Kharkiv model V-2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

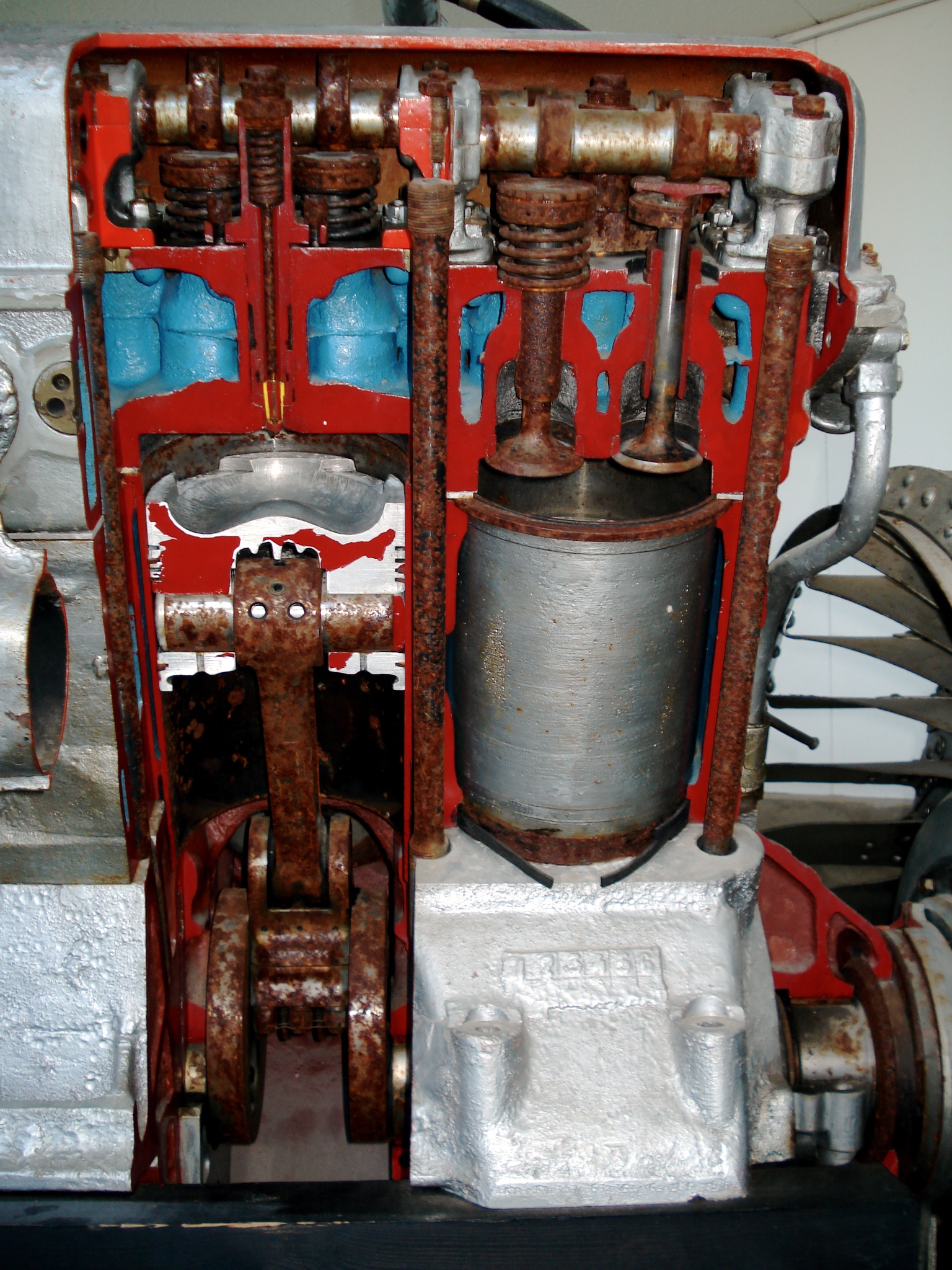 The Kharkiv model V-2 () is a
The Kharkiv model V-2 () is a
File:V-2 engine in the Kubinka Museum.jpg, V-2
File:Tank motor.jpg, V-54
File:W-2-55 Tank Engine (36980563961).jpg, V-55
File:Russian tank engine (38185188421).jpg, V-46
File:T-90 engine.jpg, V-92

 The Kharkiv model V-2 () is a
The Kharkiv model V-2 () is a Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and Russian family of diesel tank V-12 engines, the V angle at 60°, with dual overhead camshafts per bank, four valves per cylinder opened by bucket-style followers and direct fuel injection. Designed at the Kharkiv Locomotive Factory by Konstantin Chelpan and his team, it is found in the BT-7M (BT-8), T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank from World War II. When introduced, its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was more powerful than many of its contemporaries, and its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against Anti-tank warfare, ...
, KV, IS and IS-10 (T-10) tanks, and by extension, the vehicles based on them, such as the SU-85 and SU-100
The SU-100 ( Russian: самоходная установка-100, СУ-100 romanized: '' Samokhodnaya Ustanovka-''100) is a Soviet tank destroyer armed with the D-10S 100 mm anti-tank gun in a casemate superstructure. It was used extens ...
tank destroyers based on the T-34 and the ISU-122 and ISU-152 self-propelled guns based on the IS-2. Throughout its production life, output ranged from roughly .
Successive variants of the V-2 have been used in multiple Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
and Russian vehicles ever since. Heavily modernised derivatives of the V-2 remain in production, with the T-90A tank, Koalitsiya-SV self-propelled gun and BMPT Terminator armoured support vehicle equipped with a 1,000 hp V92S2, while the latest T-72B3 and T-90M tanks feature an upgraded 1,130 hp V-92S2F. Licensed production additionally continues in several countries.
History of development and production
The V-2 was in development from 1931 until1939
This year also marks the start of the World War II, Second World War, the largest and deadliest conflict in human history.
Events
Events related to World War II have a "WWII" prefix.
January
* January 1
** Coming into effect in Nazi Ger ...
by the design team of the diesel department of the Kharkiv Locomotive Works, first under the leadership of Konstantin Chelpan, who was arrested in 1938. Work was passed down to his deputy for project work, Yakov Efimovich Vikhman, and Ivan Yakovlevich Trashutin, his deputy for experimental and production work, who completed development of the engine in 1939.
Serial production for the V-2 begun on September 1, 1939. The Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
adopted the V-2 engine in the same year in three modifications: the V-2 (), the V-2K () for the KV line of tanks and the V-2V ().
Near the end of the 20th century, the V-2 was fitted with more modern modifications by the chief designer of the head design bureau for the Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant, Vladimir Ivanovich Butov.
Description
The engine was made of aluminium with a closed water-cooling system. It included a water jacket of the cylinder blocks, radiators, a water pump, a centrifugal fan, a T-valve with steam and air valves, and piping. The cooling system capacity was 90–95 liters. The radiators were connected to the surrounding air via an air valve. The T-valve, leading to both radiators, was designed for filling the cooling system with coolant.Variants
* V-2: Initial production version, 1937. Used in the BT-7M (BT-8). * V-2-34: V-2 with revised hull mounts, fuel and cooling connectors and refined clutch, 1939. Used in theT-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank from World War II. When introduced, its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was more powerful than many of its contemporaries, and its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against Anti-tank warfare, ...
, SU-85 and SU-100
The SU-100 ( Russian: самоходная установка-100, СУ-100 romanized: '' Samokhodnaya Ustanovka-''100) is a Soviet tank destroyer armed with the D-10S 100 mm anti-tank gun in a casemate superstructure. It was used extens ...
, it produced @ 1,800 rpm. The following units were attached to the engine: fuel feed pump; fuel filter; fuel pump NK-1; high-pressure fuel line; oil pump; oil filter; water pump, and alternator. The starting of the engine could be carried out using the electric starter ST-700 (the main method), or compressed air
Compressed air is air kept under a pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure. Compressed air in vehicle tires and shock absorbers are commonly used for improved traction and reduced vibration. Compressed air is an important medium for t ...
(the alternate method) using the two air cylinders located in the driver’s compartment.
* V-2K: V-2 with increased injection pressure and higher engine speed, 1939. Used in the KV-1 and KV-2, it produced at 2,000 rpm.
* V-2V: V-2 detuned for use in lighter vehicles, 1940. Used in the Voroshilovets artillery tractor, it produced .
* V-2L/P: V-2 modified for boats, not built.
* V-2SN (Нагнетатель системы, ''supercharger systems''): V-2 with a supercharger from the Mikulin AM-38 aircraft engine, 1940. Used in the KV-3, it produced .
* V-2-10 (V-2IS): V-2 with stronger cylinders and heads, improved fuel pump, larger radiator and oil cooler and modified hull mounts, 1943. Used in the IS-1, IS-2, ISU-122 and ISU-152, it produced .
* V-2-450AV-S3: V-2 modified for oil drilling equipment, it produced .
* V-4: Essentially a V-2 engine cut in half to form an inline six engine. Used in the T-50 light tank, it produced .
* V-11: Used in the IS-3; It produced . Developed into the V-44, used in the T-44.
* V-12: Used in the IS-4. Fitted with a supercharger, it produced . Produced in small numbers due to its extreme unreliability.
* V-12-5: Improved V-12, used in the T-10, it produced .
* V12-6: Used in the Object 268, it produced .
* V-46: Used in the T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet Union, Soviet main battle tanks that entered production in 1973. The T-72 was a development based on the T-64 using thought and design of the previous Object 167M. About 25,000 T-72 tanks have been built, and refu ...
, T-72M, T-62M-1 and the 2K22 Tunguska. It produced ; the Tunguska used a version.
* V-54: Used in the T-54, it produced .
* V-55: Used in the T-55, it produced .
* V-55V: Used in the T-62, it produced 580 (later 620) hp.
* V-84: Used in the T-72A, T-72B, 2S19 Msta-S and the T-90. It produced ; the Msta-S used a version.
* V-92: Used in the T-90A, 2S35 Koalitsiya-SV and T-90M.
* V-401: Detuned version of the V-54 for the AT-T artillery tractor, it produced .
Manufacturers
Before the 2nd World War, it was produced only at Engine Plant No. 75 (a branch of the Kharkov Locomotive Plant), the contractors were KhTZ, Chelyabinsk and Kirov (Leningrad) plants. After the start of the war, it was produced at the Stalingrad Tractor Plant and in Sverdlovsk at Plant No. 76. In October 1941, Plant No. 75 was evacuated to Chelyabinsk to the ChTZ site. The Kirov plant also moved there. All of them were united into a huge Tankograd. This plant became the main manufacturer of the V-2 during the war (about 50 thousand engines, including engines produced in Kharkov). Later, in 1942, production of the V-2 was also mastered at plant No. 77 in Barnaul. As of 2022, production of modifications of the V-2 engine continues at the Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant, Barnaultransmash and the Ural Diesel Engine Plant.Gallery
See also
* Maybach HL230, equivalent contemporary German tank engine * Rolls-Royce Meteor, equivalent contemporary British tank engine * Ford_GAA_engine, equivalent contemporary US tank engine * Wright_R-975_Whirlwind, another contemporary US tank engineReferences
Notes
Sources
* Diesel engines by model World War II military equipment of the Soviet Union Tank engines Malyshev Factory products {{USSR-stub