Latimer Diagram on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
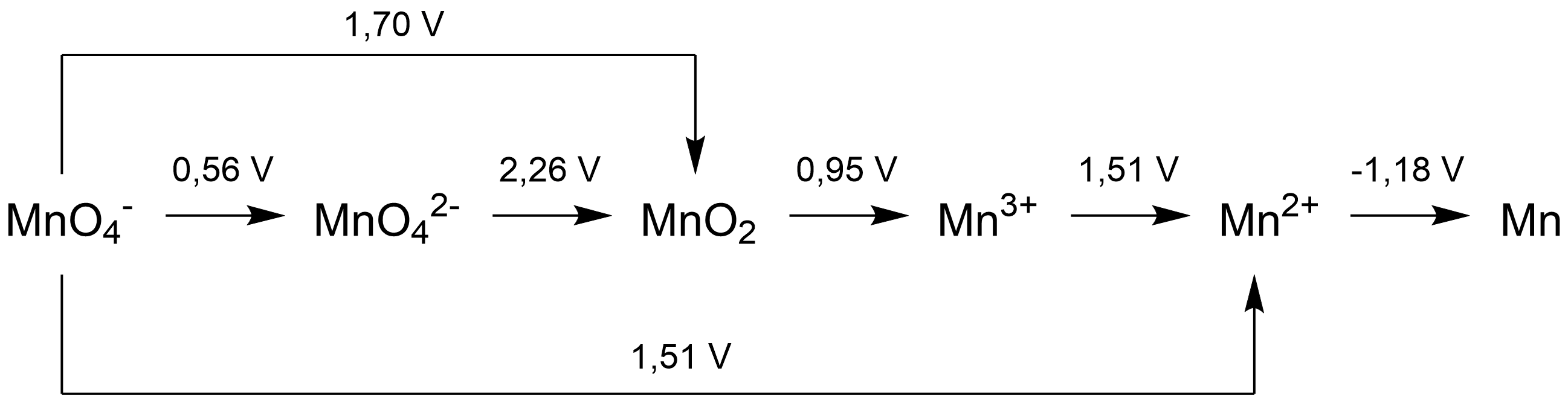 A Latimer diagram of a
A Latimer diagram of a
 The arrow between O2 and H2O2 has a value +0.68 V over it, it indicates that the
The arrow between O2 and H2O2 has a value +0.68 V over it, it indicates that the
 A Latimer diagram of a
A Latimer diagram of a chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
is a summary of the standard electrode potential
In electrochemistry, standard electrode potential E^\ominus, or E^\ominus_, is the electrode potential (a measure of the reducing power of any element or compound) which the IUPAC "Gold Book" defines as ''"the value of the standard emf ( electrom ...
data of that element. This type of diagram is named after Wendell Mitchell Latimer (1893–1955), an American chemist.
Construction
In a Latimer diagram, because by conventionredox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is t ...
reactions are shown in the direction of reduction (gain of electrons
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
), the most highly oxidized form of the element is on the left side, with successively lower oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
s to the right side. The species are connected by arrows, and the numerical value of the standard potential (in volts
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI).
Definition
One volt is defined as the electric potential between two point ...
) for the reduction is written at each arrow. For example, for oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
, the species would be in the order O2 (0), H2O2 (–1), H2O (-2):
:  The arrow between O2 and H2O2 has a value +0.68 V over it, it indicates that the
The arrow between O2 and H2O2 has a value +0.68 V over it, it indicates that the standard electrode potential
In electrochemistry, standard electrode potential E^\ominus, or E^\ominus_, is the electrode potential (a measure of the reducing power of any element or compound) which the IUPAC "Gold Book" defines as ''"the value of the standard emf ( electrom ...
for the reaction:
: O2(''g'') + 2H+ + 2''e''− ⇄ H2O2(''aq'')
is 0.68 volts.
Application
Latimer diagrams can be used in the construction of Frost diagrams, as a concise summary of the standard electrode potentials relative to the element. Since , the electrode potential is a representation of the Gibbs energy change for the given reduction. The sum of the Gibbs energy changes for subsequent reductions (e.g. from O2 to H2O2, then from H2O2 to H2O) is the same as the Gibbs energy change for the overall reduction (i.e. from O2 to H2O), in accordance with Hess's law. This can be used to find the electrode potential for non-adjacent species, which gives all the information necessary for the Frost diagram. It must be stressed that standard reduction potentials are not additive values. They cannot be directly summed up, or subtracted, from the values in volt indicated in a Latimer diagram. If needed, their calculation must be performed via the difference in Gibbs free energies. The easiest way to proceed is simply to use energies (nE) directly expressed in electron-volt (eV), because the Faraday constant ''F'' and the sign minus simplifies on both side of the equation. So, the values of E in volt must be simply multiplied by the number (n) of electron transferred in the considered half-reaction. Since the Faraday constant can disappear from the equation, no need to calculate expressed in joule. A simple examination of a Latimer diagram can also indicate if a species will disproportionate in solution under the conditions for which the electrode potentials are given: if the potential to the right of the species is higher than the potential on the left, it will disproportionate. Therefore,hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
is unstable and will disproportionate in and .
See also
* Frost diagram * Pourbaix diagram * Ellingham diagramReferences
* * {{refend Electrochemistry Potentials