Leonid Govorov on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Leonid Aleksandrovich Govorov (; – 19 March 1955) was a
 In 1923 he met in Odessa, and later married Lydia Izdebska, the daughter of a former manager of a Polish estate. In 1924 their son Vladimir was born.
Govorov obtained further military education, graduating from the Artillery course in 1926, the Higher Academy course in 1930, and the Frunze Military Academy in 1933. In 1936, Govorov was among the first officers who attended the newly founded Military Academy of Red Army General Staff, from which he graduated in 1938.
From 1936, he was head of artillery in the
In 1923 he met in Odessa, and later married Lydia Izdebska, the daughter of a former manager of a Polish estate. In 1924 their son Vladimir was born.
Govorov obtained further military education, graduating from the Artillery course in 1926, the Higher Academy course in 1930, and the Frunze Military Academy in 1933. In 1936, Govorov was among the first officers who attended the newly founded Military Academy of Red Army General Staff, from which he graduated in 1938.
From 1936, he was head of artillery in the
 In late November 1942, Govorov began planning the next operation to break the blockade of Leningrad. In December, the plan was approved by the Stavka and received the codename
In late November 1942, Govorov began planning the next operation to break the blockade of Leningrad. In December, the plan was approved by the Stavka and received the codename
 ;Soviet Awards
;Foreign Awards
;Soviet Awards
;Foreign Awards
Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
military commander. Trained as an artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
officer, he joined the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
in 1920. He graduated from several Soviet military academies, including the Military Academy of Red Army General Staff. He participated in the Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
of 1939–1940 against Finland as a senior artillery officer.
In World War II, Govorov rose to command an army in November 1941 during the Battle of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front during World War II, between October 1941 and January 1942. The Soviet defensive effort frustrated H ...
. He commanded the Leningrad Front
The Leningrad Front () was formed during the 1941 German approach on Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg) by dividing the Northern Front into the Leningrad Front and Karelian Front on August 27, 1941.
History
The Leningrad Front was immediately ...
from April 1942 to the end of the war. He reached the rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union
Marshal of the Soviet Union (, ) was the second-highest military rank of the Soviet Union. Joseph Stalin wore the uniform and insignia of Marshal after World War II.
The rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union was created in 1935 and abolished in ...
in 1944, and was awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union () was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society. The title was awarded both ...
and many other awards.Glantz p. 214 He was the father of Soviet General Vladimir Govorov.
Early years and Russian Revolution
Leonid Aleksandrovich Govorov was born into a peasant family of Russian ethnicity in the village of Butyrki inVyatka Governorate
Vyatka Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR from 1796 to 1929, with its capital in Vyatka (now Kirov, Kirov Oblast, Kirov). The ...
(now in Kirov Oblast
Kirov Oblast ( rus, Кировская область, p=ˈkʲirəfskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) located in Eastern Europe. Its administrative center is the city of Kirov. As of the 2010 census, the population ...
). He attended a technical high school in Yelabuga and enrolled in the shipbuilding department of Petrograd Polytechnical Institute. In December 1916, however, he was mobilized and was sent to the Konstantinovskye Artillery School, from which he graduated in 1917. He became an artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
officer with the rank of podporuchik.
When the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution, social change in Russian Empire, Russia, starting in 1917. This period saw Russia Dissolution of the Russian Empire, abolish its mona ...
broke out and the Russian Army disintegrated, Govorov returned home, but was conscripted into the White Guard army of Aleksandr Kolchak in October 1918, serving in an artillery battery with the 8th Kama Rifle Division of the 2nd Ufa Army Corps in the Western Army, fighting in the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
. Govorov fought in the Spring Offensive of the Russian Army, a general drive westwards by White forces in the east. He deserted in November 1919, fleeing to Tomsk
Tomsk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Tomsk Oblast in Russia, on the Tom (river), Tom River. Population:
Founded in 1604, Tomsk is one of the oldest cities in Siberia. It has six univers ...
, where he took part in an uprising against White authorities as part of a fighting squad. Govorov joined the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
in January 1920, serving in the 51st Rifle Division as an artillery battalion commander. With the division, he fought in the Siege of Perekop in November, during which Soviet forces drove Pyotr Wrangel's White Army out of Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
. Govorov was wounded twice during the year and was awarded the Order of the Red Banner
The Order of the Red Banner () was the first Soviet military decoration. The Order was established on 16 September 1918, during the Russian Civil War by decree of the All-Russian Central Executive Committee. It was the highest award of S ...
in 1921 for his actions in Crimea.
Interwar years
Kiev Military District
The Kiev Military District (; , abbreviated ) was a military district of the Imperial Russian Army and subsequently of the Red Army and Soviet Armed Forces. It was first formed in 1862, and was headquartered in Kiev (Kyiv) for most of its exist ...
. In 1938 he was appointed as lecturer in tactics at the Dzerzhinsky Artillery Academy. In 1939, he finished his first research publication.Kiselev p. 115 This was the period of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
's Great Purge
The Great Purge, or the Great Terror (), also known as the Year of '37 () and the Yezhovshchina ( , ), was a political purge in the Soviet Union that took place from 1936 to 1938. After the Assassination of Sergei Kirov, assassination of ...
. Govorov was close to being arrested, but in the end survived thanks to the intervention of Mikhail Kalinin
Mikhail Ivanovich Kalinin (, ; 3 June 1946) was a Soviet politician and Russian Old Bolshevik revolutionary who served as the first chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet (head of state) from 1938 until his resignation in 1946. From ...
and continued to rise in rank.
World War II
In 1939 the Soviet Union invaded Finland, and Govorov was appointed chief of artillery of the 7th Army, as his research while at Dzerzhinsky Artillery Academy was about assaulting and penetrating fortified enemy positions. He commanded the massive artillery assault that allowed the Soviet breakthrough along the Mannerheim Line in 1940. For this he was awarded theOrder of the Red Star
The Order of the Red Star () was a military decoration of the Soviet Union. It was established by decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR of 6 April 1930 but its statute was only defined in decree of the Presidium of the ...
and promoted to the rank of division commander. He was then appointed Deputy Inspector-General of Artillery of the Red Army.
After Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941, Govorov commanded the Artillery on the Western Front in Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
from August to October 1941. During the Battle of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front during World War II, between October 1941 and January 1942. The Soviet defensive effort frustrated H ...
, he was appointed Chief of Artillery of the 5th Army, under the command of Major General Dmitri Danilovich Lelyushenko. After Lelyushenko was wounded on 18 October Govorov assumed command of the army. During the Soviet counter-offensives in the winter of 1941–42, his army liberated Mozhaisk. As a result, he was promoted to the rank of lieutenant-general of artillery.Glantz, p. 214
Defense of Leningrad
In April 1942 Govorov was appointed commander of the Leningrad Group of Forces of theLeningrad Front
The Leningrad Front () was formed during the 1941 German approach on Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg) by dividing the Northern Front into the Leningrad Front and Karelian Front on August 27, 1941.
History
The Leningrad Front was immediately ...
, which combined the former Leningrad and Volkhov Fronts. In July, the Volkhov Front was re-established, and Govorov became the head of the entire Leningrad Front, replacing Lieutenant General M.S. Khosin. Leningrad had been cut off from the rest of the country since September 1941, and the Soviet forces were trying to lift the siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad was a Siege, military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) in the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 1941 t ...
, which was causing colossal damage to the city and suffering to the civilian population. The Road of Life, which was the only means of supply to the city, was frequently cut by regular German and Finnish air strikes. Despite several German requests Mannerheim decided that Finnish forces would not attack Leningrad. Soviet forces launched several offensives in the region in 1942, but these failed to lift the siege. The Lyuban Offensive Operation resulted in the encirclement and destruction of most of the Soviet 2nd Shock Army
The 2nd Shock Army (), sometimes translated to English as 2nd Assault Army, was a field army of the Soviet Union during the Second World War. This type of formation was created in accordance with prewar doctrine that called for Shock Armies to ''o ...
. In this situation, Govorov's background as an artilleryman was considered most valuable, since the city was under constant shelling, and one of Govorov's tasks was to launch an artillery counter-offensive against the German guns.
As soon as he became the commander of the Leningrad Front in July 1942, Govorov mounted local attacks in several sectors of the front, while preparing a much larger offensive. Together with the Volkhov Front, the Leningrad Front would break the blockade of the city by eliminating the German positions south of Ladoga Lake, where only separated the Leningrad and Volkhov Fronts. This position was called "the bottleneck". At the same time, German forces were planning Operation Northern Light () to capture the city and link up with Finnish forces. To achieve that, heavy reinforcements arrived from Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
, which the German forces had captured in July 1942. Both sides were unaware of the other's preparations. As a result, the Soviet Sinyavino Offensive failed and the 2nd Shock army was decimated for the second time in a year, but the German forces suffered heavy casualties and canceled Operation Northern Light.
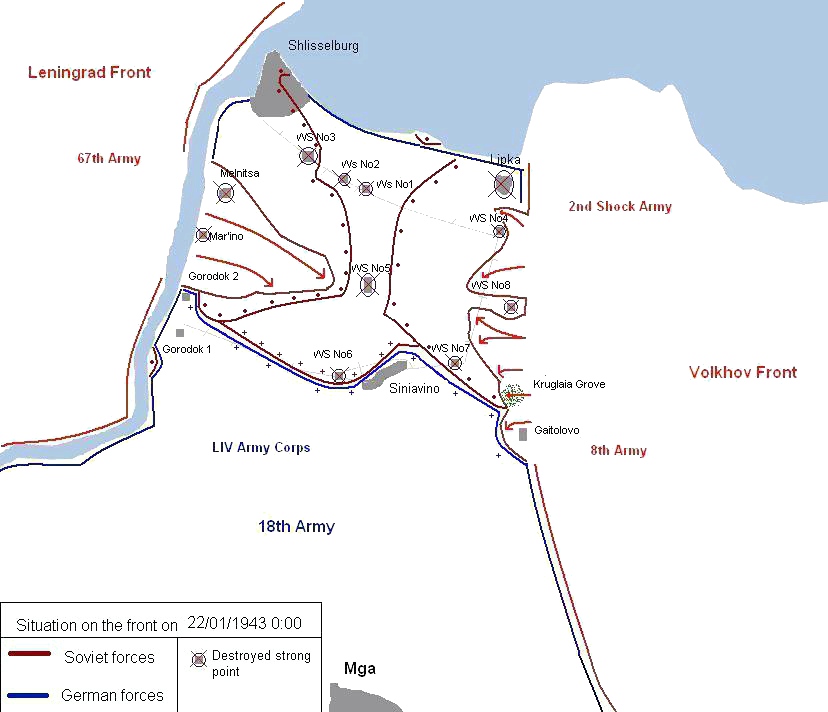
 In late November 1942, Govorov began planning the next operation to break the blockade of Leningrad. In December, the plan was approved by the Stavka and received the codename
In late November 1942, Govorov began planning the next operation to break the blockade of Leningrad. In December, the plan was approved by the Stavka and received the codename Operation Iskra
Operation Iskra (), a Soviet military operation in January 1943 during World War II, aimed to break the Wehrmacht's siege of Leningrad. Planning for the operation began shortly after the failure of the Sinyavino Offensive (1942), Sinyavino Offe ...
(Spark). Operation Iskra began on 13 January 1943, and on 18 January Soviet forces linked up, breaking the blockade. By 22 January the front line stabilized. The operation successfully opened a land corridor 8–10 km wide to the city. A railroad was swiftly built through the corridor that allowed far more supplies to reach the city than the "Road of Life", eliminating the possibility of the capture of the city and a German-Finnish link up. Govorov was promoted to Colonel General
Colonel general is a military rank used in some armies. It is particularly associated with Germany, where historically General officer#Old European system, general officer ranks were one grade lower than in the Commonwealth and the United States, ...
on 15 January and was awarded the Order of Suvorov
The Order of Suvorov () is a military decoration of the Russian Federation named in honor of Russian Generalissimo Prince Alexander Suvorov (1729–1800).
History
The Order of Suvorov was originally a Soviet Union, Soviet award established on ...
1st Class on 28 January.
The Leningrad and Volkhov Fronts tried to follow up their success with a much more ambitious offensive operation named Operation Polyarnaya Zvezda (Polar Star). This operation had the aim of decisively defeating the German Army Group North
Army Group North () was the name of three separate army groups of the Wehrmacht during World War II. Its rear area operations were organized by the Army Group North Rear Area.
The first Army Group North was deployed during the invasion of Pol ...
, but achieved very modest gains. Several other offensives were conducted by Govorov in the area in 1943, slowly expanding the corridor into Leningrad, and making other small gains. In November 1943, Govorov began planning the Leningrad-Novgorod Offensive which would drive Army Group North out of the Leningrad region. On 17 November he was promoted to army general
Army general or General of the army is the highest ranked general officer in many countries that use the French Revolutionary System. Army general is normally the highest rank used in peacetime.
In countries that adopt the general officer fou ...
.
Soviet Counter Offensive
The Soviet offensive started on 14 January 1944. By 1 March the Leningrad, Volkhov and 2nd Baltic Fronts had driven Army Group North back up to on a front, liberating the southern Leningrad region and part of the Kalinin region.Glantz p. 410 By that time, the reinforced Germans forces were at the "Panther Line", stretching fromNarva
Narva is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in the Ida-Viru County, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia border, E ...
to Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=Ru-Псков.oga, p=psˈkof; see also Names of Pskov in different languages, names in other languages) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov O ...
using Lake Pskov as a barrier, where the offensive was stopped in several heavy battles around Narva. On 18 April the Soviet forces were ordered to the defense, a new 3rd Baltic Front was created to coordinate operations near Narva and Govorov's Leningrad Front turned attention to the north.Glantz p. 409–410 In June 1944, during the Vyborg–Petrozavodsk Offensive, which led to Soviet recapture of Vyborg, Govorov was promoted to the rank of marshal of the Soviet Union
Marshal of the Soviet Union (, ) was the second-highest military rank of the Soviet Union. Joseph Stalin wore the uniform and insignia of Marshal after World War II.
The rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union was created in 1935 and abolished in ...
. Later his forces recaptured the Baltic states, and in autumn 1944 his forces blocked Army Group North in what became known as Courland Pocket
The Courland Pocket was a Pocket (military), pocket located on the Courland Peninsula in Latvia on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 9 October 1944 to 10 May 1945.
Army Group North of the ''Wehrmacht'' were ...
. On 27 January 1945, Govorov was awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union () was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society. The title was awarded both ...
.
Post-war career
In the postwar years Govorov was commander of the Leningrad Military District, and then Chief Inspector of Ground Forces. In 1948 he was appointed Commander of National Air Defence Forces, and in 1952 he also became Deputy Minister of Defence. In these posts he oversaw the modernization of the Soviet air defence system for the age of thejet aircraft
A jet aircraft (or simply jet) is an aircraft (nearly always a fixed-wing aircraft) propelled by one or more jet engines.
Whereas the engines in Propeller (aircraft), propeller-powered aircraft generally achieve their maximum efficiency at much ...
and the atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear expl ...
. But Govorov was by this time suffering from chronic heart disease, and died in March 1955. He was cremated and his ashes in the Kremlin Wall Necropolis. A street in St Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
is named after him.
Honours and awards
 ;Soviet Awards
;Foreign Awards
;Soviet Awards
;Foreign Awards
Citations and notes
References
* * * * *Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Govorov, Leonid 1897 births 1955 deaths People from Sovetsky District, Kirov Oblast People from Yaransky Uyezd Candidates of the Central Committee of the 19th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union Second convocation members of the Soviet of the Union Third convocation members of the Soviet of Nationalities Fourth convocation members of the Soviet of Nationalities Marshals of the Soviet Union Russian military personnel of World War I People of the Russian Civil War Soviet military personnel of World War II Recipients of the Order of Victory Chief Commanders of the Legion of Merit Foreign recipients of the Legion of Merit Heroes of the Soviet Union Recipients of the Order of Suvorov, 1st class Recipients of the Order of Lenin Recipients of the Order of the Red Banner Recipients of the Order of Kutuzov, 1st class Grand Officers of the Legion of Honour Recipients of the Croix de Guerre 1939–1945 (France) Russian people of World War II Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University alumni Military Academy of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union alumni Frunze Military Academy alumni Burials at the Kremlin Wall Necropolis Soviet Air Defence Force officers Residents of the Benois House Siege of Leningrad