
References
20. Young B, Lowe JS, Stevens A, Heath JW. Wheater's Functional Histology: A Text and Atlas. 6th ed. ElsevierExternal links for general reviews
*Histology at neuro.wustl.edu
*
Destroying Lipofuscin and Destroying Cancer, FightAging.org
Unfocused Pulsed Lasers Selectively Destroy Lipofuscin, AcceleratingFuture.com
Lipofuscin
{{Pathology Biomolecules Senescence