Light Armored Vehicles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A military armored ( also spelled armoured) car is a wheeled
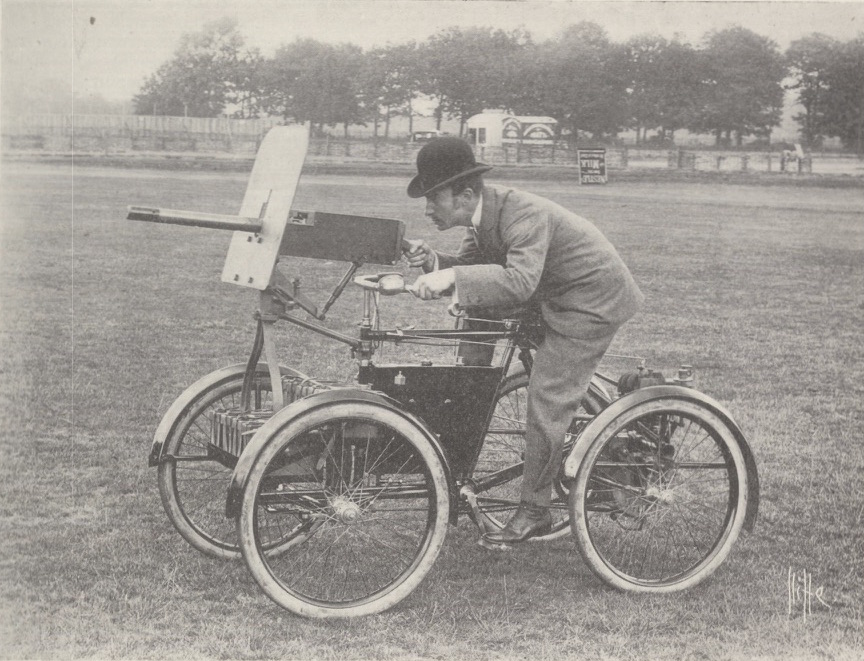 The
The
 The first armored car was the Simms' Motor War Car, designed by F.R. Simms and built by
The first armored car was the Simms' Motor War Car, designed by F.R. Simms and built by ''Death Special'' was built at the CFI plant in 
armoured fighting vehicle
An armoured fighting vehicle (British English) or armored fighting vehicle (American English) (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by vehicle armour, armour, generally combining operational mobility with Offensive (military), offensive a ...
, historically employed for reconnaissance
In military operations, military reconnaissance () or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, the terrain, and civil activities in the area of operations. In military jargon, reconnai ...
, internal security
Internal security is the act of keeping peace within the borders of a sovereign state or other Self-governance, self-governing territories, generally by upholding the national law and defending against internal security threats. This task and rol ...
, armed escort, and other subordinate battlefield tasks. With the gradual decline of mounted cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
, armored cars were developed for carrying out duties formerly assigned to light cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and body armor, armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was p ...
. Following the invention of the tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
, the armoured car remained popular due to its faster speed, comparatively simple maintenance and low production cost. It also found favor with several colonial armies as a cheaper weapon for use in underdeveloped regions. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, most armoured cars were engineered for reconnaissance and passive observation, while others were devoted to communications tasks. Some equipped with heavier armament could even substitute for tracked combat vehicles in favorable conditions—such as pursuit or flanking maneuvers during the North African campaign
The North African campaign of World War II took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943, fought between the Allies and the Axis Powers. It included campaigns in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts (Western Desert campaign, Desert Wa ...
.
Since World War II the traditional functions of the armored car have been occasionally combined with that of the armoured personnel carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world.
Acc ...
, resulting in such multipurpose designs as the BTR-40
The BTR-40 (БТР, from Бронетранспортёр, or '' Bronetransporter'', literally "armoured transporter† is a Soviet open-topped, wheeled armoured personnel carrier and reconnaissance vehicle. It is often referred to as the ''Soro ...
or the Cadillac Gage Commando
The Cadillac Gage Commando, frequently denoted as the M706 in U.S. military service, is an American armored car designed to be amphibious. It was engineered by Cadillac Gage specifically for the United States Military Police Corps during the ...
. Postwar advances in recoil control technology have also made it possible for a few armoured cars, including the B1 Centauro
The Centauro is a family of Italian military vehicles originating from a wheeled tank destroyer for light to medium territorial defense and tactical reconnaissance. It was developed by a consortium of manufacturers, the Società Consortile Iveco ...
, the Panhard AML
The Panhard AML (''automitrailleuse légère'', or "light armoured car") is an armoured car with reconnaissance capability. Designed by Panhard on a lightly armoured 4×4 chassis, it weighs an estimated 5.5 tonnes, and is thus suitable for airbo ...
, the AMX-10 RC
The AMX-10 RC is a French armoured fighting vehicle manufactured by Nexter Systems for armoured reconnaissance purposes. Equipping French cavalry units since 1979,https://imagesdefense.gouv.fr/fr/remise-du-premier-vehicule-amx-10-rc-au-2e-rh-r ...
and EE-9 Cascavel
The EE-9 ''Cascavel'' (, translated to ''Rattlesnake'') is a six-wheeled Brazilian armoured car developed primarily for reconnaissance. It was engineered by Engesa in 1970 as a replacement for Brazil's aging fleet of M8 Greyhounds. The vehicl ...
, to carry a large cannon capable of threatening many tanks.
History
Precursors
During the Middle Ages,war wagon
A war wagon is any of several historical types of early fighting vehicle involving an armed or armored animal-drawn cart or wagon.
China
One of the earliest example of using conjoined wagons in warfare as fortification is described in the Chine ...
s covered with steel plate, and crewed by men armed with primitive hand cannon
The hand cannon ( or ), also known as the gonne or handgonne, is the first true firearm and the successor of the fire lance. It is the oldest type of small arms, as well as the most mechanically simple form of metal barrel firearms. Unlike match ...
, flail
Flail may refer to:
* Flail (tool), an agricultural implement for threshing
* Flail (weapon)
A flail is a weapon consisting of a striking head attached to a handle by a flexible rope, strap, or chain. The chief tactical virtue of the flail i ...
s and musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually dis ...
s, were used by the Hussite
file:Hussitenkriege.tif, upright=1.2, Battle between Hussites (left) and Crusades#Campaigns against heretics and schismatics, Catholic crusaders in the 15th century
file:The Bohemian Realm during the Hussite Wars.png, upright=1.2, The Lands of the ...
rebels in Bohemia. These were deployed in formations where the horses and oxen were at the centre, and the surrounding wagons were chained together as protection from enemy cavalry.
With the invention of the steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
, Victorian inventors designed prototype self-propelled armored vehicles for use in sieges, although none were deployed in combat. H. G. Wells
Herbert George Wells (21 September 1866 – 13 August 1946) was an English writer, prolific in many genres. He wrote more than fifty novels and dozens of short stories. His non-fiction output included works of social commentary, politics, hist ...
' short story "The Land Ironclads
"The Land Ironclads" is a short story by British writer H. G. Wells, which originally appeared in the December 1903 issue of the ''Strand Magazine''. It features tank-like "land ironclads," armoured fighting vehicles that carry riflemen, engin ...
" provides a fictionalized account of their use.
Armed car
 The
The Motor Scout
The Motor Scout was the first armed petrol engine powered vehicle ever built. It was not intended for running over ploughed fields or charging, but it was designed to provide a cover or to support infantry and cavalry wherever good roads were a ...
was designed and built by British inventor F.R. Simms in 1898. It was the first armed petrol engine-powered vehicle ever built. The vehicle was a De Dion-Bouton
De Dion-Bouton was a French automobile manufacturer and railcar manufacturer, which operated from 1883 to 1953. The company was founded by the Marquis Jules-Albert de Dion, Georges Bouton, and Bouton's brother-in-law Charles Trépardoux.
Ste ...
quadricycle
The Quadricycle was an early form of automobile. Earliest models were propelled by a small steam engine, then designers switched to early internal combustion engines as they became available.
The word is derived from the fact that it had four ...
with a mounted Maxim machine gun
The Maxim gun is a Recoil operation, recoil-operated machine gun invented in 1884 by Hiram Maxim, Hiram Stevens Maxim. It was the first automatic firearm, fully automatic machine gun in the world.
The Maxim gun has been called "the weapon most ...
on the front bar. An iron shield in front of the car protected the driver.
Another early armed car was invented by Royal Page Davidson
Colonel Royal Page Davidson (October 9, 1870 – January 16, 1943) was an American inventor and educator, from Somerville, New Jersey. He was based in Northwestern Military and Naval Academy, which was founded by his father Harlan Page Davidson ...
at Northwestern Military and Naval Academy
Northwestern Military Academy (founded 1888) was a residential high school in Linn, Wisconsin which was founded by Harlan Page Davidson. Originally located in Highland Park, Illinois, the school was relocated to the town of Linn, Wisconsin on ...
in 1898 with the Davidson-Duryea gun carriage
The Davidson-Duryea gun carriage was originally a 3 wheel armed vehicle built by the Duryea Motor Wagon Company in 1899. The gun carriage was ordered by Royal Page Davidson of the Northwestern Military and Naval Academy in Highland Park, Illino ...
and the later Davidson Automobile Battery armored car.
However, these were not "armored cars" as the term is understood today, as they provided little protection for their crews from enemy fire.
First armoured cars
At the beginning of the 20th century, the first military armored vehicles were manufactured by adding armor and weapons to existing vehicles. The first armored car was the Simms' Motor War Car, designed by F.R. Simms and built by
The first armored car was the Simms' Motor War Car, designed by F.R. Simms and built by Vickers, Sons & Maxim
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 18 ...
of Barrow on a special Coventry
Coventry ( or rarely ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands county, in England, on the River Sherbourne. Coventry had been a large settlement for centurie ...
-built Daimler
Daimler is a German surname. It may refer to:
People
* Gottlieb Daimler (1834–1900), German inventor, industrialist and namesake of a series of automobile companies
* Adolf Daimler (1871–1913), engineer and son of Gottlieb Daimler
* Paul Da ...
chassis with a German-built Daimler motor in 1899. and a single prototype was ordered in April 1899 The prototype was finished in 1902, too late to be used during the Boer War
The Second Boer War (, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, Transvaal War, Anglo–Boer War, or South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics (the South African Republic an ...
.
The vehicle had Vickers armor, thick, and was powered by a four-cylinder Cannstatt Daimler engine, giving it a maximum speed of around . The armament, consisting of two Maxim gun
The Maxim gun is a Recoil operation, recoil-operated machine gun invented in 1884 by Hiram Maxim, Hiram Stevens Maxim. It was the first automatic firearm, fully automatic machine gun in the world.
The Maxim gun has been called "the weapon most ...
s, was carried in two turrets with 360° traverse. It had a crew of four. Simms' Motor War Car was presented at the Crystal Palace
The Crystal Palace was a cast iron and plate glass structure, originally built in Hyde Park, London, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. The exhibition took place from 1 May to 15 October 1851, and more than 14,000 exhibitors from around ...
, London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, in April 1902.
Another early armored car of the period was the French Charron, Girardot et Voigt 1902
The Charron, Girardot et Voigt 1902 was a French armoured car (French: ''Automitrailleuse blindée'') developed in 1902 by the company Charron, Girardot et Voigt. It was equipped with a Hotchkiss machine gun, and with 7 mm armour for the g ...
, presented at the ''Salon de l'Automobile et du cycle'' in Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
, on 8 March 1902. The vehicle was equipped with a Hotchkiss machine gun
The Hotchkiss machine gun was any of a line of products developed and sold by Hotchkiss et Cie, (full name Société Anonyme des Anciens Etablissements Hotchkiss et Cie), established by United States gunsmith Benjamin B. Hotchkiss. Hotchkiss mo ...
, and with armour for the gunner.
One of the first operational armored cars with four wheel (4x4) drive and partly enclosed rotating turret, was the Austro-Daimler Panzerwagen built by Austro-Daimler
Austro-Daimler was an Austrian car manufacturer from 1899 until 1934. It was a subsidiary of the Germany, German ''Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft'' (DMG) until 1909.
History
In 1890, Eduard Bierenz was appointed as Austrian retailer. The company so ...
in 1904. It was armored with thick curved plates over the body (drive space and engine) and had a thick dome-shaped rotating turret that housed one or two machine-guns. It had a four-cylinder engine giving it average cross country performance. Both the driver and co-driver had adjustable seats enabling them to raise them to see out of the roof of the drive compartment as needed.
The Spanish Schneider-Brillié was the first armored vehicle to be used in combat, being first used in the Kert Campaign
The Kert campaign () was a conflict in northern Morocco between Spain and insurgent Riffian '' harkas'' led by Mohammed Ameziane, who had called for a ''jihad'' against the Spanish occupation in the eastern Rif. It took place between 1911 and 1 ...
. The vehicle was equipped with two machineguns and built from a bus chassis.
An armored car known as the Pueblo
Pueblo refers to the settlements of the Pueblo peoples, Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, currently in New Mexico, Arizona, and Texas. The permanent communities, including some of the oldest continually occupied settlement ...
and used by the Badlwin-Felts detective agency during the Colorado Coalfield War
The Colorado Coalfield War was a major Labor dispute, labor uprising in the southern and central Colorado Front Range between September 1913 and December 1914. Striking began in late summer 1913, organized by the United Mine Workers of Ameri ...
. 
World War I
A great variety of armored cars appeared on both sides duringWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and these were used in various ways. Generally, armored cars were used by more or less independent car commanders. However, sometimes they were used in larger units up to squadron size. The cars were primarily armed with light machine guns, but larger units usually employed a few cars with heavier guns. As air power became a factor, armored cars offered a mobile platform for antiaircraft guns.
The first effective use of an armored vehicle in combat was achieved by the Belgian Army
The Land Component (, ), historically and commonly still referred to as the Belgian Army (, ), is the Land warfare, land branch of the Belgian Armed Forces. The King of the Belgians is the commander in chief. The current chief of staff of the Land ...
in August–September 1914. They had placed Cockerill Cockerill is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
;Sport and sportsmen
*Callum Cockerill-Mollett, English footballer
* Glenn Cockerill, English football manager
* Harry Cockerill (footballer) (1894–1960), English footballer
* John ...
armour plating and a Hotchkiss machine gun
The Hotchkiss machine gun was any of a line of products developed and sold by Hotchkiss et Cie, (full name Société Anonyme des Anciens Etablissements Hotchkiss et Cie), established by United States gunsmith Benjamin B. Hotchkiss. Hotchkiss mo ...
on Minerva
Minerva (; ; ) is the Roman goddess of wisdom, justice, law, victory, and the sponsor of arts, trade, and strategy. She is also a goddess of warfare, though with a focus on strategic warfare, rather than the violence of gods such as Mars. Be ...
touring cars, creating the Minerva Armored Car. Their successes in the early days of the war convinced the Belgian GHQ to create a Corps of Armoured Cars, who would be sent to fight on the Eastern front once the western front immobilized after the Battle of the Yser
The Battle of the Yser (, ) was a battle of the First World War that took place in October 1914 between the towns of Nieuwpoort, Belgium, Nieuwpoort and Diksmuide, along a stretch of the Yser River and the Yperlee Canal, in Belgium. The front ...
.
The British Royal Naval Air Service
The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty (United Kingdom), Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 April 1918, when it was merged with the British ...
dispatched aircraft to Dunkirk to defend the UK from Zeppelins. The officers' cars followed them and these began to be used to rescue downed reconnaissance pilots in the battle areas. They mounted machine guns on them and as these excursions became increasingly dangerous, they improvised boiler plate armoring on the vehicles provided by a local shipbuilder. In London Murray Sueter
Rear-Admiral Sir Murray Fraser Sueter (6 September 1872 – 3 February 1960) was a Royal Naval officer who was noted as a pioneer of naval aviation and later became a Member of Parliament (MP).
Naval career
Sueter was born in Alverstoke. Com ...
ordered "fighting cars" based on Rolls-Royce, Talbot
Talbot is a dormant automobile marque introduced in 1902 by British-French company Clément-Talbot. The founders, Charles Chetwynd-Talbot, 20th Earl of Shrewsbury and Adolphe Clément-Bayard, reduced their financial interests in their Clément ...
and Wolseley chassis. By the time Rolls-Royce Armoured Car
The Rolls-Royce armoured car is a British armoured car developed in 1914 and used during the First World War, Irish Civil War, the inter-war period in Imperial Air Control in Transjordan, Palestine and Mesopotamia, and in the early stages of the ...
s arrived in December 1914, the mobile period on the Western Front was already over.
More tactically important was the development of formed units of armored cars, such as the Canadian Automobile Machine Gun Brigade, which was the first fully mechanized unit in the history. The brigade was established on September 2, 1914, in Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital city of Canada. It is located in the southern Ontario, southern portion of the province of Ontario, at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the cor ...
, as Automobile Machine Gun Brigade No. 1 by Brigadier-General Raymond Brutinel. The brigade was originally equipped with eight Armoured Autocars mounting two machine guns. By 1918 Brutinel's force consisted of two motor machine gun brigades (each of five gun batteries containing eight weapons apiece). The brigade, and its armored cars, provided yeoman service in many battles, notably at Amiens. The RNAS section became the Royal Naval Armoured Car Division
The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 April 1918, when it was merged with the British Army's Royal Flying Corps ...
reaching a strength of 20 squadrons before disbanded in 1915. and the armoured cars passing to the army as part of the Machine Gun Corps. Only NO.1 Squadron was retained; it was sent to Russia. As the Western Front turned to trench warfare unsuitable to wheeled vehicles, the armoured cars were moved to other areas.
The 2nd Duke of Westminster took No. 2 Squadron of the RNAS to France in March 1915 in time to make a noted contribution to the Second Battle of Ypres
The Second Battle of Ypres was fought from 22 April – 25 May 1915, during the First World War, for control of the tactically-important high ground to the east and the south of the Flanders, Flemish town of Ypres, in western Belgium. The ...
, and thereafter the cars with their master were sent to the Middle East to play a part in the British campaign in Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
and elsewhere The Duke led a motorised convoy including nine armoured cars across the Western Desert in North Africa to rescue the survivors of the sinking of the SS Tara which had been kidnapped and taken to Bir Hakiem.
In Africa, Rolls Royce armoured cars were active in German South West Africa
German South West Africa () was a colony of the German Empire from 1884 until 1915, though Germany did not officially recognise its loss of this territory until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles.
German rule over this territory was punctuated by ...
and Lanchester Armoured Cars in British East Africa
East Africa Protectorate (also known as British East Africa) was a British protectorate in the African Great Lakes, occupying roughly the same area as present-day Kenya, from the Indian Ocean inland to the border with Uganda in the west. Cont ...
against German forces to the south.
Armored cars also saw action on the Eastern Front. From 18 February - 26 March 1915, the German army under General Max von Gallwitz
Max Karl Wilhelm von Gallwitz (2 May 1852 – 18 April 1937) was a German general from Breslau (Wrocław), Silesia, who served with distinction during World War I on both the Eastern and Western Fronts.
Biography
Gallwitz grew up in a Catho ...
attempted to break through the Russian lines in and around the town of Przasnysz
Przasnysz () is a town in north-central Poland. Located in the Masovian Voivodship, about north of Warsaw and about south of Olsztyn, it is the capital of Przasnysz County. It has 18,093 inhabitants (2004). It was one of the most important towns ...
, Poland, (about 110 km / 68 miles north of Warsaw) during the Battle of Przasnysz (Polish: ''Bitwa przasnyska''). Near the end of the battle, the Russians used four Russo-Balt
Russo-Balt (sometimes Russobalt or Russo-Baltique) was one of the first Russian companies that produced vehicles and aircraft between 1909 and 1923.
History
Riga factory
The Russo-Baltic Wagon Factory (; , RBVZ) was founded in 1874 in Rig ...
armored cars and a armored car to break through the Germans' lines and force the Germans to retreat.
World War II
The BritishRoyal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
(RAF) in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
was equipped with Rolls-Royce Armoured Car
The Rolls-Royce armoured car is a British armoured car developed in 1914 and used during the First World War, Irish Civil War, the inter-war period in Imperial Air Control in Transjordan, Palestine and Mesopotamia, and in the early stages of the ...
s and Morris tenders. Some of these vehicles were among the last of a consignment of ex-Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
armored cars that had been serving in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
since 1915. In September 1940 a section of the No. 2 Squadron RAF Regiment Company was detached to General Wavell's ground forces during the first offensive against the Italians in Egypt. During the actions in the October of that year the company was employed on convoy escort tasks, airfield defense, fighting reconnaissance patrols and screening operations.
During the 1941 Anglo-Iraqi War
The Anglo-Iraqi War was a British-led Allies of World War II, Allied military campaign during the Second World War against the Kingdom of Iraq, then ruled by Rashid Ali al-Gaylani who had seized power in the 1941 Iraqi coup d'état with assista ...
, some of the units located in the British Mandate of Palestine were sent to Iraq and drove Fordson armored cars. "Fordson" armored cars were Rolls-Royce armored cars which received new chassis from a Fordson
Fordson was a brand name of tractors and trucks. It was used on a range of mass-produced general-purpose tractors manufactured by Henry Ford & Son Inc from 1917 to 1920, by Ford Motor Company (U.S.) and Ford Motor Company Ltd (U.K.) from 1920 ...
truck in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
.
By the start of the new war, the German army possessed some highly effective reconnaissance vehicles, such as the ''Schwerer Panzerspähwagen
The (German for 'heavy armoured reconnaissance vehicle'), is a series of six- and eight-wheeled Armored car (military), armoured cars that were used by Nazi Germany, Germany during the World War II, Second World War.
In the German Army, armou ...
''. The Soviet BA-64
The BA-64 (, from , ''Bronirovaniy Avtomobil'', literally "armoured car") was a Soviet four-wheeled scout car, armoured scout car. Built on the chassis of a GAZ-64 or GAZ-67 jeep, it incorporated a hull loosely modeled after that of the Leichter ...
was influenced by a captured ''Leichter Panzerspähwagen
The ''Leichter Panzerspähwagen'' (German: "light armoured reconnaissance vehicle") was a series of light four-wheel drive armoured cars produced by Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1944.
Development history
The Sd.Kfz. 221 was the first in a series of ...
'' before it was first tested in January 1942.
In the second half of the war, the American M8 Greyhound
The M8 light armored car is a 6×6 armored car produced by the Ford Motor Company during World War II. It was used from 1943 by United States and British forces in Europe and the Pacific until the end of the war. The vehicle was widely exported ...
and the British Daimler Armoured Cars featured turrets mounting light guns (40 mm or less). As with other wartime armored cars, their reconnaissance roles emphasized greater speed and stealth than a tracked vehicle could provide, so their limited armor, armament and off-road capabilities were seen as acceptable compromises.
Military use
A military armored car is a type ofarmored fighting vehicle
An armoured fighting vehicle (British English) or armored fighting vehicle (American English) (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by armour, generally combining operational mobility with offensive and defensive capabilities. AFVs can b ...
having wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machin ...
s (from four to ten large, off-road wheels) instead of tracks, and usually light armor
Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, e ...
. Armored cars are typically less expensive and on roads have better speed and range than tracked military vehicles. They do however have less mobility as they have less off-road capabilities because of the higher ground pressure. They also have less obstacle climbing capabilities than tracked vehicles. Wheels are more vulnerable to enemy fire than tracks, they have a higher signature and in most cases less armor than comparable tracked vehicles. As a result, they are not intended for heavy fighting; their normal use is for reconnaissance
In military operations, military reconnaissance () or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, the terrain, and civil activities in the area of operations. In military jargon, reconnai ...
, command, control, and communications, or for use against lightly armed insurgents or rioters. Only some are intended to enter close combat, often accompanying convoys to protect soft-skinned vehicle
In military terminology, a soft-skinned vehicle, also known as a 'B' vehicle, is a vehicle that is not protected by vehicle armour. Lexicographer Eric Partridge believed the term soft-skinned vehicle first appeared in military parlance in the ear ...
.
Light armored cars, such as the British Ferret
The ferret (''Mustela furo'') is a small, domesticated species belonging to the family Mustelidae. The ferret is most likely a domesticated form of the wild European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), as evidenced by the ferret's ability to inter ...
are armed with just a machine gun. Heavier vehicles are armed with autocannon
An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a automatic firearm, fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber ( or more) armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary ammunition, incendiary shell (projectile), shells, ...
or a large caliber gun. The heaviest armored cars, such as the German, World War II era Sd.Kfz. 234 or the modern, US M1128 mobile gun system
The M1128 mobile gun system (MGS) is an eight-wheeled assault gun of the Stryker family, mounting a M68 (tank gun), 105 mm tank gun, based on the Canadian LAV III light-armored vehicle manufactured by General Dynamics Land Systems for the U.S. A ...
, mount the same guns that arm medium tanks.
Armored cars are popular for peacekeeping or internal security duties. Their appearance is less confrontational and threatening than tanks, and their size and maneuverability is said to be more compatible with tight urban spaces designed for wheeled vehicles. However, they do have a larger turning radius compared to tracked vehicles which can turn on the spot and their tires are vulnerable and are less capable in climbing and crushing obstacles. Further, when there is true combat they are easily outgunned and lightly armored. The threatening appearance of a tank is often enough to keep an opponent from attacking, whereas a less threatening vehicle such as an armored car is more likely to be attacked.
Many modern forces now have their dedicated armored car designs, to exploit the advantages noted above. Examples would be the M1117 armored security vehicle
The M1117 armored security vehicle (ASV; nicknamed Guardian) is an internal security vehicle based on the Cadillac Gage Commando, V-100 and V-150 Commando series of Armored car (military), armored cars. It was developed in the late 1990s for ser ...
of the USA or Alvis Saladin
The FV601 Saladin is a six-wheeled armoured car developed by Crossley Motors and later manufactured by Alvis. Designed in 1954, it replaced the AEC armoured car in service with the British Army from 1958 onward. The vehicle weighed 11 tonnes ...
of the post-World War II era in the United Kingdom.
Alternatively, civilian vehicles may be modified into improvised armored cars in ''ad hoc'' fashion. Many militias and irregular forces adapt civilian vehicles into AFVs (armored fighting vehicles) and troop carriers, and in some regional conflicts these "technicals" are the only combat vehicles present. On occasion, even the soldiers of national militaries are forced to adapt their civilian-type vehicles for combat use, often using improvised armor
Improvised vehicle armour is a form of vehicle armour consisting of protective materials added to a vehicle such as a car, truck, or tank in an irregular and extemporized fashion using available materials. Typically, improvised armour is adde ...
and scrounged weapons.
Scout cars
In the 1930s, a new sub-class of armored car emerged in the United States, known as the ''scout car''. This was a compact light armored car which was either unarmed or armed only with machine guns for self-defense. Scout cars were designed as purpose-built reconnaissance vehicles for passive observation and intelligence gathering. Armored cars which carried large caliber, turreted weapons systems were not considered scout cars. The concept gained popularity worldwide duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and was especially favored in nations where reconnaissance theory emphasized passive observation over combat.
Examples of armored cars also classified as scout cars include the Soviet BRDM series, the British Ferret
The ferret (''Mustela furo'') is a small, domesticated species belonging to the family Mustelidae. The ferret is most likely a domesticated form of the wild European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), as evidenced by the ferret's ability to inter ...
, the Brazilian EE-3 Jararaca
The EE-3 Jararaca is a Brazilian scout car developed for route reconnaissance, liaison, and internal security purposes. It was engineered by Engesa in response to a perceived Brazilian Army requirement for a light armored car capable of replac ...
, the Hungarian D-442 FÚG
The D-442 FUG () and D-944 PSZH () are the result of Hungarian domestic development of relatively cheap amphibious armoured scout car and armored personnel carrier series. The FUG and PSZH were exported with limited success, thus it is also known ...
, and the American Cadillac Gage Commando Scout.
See also
*Armored bus
An armoured bus or armored bus is a type of bus which provides increased protection for passengers, usually against firearm, small arms and improvised explosive devices. The bus can be a stock commercial bus with retro-fitted vehicle armour as ...
*Armored personnel carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world.
Acc ...
*Armored car (valuables)
An armored vehicle (also known as an armored cash transport car, security van, or armored truck) is an armored van or truck used to transport valuables, such as large quantities of money or other valuables, especially for banks or retail com ...
*Armored car (VIP)
A VIP armored car is a civilian vehicle with a reinforced structure that is designed to protect its occupants from assaults, bullets and blasts. Armored cars are typically manufactured with bulletproof glass and layers of armor plating, often ...
*Armoring:
**Aramid
Aramid fibers, short for aromatic polyamide, are a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers. They are used in aerospace and military applications, for ballistic-rated bulletproof vest, body armor cloth, fabric and ballistic composites ...
**Bulletproof glass
Bulletproof glass, ballistic glass, transparent armor, or bullet-resistant glass is a strong and optically transparent material that is particularly resistant to penetration by projectiles, although, like any other material, it is not completel ...
**Twaron
Twaron (a brand name of Teijin Aramid) is a para-aramid, high-performance yarn. It is a heat-resistant fibre, helps in ballistic protection and cut protection. Twaron was developed in the early 1970s by the Dutch company Akzo Nobel's division E ...
**Vehicle armor
Military vehicles are commonly armoured (or armored; see spelling differences) to withstand the impact of shrapnel, bullets, shells, rockets, and missiles, protecting the personnel inside from enemy fire. Such vehicles include armoured fightin ...
* Gun truck
*SWAT vehicle
A Tactical Police vehicle, SWAT vehicle, police armored vehicle, or police rescue vehicle is a non-military armored vehicle used by police tactical units to respond to incidents. They are most often in configurations similar to Military light u ...
*Tankette
A tankette is a tracked armoured fighting vehicle that resembles a small tank, roughly the size of a car. It is mainly intended for light infantry support and scouting.
*Technical (vehicle)
A technical, known as a non-standard tactical vehicle (NSTV) in United States military parlance, is a light improvised fighting vehicle, typically an open-backed civilian pickup truck or four-wheel drive vehicle modified to mount Small Arms and ...
Notes
References
*Crow, Duncan, and Icks, Robert J., ''Encyclopedia of Armored Cars'', Chatwell Books, Secaucus, NJ, 1976. . * {{Authority control Armoured fighting vehicles by type Internal security vehicles Paramilitary vehicles