Laricoideae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Laricoideae are a
subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
of the Pinaceae
The Pinaceae (), or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as Cedrus, cedars, firs, Tsuga, hemlocks, Pinyon_pine, piñons,
larches, pines and spruces. The family is incl ...
, a Pinophyta
Conifers () are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All ...
division family. They take their name from the genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
'' Larix'' (larches
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to the cooler regions of the northern hemisphere, where they are found in lowland forests in the high lat ...
), which contains inside most of the species of the group
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic iden ...
and is one of only two deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
genera of the pines complex (together with '' Pseudolarix'', which however belongs to a different subfamily, the Abietoideae). Ecologically important trees, the Laricoideae form pure or mixed forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
associations often dominant in the ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s in which they are present, thanks also to their biological adaptations to natural disturbances, to reproductive strategies put in place and high average longevity of the individuals. Currently are assigned to this subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
three genera ('' Larix'', '' Pseudotsuga'' and ''Cathaya
''Cathaya'' is a genus in the pine family, Pinaceae, with one known living species, ''Cathaya argyrophylla''. In foliage and cone morphology, ''Cathaya'' has been considered a member of the subfamily Laricoideae, closely related to '' Pseudotsu ...
'') and its members can be found only in Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
. The various species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
live for the most part in temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
or cold
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjectivity, subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute t ...
climates and are the more northerly conifers
Conifers () are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All e ...
; some constitute an important source of timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
and non-timber forest product
Non-timber forest products (NTFPs) are useful foods, substances, materials and/or commodities obtained from forests other than timber. Harvest ranges from wild collection to farming. They typically include game animals, fur-bearers, nuts, see ...
s.
Description
Thespecies
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
of the subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
Laricoideae are evergreen
In botany, an evergreen is a plant which has Leaf, foliage that remains green and functional throughout the year. This contrasts with deciduous plants, which lose their foliage completely during the winter or dry season. Consisting of many diffe ...
or deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
trees
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only p ...
that can reach the greater heights in the Pinaceae
The Pinaceae (), or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as Cedrus, cedars, firs, Tsuga, hemlocks, Pinyon_pine, piñons,
larches, pines and spruces. The family is incl ...
family (over 100 meters with '' Pseudotsuga menziesii var. menziesii''). The leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
are needle-like and have primary stomatal bands only on the abaxial surface (below the phloem
Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is ...
vessels). All members are monoecious
Monoecy (; adj. monoecious ) is a sexual system in seed plants where separate male and female cones or flowers are present on the same plant. It is a monomorphic sexual system comparable with gynomonoecy, andromonoecy and trimonoecy, and contras ...
, with separate sexes on the same plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
but in different reproductive structures. The annual cones
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the ''apex'' or '' vertex''.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, ...
(''strobili'') have no distinct umbo and the scales show a broad base which, at observation, completely hides the seeds
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds are the ...
from the abaxial view. These last are whitish and firmly fixed to the wing (this thin membrane also keeps the seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
well attached to the scale during maturation); furthermore, among the typical distinctive features of the group, we have the micropylar fluid of the strobilus
A strobilus (: strobili) is a structure present on many land plant species consisting of sporangia-bearing structures densely aggregated along a stem. Strobili are often called cones, but some botanists restrict the use of the term cone to the woo ...
absent, no resin
A resin is a solid or highly viscous liquid that can be converted into a polymer. Resins may be biological or synthetic in origin, but are typically harvested from plants. Resins are mixtures of organic compounds, predominantly terpenes. Commo ...
vesicles on the seeds
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds are the ...
and the presence, in the vascular cylinder of the young root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
, of two characteristic small resiniferous canals. The bark
Bark may refer to:
Common meanings
* Bark (botany), an outer layer of a woody plant such as a tree or stick
* Bark (sound), a vocalization of some animals (which is commonly the dog)
Arts and entertainment
* ''Bark'' (Jefferson Airplane album), ...
and the wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
of the genera '' Larix'' and '' Pseudotsuga'' have a similar anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
and morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
*Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
*Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies, ...
: the reddish color of the heartwood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
and the white-yellowish of the sapwood, the high specific weight
Specific may refer to:
* Specificity (disambiguation)
* Specific, a cure or therapy for a specific illness
Law
* Specific deterrence, focussed on an individual
* Specific finding, intermediate verdict used by a jury in determining the fin ...
compared to other conifers
Conifers () are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All e ...
, the distribution of late
Late or LATE may refer to:
Everyday usage
* Tardy, or late, not being on time
* Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead
Music
* ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000
* Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993
* Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Groh ...
and earlywood, the presence of resiniferous channels and their localization in the tissuets, the molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry ...
that form the resin
A resin is a solid or highly viscous liquid that can be converted into a polymer. Resins may be biological or synthetic in origin, but are typically harvested from plants. Resins are mixtures of organic compounds, predominantly terpenes. Commo ...
and extractives, the chemical, physical and mechanical properties as well as the class of resistance to the attack of pathogens
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
such as fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
and insects
Insects (from Latin ') are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed ...
are a clue of a common ancestral origin. Similar between the two genera are also some aspects of the phenology, the degree of shade tolerance, the fire-resistant marbled bark and the appearance of the young shoots.
Taxonomy
Thesubfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
Laricoideae was described with the actual name by Robert Knud Friedrich Pilger
Robert Knud Friedrich Pilger (3 July 1876, Helgoland – 1 September 1953, Berlin) Hans Melchior in late 1954 and subsequently modified by other authors in the course of time as regards the
Within the 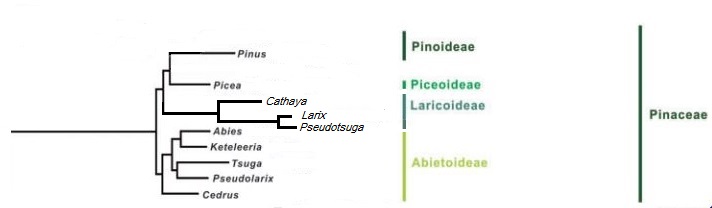 Price et al. he supposed in 1977 that the Laricoideae were a
Price et al. he supposed in 1977 that the Laricoideae were a
Taxonomicon.nl
Subfamily ''Laricoideae'' on taxonomicon.nl
The Gymnosperm Database
– Pinaceae (subfamily ''Laricoideae'')
in ''Pinaceae'' (
Subfamily Laricoideae - (Rendle) Pilger & Melchior
in ''BioLib.cz'' {{Authority control Pinaceae Plant subfamilies
taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
of belonging. Before that, the genera '' Larix'', '' Pseudotsuga'' and ''Cedrus
''Cedrus'', with the common English name cedar, is a genus of coniferous trees in the plant family Pinaceae (subfamily Abietoideae). They are native to the mountains of the western Himalayas and the Mediterranean region, occurring at altitud ...
'' were gathered in a provisional subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
called Laricinae, defined for the first time by Melchior and Werdermann always in 1954 (...''“trees that have both short and long shoots, monomorphic leaves, and strobili borne on the short shoots”''...) and rechristened immediately after with the current term. The grouping in this form was confirmed by Hart (1987) through cladistic analysis, but already in 1988 Frankis replaced ''Cedrus
''Cedrus'', with the common English name cedar, is a genus of coniferous trees in the plant family Pinaceae (subfamily Abietoideae). They are native to the mountains of the western Himalayas and the Mediterranean region, occurring at altitud ...
'' with ''Cathaya
''Cathaya'' is a genus in the pine family, Pinaceae, with one known living species, ''Cathaya argyrophylla''. In foliage and cone morphology, ''Cathaya'' has been considered a member of the subfamily Laricoideae, closely related to '' Pseudotsu ...
'' (a genus described for the first time in 1962) in a new classification (now obsolete) that saw Larix as a distinct twin group compared to ''Cathaya
''Cathaya'' is a genus in the pine family, Pinaceae, with one known living species, ''Cathaya argyrophylla''. In foliage and cone morphology, ''Cathaya'' has been considered a member of the subfamily Laricoideae, closely related to '' Pseudotsu ...
'' - '' Pseudotsuga''.
Historically the Laricoideae were the subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
of the Pinaceae
The Pinaceae (), or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as Cedrus, cedars, firs, Tsuga, hemlocks, Pinyon_pine, piñons,
larches, pines and spruces. The family is incl ...
comprising the trees with needles inserted both on the macroblasts and on the brachiblasts; for this reason in the past they have been also included in it the genera '' Pseudolarix'' (for a short time) and ''Cedrus
''Cedrus'', with the common English name cedar, is a genus of coniferous trees in the plant family Pinaceae (subfamily Abietoideae). They are native to the mountains of the western Himalayas and the Mediterranean region, occurring at altitud ...
'', subsequently eliminated following the most recent systematic updates developed on the basis of molecular genetic phylogeny, reproductive morphology, chromosome numbers and immunology
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of Immune system, immune systems in all Organism, organisms.
Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the Physiology, physiological functioning of the immune system in ...
. Currently, based on these studies, there are three genera in the subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
Laricoideae, of which one of which is monotypic as it consists of only one species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
:
subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
the genera '' Larix'' and '' Pseudotsuga'' are more closely correlated to each other (''sister taxa
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
'') than ''Cathaya
''Cathaya'' is a genus in the pine family, Pinaceae, with one known living species, ''Cathaya argyrophylla''. In foliage and cone morphology, ''Cathaya'' has been considered a member of the subfamily Laricoideae, closely related to '' Pseudotsu ...
''. This evidence is demonstrated by numerous biological and macro-micro morphological similarities between the larches
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to the cooler regions of the northern hemisphere, where they are found in lowland forests in the high lat ...
and the Douglas-firs including, but not only, a various tissues common anatomy, immunology of seed protein and the absence of the two air sacs in the pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
, typicals instead of the other Pinaceae
The Pinaceae (), or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as Cedrus, cedars, firs, Tsuga, hemlocks, Pinyon_pine, piñons,
larches, pines and spruces. The family is incl ...
. The similarities between the pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
grains of the genera '' Larix'' and '' Pseudotsuga'' however do not stop here and include other aspects as: granules not buoyant, atectate, with external wall (''exospore'') granular, pollination drop containing xylose
Xylose ( , , "wood") is a sugar first isolated from wood, and named for it. Xylose is classified as a monosaccharide of the aldopentose type, which means that it contains five carbon atoms and includes an aldehyde functional group. It is deriv ...
and the presence of an exine shell during microgametophyte germination.
Doyle and O'Leary (1935) furthermore described a pollination process very similar in '' Larix'' and '' Pseudotsuga'' where the granule, which lacks air sacs, lands on an almost stigmatic extension of the integument, the margins of which tend to inroll. The contact with the nucellus may ('' Larix'') or may not ('' Pseudotsuga'') be needed for pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
tubes to develop, but the mechanism is almost analogous. The time from pollination to fertilization in these two genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
may be over a year and the granules germination can take months (Little et al., 2014).
 Price et al. he supposed in 1977 that the Laricoideae were a
Price et al. he supposed in 1977 that the Laricoideae were a subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
sister
A sister is a woman or a girl who shares parents or a parent with another individual; a female sibling. The male counterpart is a brother. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to ref ...
of the Abietoideae rather than the Pinoideae - Piceoideae group and this version was confirmed by Hart (1987), Frankis (1988), Farjon (1990), Wang et al. (2000) and Gernandt et al. (2008), although it has not yet found application in the literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, Play (theatre), plays, and poetry, poems. It includes both print and Electroni ...
.
Dichotomous key
The dichotomous key to recognizing thegenera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
included to the subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
Laricoideae is relatively simple, since only three of them belong to it and one of these is deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
. Below is reported the taxonomic identification scheme in the form of a table:
Revisions and research
According to the latest research still in progress, the genus ''Cathaya
''Cathaya'' is a genus in the pine family, Pinaceae, with one known living species, ''Cathaya argyrophylla''. In foliage and cone morphology, ''Cathaya'' has been considered a member of the subfamily Laricoideae, closely related to '' Pseudotsu ...
'' would be attributed to the grouping of pines
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as ...
(subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
Pinoideae), leaving therefore only '' Larix'' and '' Pseudotsuga'' to forming the subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
Laricoideae. Furthermore, studying the ''mitochondrial rps3 gene'', Ran et al. (2010) found that '' Larix'' and '' Pseudotsuga'' are evolutionarily sister genera to all other Pinaceae
The Pinaceae (), or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as Cedrus, cedars, firs, Tsuga, hemlocks, Pinyon_pine, piñons,
larches, pines and spruces. The family is incl ...
, highlighting a different (sub-parallel) origin compared than the remaining species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
. Spellenberg, Earle and Nelson (2014) report that the larches
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to the cooler regions of the northern hemisphere, where they are found in lowland forests in the high lat ...
and Douglas firs evolved from the Pinaceae
The Pinaceae (), or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as Cedrus, cedars, firs, Tsuga, hemlocks, Pinyon_pine, piñons,
larches, pines and spruces. The family is incl ...
135 million years ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used w ...
and they kept a common ancestor
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder, or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from ...
until 7 million years ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used w ...
, thus forming a divided and closely related taxonomic line between them compared to the rest of the group, while maintaining a strong degree of kinship with it. For Wang et al. (2000), instead, '' Pseudotsuga'' differentiated himself from '' Larix'' in Western North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
about 65 million years ago, in an era between the late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
and the Paleocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), ...
. These revisions and interactions, which would find evidence in genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, however are not universally accepted and many botanics, researchers and scientists still use the previous classification
Classification is the activity of assigning objects to some pre-existing classes or categories. This is distinct from the task of establishing the classes themselves (for example through cluster analysis). Examples include diagnostic tests, identif ...
waiting for further developments.
For other authors, finally, the subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
Laricoideae would have no taxonomic dignity of its own, recognizing only two large multi-group clades
In biology, a clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy ...
(Pinoid and Abietoid) or subfamilies ( Pinoideae and Abietoideae) in their cladistics
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to Taxonomy (biology), biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesiz ...
systems. '' Larix'', '' Pseudotsuga'' and ''Cathaya
''Cathaya'' is a genus in the pine family, Pinaceae, with one known living species, ''Cathaya argyrophylla''. In foliage and cone morphology, ''Cathaya'' has been considered a member of the subfamily Laricoideae, closely related to '' Pseudotsu ...
'' would be included in the pines
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as ...
complex.
See also
*Pinaceae
The Pinaceae (), or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as Cedrus, cedars, firs, Tsuga, hemlocks, Pinyon_pine, piñons,
larches, pines and spruces. The family is incl ...
** Abietoideae
** Pinoideae
** Piceoideae
* Larix
* Pseudotsuga
* Cathaya
''Cathaya'' is a genus in the pine family, Pinaceae, with one known living species, ''Cathaya argyrophylla''. In foliage and cone morphology, ''Cathaya'' has been considered a member of the subfamily Laricoideae, closely related to '' Pseudotsu ...
* Subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zo ...
References
Bibliography
* ''Pinaceae
The Pinaceae (), or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as Cedrus, cedars, firs, Tsuga, hemlocks, Pinyon_pine, piñons,
larches, pines and spruces. The family is incl ...
, Drawings and Descriptions of the Genera: Abies
Firs are evergreen coniferous trees belonging to the genus ''Abies'' () in the family Pinaceae. There are approximately 48–65 extant species, found on mountains throughout much of North and Central America, Eurasia, and North Africa. The genu ...
, Cedrus
''Cedrus'', with the common English name cedar, is a genus of coniferous trees in the plant family Pinaceae (subfamily Abietoideae). They are native to the mountains of the western Himalayas and the Mediterranean region, occurring at altitud ...
, Pseudolarix, Keteleeria, Nothotsuga, Tsuga
''Tsuga'' (, from Japanese (), the name of '' Tsuga sieboldii'') is a genus of conifers in the subfamily Abietoideae of Pinaceae, the pine family. The English-language common name "hemlock" arose from a perceived similarity in the smell of it ...
, Cathaya
''Cathaya'' is a genus in the pine family, Pinaceae, with one known living species, ''Cathaya argyrophylla''. In foliage and cone morphology, ''Cathaya'' has been considered a member of the subfamily Laricoideae, closely related to '' Pseudotsu ...
, Pseudotsuga, Larix and Picea
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' is the sole genus ...
''. Aljos Farjon. Koeltz Scientific Books, 1990 - 330 pages.
*
*
External links
Taxonomicon.nl
Subfamily ''Laricoideae'' on taxonomicon.nl
The Gymnosperm Database
– Pinaceae (subfamily ''Laricoideae'')
in ''Pinaceae'' (
Missouri Botanical Garden
The Missouri Botanical Garden is a botanical garden located at 4344 Shaw Boulevard in St. Louis, Missouri. It is also known informally as Shaw's Garden for founder and philanthropy, philanthropist Henry Shaw (philanthropist), Henry Shaw. I ...
)
Subfamily Laricoideae - (Rendle) Pilger & Melchior
in ''BioLib.cz'' {{Authority control Pinaceae Plant subfamilies