Lacunar Stroke on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lacunar stroke or lacunar cerebral infarct (LACI) is the most common type of
 A silent lacunar infarction (SLI) is one type of silent stroke which usually shows no identifiable outward symptoms, and is thus termed "silent". Because stroke is a clinical diagnosis (that is, it is defined by clinical symptoms), there is debate about whether SLI are considered to be strokes, even though the pathophysiology is presumably the same. Individuals who have a SLI are often completely unaware they have had a stroke. This type of stroke often causes lesions in the surrounding brain tissue that are visibly detected via neuroimaging techniques such as
A silent lacunar infarction (SLI) is one type of silent stroke which usually shows no identifiable outward symptoms, and is thus termed "silent". Because stroke is a clinical diagnosis (that is, it is defined by clinical symptoms), there is debate about whether SLI are considered to be strokes, even though the pathophysiology is presumably the same. Individuals who have a SLI are often completely unaware they have had a stroke. This type of stroke often causes lesions in the surrounding brain tissue that are visibly detected via neuroimaging techniques such as
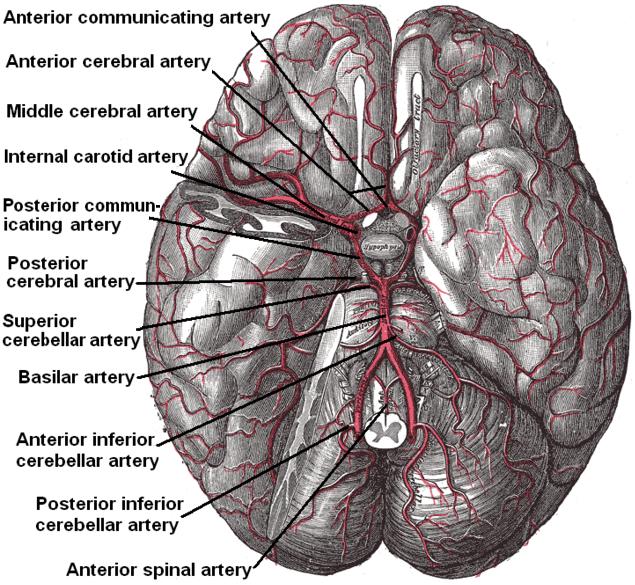 According to Koffler et al., lacunes are derived from an "occlusion of a single deep penetrating artery that arises directly from the constituents of the
According to Koffler et al., lacunes are derived from an "occlusion of a single deep penetrating artery that arises directly from the constituents of the
ischemic stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop ...
, resulting from the occlusion of small penetrating arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
that provide blood to the brain's deep structures. Patients who present with symptoms of a lacunar stroke, but who have not yet had diagnostic imaging performed, may be described as having lacunar stroke syndrome (LACS).
Much of the current knowledge of lacunar strokes comes from C. Miller Fisher's cadaver
A cadaver, often known as a corpse, is a Death, dead human body. Cadavers are used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue (biology), tissue to ...
dissections of post-mortem stroke patients. He observed "lacunae" (empty spaces) in the deep brain structures after occlusion of 200–800 μm penetrating arteries and connected them with five classic syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a sy ...
s. These syndromes are still noted today, though lacunar infarcts are diagnosed based on clinical judgment and radiologic imaging.
Signs and symptoms
Each of the five classical lacunar syndromes has a relatively distinct symptom complex. Symptoms may occur suddenly, progressively, or in a fluctuating (e.g., the capsular warning syndrome) manner. Occasionally, cortical infarcts andintracranial hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) refers to any form of Hemorrhage, bleeding Internal bleeding, within the Human skull, skull. It can result from trauma, vascular abnormalities, hypertension, or other medical conditions. ICH is broadly categorized ...
s can mimic lacunar infarcts, but true cortical signs (aphasia, visuospatial neglect, gaze deviation, and visual field defects) are always absent in lacunar strokes. The classic syndromes are as follows:
Silent lacunar infarction
 A silent lacunar infarction (SLI) is one type of silent stroke which usually shows no identifiable outward symptoms, and is thus termed "silent". Because stroke is a clinical diagnosis (that is, it is defined by clinical symptoms), there is debate about whether SLI are considered to be strokes, even though the pathophysiology is presumably the same. Individuals who have a SLI are often completely unaware they have had a stroke. This type of stroke often causes lesions in the surrounding brain tissue that are visibly detected via neuroimaging techniques such as
A silent lacunar infarction (SLI) is one type of silent stroke which usually shows no identifiable outward symptoms, and is thus termed "silent". Because stroke is a clinical diagnosis (that is, it is defined by clinical symptoms), there is debate about whether SLI are considered to be strokes, even though the pathophysiology is presumably the same. Individuals who have a SLI are often completely unaware they have had a stroke. This type of stroke often causes lesions in the surrounding brain tissue that are visibly detected via neuroimaging techniques such as MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
and computed axial tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
(CT scan). Silent strokes, including silent lacunar infarctions, have been shown to be much more common than previously thought, with an estimated prevalence rate of eleven million per year in the United States. Approximately 10% of these silent strokes are silent lacunar infarctions. While dubbed "silent" due to the immediate lack of classic stroke symptoms, SLIs can cause damage to the surrounding brain tissue and can affect various aspects of a person's mood, personality, and cognitive functioning. A SLI or any type of silent stroke places an individual at greater risk for future major stroke.
Pathophysiology
 According to Koffler et al., lacunes are derived from an "occlusion of a single deep penetrating artery that arises directly from the constituents of the
According to Koffler et al., lacunes are derived from an "occlusion of a single deep penetrating artery that arises directly from the constituents of the circle of Willis
The circle of Willis (also called Willis' circle, loop of Willis, cerebral arterial circle, and Willis polygon) is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including huma ...
, cerebellar arteries, and basilar artery
The basilar artery (U.K.: ; U.S.: ) is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood.
The two vertebral arteries and the basilar artery are known as the vertebral basilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part o ...
". Other lesions that are associated with lacunes appear in the "deep nuclei of the brain (37% putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a subcortical nucleus (neuroanatomy), nucleus with a rounded structure, in the basal ganglia nuclear group. It is located at the base of the forebrain and above the midbrain.
The putamen and c ...
, 14% thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of ...
, and 10% caudate) as well as the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
(16%) or the posterior limb of the internal capsule
The internal capsule is a paired white matter structure, as a two-way nerve tract, tract, carrying afferent nerve fiber, ascending and efferent nerve fiber, descending axon, fibers, to and from the cerebral cortex. The internal capsule is situate ...
(10%)". These lesions are less common within other brain regions such as the cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, cerebral white matter and anterior limb of the internal capsule
The internal capsule is a paired white matter structure, as a two-way nerve tract, tract, carrying afferent nerve fiber, ascending and efferent nerve fiber, descending axon, fibers, to and from the cerebral cortex. The internal capsule is situate ...
.
The two proposed mechanisms are microatheroma and lipohyalinosis. At the beginning, lipohyalinosis was thought to be the main small vessel pathology, but microatheroma now is thought to be the most common mechanism of arterial occlusion (or stenosis
Stenosis () is the abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing ...
). Occasionally, atheroma
An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal accumulation of material in the tunica intima, inner layer of an arterial wall.
The material consists of mostly macrophage, macrophage cells, or debris, containing lipids, calcium and a variabl ...
in the parent artery blocks the orifice of the penetrating artery (luminal atheroma), or atheroma involves the origin of the penetrating artery (junctional atheroma). Alternatively, hypoperfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer to fixation via perfusion, used in ...
is believed to be the mechanism when there is stenosis of the penetrating artery. When no evidence of small vessel disease is found on histologic examination, an embolic cause is assumed, either artery-to-artery embolism
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule (fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas (air embolism, gas embolism), amniotic ...
or cardioembolism. In one recent series, 25% of patients with clinical radiologically defined lacunes had a potential cardiac cause for their strokes.
More recent advances have also suggested these mechanisms may play a combined role in the aetiology of lacunar infarction. The most current theory indicates endothelial dysfunction and increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier first allow leakage of blood contents, promoting gliosis and white matter hyper-intensities on magnetic resonance imaging. Moreover, focal narrowing of brain vessels and impairment of their ability to dilate in response to various stimuli may lead to a decreased cerebral blood flow and ultimately lacunar stroke.
Advanced age, chronic hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
and diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
are risk factors. It is unclear whether there is an association with alcohol consumption, elevated cholesterol, or history of prior stroke. Lacunar strokes may result from carotid artery Carotid artery may refer to:
* Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery
* External carotid artery, an artery on each side of ...
pathology or microemboli from the heart as in atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
. Patients often recover well, but if there is enough white matter disease from lacunar pathology, one can see a subcortical dementia such as Binswanger disease.
Treatment and prognosis
Typically,tissue plasminogen activator
Tissue-type plasminogen activator, short name tPA, is a protein that facilitates the breakdown of blood clots. It acts as an enzyme to convert plasminogen into its active form plasmin, the major enzyme responsible for clot breakdown. It is a s ...
may be administered within 3 to 4.5 hours of stroke onset if the patient is without contraindications (i.e. a bleeding diathesis
In medicine (hematology), bleeding diathesis is an unusual susceptibility to bleed (hemorrhage) mostly due to hypocoagulability (a condition of irregular and slow blood clotting), in turn caused by a coagulopathy (a defect in the system of coagul ...
such as recent major surgery or cancer with brain metastases). High dose aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
can be given within 48 hours. For long term prevention of recurrence, medical regimens are typically aimed towards correcting the underlying risk factors for lacunar infarcts such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus and cigarette smoking. Anticoagulants such as heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of myocardial infarction, ...
and warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others. It is used as an anticoagulant, anticoagulant medication. It is commonly used to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who ha ...
have shown no benefit over aspirin with regards to five-year survival.
Patients who have lacunar strokes have a greater chance of surviving beyond thirty days (96%) than those with other types of stroke (85%), and better survival beyond a year (87% versus 65-70%). Between 70% and 80% are functionally independent at 1 year, compared with fewer than 50% otherwise.
Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT), also known as ergotherapy, is a healthcare profession. Ergotherapy is derived from the Greek wiktionary:ergon, ergon which is allied to work, to act and to be active. Occupational therapy is based on the assumption t ...
and physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
interventions are used in the rehabilitation of lacunar stroke. A physiotherapy program will improve joint range of motion
Range of motion (or ROM) is the linear or angular distance that a moving object may normally travel while properly attached to another.
In biomechanics and strength training, ROM refers to the angular distance and direction a joint can move be ...
of the paretic limb using passive range of motion exercises. When increases in activity are tolerated, and stability improvements are made, patients will progress from rolling to side-lying, to standing (with progressions to prone, quadruped
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion in which animals have four legs that are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four legs is said to be a quadruped (fr ...
, bridging, long-sitting and kneeling for example) and learn to transfer safely (from their bed to a chair or from a wheel chair to a car for example). Assistance and ambulation aids are used as required as the patient begins walking and lessened as function increases. Furthermore, splints
Splints is an ailment of the horse or pony, characterized by a hard, bony swelling, usually on the inside of a front leg, lying between the splint and cannon bone or on the splint bone itself. It may be "hot," meaning that it occurred recently an ...
and braces can be used to support limbs and joints to prevent or treat complications such as contracture
In pathology, a contracture is a shortening of muscles, tendons, skin, and nearby soft tissues that causes the joints to shorten and become very stiff, preventing normal movement. A contracture is usually permanent, but less commonly can be temp ...
s and spasticity
Spasticity () is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles. ...
. The rehabilitation healthcare team should also educate the patient and their family on common stroke symptoms and how to manage an onset of stroke. Continuing follow-up with a physician is essential so that the physician may monitor medication dosage and risk factors.
Epidemiology
It is estimated that lacunar infarcts account for 25% of allischemic stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop ...
s, with an annual incidence of approximately 15 per 100,000 people. They may be more frequent in men and in people of African, Mexican, and Hong Kong Chinese descent.
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lacunar Stroke Types of stroke