key col on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
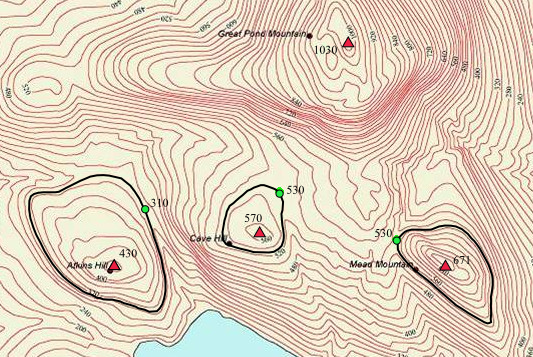 The parent peak may be either close or far from the subject peak. The summit of
The parent peak may be either close or far from the subject peak. The summit of
 This means that, while simple to define, the encirclement parent often does not satisfy the intuitive requirement that the parent peak should be close to the child peak. For example, one common use of the concept of parent is to make clear the location of a peak. If we say that Peak A has Mont Blanc for a parent, we would expect to find Peak A somewhere close to Mont Blanc. This is not always the case for the various concepts of parent, and is least likely to be the case for encirclement parentage.
Figure 3 shows a schematic range of peaks with the color underlying the minor peaks indicating the encirclement parent. In this case the encirclement parent of M is H whereas an intuitive view might be that L was the parent. Indeed, if col "k" were slightly lower, L would be the true encirclement parent.
The encirclement parent is the highest possible parent for a peak; all other definitions indicate a (possibly different) peak on the combined island, a "closer" peak than the encirclement parent (if there is one), which is still "better" than the peak in question. The differences lie in what criteria are used to define "closer" and "better."
This means that, while simple to define, the encirclement parent often does not satisfy the intuitive requirement that the parent peak should be close to the child peak. For example, one common use of the concept of parent is to make clear the location of a peak. If we say that Peak A has Mont Blanc for a parent, we would expect to find Peak A somewhere close to Mont Blanc. This is not always the case for the various concepts of parent, and is least likely to be the case for encirclement parentage.
Figure 3 shows a schematic range of peaks with the color underlying the minor peaks indicating the encirclement parent. In this case the encirclement parent of M is H whereas an intuitive view might be that L was the parent. Indeed, if col "k" were slightly lower, L would be the true encirclement parent.
The encirclement parent is the highest possible parent for a peak; all other definitions indicate a (possibly different) peak on the combined island, a "closer" peak than the encirclement parent (if there is one), which is still "better" than the peak in question. The differences lie in what criteria are used to define "closer" and "better."
 The key col and parent peak are often close to the sub-peak but this is not always the case, especially when the key col is relatively low. It is only with the advent of computer programs and geographical databases that thorough analysis has become possible.
For example, the key col of
The key col and parent peak are often close to the sub-peak but this is not always the case, especially when the key col is relatively low. It is only with the advent of computer programs and geographical databases that thorough analysis has become possible.
For example, the key col of
topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
, prominence or relative height (also referred to as autonomous height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, isoquant or isarithm) of a Function of several real variables, function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a ...
encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous.
The term (mountain top) is generally used only for ...
. The key col ("saddle") around the peak is a unique point on this contour line and the ''parent peak'' (if any) is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria.
Definitions
The prominence of a peak is the least drop in height necessary in order to get from the summit to any higher terrain. This can be calculated for a given peak in the following manner: for every path connecting the peak to higher terrain, find the lowest point on the path; the ''key col'' (or ''highestsaddle
A saddle is a supportive structure for a rider of an animal, fastened to an animal's back by a girth. The most common type is equestrian. However, specialized saddles have been created for oxen, camels and other animals.
It is not know ...
'', or ''linking col'', or ''link'') is defined as the highest of these points, along all connecting paths; the prominence is the difference between the elevation of the peak and the elevation of its key col. On a given landmass, the highest peak's prominence will be identical to its elevation. An alternative equivalent definition is that the prominence is the height of the peak's summit above the lowest contour line
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, isoquant or isarithm) of a Function of several real variables, function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a ...
encircling it, but containing no higher summit within it; see Figure 1.
Illustration
 The parent peak may be either close or far from the subject peak. The summit of
The parent peak may be either close or far from the subject peak. The summit of Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
is the parent peak of Aconcagua
Aconcagua () is a mountain in the Principal Cordillera of the Andes mountain range, in Mendoza Province, Argentina. It is the highest mountain in the Americas, the highest outside Asia, and the highest in both the Western Hemisphere and the ...
in Argentina at a distance of 17,755 km (11,032 miles), as well as the parent of the South Summit of Mount Everest at a distance of 360 m (1200 feet). The key col may also be close to the subject peak or far from it. The key col for Aconcagua, if sea level is disregarded, is the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
at a distance of 13,655 km (8,485 miles). The key col for the South Summit of Mount Everest is about 100 m (330 feet) distant.
A way to visualize prominence is to imagine raising sea level so the parent peak and subject peak are two separate islands. Then lower it until a tiny land bridge forms between the two islands. This land bridge is the key col of the subject peak, and the peak's prominence is its elevation from that key col.
One can also refer to it as the tallest possible path between the two peaks, where the key col is the lowest point on that path.
In mountaineering
Prominence is interesting to manymountaineers
Mountaineering, mountain climbing, or alpinism is a set of outdoor activities that involves ascending mountains. Mountaineering-related activities include traditional outdoor climbing, skiing, and traversing via ferratas that have become sports ...
because it is an objective measurement that is strongly correlated with the subjective significance of a summit. Peaks with low prominence are either subsidiary tops of some higher summit or relatively insignificant independent summits. Peaks with high prominence tend to be the highest points around and are likely to have extraordinary views.
Only summits with a sufficient degree of prominence are regarded as independent mountains. For example, the world's second-highest mountain is K2 (height 8,611 m, prominence 4,017 m). While Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
's South Summit (height 8,749 m, prominence 11 m) is taller than K2, it is not considered an independent mountain because it is a sub-summit of the main summit (which has a height and prominence of 8,849 m).
Many lists of mountains
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
use topographic prominence as a criterion for inclusion in the list, or ''cutoff''. John and Anne Nuttall's ''The Mountains of England and Wales'' uses a cutoff of 15 m (about 50 ft), and Alan Dawson's list of Marilyns uses 150 m (about 500 ft). (Dawson's list and the term "Marilyn" are limited to Britain and Ireland). In the contiguous United States, the famous list of "fourteener
In the mountaineering parlance of the Western United States, a fourteener (also spelled 14er) is a mountain peak with an elevation of at least . The 96 fourteeners in the United States are all west of the Mississippi River. Colorado
Co ...
s" (14,000 foot / 4268 m peaks) uses a cutoff of 300 ft / 91 m (with some exceptions). Also in the U.S., 2000 ft (610 m) of prominence has become an informal threshold that signifies that a peak has major stature.
Lists with a high topographic prominence cutoff tend to favor isolated peaks or those that are the highest point of their massif
A massif () is a principal mountain mass, such as a compact portion of a mountain range, containing one or more summits (e.g. France's Massif Central). In mountaineering literature, ''massif'' is frequently used to denote the main mass of an ...
; a low value, such as the Nuttalls', results in a list with many summits that may be viewed by some as insignificant.
While the use of prominence as a cutoff to form a list of peaks ranked by elevation is standard and is the most common use of the concept, it is also possible to use prominence as a mountain measure in itself. This generates lists of peaks ranked by prominence, which are qualitatively different from lists ranked by elevation. Such lists tend to emphasize isolated high peaks, such as range or island high points and stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a typically conical volcano built up by many alternating layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with ...
es. One advantage of a prominence-ranked list is that it needs no cutoff since a peak with high prominence is automatically an independent peak.
Parent peak
It is common to define a peak's ''parent'' as a particular peak in the higher terrain connected to the peak by the key col. If there are many higher peaks there are various ways of defining which one is the parent, not necessarily based on geological or geomorphological factors. The "parent" relationship defines a hierarchy which defines some peaks as subpeaks of others. For example, in Figure 1, the middle peak is a subpeak of the right peak, which is a subpeak of the left peak, which is the highest point on its landmass. In that example, there is no controversy about the hierarchy; in practice, there are different definitions of parent. These different definitions follow.Encirclement or island parentage
Also known as ''prominence island parentage'', this is defined as follows. In Figure 2 the key col of peak A is at the meeting place of two closed contours, one encircling A (and no higher peaks) and the other containing at least one higher peak. The encirclement parent of A is the highest peak that is inside this other contour. In terms of the falling-sea model, the two contours together bound an "island", with two pieces connected by an isthmus at the key col. The encirclement parent is the highest point on this entire island. For example, the encirclement parent ofMont Blanc
Mont Blanc (, ) is a mountain in the Alps, rising above sea level, located right at the Franco-Italian border. It is the highest mountain in Europe outside the Caucasus Mountains, the second-most prominent mountain in Europe (after Mount E ...
, the highest peak in the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
, is Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
. Mont Blanc's key col is a piece of low ground near Lake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego; , ; ; Livvi-Karelian language, Livvi: ''Oniegujärvi''; ) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic ...
in northwestern Russia (at elevation), on the divide between lands draining into the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
and Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
s. This is the meeting place of two contours, one of them encircling Mont Blanc; the other contour encircles Mount Everest. This example demonstrates that the encirclement parent can be very far away from the peak in question when the key col is low.
Prominence parentage
The (prominence) parent peak of peak A can be found by dividing the island or region in question into territories, by tracing the two hydrographic runoffs, one in each direction, downwards from the key col of every peak that is more prominent than peak A. The parent is the peak whose territory peak A is in. For hills with low prominence in Britain, a definition of "parent Marilyn" is sometimes used to classify low hills ("Marilyn" being a British term for a hill with a prominence of at least 150 m). This is found by dividing the region of Britain in question into territories, ''one for each Marilyn''. The parent Marilyn is the Marilyn whose territory the hill's summit is in. If the hill is on an island (in Britain) whose highest point is less than 150 m, it has no parent Marilyn. Prominence parentage is the only definition used in theBritish Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
because encirclement parentage breaks down when the key col approaches sea level. Using the encirclement definition, the parent of almost any small hill in a low-lying coastal area would be Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis ( ; , ) is the highest mountain in Scotland, the United Kingdom, and the British Isles. Ben Nevis stands at the western end of the Grampian Mountains in the Highland region of Lochaber, close to the town of Fort William.
The mount ...
, an unhelpful and confusing outcome. Meanwhile, "height" parentage (see below) is not used because there is no obvious choice of cutoff.
This choice of method might at first seem arbitrary, but it provides every hill with a clear and unambiguous parent peak that is taller and more prominent than the hill itself, while also being connected to it (via ridge lines). The parent of a low hill will also usually be nearby; this becomes less likely as the hill's height and prominence increase. Using prominence parentage, one may produce a "hierarchy" of peaks going back to the highest point on the island. One such chain in Britain would read:
Billinge Hill
Billinge Hill is in the Metropolitan Borough of St Helens in North West England. With a maximum elevation of , it is the highest point of Merseyside. It lies in Billinge, within the historic county boundaries of Lancashire, and it is one of t ...
→ Winter Hill → Hail Storm Hill
Hail Storm Hill, also known as Cowpe Moss, is the highest point of the Rossendale Valley, England, an area of moorland and hill country situated between the West Pennine Moors and the South Pennines. It is wholly within Lancashire, although the ...
→ Boulsworth Hill → Kinder Scout
Kinder Scout is a moorland plateau and National nature reserve (United Kingdom), National Nature Reserve in the Dark Peak of the Derbyshire Peak District in England. Part of the moor, at above sea level, is the highest point in the Peak Distric ...
→ Cross Fell → Helvellyn
Helvellyn (; possible #Names, meaning: ''pale yellow moorland'') is a mountain in the English Lake District, the highest point of the Helvellyn range, a north–south line of mountains to the north of Ambleside, between the lakes of Thirlmere a ...
→ Scafell Pike → Snowdon
Snowdon (), or (), is a mountain in Snowdonia in North Wales. It has an elevation of above sea level, which makes it both the highest mountain in Wales and the highest in the British Isles south of the Scottish Highlands. Snowdon i ...
→ Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis ( ; , ) is the highest mountain in Scotland, the United Kingdom, and the British Isles. Ben Nevis stands at the western end of the Grampian Mountains in the Highland region of Lochaber, close to the town of Fort William.
The mount ...
.
At each stage in the chain, both height and prominence increase.
Line parentage
Line parentage, also called height parentage, is similar to prominence parentage, but it requires a prominence cutoff criterion. The height parent is the closest peak to peak A (along all ridges connected to A) that has a greater height than A, and satisfies some prominence criteria. The disadvantage of this concept is that it goes against the intuition that a parent peak should always be more significant than its child. However it can be used to build an entire lineage for a peak which contains a great deal of information about the peak's position. In general, the analysis of parents and lineages is intimately linked to studying thetopology
Topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a Mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformat ...
of watersheds.
Issues in choice of summit and key col
Alteration of the landscape by humans and presence of water features can give rise to issues in the choice of location and height of a summit or col. In Britain, extensive discussion has resulted in a protocol that has been adopted by the main sources of prominence data in Britain and Ireland. Other sources of data commonly ignore human-made alterations, but this convention is not universally agreed upon; for example, some authors discount modern structures but allow ancient ones. Another disagreement concernsmountaintop removal
Mountaintop removal mining (MTR), also known as mountaintop mining (MTM), is a form of surface mining at the summit or summit ridge of a mountain. Coal seams are extracted from a mountain by removing the land, or overburden, above the seams. T ...
, though for high-prominence peaks (and for low-prominence subpeaks with intact summits), the difference in prominence values for the two conventions is typically relatively small.
Examples
Denali
Denali (), federally designated as Mount McKinley, is the highest mountain peak in North America, with a summit elevation of above sea level. It is the tallest mountain in the world from base to peak on land, measuring . On p. 20 of Helm ...
in Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
(6,194 m) is a 56 m col near Lake Nicaragua
Lake Nicaragua or Cocibolca or Granada (, , or ) is a freshwater lake in Nicaragua. Of tectonic origin and with an area of , it is the largest fresh water lake in Central America, the List of lakes by area, 19th largest lake in the world (by are ...
. Denali's encirclement parent is Aconcagua
Aconcagua () is a mountain in the Principal Cordillera of the Andes mountain range, in Mendoza Province, Argentina. It is the highest mountain in the Americas, the highest outside Asia, and the highest in both the Western Hemisphere and the ...
(6,960 m), in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, and its prominence is 6,138 m. (To further illustrate the rising-sea model of prominence, if sea level rose 56 m, North and South America would be separate continents and Denali would be 6138 m, its current prominence, above sea level. At a slightly lower level, the continents would still be connected and the high point of the combined landmass would be Aconcagua, the encirclement parent.)
While it is natural for Aconcagua to be the parent of Denali, since Denali is a major peak, consider the following situation: Peak A is a small hill on the coast of Alaska, with elevation 100 m and key col 50 m. Then the encirclement parent of Peak A is also Aconcagua, even though there will be many peaks closer to Peak A which are much higher and more prominent than Peak A (for example, Denali). This illustrates the disadvantage in using the encirclement parent.
A hill in a low-lying area like the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
will often be a direct child of Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
, with its prominence about the same as its height and its key col placed at or near the foot of the hill, well below, for instance, the 113-meter-high key col of Mont Blanc
Mont Blanc (, ) is a mountain in the Alps, rising above sea level, located right at the Franco-Italian border. It is the highest mountain in Europe outside the Caucasus Mountains, the second-most prominent mountain in Europe (after Mount E ...
.
Calculations and mathematics
When the key col for a peak is close to the peak itself, prominence is easily computed by hand using atopographic map
In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ...
. However, when the key col is far away, or when one wants to calculate the prominence of many peaks at once, software can apply surface network modeling to a digital elevation model
A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, Natural satellite, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refer ...
to find exact or approximate key cols.
Since topographic map
In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ...
s typically show elevation using contour lines
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, isoquant or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensi ...
, the exact elevation is typically bounded by an upper and lower contour, and not specified exactly. Prominence calculations may use the high contour (giving in a pessimistic estimate), the low contour (giving an optimistic estimate), their mean (giving a "midrange" or "rise" prominence) or an interpolated value (customary in Britain).
The choice of method depends largely on the preference of the author and historical precedent. Pessimistic prominence, (and sometimes optimistic prominence) were for many years used in USA and international lists, but mean prominence is becoming preferred.
Wet prominence and dry prominence
There are two varieties of topographic prominence: wet prominence and dry prominence.Adam Helman, ''The Finest Peaks–Prominence and Other Mountain Measures'', 2005. Wet prominence is the standard topographic prominence discussed in this article. Wet prominence assumes that the surface of the earth includes all permanent water, snow, and ice features. Thus, the wet prominence of the highest summit of an ocean island or landmass is always equal to the summit's elevation. Dry prominence, on the other hand, ignores water, snow, and ice features and assumes that the surface of the earth is defined by the solid bottom of those features. The dry prominence of a summit is equal to its wet prominence unless the summit is the highest point of a landmass or island, or its key col is covered by snow or ice. If its highest surface col is on water, snow, or ice, the dry prominence of that summit is equal to its wet prominence plus the depth of its highest submerged col. Because Earth has no higher summit thanMount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
, Everest's prominence is either undefined or its height from the lowest contour line. In a dry Earth, the lowest contour line would be the deepest hydrologic feature, the Challenger Deep
The Challenger Deep is the List of submarine topographical features#List of oceanic trenches, deepest known point of the seabed of Earth, located in the western Pacific Ocean at the southern end of the Mariana Trench, in the ocean territory o ...
, at 10,924 m depth. Everest's dry prominence would be this depth plus Everest's wet prominence of 8848 m, totaling 19,772 m. The dry prominence of Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea (, ; abbreviation for ''Mauna a Wākea''); is a dormant Shield volcano, shield volcano on the Hawaii (island), island of Hawaii. Its peak is above sea level, making it the List of U.S. states by elevation, highest point in Hawaii a ...
is equal to its wet prominence (4205 m) plus the depth of its highest submerged col (about 5125 m). Totaling 9330 m, this is greater than any mountain apart from Everest. The dry prominence of Aconcagua
Aconcagua () is a mountain in the Principal Cordillera of the Andes mountain range, in Mendoza Province, Argentina. It is the highest mountain in the Americas, the highest outside Asia, and the highest in both the Western Hemisphere and the ...
is equal to its wet prominence (6960 m) plus the depth of the highest submerged col of the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
(about 40 m), or about 7000 m.
Mauna Kea is relatively close to its submerged key col in the Pacific Ocean, and the corresponding contour line that surrounds Mauna Kea is a relatively compact area of the ocean floor. Whereas a contour line around Everest that is lower than 9330m from Everest's peak would surround most of the major continents of the Earth. Even just surrounding Afro-Eurasia would run a contour line through the Bering Straight, with a highest submerged col of about 40 m, or only 8888 m below the peak of Everest. As a result, Mauna Kea's prominence might be subjectively more impressive than Everest's, and some authorities have called it the tallest mountain from peak to underwater base.
Dry prominence is also useful for measuring submerged seamount
A seamount is a large submarine landform that rises from the ocean floor without reaching the water surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet, or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly a ...
s. Seamounts have a dry topographic prominence, a topographic isolation
The topographic isolation of a summit is the minimum geographical distance, horizontal distance to a point of equal elevation, representing a radius of dominance in which the peak is the highest point. It can be calculated for small hills and is ...
, and a negative topographic elevation
The elevation of a geographic ''location'' is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § ...
.
List of most prominent summits on Earth by 'dry' prominence
Prominence values are accurate to perhaps 100m owing to uncertainties in ocean sounding depths.See also
*Height above average terrain
Height above average terrain (HAAT), or (less popularly) effective height above average terrain (EHAAT), is the vertical position of an antenna site above the surrounding landscape. HAAT is used extensively in FM radio and television, as it is ...
(HAAT) – a similar measurement for FM and TV transmitters
*Ultra-prominent summit
An ultra-prominent peak, or ultra for short, is a mountain summit with a topographic prominence of or more; it is also called a P1500. The prominence of a peak is the minimum height of climb to the summit on any route from a higher peak, or fro ...
; Lists:
* List of mountain lists
*List of tallest mountains in the Solar System
This is a list of the tallest mountains in the Solar System. This list includes peaks on all celestial bodies where significant mountains have been detected. For some celestial bodies, different peaks are given across different types of measurem ...
* List of the most prominent summits of the world
** List of ultra-prominent summits of Africa
** List of ultra-prominent summits of Antarctica
** List of ultra-prominent summits of Australia
** List of ultra-prominent summits of the Alps
** List of the most prominent summits of the British Isles
**List of European ultra-prominent peaks
This is a list of all the mountains in Europe with ultra-prominent peaks with topographic prominence greater than .
European peaks by prominence
The column "Col" in the chart below denotes the highest elevation to which one must descend from a p ...
** List of ultra-prominent summits of North America
*** List of the most prominent summits of Greenland
*** List of the most prominent summits of Canada
*** List of the most prominent summits of the Rocky Mountains
***List of the most prominent summits of the United States
The following sortable table comprises the 200 Topographic prominence, most topographically prominent Summit, mountain peaks of the United States, United States of America.
The summit of a mountain or hill may be measured in three principal w ...
**** List of the most prominent summits of New England
*** List of the most prominent summits of Mexico
*** List of the most prominent summits of Central America
*** List of the most prominent summits of the Caribbean
** List of ultra-prominent summits of South America
**List of islands by highest point
This is a list of islands in the world ordered by their highest point; it lists island, islands with peaks by elevation. At the end of this article continent, continental landmasses are also included for comparison.
Island countries and territor ...
References
{{reflist Topography Physical geography Mountaineering Vertical extent