Lake Tchad on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lake Chad (, Kanuri: ''Sádǝ'', ) is an
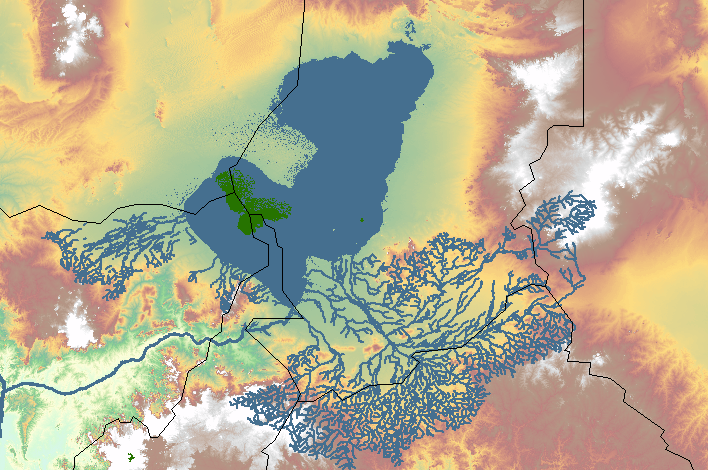 The
The
endorheic
An endorheic basin ( ; also endoreic basin and endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water (e.g. rivers and oceans); instead, the water drainage flows into permanent ...
freshwater lake located at the junction of four countries: Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
, and Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
, in western and central Africa respectively, with a catchment area in excess of . It is an important wetland ecosystem in West-Central Africa. The lakeside is rich in reeds and swamps, and the plain along the lake is fertile, making it an important irrigated agricultural area. The lake is rich in aquatic resources and is one of the important freshwater fish producing areas in Africa.
Lake Chad is divided into deeper southern parts and shallower northern parts. The water source of the lake mainly comes from rivers such as the Chari River
The Chari River, or Shari River, is a long river, flowing in Central Africa. It is the main source of water of Lake Chad, which is located at the junction of four countries: Nigeria, Niger, Chad, and Cameroon.
Geography
The Chari River flows f ...
that enter the lake. The water level varies greatly seasonally, and the area of the lake also changes dramatically. During the African humid period
The African humid period (AHP; also known by other names) was a climate period in Africa during the late Pleistocene and Holocene geologic epochs, when northern Africa was wetter than today. The covering of much of the Sahara desert by grass ...
, the lake's area reached . Due to the increasingly arid climate, the lake surface gradually shrank. In the 19th century, it still had an area of . However, due to climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
and human water diversion, it has shrunk significantly since the mid-1970s, and its area has fluctuated between .
Prehistory and history
Chad Basin
The Chad Basin is the largest endorheic basin in Africa, centered approximately on Lake Chad. It has no outlet to the sea and contains large areas of semi-arid desert and savanna. The drainage basin is approximately coterminous with the sedimenta ...
was formed by the depression of the African Shield The Western Ethiopian Shield is a small geological shield along the western border of Ethiopia. Its plutons were formed between 830 and 540 million years ago.
See also
*Craton
* Platform
*Basement
A basement is any Storey, floor of a buildi ...
. The floor of the basin is made of Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
bedrock covered by more than of sedimentary deposits. For most of the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
, the basin had abundant water sources. Towards the end of this period the climate became drier. Around 20,000–40,000 years ago, eolianite
Eolianite or aeolianite is any rock formed by the lithification of sediment deposited by aeolian processes; that is, the wind. In common use, however, the term refers specifically to the most common form of eolianite: coastal limestone consisting ...
sand dunes began to form in the north of the basin. The area of Lake Chad experienced four heydays between 39,000 BC and 300 BC, leaving thick diatomaceous earth
Diatomaceous earth ( ), also known as diatomite ( ), celite, or kieselguhr, is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous rock, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging fr ...
and lacustrine deposits
Lacustrine deposits are sedimentary rock formations which formed in the bottom of ancient lakes. A common characteristic of lacustrine deposits is that a river or stream channel has carried sediment into the basin. Lacustrine deposits form in all ...
in the strata. This has been called Mega-Chad. The maximum depth of Mega-Chad exceeds and covers an area of approximately , flowed into the Benue River
Benue River (), previously known as the Chadda River or Tchadda, is a major tributary of the Niger River. The size of its catchment basin is 319,000 km2 (123,000 sq mi). Almost its entire length of Approximation, approximately is navigable dur ...
through the Mayo Kébbi
The Mayo Kébbi is a river in Central and West Africa. The river rises in Chad, then flows west into the Bénoué River. Mayo-Kébbi Prefecture in Chad is named for it. The Mayo Kébbi is the major outlet for Lake Fianga, shared between Camer ...
, and finally flows into the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
through the Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Nige ...
.
The vast waters formed during the African humid period
The African humid period (AHP; also known by other names) was a climate period in Africa during the late Pleistocene and Holocene geologic epochs, when northern Africa was wetter than today. The covering of much of the Sahara desert by grass ...
provided conditions for the emergence of lakeside fishermen's settlements, and the Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of around 210 African languages spoken by somewhere around 70 million speakers, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributari ...
ethnic group also migrated to Lake Chad during this period. Agriculture also emerged in the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
region at this time. By 1800 BC, a pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
culture known as Gajiganna had emerged, initially as pastoralists, but, starting around 1500 BC, living in settled hamlets at the side of the lake. The archaeological discovery revealed wild grasses, mostly of the tribe Paniceae
Paniceae is a large tribe (biology), tribe of the subfamily Panicoideae in the grasses (Poaceae), the only in the monotypic taxon, monotypic supertribe Panicodae. It includes roughly 1,500 species in 84 genera, primarily found in tropical and sub ...
, and wild rice together with the earliest domesticated Pearl millet
Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum'') is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and ...
in the Lake Chad region, dating to 1200–1000 cal BC
Radiocarbon dating measurements produce ages in "radiocarbon years", which must be converted to calendar ages by a process called calibration. Calibration is needed because the atmospheric / ratio, which is a key element in calculating radiocarbo ...
. One of the oldest domesticated Pearl millet in West Africa was found in the Chad Basin, charred together with wild grasses, and their era can be traced back to 800–1000 cal BC.
Permanent villages were established to the south of the lake by 500 BC, and major archaeological discoveries include the Sao civilization
The Sao civilization (also called So) flourished in Central Africa from the 6th century BCE or 5th century BCE, to as late as the 16th century AD. The Sao lived by the Chari River basin in territory that later became part of Cameroon and Chad. The ...
. According to the records of Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine, Islamic, and ...
in the mid-2nd century AD, the Romans of the 1st century AD had already come into contact with Lake Chad through their connections with Tunisia, Tripolitania
Tripolitania (), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province of Libya.
The region had been settled since antiquity, first coming to prominence as part of the Carthaginian empire. Following the defeat ...
, and Fezzan
Fezzan ( , ; ; ; ) is the southwestern region of modern Libya. It is largely desert, but broken by mountains, uplands, and dry river valleys (wadis) in the north, where oases enable ancient towns and villages to survive deep in the otherwise in ...
. By the 5th century AD camels were being used for trans-Saharan trade via the Fezzan, or to the east via Darfur
Darfur ( ; ) is a region of western Sudan. ''Dār'' is an Arabic word meaning "home f – the region was named Dardaju () while ruled by the Daju, who migrated from Meroë , and it was renamed Dartunjur () when the Tunjur ruled the area. ...
. After the Arabs conquered North Africa during the 7th and 8th centuries, the Chad Basin became increasingly linked to the Muslim countries.
Trade and improved agricultural techniques enabled more sophisticated societies. Around 900 AD, the Kanem people who spoke the Kanuri language
Kanuri () is a Saharan dialect continuum of the Nilo–Saharan language family spoken by the Kanuri and Kanembu peoples in Nigeria, Niger, Chad and Cameroon, as well as by a diaspora community residing in Sudan.
Background
At the turn of the ...
unified numerous nomadic tribes and established the Kanem Empire Kanem may refer to:
* Kanem–Bornu Empire, existed in modern Chad and Nigeria known to Arabian geographers from the 9th century AD onward and lasted as the independent kingdom of Bornu until 1900
* Kanem Prefecture, of former prefectures of Chad
* ...
in the northeast of Lake Chad. At the beginning of the founding of the country, the Kanem people continued to live a nomadic life until the 11th century, when they were Islamized and settled in Njimi Njimi, also called Birni Njimi, N'Jimi, N'jimi, and Anjimi, was the capital of the Kanem–Bornu Empire until the 14th century. Njimi is first recorded in texts from the 12th century but was probably the empire's original capital, perhaps establishe ...
. Through trans-Saharan trade, the power of the Kanem Empire reached its peak in the 13th century, but as the empire declined in the 14th century, its southwestern vassal state of Bornu began to rise, causing the power center of the empire to shift to Bornu around 1400. In the second half of the 16th century, the Bornu Empire Bornu may refer to:
* Bornu Empire, a historical state of West Africa
* Borno State, Nigeria
{{disambig