Lake Tecopa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
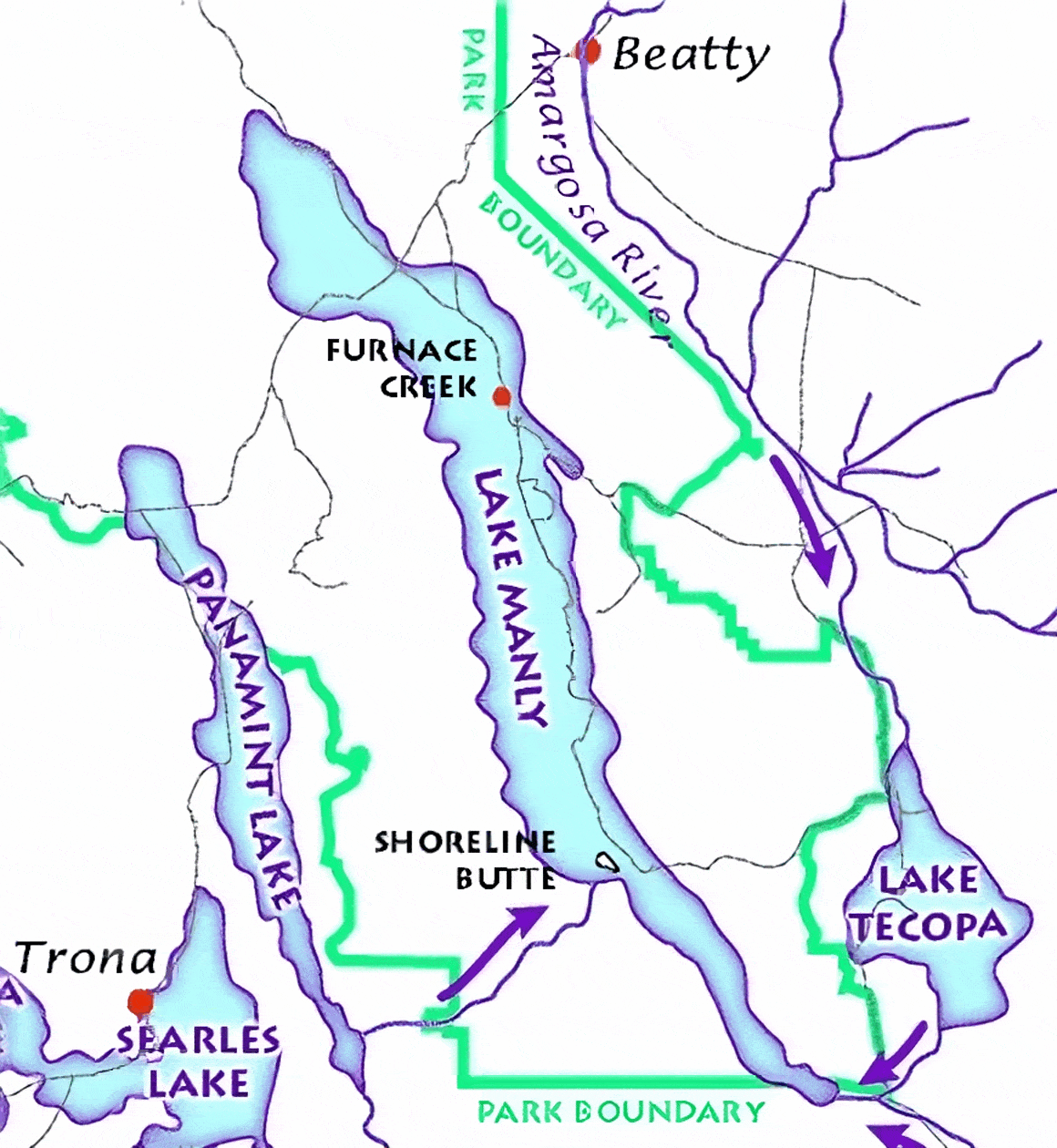 Lake Tecopa is a
Lake Tecopa is a
 Lake Tecopa occupied the Tecopa Valley, a pear-shaped valley east of southern
Lake Tecopa occupied the Tecopa Valley, a pear-shaped valley east of southern  The
The
 Various sediments were emplaced in the lake, including
Various sediments were emplaced in the lake, including
 A number of fossils were discovered in the sediments, including '' chara'',
A number of fossils were discovered in the sediments, including '' chara'',
 Lake Tecopa existed during the
Lake Tecopa existed during the
 Lake Tecopa is a
Lake Tecopa is a former lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from t ...
in Inyo County, southern California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
. It developed during the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
and the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
within a tectonic basin
A structural basin is a large-scale structural geology, structural formation of rock stratum, strata formed by tectonics, tectonic warping (Fold (geology), folding) of previously flat-lying strata into a syncline fold. They are geological dep ...
close to the border with Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, th ...
. Fed by the Amargosa River
The Amargosa River is an waterway, 185 miles (298 km) long, in southern Nevada and eastern California in the United States. The Amargosa River is one out of two rivers located in the California portion of the Mojave Desert with perennial f ...
and some neighbouring washes, it eventually culminated to a surface area of around 186,000 years ago and left sediments. Afterwards, the Amargosa River cut a gorge out of the lake and into Death Valley
Death Valley is a desert valley in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert, bordering the Great Basin Desert. It is thought to be the Highest temperature recorded on Earth, hottest place on Earth during summer.
Death Valley's Badwat ...
with its Lake Manly
Lake Manly was a pluvial lake in Death Valley, California. It forms occasionally in Badwater Basin after heavy rainfall, but at its maximum extent during the so-called "Blackwelder stand," ending approximately 120,000 years before present, the ...
, draining the lake. The present-day towns of Shoshone, California
Shoshone is a census-designated place (CDP) in Inyo County, California, United States. The population was 22 at the 2020 census, down from 31 at the 2010 census.
The town was founded in 1910. Although small, it is notable as a southern gateway ...
and Tecopa, California
Tecopa is a census-designated place (CDP) in the Mojave Desert in southeast Inyo County, California, United States. Originally occupied by the Koso and Chemehuevi Indians, Pioneers began populating what would become the CDP in the late 19th ce ...
lie within the basin of the former lake.
Hydrology
 Lake Tecopa occupied the Tecopa Valley, a pear-shaped valley east of southern
Lake Tecopa occupied the Tecopa Valley, a pear-shaped valley east of southern Death Valley
Death Valley is a desert valley in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert, bordering the Great Basin Desert. It is thought to be the Highest temperature recorded on Earth, hottest place on Earth during summer.
Death Valley's Badwat ...
, in Inyo County
Inyo County () is a county in the eastern central part of the U.S. state of California, located between the Sierra Nevada and the state of Nevada. In the 2020 census, the population was 19,016. The county seat is Independence. Inyo County is ...
, California. The cities of Barstow, California
Barstow is a city in San Bernardino County, California, in the Mojave Desert of Southern California. Located in the Inland Empire region of California, the population was 25,415 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Barstow is an impor ...
and Las Vegas, Nevada
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-l ...
lie close to the lake basin. The lake itself had a roughly triangular shape with a northern, a southwestern and a southeastern corner, and at its highstand
A raised shoreline is an ancient shoreline exposed above current water level. These landforms are formed by a relative change in sea level due to global sea level rise, isostatic rebound, and/or tectonic uplift. These surfaces are usually expos ...
it covered about . Outcrops of lake sediments occupy a length of along the Amargosa River and are wide at their broadest. Its southern margin is not clear, given that the height of the sill to the China Ranch basin is undetermined. Several islands existed in Lake Tecopa. Of these, the largest was close to Tecopa, California, and two smaller ones were north of Shoshone, California. The shores of the lake featured marshes
In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p More in general ...
and delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
s where Amargosa River or spring water entered the lake, as well as freshwater ponds where springs and streams flowed into Lake Tecopa.
At the time of the Bishop Tuff
The Bishop Tuff is a welded tuff which formed 764,800 ± 600 years ago as a rhyolite, rhyolitic pyroclastic flow during the approximately six-day eruption that formed the Long Valley Caldera. Large outcrops of the tuff are located in Inyo County, ...
eruption, Lake Tecopa was about deep. The waters of the lake were salty and had a high pH, inducing precipitation of calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
in the northern part of the lake where the Amargosa River flowed into it. There is some indication that the centre of the lake was much more saline than its shores. Salt lakes generally form when a lake has no outlet, so evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
concentrates salts in the lake water until the lake contains saltwater.
 The
The Amargosa River
The Amargosa River is an waterway, 185 miles (298 km) long, in southern Nevada and eastern California in the United States. The Amargosa River is one out of two rivers located in the California portion of the Mojave Desert with perennial f ...
flowed into Lake Tecopa, which was the river's terminal lake. Most of the water in Lake Tecopa came from the Amargosa River and to a lesser degree from the washes that drain Chicago Valley and Greenwater Valley; the total size of its catchment was about and most of its water originated in Paiute Mesa, Shoshone Mountains, Timber Mountains and Yucca Mountain
Yucca Mountain is a mountain in Nevada, near its border with California, approximately northwest of Las Vegas. Located in the Great Basin, Yucca Mountain is east of the Amargosa Desert, south of the Nevada Test and Training Range and in the ...
s.
The catchment of the Amargosa River above Tecopa, California
Tecopa is a census-designated place (CDP) in the Mojave Desert in southeast Inyo County, California, United States. Originally occupied by the Koso and Chemehuevi Indians, Pioneers began populating what would become the CDP in the late 19th ce ...
is presently about . Later, after Lake Tecopa had disappeared, the river reached Death Valley
Death Valley is a desert valley in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert, bordering the Great Basin Desert. It is thought to be the Highest temperature recorded on Earth, hottest place on Earth during summer.
Death Valley's Badwat ...
and its Lake Manly
Lake Manly was a pluvial lake in Death Valley, California. It forms occasionally in Badwater Basin after heavy rainfall, but at its maximum extent during the so-called "Blackwelder stand," ending approximately 120,000 years before present, the ...
, dramatically increasing the supply of water to the latter. Presently, the river is largely ephemeral
Ephemerality (from the Greek word , meaning 'lasting only one day') is the concept of things being transitory, existing only briefly. Academically, the term ephemeral constitutionally describes a diverse assortment of things and experiences, fr ...
except where it is fed by springs.
Geography
The former lake basin is surrounded by various hills and mountain ranges, formed by rocks ofNeoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era an ...
to Tertiary
Tertiary (from Latin, meaning 'third' or 'of the third degree/order..') may refer to:
* Tertiary period, an obsolete geologic period spanning from 66 to 2.6 million years ago
* Tertiary (chemistry), a term describing bonding patterns in organic ch ...
age. Clockwise from north they are the Resting Spring Range, the Nopah Range
The Nopah Range is a mountain range located in Inyo County, California, United States, near the eastern border with Nevada.
Geography
The mountain range lies east of the adjacent Resting Spring Range, the Owlshead Mountains and lower Death Vall ...
, the Sperry Hills, the Ibex Hills, the Greenwater Valley and the Dublin Hills; together they enclose an area of about . The region belongs to the Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast United States physiographic region, physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and Northern Mexico, northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, charac ...
of the western United States, where short ranges of mountains lie between plains. This geology consists of normal fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
s which separate graben
In geology, a graben () is a depression (geology), depressed block of the Crust (geology), crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German language, German, meaning 'ditch' or 't ...
s from horsts. It was affected by extensive tectonic activity in the past and may be still active in the present.
Presently, the towns of Shoshone, California
Shoshone is a census-designated place (CDP) in Inyo County, California, United States. The population was 22 at the 2020 census, down from 31 at the 2010 census.
The town was founded in 1910. Although small, it is notable as a southern gateway ...
, Tecopa Hot Springs, California and Tecopa, California
Tecopa is a census-designated place (CDP) in the Mojave Desert in southeast Inyo County, California, United States. Originally occupied by the Koso and Chemehuevi Indians, Pioneers began populating what would become the CDP in the late 19th ce ...
lie within the former bed of Lake Tecopa. California State Route 127 and California State Route 178
State Route 178 (SR 178) is a state highway in the U.S. state of California that exists in two constructed segments. The gap in between segments is connected by various local roads and State Route 190 (California), State Route 190 through Death ...
cross the lake basin from southwest to north and from west to east, respectively, while the Furnace Creek Road traverses it from northwest to southeast. The terrain of the region is characterized by badland
Badlands are a type of dry terrain where softer sedimentary rocks and clay-rich soils have been extensively eroded."Badlands" in '' Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 47. They are characterized by steep slopes ...
s and rugged mountains with little vegetation away from springs. A number of spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a he ...
s form oases
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentShoshone, California
Shoshone is a census-designated place (CDP) in Inyo County, California, United States. The population was 22 at the 2020 census, down from 31 at the 2010 census.
The town was founded in 1910. Although small, it is notable as a southern gateway ...
average temperatures are and often exceed , with about of rainfall. Under present-day climates, evaporation is too high and precipitation too low to allow the formation of lakes in the area. 180,000 years before present, precipitation increased to and average temperatures decreased by , lifting the regional water table
The water table is the upper surface of the phreatic zone or zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with groundwater, which may be fresh, saline, or brackish, depending on the loc ...
s.
Sediments
adularia
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar (endmember formula potassium, Kaluminium, Alsilicon, Si3oxygen, O8), is an important Silicate minerals#Tectosilicates, tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "stra ...
, clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
, gravel
Gravel () is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally on Earth as a result of sedimentation, sedimentary and erosion, erosive geological processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gr ...
and zeolite
Zeolites are a group of several microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate minerals commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula ・y where is either a meta ...
s. Some of these formed when ash or sediments were progressively altered. The sediments take the form of calcareous, sandy, silty material or mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility.Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, ...
. The sediments have undergone increasing amounts of diagenesis
Diagenesis () is the process of physical and chemical changes in sediments first caused by water-rock interactions, microbial activity, and compaction after their deposition. Increased pressure and temperature only start to play a role as sedi ...
the closer they are to the basin center. Among the minerals found at various sites are calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
, gaylussite
Gaylussite is a carbonate mineral, a hydrated sodium calcium carbonate, formula Na2Ca(CO3)2·5H2O. It occurs as translucent, vitreous white to grey to yellow monoclinic prismatic crystals. It is an unstable mineral which dehydrates in dry air and ...
, halite
Halite ( ), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pi ...
and sepiolite
Sepiolite, also known in English by the German name meerschaum ( , ; ; meaning " sea foam"), is a soft white clay mineral, often used to make tobacco pipes (known as meerschaum pipes). A complex magnesium silicate, a typical chemical formula ...
.
After the lake was breached, these deposits were deeply eroded and exposed, showing thicknesses exceeding . The sediments of Lake Tecopa have been heavily researched, e.g. whether similar deposits on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
would be remotely detectable. Mining for bentonite
Bentonite ( ) is an Absorption (chemistry), absorbent swelling clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite (a type of smectite) which can either be Na-montmorillonite or Ca-montmorillonite. Na-montmorillonite has a considerably greater swelli ...
and pumicite took place from the 1920s to the 1950s.
Tufa
Tufa is a variety of limestone formed when carbonate minerals precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water in ambient temperature, unheated rivers or lakes. hot spring, Geothermally heated hot springs sometimes produce similar (but less ...
deposits are found within the lake and partly embedded in its sediments; they were generated from carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group ...
precipitation within the lake, a process facilitated by the physical properties of the lake water. Many of these tufa deposits occur where fault-controlled spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a he ...
s discharged water into the lake.
Several tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a Volcano, volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.
Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, ...
layers have been identified, including the 2.003 million years old Huckleberry Ridge Tuff
The Huckleberry Ridge Tuff is a tuff formation created by the Huckleberry Ridge eruption that formed the Island Park Caldera that lies partially in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming and stretches westward into Idaho into a region known as Islan ...
, the 706,000 years old Bishop Tuff
The Bishop Tuff is a welded tuff which formed 764,800 ± 600 years ago as a rhyolite, rhyolitic pyroclastic flow during the approximately six-day eruption that formed the Long Valley Caldera. Large outcrops of the tuff are located in Inyo County, ...
and the 602,000 years old Lava Creek Tuff
The Lava Creek Tuff is a voluminous sheet of ash-flow tuff located in Wyoming, Montana and Idaho, United States. It was created during the Lava Creek eruption around 630,000 years ago, which led to the formation of the Yellowstone Caldera. Thi ...
as well as the 2, 1.2-0.8 million years old Glass Mountain tuffs. They form tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock co ...
layers which are very conspicuous in the lake sediments.
Biology
 A number of fossils were discovered in the sediments, including '' chara'',
A number of fossils were discovered in the sediments, including '' chara'', diatoms
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma'') is any member of a large group comprising several Genus, genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of Earth's B ...
, ostracods
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 33,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant) have been identified,Brandão, S.N.; Antonietto, L.S; Nery, D.G.; Santos, S.G.; Karano ...
, snails
A snail is a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gas ...
and vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
. Flamingo
Flamingos or flamingoes () are a type of wading bird in the family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas (including the Caribbe ...
s lived around the lake. Among mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s are ''Camelops
''Camelops'' is an extinct genus of camel that lived in North and Central America from the middle Pliocene (from around 4-3.2 million years ago) to the end of the Pleistocene (around 13-12,000 years ago). It is more closely related to living cam ...
'', '' Equus'', mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabi ...
and muskrat
The muskrat or common muskrat (''Ondatra zibethicus'') is a medium-sized semiaquatic rodent native to North America and an introduced species in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America.
The muskrat is found in wetlands over various climates ...
. Footprints have been observed at the edges of the lake basin.
Arcellacea and foraminifera
Foraminifera ( ; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are unicellular organism, single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class (biology), class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular Ectoplasm (cell bio ...
have been found in lake sediments, including '' Bolivina goudkoffi'', '' Centropyxis constricta'', '' Lobatula lobatula'' and a few other, less widespread species. Foraminifera are mostly ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
ic, and since Lake Tecopa was never connected to the ocean, they were most likely transported there by birds.
History
 Lake Tecopa existed during the
Lake Tecopa existed during the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
and Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
. The basin of Lake Tecopa formed between 7 and 11 million years ago, but was then tectonically stable during the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
, although tectonic or magmatic
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
activity may be occurring north of Shoshone. From about 5 million years ago to about 186,000 years before present, the lake developed inside the basin.
Extensive faulting of lake deposits makes it difficult to reconstruct its history. About 2 million years ago, the Amargosa Desert
The Amargosa Desert is located in Nye County in western Nevada, United States, along the California–Nevada border, comprising the northeastern portion of the geographic Amargosa Valley, north of the Ash Meadows National Wildlife Refuge.
T ...
began to drain into Lake Tecopa and a shallow lake existed back then, but between 1.6 and 0.9 million years ago the lake often became a playa. It is unlikely that the lake was ephemeral, however, given the presence of fossils in the lake sediments of foraminifera which do not tolerate such drying. Probably owing to uplift of the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
and expansion of the catchment
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, th ...
, water levels at Lake Tecopa increased during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
and reached highstands concurrently with other lakes in the Great Basin
The Great Basin () is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets to the ocean, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja Californi ...
. The highest shoreline occurs at about elevation (subsequently tectonically deformed) about 186,000 years before present; it appears to coincide with the Eetza highstand of Lake Lahontan
Lake Lahontan was a large endorheic prehistoric lake during the Pleistocene that occupied modern northwestern Nevada and extended into northeastern California and southern Oregon. The area of the former lake is a large portion of the Great Basi ...
and oxygen isotope stages 8, 7 and 6. Some doubts have been raised about this chronology, however.
At some point after 579,000 years ago, a large slump occurred at the southwestern area of the lake, possibly triggered by an earthquake. Such earthquake activity is also responsible for the formation of seismites within the lake sediments. A number of faults criss-cross the area, several of them follow the borders of the Tecopa basin. Finally, there is evidence of uplift in parts of the southern basin.
About 200,000 - 150,000 years before present, the lake overflowed and disappeared. Several different dates have been given for the time when the lake breached its boundaries, but it likely happened shortly after highstand. A long gorge was formed by the breaching event, which was triggered either by a river capture
Stream capture, river capture, river piracy or stream piracy is a geomorphological phenomenon occurring when a stream or river drainage system or watershed is diverted from its own bed, and flows down to the bed of a neighbouring stream. This ...
-like process or by overflow. Subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope mov ...
in Death Valley may be ultimately responsible for the drainage change. It is possible that Lake Tecopa briefly reformed later, due to a temporary blockage of its outflow, and that at times the Amargosa River was blocked upstream from Lake Tecopa.
The existence of the lake beds was described first by Levi F. Noble in 1926. In 1931, Eliot Blackwelder
Eliot Blackwelder (June 4, 1880 – January 14, 1969) was an American geologist and educator. Known primarily as a field geologist, from 1922 to 1945 he was head of the Stanford University department of geology. He served as president of the G ...
identified these lakebeds as the remnants of what he named Lake Tecopa. The area of the former lake has been the subject of numerous studies comprising various fields of geology but also biology, and an important target for field studies and field trip
A field trip or excursion is a journey by a group of associated peers, such as coworkers or school students, to a place away from their normal environment for the purpose of education or leisure, either within their country or abroad.
When ar ...
s. Research in the paleoclimatic conditions of the region has received impetus from the Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository
The Yucca Mountain Nuclear Waste Repository, as designated by the Nuclear Waste Policy Act amendments of 1987, is a proposed deep geological repository storage facility within Yucca Mountain for spent nuclear fuel and other high-level radioact ...
, since the future climate of the region is important in establishing how secure the nuclear waste would be.
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * {{Pleistocene Lakes and Seas Tecopa Natural history of Inyo County, California Pleistocene North America