Leeds Priory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
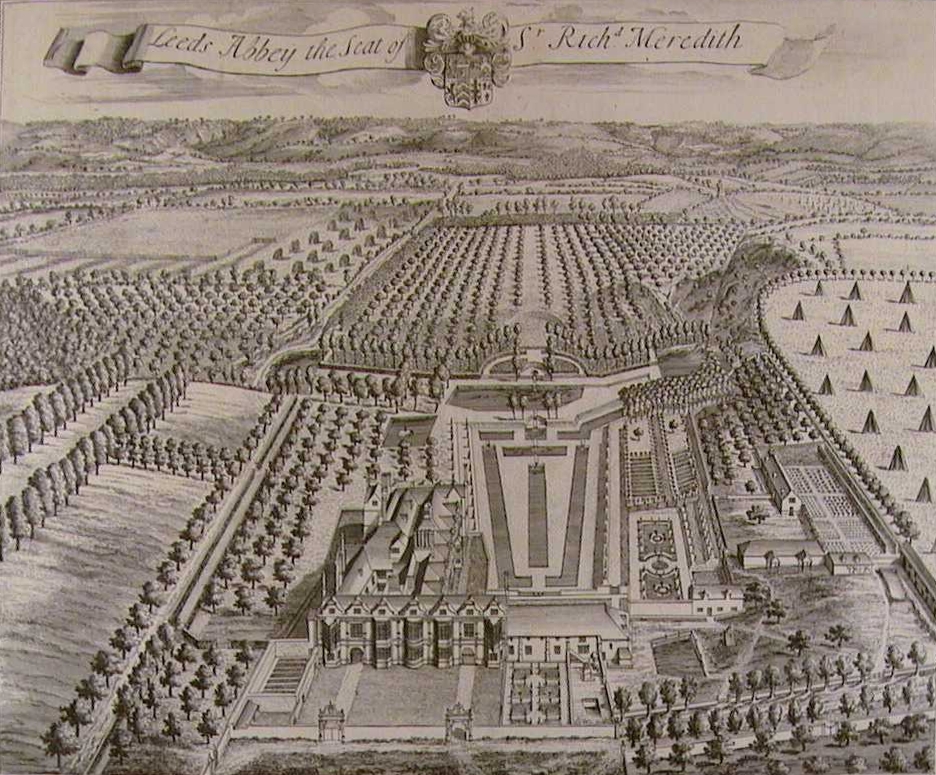
Leeds Priory, also known as Leeds Abbey, was a
 By 1487, the priory was deeply in debt.
By 1487, the priory was deeply in debt.
priory
A priory is a monastery of men or women under religious vows that is headed by a prior or prioress. They were created by the Catholic Church. Priories may be monastic houses of monks or nuns (such as the Benedictines, the Cistercians, or t ...
in Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
, Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
, England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, that was founded in 1119 and dissolved in 1539. A mansion was later built on the site of the priory; it was demolished in the late 18th century. The site of the former priory is a scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage, visu ...
.
Description
The original priory church was built in theNorman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 9th and 10th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norma ...
style. Materials used in the construction were Kentish Ragstone
Rag-stone is a name given by some architectural writers to work done with stones that are quarried in thin pieces, such as Horsham Stone, sandstone, Yorkshire stone, and the slate stones, but this is more properly flag or slab work. Near Londo ...
, with Caen stone
Caen stone () is a light creamy-yellow Jurassic limestone quarried in north-western France near the city of Caen. The limestone is a fine grained oolitic limestone formed in shallow water lagoons in the Bathonian Age about 167 million years ...
corners. It had a vaulted porch, similar to that to be seen today at Snettisham
Snettisham is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. It is located near the west coast of Norfolk, some south of the seaside resort of Hunstanton, north of the town of King's Lynn and northwest of the city of Norwich ...
church, Norfolk
Norfolk ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in England, located in East Anglia and officially part of the East of England region. It borders Lincolnshire and The Wash to the north-west, the North Sea to the north and eas ...
. In the 1320s, the nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
was rebuilt, and the north transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform ("cross-shaped") cruciform plan, churches, in particular within the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque a ...
was enlarged in the Decorated style
English Gothic is an architectural style that flourished from the late 12th until the mid-17th century. The style was most prominently used in the construction of cathedrals and churches. Gothic architecture's defining features are pointed a ...
. The south transept may have been rebuilt at this time. At a later date, probably in the late 1380s or early 1390s, the presbytery was replaced. This was a reversal of the normal process, where the presbytery was rebuilt before the nave and transepts. A probable cause was the sharply rising ground immediately east of the church presenting a barrier to extension. The chapter house
A chapter house or chapterhouse is a building or room that is part of a cathedral, monastery or collegiate church in which meetings are held. When attached to a cathedral, the cathedral chapter meets there. In monasteries, the whole communi ...
adjoined the south transept, built c. 1160.
The main church formed the northern part of the priory, with ranges to the east, west, and south. The warming house
The calefactory (also ''warming house'') was an important room or building in a medieval monastery in Western Europe. In the present day it is a communal place of recreation and fellowship in religious houses such as monasteries, priories, and ...
was probably in the south range. The kitchen was adjoining the south range.
History
The Priory of St Mary and St Nicholas, also known as Leeds Abbey, was founded in 1119. Its founders were Robert de Crevequer and his sonAdam
Adam is the name given in Genesis 1–5 to the first human. Adam is the first human-being aware of God, and features as such in various belief systems (including Judaism, Christianity, Gnosticism and Islam).
According to Christianity, Adam ...
. The priory was occupied by Augustinian canons
The Canons Regular of St. Augustine are Catholic priests who live in community under a rule ( and κανών, ''kanon'', in Greek) and are generally organised into religious orders, differing from both secular canons and other forms of religio ...
. In 1177, Robert de Crevequer's son, also named Robert
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, prais ...
, bequeathed a fulling mill
Fulling, also known as tucking or walking ( Scots: ''waukin'', hence often spelt waulking in Scottish English), is a step in woollen clothmaking which involves the cleansing of woven cloth (particularly wool) to eliminate (lanolin) oils, dirt, ...
on the River Len
The River Len is a river in Kent, England. It rises at a spring in ''Bluebell Woods'' to the southeast of the village centre of Lenham from the source of the River Great Stour; both rise on the Greensand Ridge. Its length is c. It enters the ...
to the priory in his will. The mill remained in the ownership of the priory until its dissolution. As well as Brandescombe Mill, the priory also possessed Abbey Mill at its dissolution.
In 1198, Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III (; born Lotario dei Conti di Segni; 22 February 1161 – 16 July 1216) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 until his death on 16 July 1216.
Pope Innocent was one of the most power ...
confirmed the priory as falling under the See of Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, in the county of Kent, England; it was a county borough until 1974. It lies on the River Stour, Kent, River Stour. The city has a mild oceanic climat ...
. In 1368, the donations of the de Crevequers were confirmed by King Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
, who also confirmed his patronage of the priory. In 1384, the priory was valued at £220. 12s. 8d. About this time, during the reign of King Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward, Prince of Wales (later known as the Black Prince), and Joan, Countess of Kent. R ...
, canon Thomas Hazlewood came to Leeds Priory. He wrote several history books here, including ''A Compendious Chronicle''. In 1452, King Richard III
Richard III (2 October 1452 – 22 August 1485) was King of England from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the Plantagenet dynasty and its cadet branch the House of York. His defeat and death at the Battle of Boswor ...
confirmed the liberties of the priory.
 By 1487, the priory was deeply in debt.
By 1487, the priory was deeply in debt. James Goldwell
James Goldwell (died 15 February 1499) was a medieval Dean of Salisbury and Bishop of Norwich.
Life
Goldwell was one of the sons of William and Avice Goldwell, both of whom died in 1485. He had a brother, Nicholas Goldwell, who survived him. H ...
, Bishop of Norwich
The Bishop of Norwich is the Ordinary (Catholic Church), ordinary of the Church of England Anglican Diocese of Norwich, Diocese of Norwich in the Province of Canterbury. The diocese covers most of the county of Norfolk and part of Suffolk. Th ...
, made generous donations to the priory, and gave sufficient support for an additional priest. Leeds Priory was dissolved in 1539, then being valued at £362. 7s. 7d. The last prior, Thomas Day, received a pension
A pension (; ) is a fund into which amounts are paid regularly during an individual's working career, and from which periodic payments are made to support the person's retirement from work. A pension may be either a " defined benefit plan", wh ...
of £80 per annum from the King.
After the priory had been dissolved, the King leased it to Anthony St Leger for 21 years, at a rent of £22. 17s. 2d. per annum. The lease included both mills and of land, and all houses etc. associated with the priory. The priory itself was demolished and the materials carried away. In 1551, King Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. The only surviving son of Henry VIII by his thi ...
granted the site of the priory and land and woods in Broomfield, Langley, Leeds and Sutton Valence
Sutton Valence (in the past also called Sudtone, Town Sutton and Sutton Hastings, see below) is a village about five miles (8 km) SE of Maidstone, Kent, England on the A274 road going south to Headcorn and Tenterden. It is on the Greensand ...
amounting to to St Leger to be held ''in capite''. The remainder of the estate had been assigned in 1542 by King Henry VIII to the Dean and Chapter of Rochester.
In 1559, Warham St Leger
Sir Warham St Leger PC (Ire) ( – 1597) was an English soldier, administrator, and politician, who sat in the Irish House of Commons in the Parliament of 1585–1586.
Birth and origins
Warham was probably born in 1525 in England, the second so ...
inherited the priory from his father. In 1573, St Leger transferred the estate to Sir William Meredith, of Stansty
Stansty () is an area and electoral ward in Wrexham County Borough, Wales, lying to the immediate north-west of the city of Wrexham. It is a former civil parish and township. Stansty is also an electoral ward to Wrexham County Borough Council. ...
, Denbighshire
Denbighshire ( ; ) is a county in the north-east of Wales. It borders the Irish Sea to the north, Flintshire to the east, Wrexham to the southeast, Powys to the south, and Gwynedd and Conwy to the west. Rhyl is the largest town, and Ruthi ...
. A pigeon house
A dovecote or dovecot , doocot ( Scots) or columbarium is a structure intended to house pigeons or doves. Dovecotes may be free-standing structures in a variety of shapes, or built into the end of a house or barn. They generally contain pig ...
was erected in the grounds of the priory. In 1581, Meredith's son, also named William, purchased certain lands in Warham St Leger that had previously formed part of the estate. The estate passed through Sir Richard Meredith to Sir Roger Meredith in 1723. Sir Roger died in 1738 and left the estate to his niece Susanna Meredith. On her death in 1758, the estate passed to Sir George Oxenden. In 1765, Oxenden sold the estate to John Calcraft, of Ingress, Kent, who considerably extended the house and landscaped the grounds. Calcraft died in 1772, and the estate passed to his son, John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
. The mansion was demolished at the end of the 18th century.
The dovecote of the mansion remains and is on the Historic England
Historic England (officially the Historic Buildings and Monuments Commission for England) is an executive non-departmental public body of the British Government sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. It is tasked with prot ...
Heritage at Risk Register
An annual ''Heritage at Risk Register'' is published by Historic England. The survey is used by national and local government, a wide range of individuals and heritage groups to establish the extent of risk and to help assess priorities for acti ...
.
Burials
*Eleanor de Ferrers, wife ofRoger de Leybourne
Sir Roger de Leybourne (1215–1271) was an English soldier, landowner and royal servant during the Second Barons' War.
Origins
Roger was the younger son of another Sir Roger de Leybourne, by his first wife, Eleanor, the daughter and heires ...
Excavations
The site of the priory was partially excavated in 1846. In 1973, an excavation of the site took place over eleven weeks in total, covering all four seasons. Members of the Archaeological Society of Sir Joseph Williamson's Mathematical School, Rochester, theKent Archaeological Society
The Kent Archaeological Society was founded in 1857 to promote the study and publication of archaeology and history, specifically that pertaining to the ancient county of Kent in England. This includes the modern administrative county as well as ar ...
, the Sittingbourne and Swale Archaeological Group and the Thameside Archaeological Group assisted in the excavation.
See also
*List of scheduled monuments in Maidstone
There are 27 scheduled monuments in Maidstone, Kent, England. In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is an archaeological site or historic building of "national importance" that has been given protection against unauthorised change by being ...
References
Sources
* * * * * {{Leeds, Kent Monasteries in Kent 1539 disestablishments in England History of Kent Borough of Maidstone 1119 establishments in England Christian monasteries established in the 1110s Gardens by Capability Brown Augustinian monasteries in England