Kyphotic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kyphosis () is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the
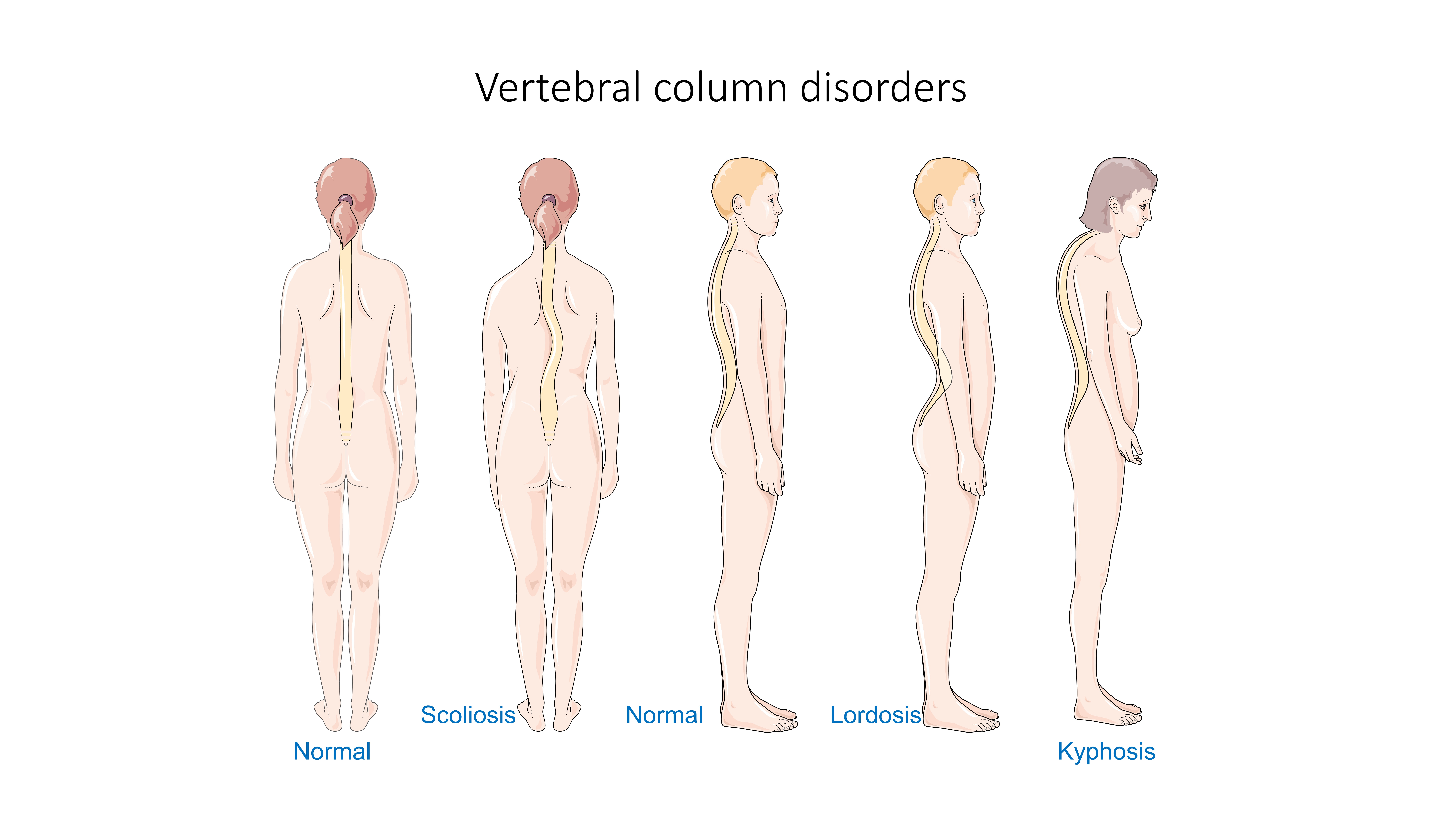
 Kyphosis can be graded in severity by the
Kyphosis can be graded in severity by the
Image:kyphosis brace1.jpg, Modern brace for the treatment of a thoracic kyphosis. The brace is constructed using a CAD/CAM device.
Image:kyphosis brace 3.jpg, Modern brace for the treatment of lumbar or thoracolumbar kyphosis. The brace is constructed using a CAD/CAM device. Restoration of the lumbar lordosis is the main aim.
Kypho
definition and other related medical terms {{Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system Deforming dorsopathies External signs of ageing
spine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Spinal column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoology), ...
as it occurs in the thoracic
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main ...
and sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the cervical and lumbar
In tetrapod anatomy, lumbar is an adjective that means of or pertaining to the abdominal segment of the torso, between the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm and the sacrum.
Naming and location
The lumbar region is sometimes referred to as the lowe ...
regions of the spine is called lordosis
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical vertebrae, cervical regio ...
.
It can result from degenerative disc disease
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition typically brought on by the aging process in which there are anatomic changes and possibly a loss of function of one or more intervertebral discs of the vertebral column, spine. DDD can take ...
; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease
Scheuermann's disease is a skeletal disorder. It describes a condition where the vertebrae grow unevenly with respect to the sagittal plane; that is, the posterior angle is often greater than the anterior. This uneven growth results in the sig ...
; Copenhagen disease
Copenhagen disease, sometimes known as Copenhagen syndrome or progressive non-infectious anterior vertebral fusion (PAVF), is a very rare childhood spinal disorder of unknown cause, with distinctive radiological features. It is characterized b ...
, osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
with compression fracture
A compression fracture is a collapse of a vertebra. It may be due to trauma or due to a weakening of the vertebra (compare with burst fracture). This weakening is seen in patients with osteoporosis or osteogenesis imperfecta, lytic lesions from ...
s of the vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
; multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibody, antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone ...
; or trauma.
A normal thoracic spine extends from the 1st thoracic to the 12th thoracic vertebra and should have a slight kyphotic angle, ranging from 20° to 45°. When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45° it is called kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis". Scheuermann's kyphosis is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial and is seen more frequently in males than females.
In the sense of a deformity, it is the pathological curving of the spine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Spinal column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoology), ...
, where parts of the spinal column lose some or all of their lordotic
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical regions of the human sp ...
profile. This causes a bowing of the back
The human back, also called the dorsum (: dorsa), is the large posterior area of the human body, rising from the top of the buttocks to the back of the neck. It is the surface of the body opposite from the chest and the abdomen. The vertebral c ...
, seen as a slouching posture. Kyphosis is distinguished from scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others ...
, a condition in which the spine has a sideways curve.
While most cases of kyphosis are mild and only require routine monitoring, serious cases can be debilitating. High degrees of kyphosis can cause severe pain and discomfort, breathing and digestion difficulties, cardiovascular
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart a ...
irregularities, neurological
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the s ...
compromise and, in the more severe cases, significantly shortened life spans. These types of high-end curves typically do not respond well to conservative treatment and almost always warrant spinal fusion
Spinal fusion, also called spondylodesis or spondylosyndesis, is a surgery performed by Orthopedic surgery#Practice, orthopaedic surgeons or neurosurgeons that joins two or more vertebrae. This procedure can be performed at any level in the spine ...
surgery, which can restore the body's natural degree of curvature.
Signs and symptoms

Complications
The risk of serious complications from spinal fusion surgery for kyphosis is estimated to be 5%, similar to the risks of surgery forscoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others ...
. Possible complications include inflammation of the soft tissue or deep inflammatory processes, breathing impairments, bleeding, and nerve injuries. According to the latest evidence, the actual rate of complications may be substantially higher. Even among those who do not develop serious complications, 5% of patients require reoperation within five years of the procedure, and in general it is not yet clear what one would expect from spine surgery during the long-term. Given that the signs and symptoms of spinal deformity cannot be changed by surgical intervention, surgery remains essentially a cosmetic choice. However, the cosmetic effects of surgery are not necessarily stable.
Diagnosis
Classification
There are several kinds of kyphosis (ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social cir ...
codes are provided):
* Postural kyphosis (M40.0), the most common type, normally attributed to slouching, can occur in both the old and the young. In the young, it can be called "slouching" and is reversible by correcting muscular imbalances. In the old, it may be a case of hyperkyphosis and called "dowager's hump". About one third of the most severe hyperkyphosis cases in older people have vertebral fractures. Otherwise, the aging body does tend towards a loss of musculoskeletal integrity, and hyperkyphosis can develop due to aging alone.
* Scheuermann's kyphosis
Scheuermann's disease is a skeletal disorder. It describes a condition where the vertebrae grow unevenly with respect to the sagittal plane; that is, the posterior angle is often greater than the anterior. This uneven growth results in the sig ...
(M42.0) is significantly worse cosmetically and can cause varying degrees of pain, and can also affect different areas of the spine (the most common being the midthoracic area). Scheuermann's kyphosis is considered a form of juvenile osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a family of orthopedic diseases of the joint that occur in children, adolescents and rapidly growing animals, particularly pigs, horses, dogs, and broiler chickens. They are characterized by interruption of the blood supply of ...
of the spine and is more commonly called Scheuermann's disease. It is found mostly in teenagers and presents a significantly worse deformity than postural kyphosis. A patient with Scheuermann's kyphosis cannot consciously correct posture. The apex of the curve, located in the thoracic vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
, is quite rigid. The patient may feel pain at this apex, which can be aggravated by physical activity and by long periods of standing or sitting. This can have a significantly detrimental effect on their lives, as their level of activity is curbed by their condition; they may feel isolated or uneasy amongst peers if they are children, depending on the level of deformity. Whereas in postural kyphosis, the vertebrae and discs appear normal, in Scheuermann's kyphosis, they are irregular, often herniated, and wedge-shaped over at least three adjacent levels. Fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
is a very common symptom, most likely because of the intense muscle work that has to be put into standing or sitting properly. The condition appears to run in families. Most patients who undergo surgery to correct their kyphosis have Scheuermann's disease.
* Congenital kyphosis (Q76.4) can result in infants whose spinal column has not developed correctly in the womb. Vertebrae may be malformed or fused together and can cause further progressive kyphosis as the child develops. Surgical treatment may be necessary at a very early stage and can help maintain a normal curve in coordination with consistent follow-ups to monitor changes. However, the decision to carry out the procedure can be very difficult due to the potential risks to the child. A congenital kyphosis can also suddenly appear in the teenage years, more commonly in children with cerebral palsy and other neurological disorders.
* Nutritional kyphosis can result from nutritional deficiencies
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a Deficiency (medicine), deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and Vitamin deficiency, other nutrients whic ...
, especially during childhood, such as vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D def ...
(producing rickets
Rickets, scientific nomenclature: rachitis (from Greek , meaning 'in or of the spine'), is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children and may have either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stun ...
), which softens bones and results in the curving of the spine and limbs under the child's body weight.
* Gibbus deformity
Gibbus deformity is a form of structural kyphosis typically found in the upper lumbar and lower thoracic vertebrae, where one or more adjacent vertebrae become wedged. Gibbus deformity most often develops in young children as a result of spinal tu ...
is a form of structural kyphosis, often a ''sequela'' to tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
.
* Post-traumatic kyphosis (M84.0) can arise from untreated or ineffectively treated vertebral fractures.
Grading
 Kyphosis can be graded in severity by the
Kyphosis can be graded in severity by the Cobb angle
Cobb may refer to:
People
* Cobb (surname), a list of people and fictional characters with the surname Cobb
* Cobb Rooney (1900–1973), American professional football running back
Places New Zealand
* Cobb River
* Cobb Reservoir
* Cobb Powe ...
. Also, ''sagittal balance'' can be measured. The sagittal balance is the horizontal distance between the center of C7 and the superior-posterior border of the endplate
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
of S1 on a lateral radiograph.
Treatments
A diagnosis of kyphosis is generally made through observation and measurement. Idiopathic causes, such as vertebral wedging or other abnormalities, can be confirmed through X-ray. Osteoporosis, a potential cause of kyphosis, can be confirmed with abone density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although medicine#Clinical practice, clinically it is measured by ...
scan. Postural thoracic kyphosis can often be treated with posture reeducation and focused strengthening exercises. Idiopathic thoracic kyphosis due to vertebral wedging, fractures, or vertebral abnormalities is more difficult to manage, since assuming a correct posture may not be possible with structural changes in the vertebrae. Children who have not completed their growth may show long-lasting improvements with bracing. Exercises may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort associated with overstretched back muscles. A variety of gravity-assisted positions or gentle traction can minimize pain associated with nerve root A nerve root () is the initial segment of a nerve leaving the central nervous system. Nerve roots can be classified as:
* Cranial nerve roots: the initial or proximal segment of one of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves leaving the central nervous s ...
impingement. Surgery may be recommended for severe idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin.
For some medical conditions, one or more causes are somewhat understood, but in a certain percentage of people with the condition, the cause ...
kyphosis.
Brace
Body brace
A back brace is a device designed to limit the motion of the spine in cases of bone fracture or in post-operative spinal fusiona, as well as a preventative measure against some progressive conditions or to correct a patient's posture.
Common bac ...
s showed benefit in a randomised controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical t ...
.
The Milwaukee brace
The Milwaukee brace, also known as a cervico-thoraco-lumbo-sacral orthosis or CTLSO, is a back brace most often used in the treatment of spinal curvatures (such as scoliosis or kyphosis) in children but also, more rarely, in adults to prevent coll ...
is one particular body brace that is often used to treat kyphosis in the US. Modern CAD/CAM
CAD/CAM refers to the integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM). Both of these require powerful computers. ''CAD'' software helps designers and draftsmen; ''CAM'' "reduces manpower costs" in the manufacturi ...
braces are used in Europe to treat different types of kyphosis. These are much easier to wear and have better in-brace corrections than reported for the Milwaukee brace. Since there are different curve patterns (thoracic
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main ...
, thoracolumbar
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
, and lumbar
In tetrapod anatomy, lumbar is an adjective that means of or pertaining to the abdominal segment of the torso, between the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm and the sacrum.
Naming and location
The lumbar region is sometimes referred to as the lowe ...
), different types of brace are in use, with different advantages and disadvantages.
Physical therapy
In Germany, a standard treatment for both Scheuermann's disease and lumbar kyphosis is the Schroth method, a system of physical therapy for scoliosis and related spinal deformities. It involves lying supine, placing a pillow under the scapular region and posteriorly stretching the cervical spine. In China, many people use spinal care mattresses to correct kyphosis while sleeping.Surgery
Surgical treatment can be used in severe cases. In patients with progressive kyphotic deformity due to vertebral collapse, a procedure called akyphoplasty
Vertebral augmentation, including vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, refers to similar percutaneous spinal procedures in which bone cement is injected through a small hole in the skin into a fractured vertebra in order to relieve back pain caused ...
may arrest the deformity and relieve the pain. Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure, requiring only a small opening in the skin. The main goal is to return the damaged vertebra as close as possible to its original height.
Society and culture
People affected by condition
*Şehzade Cihangir
Şehzade Cihangir (; 1531 – 27 November 1553) was an Ottoman prince, the sixth and youngest child of Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent and his wife Roxelana, Hürrem Sultan.
Life
Cihangir was born in 1531 in Constantinople during the reign of h ...
* Nicolas Ferry
* Godfrey IV, Duke of Lower Lorraine
Godfrey IV (died 26 or 27 February 1076), known as the Hunchback, was Duke of Lower Lorraine from 1069 until his death in 1076, succeeding his father Godfrey the Bearded.
In the year of his accession, he married Margravine Matilda of Tuscany, da ...
* Topper Headon
Nicholas Bowen "Topper" Headon (born 30 May 1955) is an English drummer and multi-instrumentalist, best known as the drummer of punk rock band the Clash. Headon was inducted in the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame with the rest of the Clash in 2003.
...
* Inge the Hunchback
Inge Haraldsson (; 1135 – 3 February 1161) was king of Norway (being Inge I) from 1136 to 1161. Inge’s reign fell within the start of the period known in Norwegian history as the civil war era, and he was never the sole ruler of the country. ...
* Konrad II the Hunchback
Konrad II the Hunchback () (1252/65 – 11 October 1304) was Duke of Ścinawa from 1278 to 1284, patriarch of Aquileia in 1299, and Duke of Żagań from 1284 until his death.
Biography
He was the second son of Konrad I, Duke of Głogów by his fi ...
* Benjamin Lay
Benjamin Lay (January 26, 1682 – February 8, 1759) was an English-born writer, farmer and activist. Born in Copford, Essex into a Quakers, Quaker family, he underwent an apprenticeship as a glovemaker before running away to London and finding ...
* Georg Christoph Lichtenberg
Georg Christoph Lichtenberg (; 1 July 1742 – 24 February 1799) was a German physicist, satirist, and Anglophile. He was the first person in Germany to hold a professorship explicitly dedicated to experimental physics. He is remembered for his p ...
* Louis the Hunchback
* Mahmud I
Mahmud I (, ; 2 August 1696 13 December 1754), known as Mahmud the Hunchback, was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1730 to 1754. He took over the throne after the quelling of the Patrona Halil rebellion. His reign was marked by wars in P ...
* Margaret of Bavaria (1442–1479)
* Pepin the Hunchback
Pepin (or Pippin) the Hunchback (, ; 768/769 – 811) was a Franks, Frankish prince. He was the eldest son of Charlemagne and noblewoman Himiltrude. He developed a kyphosis, humped back after birth, leading early medieval historians to give him ...
* Charles Proteus Steinmetz
Charles Proteus Steinmetz (born Karl August Rudolph Steinmetz; April 9, 1865 – October 26, 1923) was a Prussian mathematician and electrical engineer and professor at Union College. He fostered the development of alternating current that made ...
* Władysław the Hunchback
Władysław the Hunchback (; – 5 June 1351 or April 1352), was a Polish people, Polish prince, member of the House of Piast. He was Duke of Dobrzyń nad Wisłą, Dobrzyń during 1312-1327 (until 1316 under the regency of his mother and uncle) an ...
Popular culture
One of the most well-known and enduring depictions of kyphosis isQuasimodo
Quasimodo (from Quasimodo Sunday) is the titular protagonist of the French novel '' The Hunchback of Notre-Dame'' (1831) by Victor Hugo. Born with numerous deformities, most notably a hunched back, Quasimodo serves as the bell-ringer for Notre ...
, the eponymous hero of Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo, vicomte Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romanticism, Romantic author, poet, essayist, playwright, journalist, human rights activist and politician.
His most famous works are the novels ''The Hunchbac ...
's 1831 novel ''The Hunchback of Notre-Dame
''The Hunchback of Notre-Dame'' (, originally titled ''Notre-Dame de Paris. 1482'') is a French Gothic novel by Victor Hugo, published in 1831. The title refers to the Notre-Dame Cathedral, which features prominently throughout the novel. I ...
'', which solidified the popular conception of the hunchback as a destitute and pitiable outcast from European society. The legendary Comprachicos
Comprachicos are groups in European folklore who were said to physically cripple and deform children to work as beggars or living curiosities. The most common methods said to be used in this practice included stunting children's growth by physica ...
of the sort popularized in Hugo's similar work ''The Man Who Laughs
''The Man Who Laughs'' (also published under the title ''By Order of the King'' from its subtitle in French) is a Gothic novel by Victor Hugo, originally published in April 1869 under the French title ''L'Homme qui rit''. It takes place in Engl ...
'' are instead described as being able to turn able-bodied young children into hunchbacks, alongside a variety of other deformities, using poisons and mutilation, before selling their results into bondage as court dwarf
Several dwarfism, dwarfs over the course of history were employed as court dwarfs. They were History of slavery, owned and traded amongst Courtier, people of the court, and delivered as gifts to fellow kings and queens. Visual effect
Court dwarfs ...
s or freak show
A freak show is an exhibition of biological rarities, referred to in popular culture as "Freak, freaks of nature". Typical features would be physically unusual Human#Anatomy and physiology, humans, such as those uncommonly large or small, t ...
performers.
Early horror film
Horror is a film genre that seeks to elicit physical or psychological fear in its viewers. Horror films often explore dark subject matter and may deal with Transgressive art, transgressive topics or themes. Broad elements of the genre include Mo ...
s developed the hunchbacked Igor as a stock character
A stock character, also known as a character archetype, is a type of character in a narrative (e.g. a novel, play, television show, or film) whom audiences recognize across many narratives or as part of a storytelling tradition or convention. Th ...
assistant to a mad scientist
The mad scientist (also mad doctor or mad professor) is a stock character of a scientist who is perceived as "mad, bad and dangerous to know" or "insanity, insane" owing to a combination of unusual or unsettling personality traits and the unabas ...
.
See also
* Bethlem myopathy 2 *Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
* Copenhagen disease
Copenhagen disease, sometimes known as Copenhagen syndrome or progressive non-infectious anterior vertebral fusion (PAVF), is a very rare childhood spinal disorder of unknown cause, with distinctive radiological features. It is characterized b ...
* Loeys–Dietz syndrome
Loeys–Dietz syndrome (LDS) is an autosomal dominant genetic connective tissue disorder. It has features similar to Marfan syndrome and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. The disorder is marked by aneurysms in the aorta, often in children, and the aorta m ...
* Pott disease
Pott's disease, or Pott disease, named for British surgeon Percivall Pott who first described the symptoms in 1799, is tuberculosis of the vertebral column, spine, usually due to haematogenous spread from other sites, often the lungs. The lowe ...
References
External links
Kypho
definition and other related medical terms {{Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system Deforming dorsopathies External signs of ageing