Ketocarotenoid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic 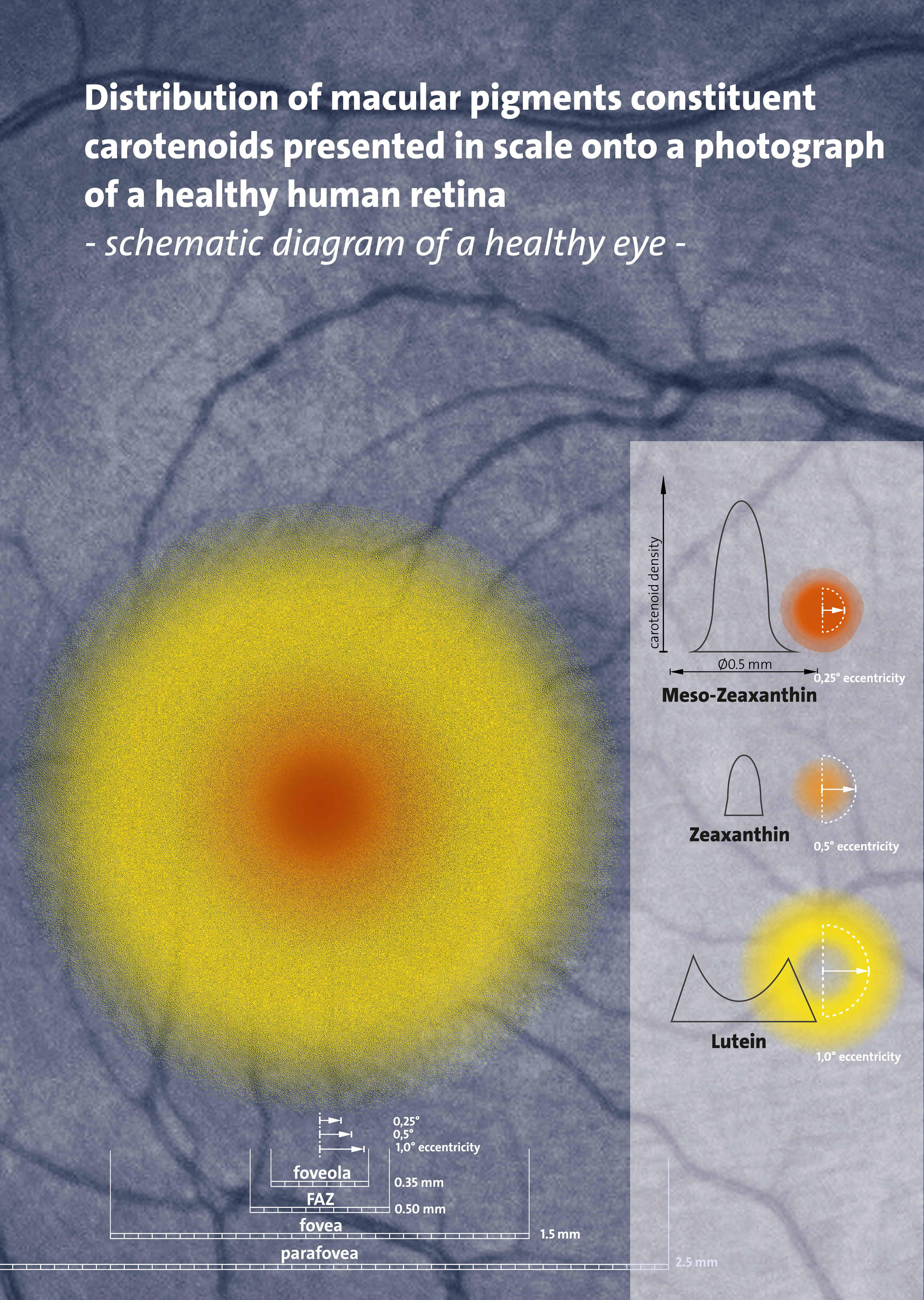 Carotenoids serve two key roles in plants and algae: they absorb light energy for use in
Carotenoids serve two key roles in plants and algae: they absorb light energy for use in
pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
s that are produced by plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s and algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkin
A pumpkin is a cultivar, cultivated winter squash in the genus ''Cucurbita''. The term is most commonly applied to round, orange-colored squash varieties, but does not possess a scientific definition. It may be used in reference to many dif ...
s, carrot
The carrot ('' Daucus carota'' subsp. ''sativus'') is a root vegetable, typically orange in colour, though heirloom variants including purple, black, red, white, and yellow cultivars exist, all of which are domesticated forms of the wild ...
s, parsnip
The parsnip (''Pastinaca sativa'') is a root vegetable closely related to carrot and parsley, all belonging to the flowering plant family Apiaceae. It is a biennial plant usually grown as an annual. Its long taproot has cream-colored skin an ...
s, corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
, tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es, canaries, flamingo
Flamingos or flamingoes () are a type of wading bird in the family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas (including the Caribbe ...
s, salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
, lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
, shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchi ...
, and daffodils. Over 1,100 identified carotenoids can be further categorized into two classes xanthophyll
Xanthophylls (originally phylloxanthins) are yellow pigments that occur widely in nature and form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group; the other division is formed by the carotenes. The name is from Greek: (), meaning "yellow", an ...
s (which contain oxygen) and carotene
The term carotene (also carotin, from the Latin ''carota'', "carrot") is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals (with the ex ...
s (which are purely hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
s and contain no oxygen).
All are derivatives of tetraterpene
Tetraterpenes are terpenes consisting of eight isoprene units and have the molecular formula C40H64. Tetraterpenoids (including many carotenoids) are tetraterpenes that have been chemically modified, as indicated by the presence of oxygen-contai ...
s, meaning that they are produced from 8 isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. It is produced by many plants and animals (including humans) and its polymers ar ...
units and contain 40 carbon atoms. In general, carotenoids absorb wavelengths ranging from 400 to 550 nanometers (violet to green light). This causes the compounds to be deeply colored yellow, orange, or red. Carotenoids are the dominant pigment in autumn leaf color
Autumn leaf color is a phenomenon that affects the normally green leaves of many deciduous trees and shrubs by which they take on, during a few weeks in the autumn season, various shades of yellow, orange, red, purple, and brown. The phenomenon ...
ation of about 15-30% of tree species, but many plant colors, especially reds and purples, are due to polyphenol
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring phenols. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include phenolic acids, flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as ...
s.
 Carotenoids serve two key roles in plants and algae: they absorb light energy for use in
Carotenoids serve two key roles in plants and algae: they absorb light energy for use in photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
, and they provide photoprotection
Photoprotection is the biochemical process that helps organisms cope with molecular damage caused by sunlight. Plants and other oxygenic phototrophs have developed a suite of photoprotective mechanisms to prevent photoinhibition and oxidative str ...
via non-photochemical quenching
Non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) is a mechanism employed by plants and algae to protect themselves from the adverse effects of high light intensity. It involves the quenching of singlet excited state chlorophylls (Chl) via enhanced internal conv ...
. Carotenoids that contain unsubstituted beta-ionone rings (including β-carotene, α-carotene, β-cryptoxanthin, and γ-carotene) have vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
activity (meaning that they can be converted to retinol
Retinol, also called vitamin A1, is a fat-soluble vitamin in the vitamin A family that is found in food and used as a dietary supplement. Retinol or other forms of vitamin A are needed for vision, cellular development, maintenance of skin and ...
). In the eye, lutein
Lutein (;"Lutein"
''meso''-zeaxanthin, and


 Carotenoids are produced by all photosynthetic organisms and are primarily used as
Carotenoids are produced by all photosynthetic organisms and are primarily used as C40
zeaxanthin
Zeaxanthin is one of the most common carotenoids in nature, and is used in the xanthophyll cycle. Synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms, it is the pigment that gives paprika (made from bell peppers), corn, saffron, goji ( wolfberries) ...
are present as macular pigments whose importance in visual function, as of 2016, remains under clinical research
Clinical research is a branch of medical research that involves people and aims to determine the effectiveness (efficacy) and safety of medications, devices, diagnostic products, and treatment regimens intended for improving human health. The ...
.
Structure and function


accessory pigment Accessory pigments are light-absorbing compounds, found in photosynthetic organisms, that work in conjunction with chlorophyll ''a''. They include other forms of this pigment, such as chlorophyll ''b'' in green algal and vascular ("higher") plan ...
s to chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
in the light-harvesting part of photosynthesis.
They are highly unsaturated with conjugated double bonds, which enables carotenoids to absorb light of various wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
s. At the same time, the terminal groups regulate the polarity and properties within lipid membranes.
Most carotenoids are tetraterpenoids, regular isoprenoids
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes" ...
. Several modifications to these structures exist: including cyclization
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where ...
, varying degrees of saturation or unsaturation, and other functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
s. Carotenes typically contain only carbon and hydrogen, i.e., they are hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
s. Prominent members include α-carotene, β-carotene, and lycopene
Lycopene is an organic compound classified as a tetraterpene and a carotene. Lycopene (from the Neo-Latin '' Lycopersicon'', the name of a former tomato genus) is a bright red carotenoid hydrocarbon found in tomatoes and other red fruits and ve ...
, are known as ''carotene
The term carotene (also carotin, from the Latin ''carota'', "carrot") is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals (with the ex ...
s''. Carotenoids containing oxygen include lutein
Lutein (;"Lutein"

 The most common carotenoids include lycopene and the vitamin A precursor β-carotene. In plants, the xanthophyll
The most common carotenoids include lycopene and the vitamin A precursor β-carotene. In plants, the xanthophyll
zeaxanthin
Zeaxanthin is one of the most common carotenoids in nature, and is used in the xanthophyll cycle. Synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms, it is the pigment that gives paprika (made from bell peppers), corn, saffron, goji ( wolfberries) ...
. They are known as ''xanthophyll
Xanthophylls (originally phylloxanthins) are yellow pigments that occur widely in nature and form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group; the other division is formed by the carotenes. The name is from Greek: (), meaning "yellow", an ...
s''. Their color, ranging from pale yellow through bright orange to deep red, is directly related to their structure, especially the length of the conjugation. Xanthophylls are often yellow, giving their class name.
Carotenoids also participate in different types of cell signaling. They are able to signal the production of abscisic acid
Abscisic acid (ABA or abscisin II) is a plant hormone. ABA functions in many plant developmental processes, including seed and bud dormancy, the control of organ size and stomatal closure. It is especially important for plants in the response to ...
, which regulates plant growth, seed dormancy
Seed dormancy is an evolutionary adaptation that prevents seeds from germinating during unsuitable ecological conditions that would typically lead to a low probability of seedling survival. Dormant seeds do not germinate in a specified period of ...
, embryo maturation and germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
, cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
and elongation, floral growth, and stress responses.
Photophysics
The length of the multiple conjugated double bonds determines their color and photophysics. After absorbing a photon, the carotenoid transfers its excited electron tochlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
for use in photosynthesis. Upon absorption of light, carotenoids transfer excitation energy to and from chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
. The singlet-singlet energy transfer is a lower energy state transfer and is used during photosynthesis. The triplet-triplet transfer is a higher energy state and is essential in photoprotection. Light produces damaging species during photosynthesis, with the most damaging being reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
(ROS). As these high energy ROS are produced in the chlorophyll the energy is transferred to the carotenoid’s polyene tail and undergoes a series of reactions in which electrons are moved between the carotenoid bonds in order to find the most balanced (lowest energy) state for the carotenoid.
Carotenoids defend plants against singlet oxygen
Singlet oxygen, systematically named dioxygen(singlet) and dioxidene, is a gaseous inorganic chemistry, inorganic chemical with the formula O=O (also written as or ), which is in a quantum state where all electrons are Radical (chemistry), spin p ...
, by both energy transfer and by chemical reactions. They also protect plants by quenching triplet chlorophyll. By protecting lipids from free-radical damage, which generate charged lipid peroxides and other oxidised derivatives, carotenoids support crystalline architecture and hydrophobicity of lipoproteins and cellular lipid structures, hence oxygen solubility and its diffusion therein.
Structure-property relationships
Like somefatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
s, carotenoids are lipophilic
Lipophilicity (from Greek language, Greek λίπος "fat" and :wikt:φίλος, φίλος "friendly") is the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such compounds are c ...
due to the presence of long unsaturated aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated (in which all ...
chains. As a consequence, carotenoids are typically present in plasma lipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary function is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids. They consist of a triglyceride and cholesterol center, sur ...
s and cellular lipid structures.
Regulation
The regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis is influenced by various factors, including: * Gene Expression: Many carotenoid biosynthetic genes are upregulated by light, enhancing the expression of PSY and subsequently increasing carotenoid production. * Hormonal Regulation: Phytohormones such asauxins
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essenti ...
and abscisic acid
Abscisic acid (ABA or abscisin II) is a plant hormone. ABA functions in many plant developmental processes, including seed and bud dormancy, the control of organ size and stomatal closure. It is especially important for plants in the response to ...
modulate carotenoid biosynthesis. Notably, abscisic acid enhances carotenoid accumulation under stress conditions.
* Environmental Factors: Stressors like drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
or pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
attack can trigger carotenoid accumulation as a protective response, thereby enhancing plant resilience.
Morphology
Carotenoids are located primarily outside thecell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
in different cytoplasm organelles, lipid droplet
Lipid droplets, also referred to as lipid bodies, oil bodies or adiposomes, are lipid-rich cellular organelles that regulate the storage and hydrolysis of neutral lipids and are found largely in the adipose tissue. They also serve as a reservoir ...
s, cytosomes and granules. They have been visualised and quantified by raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after physicist C. V. Raman) is a Spectroscopy, spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Ra ...
in an algal
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular microalgae, s ...
cell.
With the development of monoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a Lineage (evolution), cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Mon ...
to ''trans-''lycopene
Lycopene is an organic compound classified as a tetraterpene and a carotene. Lycopene (from the Neo-Latin '' Lycopersicon'', the name of a former tomato genus) is a bright red carotenoid hydrocarbon found in tomatoes and other red fruits and ve ...
it was possible to localise this carotenoid in different animal and human cells.
Foods
Beta-carotene, found inpumpkin
A pumpkin is a cultivar, cultivated winter squash in the genus ''Cucurbita''. The term is most commonly applied to round, orange-colored squash varieties, but does not possess a scientific definition. It may be used in reference to many dif ...
s, sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its sizeable, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable, which is a staple food in parts of ...
, carrot
The carrot ('' Daucus carota'' subsp. ''sativus'') is a root vegetable, typically orange in colour, though heirloom variants including purple, black, red, white, and yellow cultivars exist, all of which are domesticated forms of the wild ...
s and winter squash
Winter squash is an annual fruit representing several squash species within the genus '' Cucurbita''. Late-growing, less symmetrical, odd-shaped, rough or warty varieties, small to medium in size, but with long-keeping qualities and hard rinds, ...
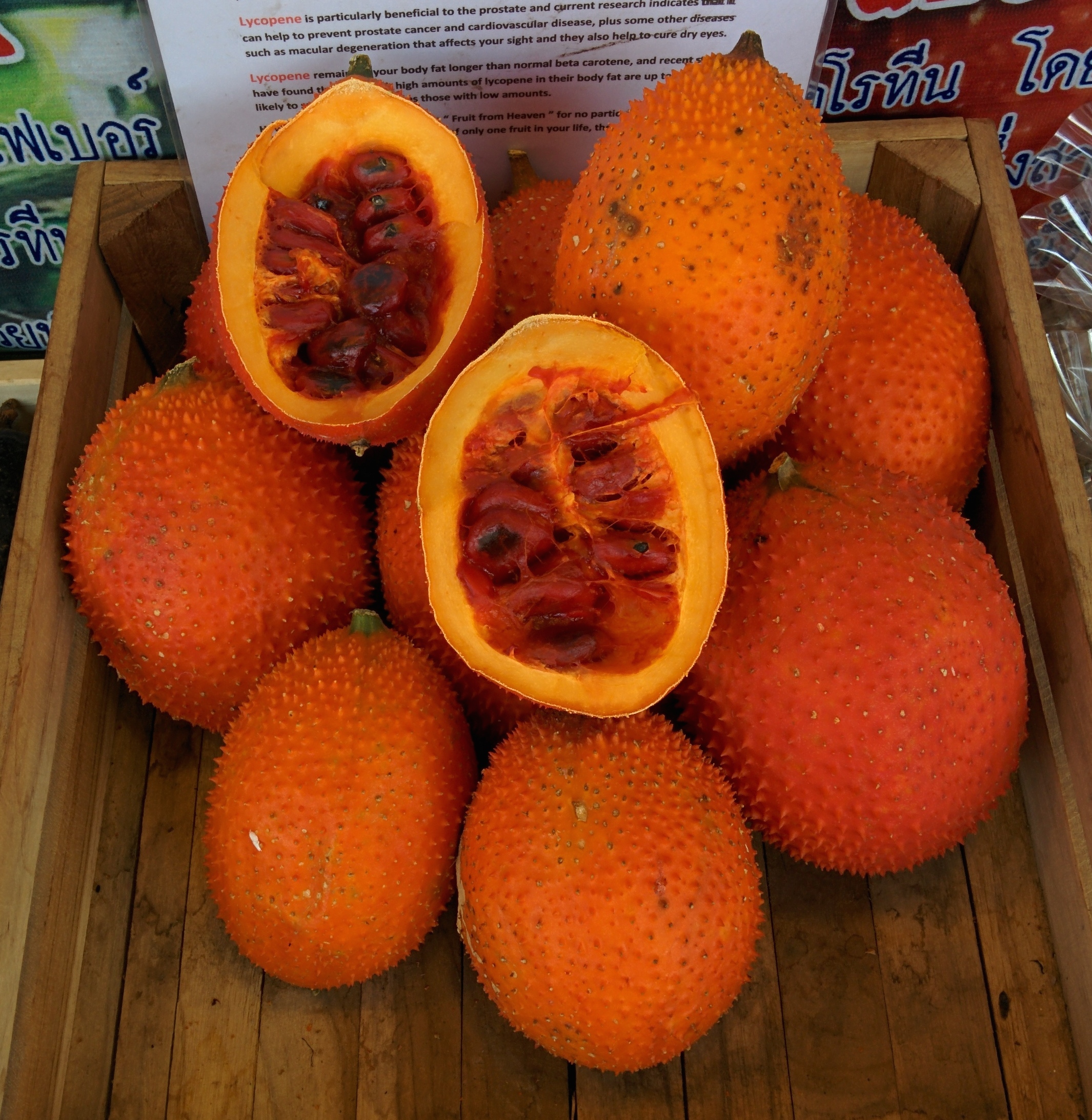
, is responsible for their orange-yellow colors. Dried carrots have the highest amount of carotene of any food per 100-gram serving, measured in retinol activity equivalents (provitamin A equivalents). Vietnamese gac
Gac or GAC may refer to:
*Gấc, pronounced �ək̚˧˦ a Southeast Asian fruit of the species ''Momordica cochinchinensis''
*Gać (disambiguation), a common Polish place-name Acronyms Companies and organisations
* GAC Group, a Chinese automo ...
fruit contains the highest known concentration of the carotenoid lycopene
Lycopene is an organic compound classified as a tetraterpene and a carotene. Lycopene (from the Neo-Latin '' Lycopersicon'', the name of a former tomato genus) is a bright red carotenoid hydrocarbon found in tomatoes and other red fruits and ve ...
. Although green, kale
Kale (), also called leaf cabbage, belongs to a group of cabbage (''Brassica oleracea'') cultivars primarily grown for their Leaf vegetable, edible leaves; it has also been used as an ornamental plant. Its multiple different cultivars vary quite ...
, spinach
Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') is a leafy green flowering plant native to Central Asia, Central and Western Asia. It is of the order Caryophyllales, family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. Its leaves are a common vegetable consumed eit ...
, collard greens
Collard is a group of loose-leafed cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'' (the same species as many common vegetables like cabbage and broccoli). Part of the acephala cultivar group (or kale group), collard is also classified as the variety ''B.& ...
, and turnip greens contain substantial amounts of beta-carotene. The diet of flamingo
Flamingos or flamingoes () are a type of wading bird in the family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas (including the Caribbe ...
s is rich in carotenoids, imparting the orange-colored feathers of these birds.
Carotenoids, especially provitamin A carotenoids such as β-carotene, are essential for human health. Their benefits include:
* Supporting vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, particularly in low-light conditions.
* Enhancing immune function
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as cancer cells, parasitic worms, and also objects such as ...
.
* Contributing to skin health.
* Providing antioxidant properties that may reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheuma ...
and certain cancers
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
.
Reviews of preliminary research in 2015 indicated that foods high in carotenoids may reduce the risk of head and neck cancers
Head and neck cancer is a general term encompassing multiple cancers that can develop in the head and neck region. These include cancers of the mouth, tongue, gums and lips (oral cancer), voice box ( laryngeal), throat ( nasopharyngeal, orophary ...
and prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ...
. There is no correlation between consumption of foods high in carotenoids and vitamin A and the risk of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
.
Humans and other animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s are mostly incapable of synthesizing carotenoids, and must obtain them through their diet. Carotenoids are a common and often ornamental feature in animals. For example, the pink color of salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
, and the red coloring of cooked lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
s and scales of the yellow morph of common wall lizards are due to carotenoids. It has been proposed that carotenoids are used in ornamental traits (for extreme examples see puffin
Puffins are any of three species of small alcids (auks) in the bird genus ''Fratercula''. These are pelagic seabirds that feed primarily by diving in the water. They breed in large colonies on coastal cliffs or offshore islands, nesting in crev ...
birds) because, given their physiological and chemical properties, they can be used as visible indicators of individual health, and hence are used by animals when selecting potential mates.
Carotenoids from the diet are stored in the fatty tissues of animals, and exclusively carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly mu ...
animals obtain the compounds from animal fat. In the human diet, absorption
Absorption may refer to:
Chemistry and biology
*Absorption (biology), digestion
**Absorption (small intestine)
*Absorption (chemistry), diffusion of particles of gas or liquid into liquid or solid materials
*Absorption (skin), a route by which su ...
of carotenoids is improved when consumed with fat in a meal. Cooking carotenoid-containing vegetables in oil and shredding the vegetable both increase carotenoid bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. H ...
.
Plant colors

 The most common carotenoids include lycopene and the vitamin A precursor β-carotene. In plants, the xanthophyll
The most common carotenoids include lycopene and the vitamin A precursor β-carotene. In plants, the xanthophyll lutein
Lutein (;"Lutein"
 The basic building blocks of carotenoids are
The basic building blocks of carotenoids are
chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
. When chlorophyll is not present, as in autumn foliage, the yellows and oranges of the carotenoids are predominant. For the same reason, carotenoid colors often predominate in ripe fruit after being unmasked by the disappearance of chlorophyll.
Carotenoids are responsible for the brilliant yellows and oranges that tint deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
foliage (such as dying autumn leaves) of certain hardwood species as hickories, ash, maple
''Acer'' is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the soapberry family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated si ...
, yellow poplar
''Liriodendron tulipifera''—known as the tulip tree, American tulip tree, tulipwood, tuliptree, tulip poplar, whitewood, fiddletree, lynn-tree, hickory-poplar, and yellow-poplar—is the North American representative of the two-species genus ...
, aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species in the Populus sect. Populus, of the ''Populus'' (poplar) genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
* ''Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (China, south of ''P. tremula'')
* ''Populus da ...
, birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 3 ...
, black cherry, sycamore
Sycamore is a name which has been applied to several types of trees, but with somewhat similar leaf forms. The name derives from the Ancient Greek () meaning .
Species of otherwise unrelated trees known as sycamore:
* ''Acer pseudoplatanus'', a ...
, cottonwood, sassafras, and alder
Alders are trees of the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus includes about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species ex ...
. Carotenoids are the dominant pigment in autumn leaf coloration of about 15-30% of tree species. However, the reds, the purples, and their blended combinations that decorate autumn foliage usually come from another group of pigments in the cells called anthocyanin
Anthocyanins (), also called anthocyans, are solubility, water-soluble vacuole, vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart named a chemical compou ...
s. Unlike the carotenoids, these pigments are not present in the leaf throughout the growing season, but are actively produced towards the end of summer.
Bird colors and sexual selection
Dietary carotenoids and their metabolic derivatives are responsible for bright yellow to red coloration in birds. Studies estimate that around 2956 modern bird species display carotenoid coloration and that the ability to utilize these pigments for external coloration has evolved independently many times throughout avian evolutionary history. Carotenoid coloration exhibits high levels ofsexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
, with adult male birds generally displaying more vibrant coloration than females of the same species.
These differences arise due to the selection of yellow and red coloration in males by female preference. In many species of birds, females invest greater time and resources into raising offspring than their male partners. Therefore, it is imperative that female birds carefully select high quality mates. Current literature supports the theory that vibrant carotenoid coloration is correlated with male quality—either though direct effects on immune function and oxidative stress, or through a connection between carotenoid metabolizing pathways and pathways for cellular respiration.
It is generally considered that sexually selected traits, such as carotenoid-based coloration, evolve because they are honest signals of phenotypic and genetic quality. For instance, among males of the bird species '' Parus major'', the more colorfully ornamented males produce sperm that is better protected against oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal ...
due to increased presence of carotenoid antioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants ...
s. However, there is also evidence that attractive male coloration may be a faulty signal of male quality. Among stickleback
The sticklebacks are a family of ray-finned fishes, the Gasterosteidae which have a Holarctic distribution in fresh, brackish and marine waters. They were thought to be related to the pipefish and seahorses but are now thought to be more close ...
fish, males that are more attractive to females due to carotenoid colorants appear to under-allocate carotenoids to their germline cells. Since carotinoids are beneficial antioxidants, their under-allocation to germline
In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that develop into germ cells. In other words, they are the cells that form gametes ( eggs and sperm), which can come together to form a zygote. They dif ...
cells can lead to increased oxidative DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified ...
to these cells. Therefore, female sticklebacks may risk fertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate ...
and the viability of their offspring by choosing redder, but more deteriorated partners with reduced sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
quality.
Aroma chemicals
Products of carotenoid degradation such asionone
The ionones, from greek ἴον ion "violet", are a series of closely related chemical substances that are part of a group of compounds known as rose ketones, which also includes damascones and damascenones. Ionones are aroma compounds found in ...
s, damascones and damascenones are also important fragrance chemicals that are used extensively in the perfume
Perfume (, ) is a mixture of fragrance, fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), Fixative (perfumery), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agre ...
s and fragrance industry. Both β-damascenone and β-ionone although low in concentration in rose
A rose is either a woody perennial plant, perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred Rose species, species and Garden roses, tens of thousands of cultivar ...
distillates are the key odor-contributing compounds in flowers. In fact, the sweet floral smells present in black tea
Black tea (also literally translated as red tea from various East Asian languages) is a type of tea that is more tea processing, oxidized than oolong, yellow tea, yellow, white tea, white, and green tea, green teas. Black tea is generally st ...
, aged tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
, and many fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
s are due to the aromatic compounds resulting from carotenoid breakdown.
Disease
Some carotenoids are produced by bacteria to protect themselves from oxidative immune attack. The ''aureus'' (golden) pigment that gives some strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'' their name is a carotenoid called staphyloxanthin. This carotenoid is a virulence factor with an antioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants ...
action that helps the microbe evade death by reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
used by the host immune system.
Biosynthesis
isopentenyl diphosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate, or IDP) is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway (commonly called the mevalonate pathway) and in the ''non-mevalonate'' MEP pathway of i ...
(IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). These two isoprene isomers are used to create various compounds depending on the biological pathway used to synthesize the isomers. Plants are known to use two different pathways for IPP production: the cytosolic mevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as ''mevalonat ...
pathway (MVA) and the plastidic methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP). In animals, the production of cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
starts by creating IPP and DMAPP using the MVA. For carotenoid production plants use MEP to generate IPP and DMAPP. The MEP pathway results in a 5:1 mixture of IPP:DMAPP. IPP and DMAPP undergo several reactions, resulting in the major carotenoid precursor, geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP). GGPP can be converted into carotenes or xanthophylls by undergoing a number of different steps within the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway.
Carotenoids serve as precursors to vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
.
MEP pathway
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, also known as triose phosphate or 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde and abbreviated as G3P, GA3P, GADP, GAP, TP, GALP or PGAL, is a metabolite that occurs as an intermediate in several central pathways of all organisms.Nelson, D ...
and pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic ...
, intermediates of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
, are converted to deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) catalyzed by DXP synthase (DXS). DXP reductoisomerase catalyzes the reduction by NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require N ...
and subsequent rearrangement. The resulting MEP is converted to 4-(cytidine 5’-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol (CDP-ME) in the presence of CTP using the enzyme MEP cytidylyltransferase. CDP-ME is then converted, in the presence of ATP, to 2-phospho-4-(cytidine 5’-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol (CDP-ME2P). The conversion to CDP-ME2P is catalyzed by CDP-ME kinase. Next, CDP-ME2P is converted to 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (MECDP). This reaction occurs when MECDP synthase catalyzes the reaction and CMP is eliminated from the CDP-ME2P molecule. MECDP is then converted to (e)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate (HMBDP) via HMBDP synthase in the presence of flavodoxin and NADPH. HMBDP is reduced to IPP in the presence of ferredoxin
Ferredoxins (from Latin ''ferrum'': iron + redox, often abbreviated "fd") are iron–sulfur proteins that mediate electron transfer in a range of metabolic reactions. The term "ferredoxin" was coined by D.C. Wharton of the DuPont Co. and applied t ...
and NADPH by the enzyme HMBDP reductase. The last two steps involving HMBPD synthase and reductase can only occur in completely anaerobic
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to:
*Adhesive#Anaerobic, Anaerobic ad ...
environments. IPP is then able to isomerize to DMAPP via IPP isomerase.
Carotenoid biosynthetic pathway
Carotenoid biosynthesis occurs primarily in the plastids of plant cells, particularly withinchloroplasts
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
and chromoplasts
Chromoplasts are plastids, heterogeneous organelles responsible for pigment synthesis and storage in specific photosynthetic eukaryotes. It is thought (according to symbiogenesis) that like all other plastids including chloroplasts and leucop ...
. The biosynthetic pathway initiates with the condensation of two molecules of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of diterpenes and diterpenoids. It is also the precursor to carotenoids, gibberellins, tocopherols, and chlorophylls.
It is also a precursor to geranylgeranylated proteins, whic ...
(GGPP), a 20-carbon isoprenoid precursor. The key steps in this pathway are as follows:
# Formation of phytoene: The enzyme phytoene synthase
Phytoene synthase (, ''prephytoene-diphosphate synthase'', ''15-cis-phytoene synthase'', ''PSase'', ''geranylgeranyl-diphosphate geranylgeranyltransferase'') is a transferase enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of carotenoids. It catalyzes the con ...
(PSY) catalyzes the condensation of two GGPP molecules to produce phytoene
Phytoene () is a 40-carbon intermediate in the biosynthesis of carotenoids. The synthesis of phytoene is the first committed step in the synthesis of carotenoids in plants. Phytoene is produced from two molecules of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate ( ...
, a colorless carotenoid.
# Desaturation to lycopene: Phytoene undergoes a series of desaturation reactions facilitated by enzymes such as phytoene desaturase (PDS) and ζ-carotene isomerase (Z-ISO), resulting in the formation of lycopene
Lycopene is an organic compound classified as a tetraterpene and a carotene. Lycopene (from the Neo-Latin '' Lycopersicon'', the name of a former tomato genus) is a bright red carotenoid hydrocarbon found in tomatoes and other red fruits and ve ...
, a red carotenoid.
# Cyclization to carotenoids: Lycopene is cyclized into various carotenoids, including α-carotene and β-carotene, through the action of lycopene cyclase (LCY), which catalyzes cyclization at the ends of the lycopene molecule.
# Further modifications: Subsequent modifications, such as hydroxylation and oxidation, lead to the formation of xanthophylls (e.g., lutein
Lutein (;"Lutein"
zeaxanthin
Zeaxanthin is one of the most common carotenoids in nature, and is used in the xanthophyll cycle. Synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms, it is the pigment that gives paprika (made from bell peppers), corn, saffron, goji ( wolfberries) ...
) and other derivatives.
Two GGPP molecules condense via phytoene synthase
Phytoene synthase (, ''prephytoene-diphosphate synthase'', ''15-cis-phytoene synthase'', ''PSase'', ''geranylgeranyl-diphosphate geranylgeranyltransferase'') is a transferase enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of carotenoids. It catalyzes the con ...
(PSY), forming the 15-cis isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the exi ...
of phytoene
Phytoene () is a 40-carbon intermediate in the biosynthesis of carotenoids. The synthesis of phytoene is the first committed step in the synthesis of carotenoids in plants. Phytoene is produced from two molecules of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate ( ...
. PSY belongs to the squalene/phytoene synthase family and is homologous to squalene synthase
Squalene synthase (SQS) or farnesyl-diphosphate:farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyl transferase is an enzyme localized to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. SQS participates in the terpenoid, isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway, catalyzing a two-s ...
that takes part in steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
biosynthesis. The subsequent conversion of phytoene into all-trans-lycopene
Lycopene is an organic compound classified as a tetraterpene and a carotene. Lycopene (from the Neo-Latin '' Lycopersicon'', the name of a former tomato genus) is a bright red carotenoid hydrocarbon found in tomatoes and other red fruits and ve ...
depends on the organism. Bacteria and fungi employ a single enzyme, the bacterial phytoene desaturase (CRTI) for the catalysis. Plants and cyanobacteria however utilize four enzymes for this process. The first of these enzymes is a plant-type phytoene desaturase which introduces two additional double bonds into 15-cis-phytoene by dehydrogenation
In chemistry, dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the removal of hydrogen, usually from an organic molecule. It is the reverse of hydrogenation. Dehydrogenation is important, both as a useful reaction and a serious problem. At ...
and isomerizes two of its existing double bonds from trans to cis producing 9,15,9’-tri-cis-ζ-carotene. The central double bond of this tri-cis-ζ-carotene is isomerized by the zeta-carotene isomerase Z-ISO and the resulting 9,9'-di-cis-ζ-carotene is dehydrogenated again via a ζ-carotene desaturase (ZDS). This again introduces two double bonds, resulting in 7,9,7’,9’-tetra-cis-lycopene. CRTISO
Prolycopene isomerase (, ''CRTISO'', ''carotene cis-trans isomerase'', ''ZEBRA2 (gene)'', ''carotene isomerase'', ''carotenoid isomerase'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''7,9,7',9'-tetracis-lycopene cis-trans-isomerase''. This enzyme catalyse ...
, a carotenoid isomerase, is needed to convert the cis-lycopene into an all-trans lycopene in the presence of reduced FAD
A fad, trend, or craze is any form of collective behavior that develops within a culture, a generation, or social group in which a group of people enthusiastically follow an impulse for a short time period.
Fads are objects or behaviors tha ...
.
This all-trans lycopene is cyclized; cyclization
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where ...
gives rise to carotenoid diversity, which can be distinguished based on the end groups. There can be either a beta ring or an epsilon ring, each generated by a different enzyme ( lycopene beta-cyclase eta-LCYor lycopene epsilon-cyclase psilon-LCY. α-Carotene is produced when the all-trans lycopene first undergoes reaction with epsilon-LCY then a second reaction with beta-LCY; whereas β-carotene is produced by two reactions with beta-LCY. α- and β-Carotene are the most common carotenoids in the plant photosystem
Photosystems are functional and structural units of protein complexes involved in photosynthesis. Together they carry out the primary photochemistry of photosynthesis: the absorption of light and the transfer of energy and electrons. Photosystems ...
s but they can still be further converted into xanthophylls by using beta-hydrolase and epsilon-hydrolase, leading to a variety of xanthophylls.
Key enzymes
Several enzymes play critical roles in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway: # Phytoene synthase (PSY): Catalyzes the first committed step in carotenoid biosynthesis, converting GGPP into phytoene. # Phytoene desaturase (PDS): Introduces double bonds into phytoene, facilitating its conversion into lycopene. # Lycopene cyclase (LCY): Responsible for the cyclization of lycopene into α-carotene or β-carotene. # Carotenoid hydroxylases: Enzymes such as lutein epoxide cyclase (LUT) introduce hydroxyl groups into carotenoids, leading to the formation of xanthophylls.Regulation
It is believed that both DXS and DXR are rate-determining enzymes, allowing them to regulate carotenoid levels. This was discovered in an experiment where DXS and DXR were genetically overexpressed, leading to increased carotenoid expression in the resulting seedlings. Also, J-protein (J20) and heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) chaperones are thought to be involved in post-transcriptional regulation of DXS activity, such that mutants with defective J20 activity exhibit reduced DXS enzyme activity while accumulating inactive DXS protein. Regulation may also be caused by externaltoxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. They occur especially as proteins, often conjugated. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived ...
s that affect enzymes and proteins required for synthesis. Ketoclomazone is derived from herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page f ...
s applied to soil and binds to DXP synthase. This inhibits DXP synthase, preventing synthesis of DXP and halting the MEP pathway. The use of this toxin leads to lower levels of carotenoids in plants grown in the contaminated soil. Fosmidomycin, an antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
, is a competitive inhibitor
Competitive inhibition is interruption of a chemical pathway owing to one chemical substance inhibiting the effect of another by competing with it for binding or bonding. Any metabolic or chemical messenger system can potentially be affected b ...
of DXP reductoisomerase due to its similar structure to the enzyme. Application of said antibiotic prevents reduction of DXP, again halting the MEP pathway.
Naturally occurring carotenoids
* Hydrocarbons ** Lycopersene 7,8,11,12,15,7',8',11',12',15'-Decahydro-γ,γ-carotene ** Phytofluene **Lycopene
Lycopene is an organic compound classified as a tetraterpene and a carotene. Lycopene (from the Neo-Latin '' Lycopersicon'', the name of a former tomato genus) is a bright red carotenoid hydrocarbon found in tomatoes and other red fruits and ve ...
** Hexahydrolycopene 15-''cis''-7,8,11,12,7',8'-Hexahydro-γ,γ-carotene
** Torulene 3',4'-Didehydro-β,γ-carotene
** α-Zeacarotene
α-Zeacarotene (alpha-zeacarotene) is a form of carotene with a β-ionone ring at one end and a ζ-ionone ring at the opposite end. It is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of various carotenoids and plays a crucial role in the metabolic pathw ...
7',8'-Dihydro-ε,γ-carotene
** α-Carotene
** β-Carotene
** γ-Carotene
** δ-Carotene
δ-Carotene (''delta''-carotene) or ε,ψ-carotene is a form of carotene with an ε-ring at one end, and the other uncyclized, labelled ψ (psi). It is an intermediate synthesis product in some photosynthetic plants between lycopene
Lycopene ...
** ε-Carotene
ε-Carotene (''epsilon''-carotene) is a carotene
The term carotene (also carotin, from the Latin ''carota'', "carrot") is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants b ...
** ζ-Carotene
* Alcohols
** Alloxanthin
** Bacterioruberin 2,2'-Bis(3-hydroxy-3-methylbutyl)-3,4,3',4'-tetradehydro-1,2,1',2'-tetrahydro-γ,γ-carotene-1,1'-diol
** Cynthiaxanthin
** Pectenoxanthin
** Cryptomonaxanthin (3R,3'R)-7,8,7',8'-Tetradehydro-β,β-carotene-3,3'-diol
** Crustaxanthin β,-Carotene-3,4,3',4'-tetrol
** Gazaniaxanthin (3R)-5'-cis-β,γ-Caroten-3-ol
** OH-Chlorobactene 1',2'-Dihydro-f,γ-caroten-1'-ol
** Loroxanthin β,ε-Carotene-3,19,3'-triol
** Lutein
Lutein (;"Lutein"
Lycoxanthin γ,γ-Caroten-16-ol
** Rhodopin 1,2-Dihydro-γ,γ-caroten-l-ol
** Rhodopinol a.k.a. Warmingol 13-''cis''-1,2-Dihydro-γ,γ-carotene-1,20-diol
** Saproxanthin 3',4'-Didehydro-1',2'-dihydro-β,γ-carotene-3,1'-diol
**
Zeaxanthin
Zeaxanthin is one of the most common carotenoids in nature, and is used in the xanthophyll cycle. Synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms, it is the pigment that gives paprika (made from bell peppers), corn, saffron, goji ( wolfberries) ...
* Glycosides
** Oscillaxanthin 2,2'-Bis(β-L-rhamnopyranosyloxy)-3,4,3',4'-tetradehydro-1,2,1',2'-tetrahydro-γ,γ-carotene-1,1'-diol
** Phleixanthophyll 1'-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3',4'-didehydro-1',2'-dihydro-β,γ-caroten-2'-ol
* Ethers
** Rhodovibrin 1'-Methoxy-3',4'-didehydro-1,2,1',2'-tetrahydro-γ,γ-caroten-1-ol
** Spheroidene 1-Methoxy-3,4-didehydro-1,2,7',8'-tetrahydro-γ,γ-carotene
* Epoxides
** Diadinoxanthin 5,6-Epoxy-7',8'-didehydro-5,6-dihydro—carotene-3,3-diol
** Luteoxanthin 5,6: 5',8'-Diepoxy-5,6,5',8'-tetrahydro-β,β-carotene-3,3'-diol
** Mutatoxanthin
** Citroxanthin
** Zeaxanthin furanoxide 5,8-Epoxy-5,8-dihydro-β,β-carotene-3,3'-diol
** Neochrome 5',8'-Epoxy-6,7-didehydro-5,6,5',8'-tetrahydro-β,β-carotene-3,5,3'-triol
** Foliachrome
** Trollichrome
** Vaucheriaxanthin 5',6'-Epoxy-6,7-didehydro-5,6,5',6'-tetrahydro-β,β-carotene-3,5,19,3'-tetrol
* Aldehydes
** Rhodopinal
** Warmingone 13-cis-1-Hydroxy-1,2-dihydro-γ,γ-caroten-20-al
** Torularhodinaldehyde 3',4'-Didehydro-β,γ-caroten-16'-al
* Acids and acid esters
** Torularhodin 3',4'-Didehydro-β,γ-caroten-16'-oic acid
** Torularhodin methyl ester Methyl 3',4'-didehydro-β,γ-caroten-16'-oate
* Ketones
** Astacene
** Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is a keto- carotenoid within a group of chemical compounds known as carotenoids or terpenes. Astaxanthin is a metabolite of zeaxanthin and canthaxanthin, containing both hydroxyl and ketone functional groups.
It is a lipid-solu ...
** Canthaxanthin
Canthaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid pigment widely distributed in nature. Carotenoids belong to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenoids. The chemical formula of canthaxanthin is C40H52O2. It was first isolated in edible mushrooms. It ...
a.k.a. Aphanicin, Chlorellaxanthin β,β-Carotene-4,4'-dione
** Capsanthin (3R,3'S,5'R)-3,3'-Dihydroxy-β,κ-caroten-6'-one
** Capsorubin (3S,5R,3'S,5'R)-3,3'-Dihydroxy-κ,κ-carotene-6,6'-dione
** Cryptocapsin (3'R,5'R)-3'-Hydroxy-β,κ-caroten-6'-one
** 2,2'-Diketospirilloxanthin 1,1'-Dimethoxy-3,4,3',4'-tetradehydro-1,2,1',2'-tetrahydro-γ,γ-carotene-2,2'-dione
** Echinenone β,β-Caroten-4-one
** 3'-Hydroxyechinenone
3′-Hydroxyechinenone is a keto-carotenoid pigment found in cyanobacteria and microalgae. Carotenoids belong to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenoids. The chemical formula of canthaxanthin is C40H54O2. It is found non-covalently ...
** Flexixanthin 3,1'-Dihydroxy-3',4'-didehydro-1',2'-dihydro-β,γ-caroten-4-one
** 3-OH-Canthaxanthin a.k.a. Adonirubin a.k.a. Phoenicoxanthin 3-Hydroxy-β,β-carotene-4,4'-dione
** Hydroxyspheriodenone 1'-Hydroxy-1-methoxy-3,4-didehydro-1,2,1',2',7',8'-hexahydro-γ,γ-caroten-2-one
** Okenone 1'-Methoxy-1',2'-dihydro-c,γ-caroten-4'-one
** Pectenolone 3,3'-Dihydroxy-7',8'-didehydro-β,β-caroten-4-one
** Phoeniconone a.k.a. Dehydroadonirubin 3-Hydroxy-2,3-didehydro-β,β-carotene-4,4'-dione
** Phoenicopterone β,ε-caroten-4-one
** Rubixanthone 3-Hydroxy-β,γ-caroten-4'-one
** Siphonaxanthin 3,19,3'-Trihydroxy-7,8-dihydro-β,ε-caroten-8-one
* Esters of alcohols
** Astacein 3,3'-Bispalmitoyloxy-2,3,2',3'-tetradehydro-β,β-carotene-4,4'-dione or 3,3'-dihydroxy-2,3,2',3'-tetradehydro-β,β-carotene-4,4'-dione dipalmitate
** Fucoxanthin
Fucoxanthin is a xanthophyll, with formula C42H58O6. It is found as an accessory pigment in the chloroplasts of brown algae and most other heterokonts, giving them a brown or olive-green color. Fucoxanthin absorbs light primarily in the blue-gree ...
3'-Acetoxy-5,6-epoxy-3,5'-dihydroxy-6',7'-didehydro-5,6,7,8,5',6'-hexahydro-β,β-caroten-8-one
** Isofucoxanthin 3'-Acetoxy-3,5,5'-trihydroxy-6',7'-didehydro-5,8,5',6'-tetrahydro-β,β-caroten-8-one
** Physalien
** Siphonein 3,3'-Dihydroxy-19-lauroyloxy-7,8-dihydro-β,ε-caroten-8-one or 3,19,3'-trihydroxy-7,8-dihydro-β,ε-caroten-8-one 19-laurate
* Apocarotenoid Apocarotenoids are organic compounds which occur widely in living organisms. They are derived from carotenoids by oxidative cleavage,
catalyzed by carotenoid oxygenases. Examples include the vitamin A retinoids retinal, retinoic acid, and retinol; a ...
s
** β-Apo-2'-carotenal 3',4'-Didehydro-2'-apo-b-caroten-2'-al
** Apo-2-lycopenal
** Apo-6'-lycopenal 6'-Apo-y-caroten-6'-al
** Azafrinaldehyde 5,6-Dihydroxy-5,6-dihydro-10'-apo-β-caroten-10'-al
** Bixin 6'-Methyl hydrogen 9'-cis-6,6'-diapocarotene-6,6'-dioate
** Citranaxanthin 5',6'-Dihydro-5'-apo-β-caroten-6'-one or 5',6'-dihydro-5'-apo-18'-nor-β-caroten-6'-one or 6'-methyl-6'-apo-β-caroten-6'-one
** Crocetin
Crocetin is a natural apocarotenoid dicarboxylic acid, a diterpenoid, and a branched-chain dicarboxylic acid. It was the first plant carotenoid to be recognized as early as 1818 while the history of saffron cultivation reaches back more than 3 ...
8,8'-Diapo-8,8'-carotenedioic acid
** Crocetinsemialdehyde 8'-Oxo-8,8'-diapo-8-carotenoic acid
** Crocin Digentiobiosyl 8,8'-diapo-8,8'-carotenedioate
** Hopkinsiaxanthin 3-Hydroxy-7,8-didehydro-7',8'-dihydro-7'-apo-b-carotene-4,8'-dione or 3-hydroxy-8'-methyl-7,8-didehydro-8'-apo-b-carotene-4,8'-dione
** Methyl apo-6'-lycopenoate
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as ...
Methyl 6'-apo-y-caroten-6'-oate
** Paracentrone 3,5-Dihydroxy-6,7-didehydro-5,6,7',8'-tetrahydro-7'-apo-b-caroten-8'-one or 3,5-dihydroxy-8'-methyl-6,7-didehydro-5,6-dihydro-8'-apo-b-caroten-8'-one
** Sintaxanthin 7',8'-Dihydro-7'-apo-b-caroten-8'-one or 8'-methyl-8'-apo-b-caroten-8'-one
* Nor- and seco-carotenoids
** Actinioerythrin 3,3'-Bisacyloxy-2,2'-dinor-b,b-carotene-4,4'-dione
** β-Carotenone 5,6:5',6'-Diseco-b,b-carotene-5,6,5',6'-tetrone
** Peridinin 3'-Acetoxy-5,6-epoxy-3,5'-dihydroxy-6',7'-didehydro-5,6,5',6'-tetrahydro-12',13',20'-trinor-b,b-caroten-19,11-olide
** Pyrrhoxanthininol 5,6-epoxy-3,3'-dihydroxy-7',8'-didehydro-5,6-dihydro-12',13',20'-trinor-b,b-caroten-19,11-olide
** Semi-α-carotenone 5,6-Seco-b,e-carotene-5,6-dione
** Semi-β-carotenone 5,6-seco-b,b-carotene-5,6-dione or 5',6'-seco-b,b-carotene-5',6'-dione
** Triphasiaxanthin 3-Hydroxysemi-b-carotenone 3'-Hydroxy-5,6-seco-b,b-carotene-5,6-dione or 3-hydroxy-5',6'-seco-b,b-carotene-5',6'-dione
* Retro-carotenoids and retro-apo-carotenoids
** Eschscholtzxanthin 4',5'-Didehydro-4,5'-retro-b,b-carotene-3,3'-diol
** Eschscholtzxanthone 3'-Hydroxy-4',5'-didehydro-4,5'-retro-b,b-caroten-3-one
** Rhodoxanthin 4',5'-Didehydro-4,5'-retro-b,b-carotene-3,3'-dione
** Tangeraxanthin 3-Hydroxy-5'-methyl-4,5'-retro-5'-apo-b-caroten-5'-one or 3-hydroxy-4,5'-retro-5'-apo-b-caroten-5'-one
* Higher carotenoids
** Nonaprenoxanthin 2-(4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butenyl)-7',8',11',12'-tetrahydro-e,y-carotene
** Decaprenoxanthin 2,2'-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butenyl)-e,e-carotene
** C.p. 450 2- -Hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-butenyl2'-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-b,b-carotene
** C.p. 473 2'-(4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-2-butenyl)-2-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-3',4'-didehydro-l',2'-dihydro-β,γ-caroten-1'-ol
** Bacterioruberin 2,2'-Bis(3-hydroxy-3-methylbutyl)-3,4,3',4'-tetradehydro-1,2,1',2'-tetrahydro-γ,γ-carotene-1,1'-diol
See also
*List of phytochemicals in food
The following is a list of phytochemicals present in foods.
Terpenoids (isoprenoids)
Carotenoids ( tetraterpenoids)
''Carotenes''
orange pigments
* α-Carotene – to vitamin A: carrots, pumpkins, maize, tangerine, orange
* β-Carote ...
* CRT (genetics)
CRT is the gene cluster responsible for the biosynthesis of carotenoids. Those genes are found in eubacteria,Carotenoid biosynthetic pathway: molecular phylogenies and evolutionary behavior of crt genes in eubacteria. Phadwal K, Gene, 17 January 2 ...
, gene cluster
A gene cluster is a group of two or more genes found within an organism's DNA that encode similar peptide, polypeptides or proteins which collectively share a generalized function and are often located within a few thousand base pairs of each othe ...
responsible for the biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthe ...
of carotenoids
* E number#E100–E199 (colours)
* Phytochemistry
Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human and ...
References
External links
* {{Authority control Bioindicators Photosynthesis