Landsat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of
 In 1965,
In 1965,
ImageSize = width:750 height:auto barincrement:21
PlotArea = left:70 bottom:30 top:10 right:10
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal format:yyyy
Colors =
id:canvas value:gray(0.97)
id:grid1 value:gray(0.8)
id:grid2 value:gray(0.6)
BackgroundColors = canvas:canvas
DateFormat = mm/dd/yyyy
Period = from:01/01/1972 till:01/01/2022
AlignBars = justify
ScaleMajor = increment:2 start:1973 unit:year grid:grid1
ScaleMinor = increment:1 start:1974 unit:year
BarData =
bar:Landsat1 text:"Landsat 1"
bar:Landsat2 text:"Landsat 2"
bar:Landsat3 text:"Landsat 3"
bar:Landsat4 text:"Landsat 4"
bar:Landsat5 text:"Landsat 5"
bar:Landsat6 text:"Landsat 6"
bar:Landsat7 text:"Landsat 7"
bar:Landsat8 text:"Landsat 8"
bar:Landsat9 text:"Landsat 9"
PlotData =
align:left anchor:from fontsize:M width:13 shift:(4,-6) textcolor:black
bar:Landsat1 from:07/23/1972 till:01/06/1978 color:blue
bar:Landsat2 from:01/22/1975 till:02/25/1982 color:blue
bar:Landsat3 from:03/05/1978 till:03/31/1983 color:blue
bar:Landsat4 from:07/16/1982 till:12/14/1993 color:orange
bar:Landsat5 from:03/01/1984 till:06/05/2013 color:orange
bar:Landsat6 from:10/05/1993 till:10/05/1993 color:black
bar:Landsat7 from:04/15/1999 till:05/31/2003 color:red
bar:Landsat7 from:05/31/2003 till:end color:coral
bar:Landsat8 from:02/11/2013 till:end color:green
bar:Landsat9 from:09/27/2021 till:end color:green
* Original MSS pixel size was 79 x 57 meters; production systems now resample the data to 60 meters.
* TM Band 6 was acquired at 120-meter resolution, but products are resampled to 30-meter pixels.
* ETM+ Band 6 is acquired at 60-meter resolution, but products are resampled to 30-meter pixels.
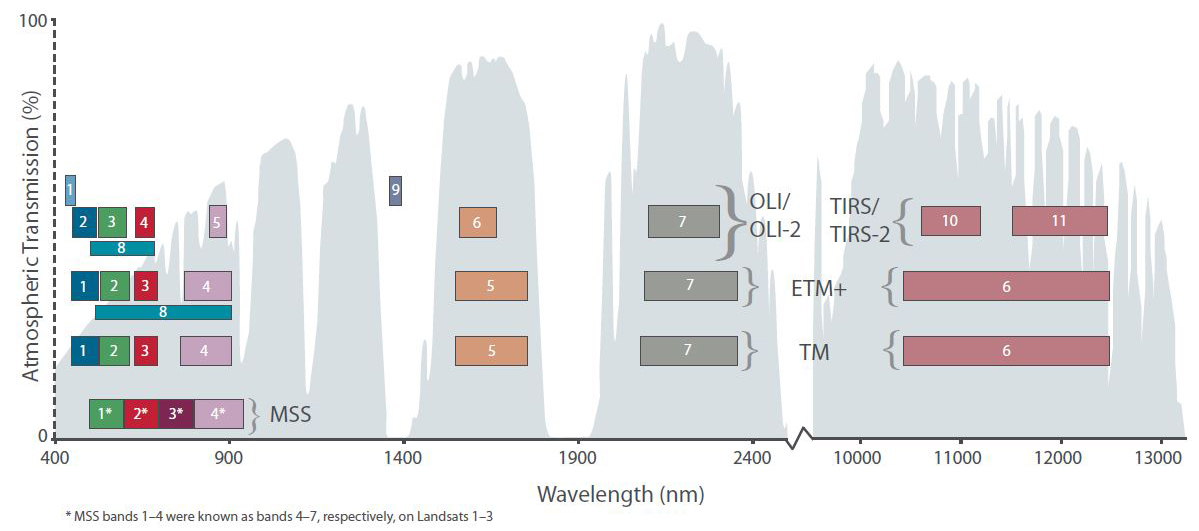
* TIRS bands are acquired at 100 meter resolution, but are resampled to 30 meter in delivered data product.
An advantage of Landsat imagery, and remote sensing in general, is that it provides data at a synoptic global level that is impossible to replicate with in situ measurements. However, there are tradeoffs between the local detail of the measurements (radiometric resolution, number of spectral bands) and the spatial scale of the area being measured. Landsat imagery is coarse in spatial resolution compared to using other remote sensing methods, such as imagery from airplanes. Compared to other satellites, Landsat’s spatial resolution is relatively high, yet revisit time is relatively less frequent.
satellite imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell ima ...
of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
. It is a joint NASA / USGS program. On 23 July 1972, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite was launched. This was eventually renamed to Landsat 1 in 1975. The most recent, Landsat 9
Landsat 9 is an Earth observation satellite launched on 27 September 2021 from Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Space Force Base on an Atlas V 401 launch vehicle. NASA is in charge of building, launching, and testing the satellite, while ...
, was launched on 27 September 2021.
The instruments on the Landsat satellites have acquired millions of images. The images, archived in the United States and at Landsat receiving stations around the world, are a unique resource for global change research and applications in agriculture, cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an ...
, geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
, forestry, regional planning, surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as c ...
and education, and can be viewed through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) "EarthExplorer" website. Landsat 7
Landsat 7 is the seventh satellite of the Landsat program. Launched on 15 April 1999, Landsat 7's primary goal is to refresh the global archive of satellite photos, providing up-to-date and cloud-free images. The Landsat program is managed and ...
data has eight spectral bands with spatial resolutions ranging from ; the temporal resolution is 16 days. Landsat images are usually divided into scenes for easy downloading. Each Landsat scene is about 115 miles long and 115 miles wide (or 100 nautical miles long and 100 nautical miles wide, or 185 kilometers long and 185 kilometers wide).
History
 In 1965,
In 1965, William T. Pecora
William Thomas Pecora (February 1, 1913 – July 19, 1972) was an American geologist.
Life and career
Willam Thomas Pecora was born on February 1, 1913, in Belleville, New Jersey, son of Cono and Anna (Amabile) Pecora. Both parents were born in ...
, the then director of the United States Geological Survey, proposed the idea of a remote sensing satellite program to gather facts about the natural resources of our planet. Pecora stated that the program was “conceived in 1966 largely as a direct result of the demonstrated utility of the Mercury and Gemini orbital photography to Earth resource studies.” While weather satellites had been monitoring Earth’s atmosphere since 1960 and were largely considered useful, there was no appreciation of terrain data from space until the mid-1960s. So, when Landsat 1 was proposed, it met with intense opposition from the Bureau of Budget and those who argued high-altitude aircraft would be the fiscally responsible choice for Earth remote sensing. Concurrently, the Department of Defense feared that a civilian program such as Landsat would compromise the secrecy of their reconnaissance missions. Additionally, there were also geopolitical concerns about photographing foreign countries without permission. In 1965, NASA began methodical investigations of Earth remote sensing using instruments mounted on planes. In 1966, the USGS convinced the Secretary of the Interior, Stewart Udall
Stewart Lee Udall (January 31, 1920 – March 20, 2010) was an American politician and later, a federal government official. After serving three terms as a congressman from Arizona, he served as Secretary of the Interior from 1961 to 1969, unde ...
, to announce that the Department of the Interior (DOI) was going to proceed with its own Earth-observing satellite program. This savvy political stunt coerced NASA to expedite the building of Landsat. But budgetary constraints and sensor disagreements between application agencies (notably the Department of Agriculture
An agriculture ministry (also called an) agriculture department, agriculture board, agriculture council, or agriculture agency, or ministry of rural development) is a ministry charged with agriculture. The ministry is often headed by a minister f ...
and DOI) again stymied the satellite construction process. Finally, by 1970 NASA had a green light to build a satellite. Remarkably, within only two years, Landsat 1 was launched, heralding a new age of remote sensing of land from space.
The Hughes Aircraft Company
The Hughes Aircraft Company was a major American aerospace and defense contractor founded on February 14, 1934 by Howard Hughes in Glendale, California, as a division of Hughes Tool Company. The company was known for producing, among other p ...
from Santa Barbara Research Center initiated, designed, and fabricated the first three Multispectral Scanners (MSS) in 1969. The first MSS prototype, designed by Virginia Norwood, was completed within nine months, in the fall of 1970. It was tested by scanning Half Dome at Yosemite National Park. For this design work Norwood is called "The Mother of Landsat."
Working at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Valerie L. Thomas managed the development of early Landsat image processing software systems and became the resident expert on the Computer Compatible Tapes, or CCTs, that were used to store early Landsat imagery. Thomas was one of the image processing specialists who facilitated the ambitious Large Area Crop Inventory Experiment, known as LACIE — a project that showed for the first time that global crop monitoring could be done with Landsat satellite imagery.
The program was initially called the Earth Resources Technology Satellites Program, which was used from 1966 to 1975. In 1975, the name was changed to Landsat. In 1979, President of the United States Jimmy Carter's Presidential Directive 54 transferred Landsat operations from NASA to National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), recommended development of a long term operational system with four additional satellites beyond Landsat 3, and recommended transition to private sector operation of Landsat. This occurred in 1985 when the Earth Observation Satellite Company (EOSAT), a partnership of Hughes Aircraft Company
The Hughes Aircraft Company was a major American aerospace and defense contractor founded on February 14, 1934 by Howard Hughes in Glendale, California, as a division of Hughes Tool Company. The company was known for producing, among other p ...
and RCA, was selected by NOAA to operate the Landsat system with a ten-year contract. EOSAT operated Landsat 4 and Landsat 5, had exclusive rights to market Landsat data, and was to build Landsats 6 and 7.
In 1989, this transition had not been fully completed when NOAA's funding for the Landsat program was due to run out (NOAA had not requested any funding, and U.S. Congress had appropriated only six months of funding for the fiscal year) and NOAA directed that Landsat 4 and Landsat 5 be shut down.
The head of the newly formed National Space Council, Vice President Dan Quayle, noted the situation and arranged emergency funding that allowed the program to continue with the data archives intact.
Again in 1990 and 1991, Congress provided only half of the year's funding to NOAA, requesting that agencies that used Landsat data provide the funding for the other six months of the upcoming year.
In 1992, various efforts were made to procure funding for follow on Landsats and continued operations, but by the end of the year EOSAT ceased processing Landsat data. Landsat 6 was finally launched on 5 October 1993, but was lost in a launch failure. Processing of Landsat 4 and 5 data was resumed by EOSAT in 1994. NASA finally launched Landsat 7 on 15 April 1999.
The value of the Landsat program was recognized by Congress in October 1992 when it passed the Land Remote Sensing Policy Act (Public Law 102-555) authorizing the procurement of Landsat 7 and assuring the continued availability of Landsat digital data and images, at the lowest possible cost, to traditional and new users of the data.
Satellite chronology
;TimelineSpatial and spectral resolution
Landsat 1 through 5 carried the Landsat Multispectral Scanner (MSS). Landsat 4 and 5 carried both the MSS and Thematic Mapper (TM) instruments. Landsat 7 uses theEnhanced Thematic Mapper Plus
''Enhanced'' is a 2019 Canadian-Japanese action film produced, written and directed by James Mark. The film premiered at the 2019 Toronto After Dark Film Festival.
Plot
A sinister government organization hunts down mutants, and one of such is a y ...
(ETM+) scanner. Landsat 8 uses two instruments, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) for optical bands and the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) for thermal bands. The band designations, bandpasses, and pixel sizes for the Landsat instruments are:

MultiSpectral Scanner (MSS) sensor design
The Multispectral Scanner (MSS) onboard Landsat missions 1 through 5 was originally built with an engineering solution that allowed the United States to develop Landsat-1 at least five years ahead of the French SPOT. The original MSS had a fused silica dinner-plate mirror epoxy bonded to three invar tangent bars mounted to base of a nickel/gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
brazed Invar frame in a Serrurier truss that was arranged with four "Hobbs-Links" (conceived by Dr. Gregg Hobbs), crossing at mid-truss. This construct ensured the secondary mirror would simply oscillate about the primary optic axis to maintain focus despite vibration inhere