Languages Of The Czech Republic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 With an estimated population of 10.5 million as of 2022, compared to 9.3 million at the beginning of the 20th century, the population growth of the Czech Republic has been limited, due to low fertility rates and loss of population in and around World Wars I and II. Population loss during World War I was approximately 350,000. At the beginning of World War II the population of the Czech Republic reached its maximum (11.2 million). Due to the expulsion of the German residents after World War II, the Czech Republic lost about 3 million inhabitants and in 1947 the population was only 8.8 million. Population growth resumed, and in 1994 the population was 10.33 million.
From 1994 to 2003 natural growth was slightly negative (−0.15% per year) and the population decreased to 10.2 million. Since 2005, natural growth has been positive, but in recent times the most important influence on the population of the Czech Republic has been immigration: approximately 300,000 during the 2010s.
*One birth every 5 minutes
*One death every 5 minutes
*One net migrant every 44 minutes
*Net gain of one person every 131 minutes
With an estimated population of 10.5 million as of 2022, compared to 9.3 million at the beginning of the 20th century, the population growth of the Czech Republic has been limited, due to low fertility rates and loss of population in and around World Wars I and II. Population loss during World War I was approximately 350,000. At the beginning of World War II the population of the Czech Republic reached its maximum (11.2 million). Due to the expulsion of the German residents after World War II, the Czech Republic lost about 3 million inhabitants and in 1947 the population was only 8.8 million. Population growth resumed, and in 1994 the population was 10.33 million.
From 1994 to 2003 natural growth was slightly negative (−0.15% per year) and the population decreased to 10.2 million. Since 2005, natural growth has been positive, but in recent times the most important influence on the population of the Czech Republic has been immigration: approximately 300,000 during the 2010s.
*One birth every 5 minutes
*One death every 5 minutes
*One net migrant every 44 minutes
*Net gain of one person every 131 minutes



''0–14 years:'' 15.17% (male 834,447 /female 789,328)
''15–24 years:'' 9.2% (male 508,329 /female 475,846)
''25–54 years:'' 43.29% (male 2,382,899 /female 2,249,774)
''55–64 years:'' 12.12% (male 636,357 /female 660,748)
''65 years and over:'' 20.23% (male 907,255 /female 1,257,515) Median age *total: 43.3 years. Country comparison to the world: 28th *male: 42 years *female: 44.7 years (2020 est.)
File:Population pyramid CZE 1980rel.png, 1980
File:Population_pyramid_CZE_1990rel.png, 1990
File:Population_pyramid_CZE_1999rel.png, 1999
File:Population_pyramid_CZE_2007rel.png, 2007
File:Czech Republic single age population pyramid 2020.png, 2020
 Source: Czech Demographic Handbook, Czech Statistical Office – Data and time series
Source: Czech Demographic Handbook, Czech Statistical Office – Data and time series
File:C 1991.png, Czechs in 1991
File:C 2001.png, Czechs in 2001
File:C 2011.png, Czechs in 2011
The legal position of the minorities is defined foremost in the Act No. 273/2001 Coll. (The Rights of the Minorities Act) which implements the
 The German minority of the Czech Republic, historically the largest minority of the country, was almost entirely removed when 3 million were forcibly expelled in 1945–6 on the basis of the
The German minority of the Czech Republic, historically the largest minority of the country, was almost entirely removed when 3 million were forcibly expelled in 1945–6 on the basis of the
at ''
Today, there are about 7000 Greeks in the country (3219 according to 2001 census data), mostly in the 3 biggest towns –
 According to the Czech Statistical Office as of 31 December 2020 there were 632,570 legal foreign residents in the Czech Republic (5.1% of the total population). Residents from
According to the Czech Statistical Office as of 31 December 2020 there were 632,570 legal foreign residents in the Czech Republic (5.1% of the total population). Residents from
 The
The
Czech Statistical Office
state institution responsible to provide official data about Czech Republic
Czechia – EU member country profile
European Union * {{Demographics of Europe
Demographic
Demography () is the statistics, statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.
Demographic analy ...
features of the population of the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
include population density, ethnicity
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they Collective consciousness, collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, ...
, education level, health of the population, economic status, and religious affiliations.
Population
 With an estimated population of 10.5 million as of 2022, compared to 9.3 million at the beginning of the 20th century, the population growth of the Czech Republic has been limited, due to low fertility rates and loss of population in and around World Wars I and II. Population loss during World War I was approximately 350,000. At the beginning of World War II the population of the Czech Republic reached its maximum (11.2 million). Due to the expulsion of the German residents after World War II, the Czech Republic lost about 3 million inhabitants and in 1947 the population was only 8.8 million. Population growth resumed, and in 1994 the population was 10.33 million.
From 1994 to 2003 natural growth was slightly negative (−0.15% per year) and the population decreased to 10.2 million. Since 2005, natural growth has been positive, but in recent times the most important influence on the population of the Czech Republic has been immigration: approximately 300,000 during the 2010s.
*One birth every 5 minutes
*One death every 5 minutes
*One net migrant every 44 minutes
*Net gain of one person every 131 minutes
With an estimated population of 10.5 million as of 2022, compared to 9.3 million at the beginning of the 20th century, the population growth of the Czech Republic has been limited, due to low fertility rates and loss of population in and around World Wars I and II. Population loss during World War I was approximately 350,000. At the beginning of World War II the population of the Czech Republic reached its maximum (11.2 million). Due to the expulsion of the German residents after World War II, the Czech Republic lost about 3 million inhabitants and in 1947 the population was only 8.8 million. Population growth resumed, and in 1994 the population was 10.33 million.
From 1994 to 2003 natural growth was slightly negative (−0.15% per year) and the population decreased to 10.2 million. Since 2005, natural growth has been positive, but in recent times the most important influence on the population of the Czech Republic has been immigration: approximately 300,000 during the 2010s.
*One birth every 5 minutes
*One death every 5 minutes
*One net migrant every 44 minutes
*Net gain of one person every 131 minutes
Total population
Life expectancy
:total population: 79.5 years. Country comparison to the world: 56th :male: 76.55 years :female: 82.61 years (2021 est.) Death rate :10.72 deaths/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 23rd Averagelife expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
at age 0 of the total population.

Fertility

Population density and urban areas
Age structure
2020''0–14 years:'' 15.17% (male 834,447 /female 789,328)
''15–24 years:'' 9.2% (male 508,329 /female 475,846)
''25–54 years:'' 43.29% (male 2,382,899 /female 2,249,774)
''55–64 years:'' 12.12% (male 636,357 /female 660,748)
''65 years and over:'' 20.23% (male 907,255 /female 1,257,515) Median age *total: 43.3 years. Country comparison to the world: 28th *male: 42 years *female: 44.7 years (2020 est.)
Vital statistics
Total fertility rates by region
Current vital statistics
*Deaths January–February 2021 = 30,031 *Deaths January–February 2022 = 21,422 *Deaths January–February 2023 = 20,625 *Deaths January–February 2024 = 20,462 *Deaths January–February 2025 = 20,506Structure of the population
Education
Literacy
definition: NA :total population: 99% :male: 99% :female: 99% (2011 est.)Employment and income
Unemployment, youth ages 15–24
:Total: 8%. Country comparison to the world: 155th :Male: 7.2% :Female: 9.2% (2020 est.)Ethnic groups
The majority of the million inhabitants of the Czech Republic are ethnically and linguisticallyCzech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus
*Czech (surnam ...
(95%). They are descendants of Slavic people
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and N ...
from the Black Sea-Carpathian region who settled in Bohemia, Moravia and parts of present-day Austria in the 6th century AD. Other ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
s include Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, Romani people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
, Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
, and Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
. Historical minorities like Germans and Poles are declining due to assimilation. There is also a growing community from Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
. Other ethnic communities like Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, Turks, Italians, and Yugoslavs
Yugoslavs or Yugoslavians ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Jugoslaveni/Jugosloveni, Југославени/Југословени; ; ) is an identity that was originally conceived to refer to a united South Slavic people. It has been used in two connotations: ...
are found in Prague. Since the dissolution of Czechoslovakia
The dissolution of Czechoslovakia, which took effect on December 31, 1992, was the Self-determination, self-determined Partition (politics), partition of the federal republic of Fifth Czechoslovak Republic, Czechoslovakia into the independent ...
, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
living in the Czech Republic have comprised roughly 3% of the population.
There are different groups of national and ethnic minorities in the Czech Republic. The only "old minority" is Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
in the Trans-Olza
Trans-Olza (, ; , ''Záolší''; ), also known as Trans-Olza Silesia (), is a territory in the Czech Republic which was disputed between Poland and Czechoslovakia during the Interwar Period. Its name comes from the Olza River.
The history of ...
region, while the "new minorities" are scattered among the majority population (generally in the larger towns). While some of the minorities have the whole social structure of Czech society (Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
, Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
), other represent only some of the social groups (i.e. Russian newcomers of middle class, and Romani people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
who generally represent the underclass).
1880–1910
After World War I
1 In 2011 a large part of the population did not claim any ethnicity, before the census it was widely mediatized that the question is not mandatory. The vast majority of those who did so are presumed to be ethnic Czechs, number of whom dropped by roughly the same amount that the number of undeclared people rose, circa 2.5 million.Charter of Fundamental Rights and Basic Freedoms
The Charter of Fundamental Rights and Freedoms (, ) is a document enacted in 1991 by the Czechoslovak Federative Republic and currently continued as part of the constitutional systems of both the Czech Republic and Slovak Republic.
Differences ...
, Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities
The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities (FCNM) is a multilateral treaty of the Council of Europe aimed at protecting the minority rights, rights of minorities. It came into effect in 1998 and by 2009 it had been ratif ...
and ''Recommendation of the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; , CdE) is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it is Europe's oldest intergovernmental organisation, represe ...
No. 1201''. There is a number of other enactments which to lesser extent deal with the minorities.
A special situation applies in the case of Moravians
Moravians ( or Colloquialism, colloquially , outdated ) are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group from the Moravia region of the Czech Republic, who speak the Moravian dialects of Czech language, Czech or Czech language#Common Czech, Common ...
and Silesians
Silesians (; Silesian German: ''Schläsinger'' ''or'' ''Schläsier''; ; ; ) is both an ethnic as well as a geographical term for the inhabitants of Silesia, a historical region in Central Europe divided by the current national boundaries o ...
, who are frequently allocated within the group of Czechs when it comes to the statistical data.
Officially recognized minorities
Minorities, which "traditionally and on a long term basis live within the territory of the Czech Republic" enjoy some privileges. As of 2022 there are 14 such officially recognized minorities, which are (alphabetically):Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
, Bulgarians
Bulgarians (, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and its neighbouring region, who share a common Bulgarian ancestry, culture, history and language. They form the majority of the population in Bulgaria, ...
, Croatians
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They also f ...
, Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
, Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
, Romani people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
, Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
, Rusyns
Rusyns, also known as Carpatho-Rusyns, Carpatho-Russians, Ruthenians, or Rusnaks, are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group from the Carpathian Rus', Eastern Carpathians in Central Europe. They speak Rusyn language, Rusyn, an East Slavic lan ...
, Serbians
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
and Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese people living outside Vietna ...
.
Citizens belonging to the officially recognized minorities enjoy the right to "use their language in communication with authorities and in courts of law". Article 25 of the Czech Charter of Fundamental Rights and Basic Freedoms
The Charter of Fundamental Rights and Freedoms (, ) is a document enacted in 1991 by the Czechoslovak Federative Republic and currently continued as part of the constitutional systems of both the Czech Republic and Slovak Republic.
Differences ...
provides the right of the national and ethnic minorities to education and communication with authorities in their own language. Act No. 500/2004 Coll. (''The Administrative Rule'') in its paragraph 16 (4) (''Procedural Language'') provides that a citizen of the Czech Republic who belongs to a national or an ethnic minority, which traditionally and on a long-term basis lives within the territory of the Czech Republic, has the right to address an administrative agency and proceed before it in the language of the minority. In the case that the administrative agency does not have an employee with knowledge of the language, the agency is bound to obtain a translator at the agency's own expense. According to Act No. 273/2001 (''About The Rights of Members of Minorities'') paragraph 9 (''The right to use language of a national minority in dealing with authorities and in the courts of law'') the same also applies to members of national minorities in the courts of law.
Bulgarians
The economic migration of Bulgarians to the Czech Republic began in the 1990s. 4,363 citizens claimed to have Bulgarian nationality in the 2001 census. They mostly live in the large cities and towns, such as Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
, Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
, Ostrava
Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opa ...
, Karlovy Vary
Karlovy Vary (; , formerly also spelled ''Carlsbad'' in English) is a spa town, spa city in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 49,000 inhabitants. It is located at the confluence of the Ohře and Teplá (river), Teplá ri ...
, Kladno
Kladno (; ) is a city in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 70,000 inhabitants. It is the largest city in the region and has a rich industrial history.
Administrative division
Kladno consists of six municipal parts ...
, Ústí nad Labem
Ústí nad Labem (; ) is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 91,000 inhabitants and is the capital of the Ústí nad Labem Region. It is a major industrial centre and, besides being an active river port, is an important railway junction.
...
, Děčín
Děčín (; ) is a city in the Ústí nad Labem Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 46,000 inhabitants. It is the seventth largest municipality in the country by area. Děčín is an important traffic junction.
Administrative division
Děč ...
, and Havířov
Havířov () is a city in Karviná District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 69,000 inhabitants, making it the second largest city in the region. Havířov was founded in 1955 and is the youngest Czech city. It is ...
. Nowadays the newcomers from Bulgaria aim for these areas in particular, where they can join an already established community. Many of these economic immigrants have dual citizenship of both the Czech Republic and Bulgaria. However most of the recent immigrants still only have Bulgarian citizenship.
The Bulgarian Cultural Organisation publishes the magazine ''Roden Glas'', while a folklore organisation ''Kytka'' promotes traditional Bulgarian dances. Among other organisations are ''Pirin'', ''Zaedno'', ''Vazraždane'' and ''Hyshove''.
As an officially recognized minority the Bulgarian citizens of the Czech Republic enjoy the right to use their language in communication with authorities and in the courts of law. They also enjoy a number of other rights connected to the status of recognized minority, e.g. the right to education in their own language: the first Bulgarian school in the current Czech Republic was established in 1946 in Prague.
Germans
 The German minority of the Czech Republic, historically the largest minority of the country, was almost entirely removed when 3 million were forcibly expelled in 1945–6 on the basis of the
The German minority of the Czech Republic, historically the largest minority of the country, was almost entirely removed when 3 million were forcibly expelled in 1945–6 on the basis of the Potsdam agreement
The Potsdam Agreement () was the agreement among three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union after the war ended in Europe that was signed on 1 August 1945 and published the following day. A ...
. The constitution guarantees rights for minority languages, however there are 13 municipalities with German minority constituting 10% of population, which qualifies for such provisions.Peter Josika: Mehrsprachig: Ein Faktor der Versöhnungat ''
Prager Zeitung
The ''Prager Zeitung'' was a German newspaper in the Czech Republic issued weekly in Prague; it now publishes online only.
History and profile
''Prager Zeitung'' was founded in 1991. It considers itself as a successor of the '' Prager Tagblatt' ...
'', 21 August 2007. There is no bilingual education system in Western and Northern Bohemia, where the German minority is mostly concentrated. However, this is in large part due to the absence of German-speaking youth, a heritage of the post-war policy of the Communist government.
According to the 2001 census there remain 13 municipalities and settlements in the Czech Republic with more than 10% Germans.
Many representatives of expellees' organizations support the erection of bilingual signs in all formerly German-speaking territory as a visible sign of the bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
linguistic and cultural heritage
Cultural heritage is the heritage of tangible and intangible heritage assets of a group or society that is inherited from past generations. Not all heritages of past generations are "heritage"; rather, heritage is a product of selection by socie ...
of the region, but their efforts are not supported by some of the current inhabitants, as the vast majority of the current population is not of German descent.
The German-Czech Declaration of 21 January 1997 covered the two most critical issues—the role of some Sudeten Germans
German Bohemians ( ; ), later known as Sudeten Germans ( ; ), were ethnic Germans living in the Czech lands of the Bohemian Crown, which later became an integral part of Czechoslovakia. Before 1945, over three million German Bohemians constitute ...
in the breakup of Czechoslovakia in 1938 and their expulsion after World War II.
Greeks
Another influential minority are Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
. Large numbers of Greeks arrived in Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
during the end of the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War () took place from 1946 to 1949. The conflict, which erupted shortly after the end of World War II, consisted of a Communism, Communist-led uprising against the established government of the Kingdom of Greece. The rebels decl ...
. The first transports of Greek children arrived in 1948 and 1949. Later, more transports, also including adults, arrived. They were partly leftists, communists and guerillas with their relatives, hence the willingness of Czechoslovak government to allow the immigration. This was viewed rather as a temporary solution. After the defeat of DSE and other left-wing guerillas, the Greeks stayed in Czechoslovakia. In total more than 12,000 Greeks immigrated to Czechoslovakia between 1948 and 1950.Today, there are about 7000 Greeks in the country (3219 according to 2001 census data), mostly in the 3 biggest towns –
Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
, Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
, Ostrava
Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opa ...
– and also in Bohumín
Bohumín (; , ) is a town in Karviná District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 20,000 inhabitants.
Administrative division
Bohumín consists of seven municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 202 ...
, Havířov
Havířov () is a city in Karviná District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 69,000 inhabitants, making it the second largest city in the region. Havířov was founded in 1955 and is the youngest Czech city. It is ...
, Jeseník
Jeseník (; until 1947 Frývaldov (); , ) is a spa town in the Olomouc Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 10,000 inhabitants.
Administrative division
Jeseník consists of three municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 202 ...
, Karviná
Karviná (; , ) is a city in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 49,000 inhabitants. It lies on the Olza (river), Olza River in the historical region of Cieszyn Silesia.
Karviná is known as an industrial city with t ...
, Krnov
Krnov (; , or ''Krnów'') is a town in Bruntál District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 23,000 inhabitants.
Administrative division
Krnov consists of three municipal parts (in brackets population according to ...
, Šumperk
Šumperk (; ) is a town in the Olomouc Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 25,000 inhabitants. It is an industrial town, but it also contains valuable historical and architectural monuments. The historic town centre is well preserved and i ...
, Třinec
Třinec (; ; ) is a city in Frýdek-Místek District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 34,000 inhabitants, making it the least populated Statutory city (Czech Republic), statutory city in the country.
The city ...
, Vrbno pod Pradědem Vrbno may refer to:
* Vrbno pod Pradědem, a town in the Czech Republic
* Vrbno nad Lesy, a village in the Czech Republic
* Vrbno (Hořín), a village in the Czech Republic
* Vrbno, Šentjur, a village in Slovenia
* Vrbno, Croatia, a village n ...
and Žamberk
Žamberk (; ) is a town in Ústí nad Orlicí District in the Pardubice Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 5,800 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected as an Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument zon ...
(apart from the last one these towns are in Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
).
Poles
The most concentrated linguistic minority in the Czech Republic are ethnic Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
, historically the plurality, today constituting about 10% of the population of Karviná
Karviná (; , ) is a city in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 49,000 inhabitants. It lies on the Olza (river), Olza River in the historical region of Cieszyn Silesia.
Karviná is known as an industrial city with t ...
and Frýdek-Místek
Frýdek-Místek (, ; ) is a city in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 54,000 inhabitants. The historic centres of both Frýdek and Místek are well preserved and are protected as two Cultural monument (Czech Republic) ...
districts. Poles have the right to use their language in official dealings; the public media ( Czech TV and Czech Radio
Czech Radio (, ČRo) is the public radio broadcaster of the Czech Republic operating continuously since 1923. It is the oldest national radio broadcaster in continental Europe and the second-oldest in Europe after the BBC. Czech Radio was esta ...
) regularly broadcast in Polish; and there are many Polish primary and secondary schools in the area. The Polish minority has been decreasing substantially since World War II as education in Polish was difficult to obtain, while Czech authorities did not permit bilingual signs to maintain Polish awareness among the population.
The erection of bilingual signs has technically been permitted since 2001, if a minority constitutes 10% of the population of a municipality. The requirement that a petition be signed by the members of minority was cancelled, thus simplifying the whole process. Still, only a couple of villages with large Polish minorities have bilingual signs (Vendryně
Vendryně () is a municipality and village in Frýdek-Místek District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 4,500 inhabitants. It lies in the historical region of Cieszyn Silesia on the banks of the Olza River. The ...
/Wędrynia for instance).
Romanis
Another minority is the Roma
Roma or ROMA may refer to:
People, characters, figures, names
* Roma or Romani people, an ethnic group living mostly in Europe and the Americas.
* Roma called Roy, ancient Egyptian High Priest of Amun
* Roma (footballer, born 1979), born ''Paul ...
, who nonetheless have very little influence on Czech policy. Around 90% of the Roma that lived in the Czech Republic prior to World War II were exterminated by the Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
Porajmos. The Roma there now are 80% post-war immigrants from Slovakia or Hungary, or the descendants thereof. In total, the Roma in the CR now number around 200,000. There is Romani press in the CR, written in both Czech and Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Romani people, or Roma, an ethnic group of Indo-Aryan origin
** Romani language, an Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani communities
** Romanichal, Romani subgroup in the United Kingdom
* Romanians (Romanian ...
, but Romani radio is broadcast in Czech and there is no Romani television. Romani is also absent from legislative, judiciary, and other political texts but it has recently entered some university and elementary school courses. Life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
, literacy
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was ...
, median wage, school enrolment, and other socio-economic markers remain low while Roma compose the majority of prison and habitual offender populations despite accounting for only a fraction of a percent of Czech population.
Immigration
 According to the Czech Statistical Office as of 31 December 2020 there were 632,570 legal foreign residents in the Czech Republic (5.1% of the total population). Residents from
According to the Czech Statistical Office as of 31 December 2020 there were 632,570 legal foreign residents in the Czech Republic (5.1% of the total population). Residents from Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
are the largest group (165,356), followed by residents of Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
(124,544). There are also Asian immigrant communities in the Czech Republic. The largest is the Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese people living outside Vietna ...
one (62,842) followed by the Mongolians (10,135) and the Chinese (7,940). During the communist era the governments of Czechoslovakia and Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
had a deal concerning the education of Vietnamese people in Czechoslovakia. Vietnamese people came to Czechoslovakia for the first time in 1956 and then the number of new migrants grew until the fall of communism. First generation Vietnamese work mostly as small-scale businessmen in markets. Still, many Vietnamese are without Czech citizenship. One of the towns with the largest Vietnamese communities is Cheb
Cheb (; ) is a town in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 33,000 inhabitants. It lies on the Ohře River.
Before the Expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia, expulsion of Germans in 1945, the town was the centre of the G ...
.
Other large immigrant groups come from Russia (41,692), Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
(20,733), Germany (20,861), Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
(17,917) and Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
(18,396).
Czech Republic Net migration data
Recent trends
Foreign-born population
;See also * Armenians in the Czech Republic *Chinese people in the Czech Republic
Chinese people in the Czech Republic form one of the country's smaller migrant communities.
Migration history
A few Chinese settled in Czechoslovakia prior to World War II. They consisted largely of overland migrants from Wenzhou, Zhejiang. Mos ...
*Croats in the Czech Republic
Croats are one of the 14 recognized minorities in the Czech Republic.
According to the 2021 census, 2,400 Croats live in the Czech Republic, half of which stated their Croatian nationality in combination with another nationality. Out of that num ...
* Germans in the Czech Republic
* Greeks in the Czech Republic
*History of the Jews in the Czech Republic
The history of the Jews in the Czech lands, historically the Lands of the Bohemian Crown, including the modern Czech Republic (i.e. Bohemia, Moravia, and the southeast or Czech Silesia), goes back at least 1100 years. There is evidence that J ...
* Koreans in the Czech Republic
* Macedonians in the Czech Republic
*Mongolians in the Czech Republic
Mongolians in the Czech Republic form one of the country's smaller ethnic groups. Although the workers from Mongolia comprised 3.6% of the foreign workforce , the group has grown over the last decade and numbered 10,236 men and women holding Mongo ...
*Polish minority in the Czech Republic
The Polish minority in the Czech Republic is a Polish national minority living mainly in the Trans-Olza region of western Cieszyn Silesia. The Polish community is the only national (or ethnic) minority in the Czech Republic that is linked to a sp ...
* Portuguese in the Czech Republic
* Romani people in the Czech Republic
* Slovaks in the Czech Republic
* Turks in the Czech Republic
*Ukrainians in the Czech Republic
There is a large national community of Ukrainians in the Czech Republic. The Ukrainian national minority in the Czech Republic together with the citizens of Ukraine make up the largest membership base with more than 203,198 members.
Labour migr ...
*Vietnamese people in the Czech Republic
Vietnamese people in the Czech Republic, including citizens and non-citizens, are the third-largest ethnic minority in the country overall (after Slovaks and Ukrainians), and the largest Asian ethnic group, numbering more than 38,000 people acco ...
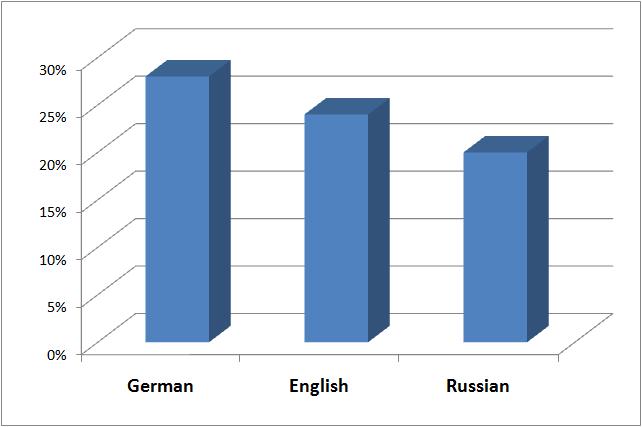
Languages
 The
The Czech language
Czech ( ; ), historically known as Bohemian ( ; ), is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. Spoken by over 12 million people including second language speakers, it serves as the official language of the ...
(divided into three dialects in Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
, four dialects in Moravia, and two dialects in Czech Silesia
Czech Silesia (; ) is the part of the historical region of Silesia now in the Czech Republic. While it currently has no formal boundaries, in a narrow geographic sense, it encompasses most or all of the territory of the Czech Republic within the ...
) is the official language of the state. There is also the transitional Cieszyn Silesian dialect
The Cieszyn Silesian dialect or Teschen Silesian dialect (Cieszyn Silesian: ''cieszyńsko rzecz''; or '; ; Silesian: ''ćeszyński djalekt'') is one of the Silesian dialects. It has its roots mainly in Old Polish and also has strong influence ...
as well as the Polish language
Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spo ...
in Cieszyn Silesia
Cieszyn Silesia, Těšín Silesia or Teschen Silesia ( ; or ; or ) is a historical region in south-eastern Silesia, centered on the towns of Cieszyn and Český Těšín and bisected by the Olza River. Since 1920 it has been divided betwe ...
, both spoken in Czech Silesia. Various Sudeten German dialects are currently practically extinct: present Czech Germans speak mainly Czech and/or Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the umbrella term for the standard language, standardized varieties of the German language, which are used in formal contexts and for commun ...
. Czech Sign Language
Czech Sign Language (, ČZJ) is the sign language of the deaf community in the Czech Republic. It presumably emerged around the time of the first deaf school in Bohemia (1786). It belongs to the French sign-language family and is partially intel ...
is the language of most of the deaf community.
For other languages spoken in the Czech Republic, see the above section on officially recognised minorities.
Religion
The 2021 census did not contain list of religious organisations and they had to be written by the respondent (unlike in the previous ones). Therefore another 231 thousand people responded with ''catholicism'' or similar response, 71 thousand people identified simply with ''Christianity'' and 27 thousand people claimed to be ''protestants'' or ''evangelicals''. Moreover, after doubling their followers the Orthodox Church of the Czech Lands and Slovakia was the 2nd strongest church in 2021 census with 40,681 faithful. Almost half (45.2%) of the Czech population prefer not to respond to religious questions in the Census. Others claim to have no religion or that they are withoutreligious affiliation
Religious identity is a specific type of identity formation. Particularly, it is the sense of group membership to a religion and the importance of this group membership as it pertains to one's self-concept. Religious identity is not necessarily the ...
(34.2%). In comparison, one in every five claims to have some personal belief (20.6%).
The largest denominations are Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, estimated at 10.3% of the population, Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
(0.5%), Hussite
file:Hussitenkriege.tif, upright=1.2, Battle between Hussites (left) and Crusades#Campaigns against heretics and schismatics, Catholic crusaders in the 15th century
file:The Bohemian Realm during the Hussite Wars.png, upright=1.2, The Lands of the ...
s (0.4%). Other organized religions, including non-organized believers, totalled about (9.4%) (as of Census 2011).
According to the Eurobarometer Poll
Eurobarometer is a series of public opinion surveys conducted regularly on behalf of the European Commission and other EU institutions since 1974. These surveys address a wide variety of topical issues relating to the European Union throughout ...
2005, 19% of Czech citizens responded that "they believe there is a God", whereas 50% answered that "they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 30% that "they do not believe there is any sort of spirit, god, or life force"; the percentage of believers is thus the lowest of EU countries after Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
with 16%.
See also
* Husák's Children A generation of people born in Czechoslovakia during the baby boom which started in the early 1970sNotes
References
External links
Czech Statistical Office
state institution responsible to provide official data about Czech Republic
Czechia – EU member country profile
European Union * {{Demographics of Europe