Lassa Virus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lassa virus (LASV) is an
 Lassa viruses are enveloped, single-stranded, bisegmented, ambisense
Lassa viruses are enveloped, single-stranded, bisegmented, ambisense
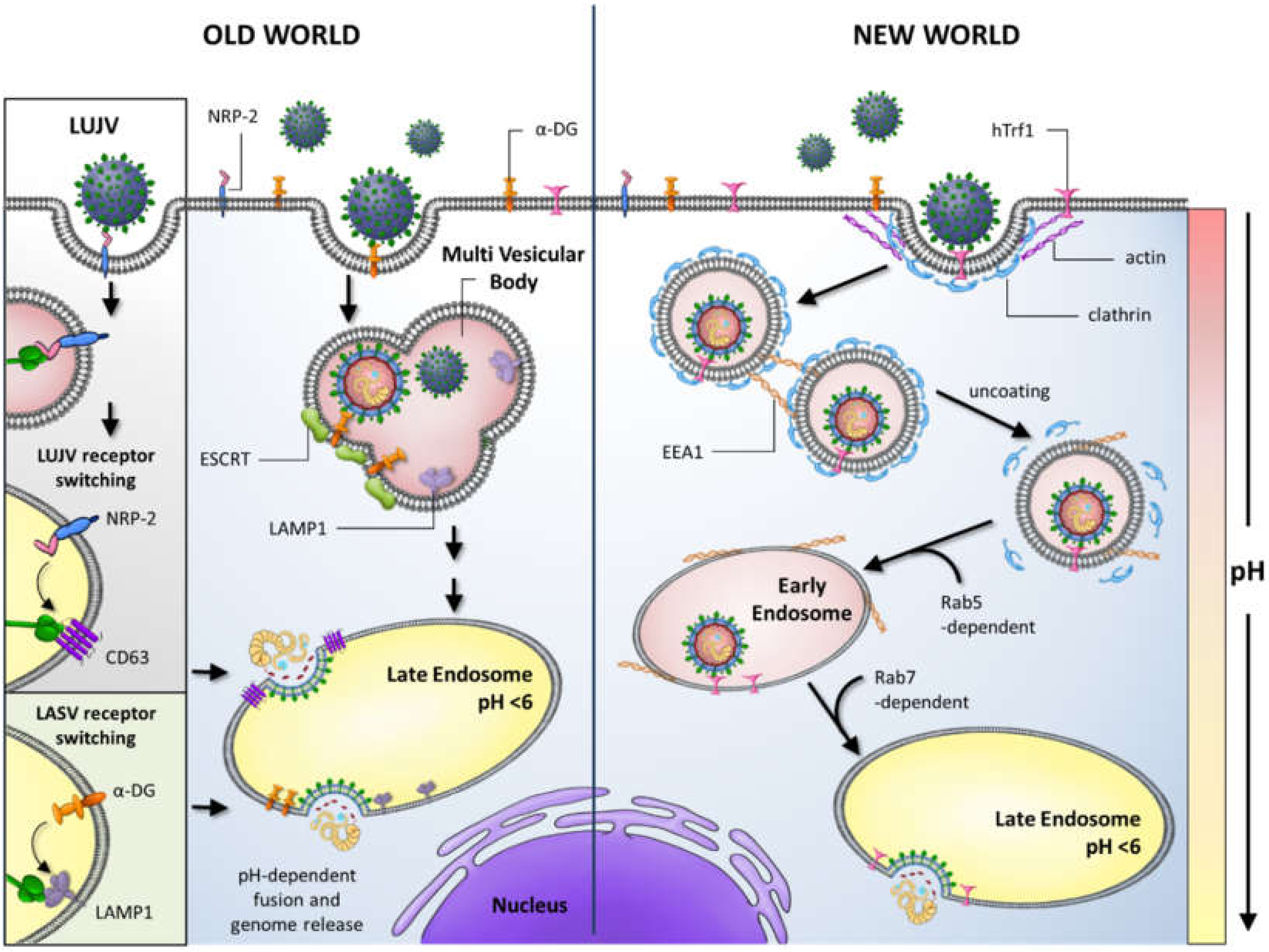 Lassa virus gains entry into the host cell by means of the cell-surface receptor the alpha-dystroglycan (alpha-DG), a versatile receptor for proteins of the
Lassa virus gains entry into the host cell by means of the cell-surface receptor the alpha-dystroglycan (alpha-DG), a versatile receptor for proteins of the
 The life cycle of Lassa virus is similar to the Old World arenaviruses. Lassa virus enters the cell by the
The life cycle of Lassa virus is similar to the Old World arenaviruses. Lassa virus enters the cell by the
arenavirus
An arenavirus is a bi- or trisegmented ambisense RNA virus that is a member of the family ''Arenaviridae''. These viruses infect rodents and occasionally humans. A class of novel, highly divergent arenaviruses, properly known as reptarenavirus ...
that causes Lassa hemorrhagic fever,
a type of viral hemorrhagic fever
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a diverse group of diseases. "Viral" means a health problem caused by infection from a virus, " hemorrhagic" means to bleed, and "fever" means an unusually high body temperature. Bleeding and fever are comm ...
(VHF), in humans and other primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
s. Lassa virus is an emerging virus and a select agent, requiring Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment. It is endemic in West African countries, especially Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered to the southeast by Liberia and by Guinea to the north. Sierra Leone's land area is . It has a tropical climate and envi ...
, the Republic of Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
, Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, and Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Lib ...
, where the annual incidence of infection is between 300,000 and 500,000 cases, resulting in 5,000 deaths per year.
As of 2012 discoveries within the Mano River region of west Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
have expanded the endemic zone between the two known Lassa endemic regions, indicating that LASV is more widely distributed throughout the tropical wooded savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
ecozone in west Africa. There are no approved vaccines against Lassa fever for use in humans.
Discovery
In 1969, missionary nurse Laura Wine fell ill with a mysterious disease she contracted from an obstetrical patient in Lassa, a village inBorno State
Borno is a States of Nigeria, state in the North East (Nigeria), North-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria. It is bordered by Yobe State, Yobe to the west, Gombe State, Gombe to the southwest, and Adamawa State, Adamawa to the south while its ea ...
, Nigeria. She was then transported to Jos, where she died. Subsequently, two others became infected, one of whom was fifty-two-year-old nurse Lily Pinneo who had cared for Laura Wine. Samples from Pinneo were sent to Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Stat ...
in New Haven
New Haven is a city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is located on New Haven Harbor on the northern shore of Long Island Sound. With a population of 135,081 as determined by the 2020 U.S. census, New Haven is the third largest city in Co ...
where a new virus, that would later be known as Lassa virus, was isolated for the first time by Jordi Casals-Ariet, Sonja Buckley, and others. Casals contracted the fever, and nearly lost his life; one technician died from it. By 1972, the multimammate rat, ''Mastomys natalensis
The Natal multimammate mouse (''Mastomys natalensis'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is also known as the Natal multimammate rat, the common African rat, African soft fur rat or the African soft-furred mouse. The Natal multimam ...
,'' was found to be the main reservoir of the virus in West Africa, able to shed virus in its urine and feces without exhibiting visible symptoms.
Virology
Structure and genome
 Lassa viruses are enveloped, single-stranded, bisegmented, ambisense
Lassa viruses are enveloped, single-stranded, bisegmented, ambisense RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virus characterized by a ribonucleic acid (RNA) based genome. The genome can be single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or double-stranded (Double-stranded RNA, dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include influenza, SARS, ...
es. Their genome is contained in two RNA segments that code for two proteins each, one in each sense, for a total of four viral proteins.
The large segment encodes a small zinc finger
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) which stabilizes the fold. The term ''zinc finger'' was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a ...
protein (Z) that regulates transcription and replication,
and the RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Using the e ...
(L). The small segment encodes the nucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins.
Structures
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating inte ...
(NP) and the surface glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
precursor (GP, also known as the ''viral spike''), which is proteolytically cleaved into the envelope glycoproteins GP1 and GP2 that bind to the alpha-dystroglycan receptor and mediate host cell entry.
Lassa fever causes hemorrhagic fever frequently shown by immunosuppression. Lassa virus replicates very rapidly, and demonstrates temporal control in replication. The first replication step is transcription of mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
copies of the negative- or minus-sense genome. This ensures an adequate supply of viral proteins for subsequent steps of replication, as the NP and L proteins are translated from the mRNA. The positive- or plus-sense genome, then makes viral complementary RNA (vcRNA) copies of itself. The RNA copies are a template for producing negative-sense progeny, but mRNA is also synthesized from it. The mRNA synthesized from vcRNA are translated to make the GP and Z proteins. This temporal control allows the spike proteins to be produced last, and therefore, delay recognition by the host immune system.
Nucleotide studies of the genome have shown that Lassa has four lineages: three found in Nigeria and the fourth in Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. The Nigerian strains seem likely to have been ancestral to the others but additional work is required to confirm this.
Receptors
 Lassa virus gains entry into the host cell by means of the cell-surface receptor the alpha-dystroglycan (alpha-DG), a versatile receptor for proteins of the
Lassa virus gains entry into the host cell by means of the cell-surface receptor the alpha-dystroglycan (alpha-DG), a versatile receptor for proteins of the extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and bio ...
. It shares this receptor with the prototypic Old World arenavirus lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Receptor recognition depends on a specific sugar modification of alpha-dystroglycan by a group of glycosyltransferases known as the LARGE proteins. Specific variants of the genes encoding these proteins appear to be under positive selection in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
where Lassa is endemic. Alpha-dystroglycan is also used as a receptor by viruses of the New World clade C arenaviruses (Oliveros and Latino viruses). In contrast, the New World arenaviruses of clades A and B, which include the important viruses Machupo, Guanarito, Junin, and Sabia in addition to the non pathogenic Amapari virus, use the transferrin receptor 1. A small aliphatic amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
at the GP1 glycoprotein amino acid position 260 is required for high-affinity binding to alpha-DG. In addition, GP1 amino acid position 259 also appears to be important, since all arenaviruses showing high-affinity alpha-DG binding possess a bulky aromatic amino acid (tyrosine or phenylalanine) at this position.
Unlike most enveloped viruses which use clathrin
Clathrin is a protein that plays a role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated by Barbara Pearse in 1976. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When the triskel ...
coated pits for cellular entry and bind to their receptors in a pH dependent fashion, Lassa and lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus instead use an endocytotic pathway independent of clathrin, caveolin
In molecular biology, caveolins are a family of integral membrane proteins that are the principal components of caveolae membranes and involved in receptor-independent endocytosis. Caveolins may act as scaffolding proteins within caveolar me ...
, dynamin
Dynamin is a GTPase protein responsible for endocytosis in the eukaryotic cell. Dynamin is part of the "dynamin superfamily", which includes classical dynamins, dynamin-like proteins, MX1, Mx proteins, OPA1, MFN1, mitofusins, and Guanylate-bindin ...
and actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
. Once within the cell the viruses are rapidly delivered to endosome
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of the endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membra ...
s via vesicular trafficking albeit one that is largely independent of the small GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a ...
s Rab5 and Rab7. On contact with the endosome pH-dependent membrane fusion occurs mediated by the envelope glycoprotein, which at the lower pH of the endosome binds the lysosome protein LAMP1 which results in membrane fusion and escape from the endosome.
Life cycle
 The life cycle of Lassa virus is similar to the Old World arenaviruses. Lassa virus enters the cell by the
The life cycle of Lassa virus is similar to the Old World arenaviruses. Lassa virus enters the cell by the receptor-mediated endocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME), also called clathrin-mediated endocytosis, is a process by which cells absorb metabolites, hormones, proteins – and in some cases viruses – by the inward budding of the plasma membrane (invagination). This ...
. Which endocytotic pathway is used is not known yet, but at least the cellular entry is sensitive to cholesterol depletion. It was reported that virus internalization is limited upon cholesterol depletion. The receptor used for cell entry is alpha-dystroglycan
Dystroglycan is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DAG1'' gene.
Dystroglycan is one of the dystrophin-associated glycoproteins, which is encoded by a 5.5 kb transcript in ''Homo sapiens'' on chromosome 3. There are two exons that are ...
, a highly conserved and ubiquitously expressed cell surface receptor for extracellular matrix proteins. Dystroglycan, which is later cleaved into alpha-dystroglycan and beta-dystroglycan is originally expressed in most cells to mature tissues, and it provides molecular link between the ECM and the actin-based cytoskeleton. After the virus enters the cell by alpha-dystroglycan mediated endocytosis, the low-pH environment triggers pH-dependent membrane fusion and releases RNP (viral ribonucleoprotein) complex into the cytoplasm. Viral RNA is unpacked, and replication and transcription initiate in the cytoplasm. As replication starts, both S and L RNA genomes synthesize the antigenomic S and L RNAs, and from the antigenomic RNAs, genomic S and L RNA are synthesized. Both genomic and antigenomic RNAs are needed for transcription and translation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English la ...
. The S RNA encodes GP and NP (viral nucleocapsid protein) proteins, while L RNA encodes Z and L proteins. The L protein most likely represents the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. When the cell is infected by the virus, L polymerase is associated with the viral RNP and initiates the transcription of the genomic RNA. The 5’ and 3’ terminal 19 nt viral promoter regions of both RNA segments are necessary for recognition and binding of the viral polymerase
In biochemistry, a polymerase is an enzyme (Enzyme Commission number, EC 2.7.7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids. DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are used to assemble DNA and RNA molecules, respectively, by ...
. The primary transcription first transcribes mRNAs from the genomic S and L RNAs, which code NP and L proteins, respectively. Transcription terminates at the stem-loop (SL) structure within the intergenomic region. Arenaviruses use a cap snatching
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. The origin of the word "cap" comes from the Old French word "chapeau" which means "head co ...
strategy to gain the cap structures from the cellular mRNAs, and it is mediated by the endonuclease
In molecular biology, endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain (namely DNA or RNA). Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (with regard to sequence), while man ...
activity of the L polymerase and the cap binding activity of NP. Antigenomic RNA transcribes viral genes GPC and Z, encoded in genomic orientation, from S and L segments respectively. The antigenomic RNA also serves as the template for the replication. After translation of GPC, it is posttranslationally modified in the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
. GPC is cleaved into GP1 and GP2 at the later stage of the secretory pathway. It has been reported that the cellular protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
SKI-1/S1P is responsible for this cleavage. The cleaved glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
s are incorporated into the virion
A virion (plural, ''viria'' or ''virions'') is an inert virus particle capable of invading a Cell (biology), cell. Upon entering the cell, the virion disassembles and the genetic material from the virus takes control of the cell infrastructure, t ...
envelope when the virus buds and release from the cell membrane.
Pathogenesis
Lassa fever
Lassa fever, also known as Lassa hemorrhagic fever, is a type of viral hemorrhagic fever caused by the Lassa virus. Many of those infected by the virus asymptomatic, do not develop symptoms. When symptoms occur they typically include fever, wea ...
is caused by the Lassa virus. The symptoms include flu-like illness characterized by fever, general weakness, cough, sore throat, headache, and gastrointestinal manifestations. Hemorrhagic manifestations include vascular permeability.
Upon entry, the Lassa virus infects almost every tissue in the human body. It starts with the mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
, intestine, lungs and urinary system, and then progresses to the vascular system.
The main targets of the virus are antigen-presenting cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a Cell (biology), cell that displays an antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize the ...
s, mainly dendritic cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system ...
s and endothelial cells.
In 2012 it was reported how Lassa virus nucleoprotein (NP) sabotages the host's innate immune system
The innate immune system or nonspecific immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies in vertebrates (the other being the adaptive immune system). The innate immune system is an alternate defense strategy and is the dominant immune s ...
response. Generally, when a pathogen enters into a host, innate defense system recognizes the pathogen-associated molecular pattern
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are small molecular motifs conserved within a class of microbes, but not present in the host. They are recognized by toll-like receptors (TLRs) and other pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in both p ...
s (PAMP) and activates an immune response. One of the mechanisms detects double stranded RNA (dsRNA), which is only synthesized by negative-sense viruses. In the cytoplasm, dsRNA receptors, such as RIG-I
RIG-I (retinoic acid-inducible gene I) is a cytosolic pattern recognition receptor (PRR) that can mediate induction of a type-I interferon (IFN1) response. RIG-I is an essential molecule in the innate immune system for recognizing cells that ...
(retinoic acid-inducible gene I) and MDA-5 (melanoma differentiation associated gene 5), detect dsRNAs and initiate signaling pathways that translocate IRF-3 (interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten ...
regulatory factor 3) and other transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s to the nucleus. Translocated transcription factors activate expression of interferons 𝛂 and 𝛃, and these initiate adaptive immunity
The adaptive immune system (AIS), also known as the acquired immune system, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized cells, organs, and processes that eliminate pathogens specifically. The ac ...
. NP encoded in Lassa virus is essential in viral replication
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome ...
and transcription, but it also suppresses host innate IFN response by inhibiting translocation of IRF-3. NP of Lassa virus is reported to have an exonuclease
Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3′ or the 5′ end occurs. Its close relative is th ...
activity to only dsRNAs. the NP dsRNA exonuclease activity counteracts IFN responses by digesting the PAMPs thus allowing the virus to evade host immune responses. NP has anti-PKR kinase activity and uses PKR for its proviral activity. Z protein utilizes cellular myristoylation mechanism to target itself to the membrane, it also modulates vRNP, inhibition of myristoylation would completely inhibit the viral cycle.
See also
* Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness InnovationsReferences
{{Taxonbar, from=Q24719561, from2=Q1806636 Animal viral diseases Biological agents Biosafety level 4 pathogens Arenaviridae Tropical diseases Zoonotic viral diseases