Kappa Pavonis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kappa Pavonis (κ Pav) is a variable star in the
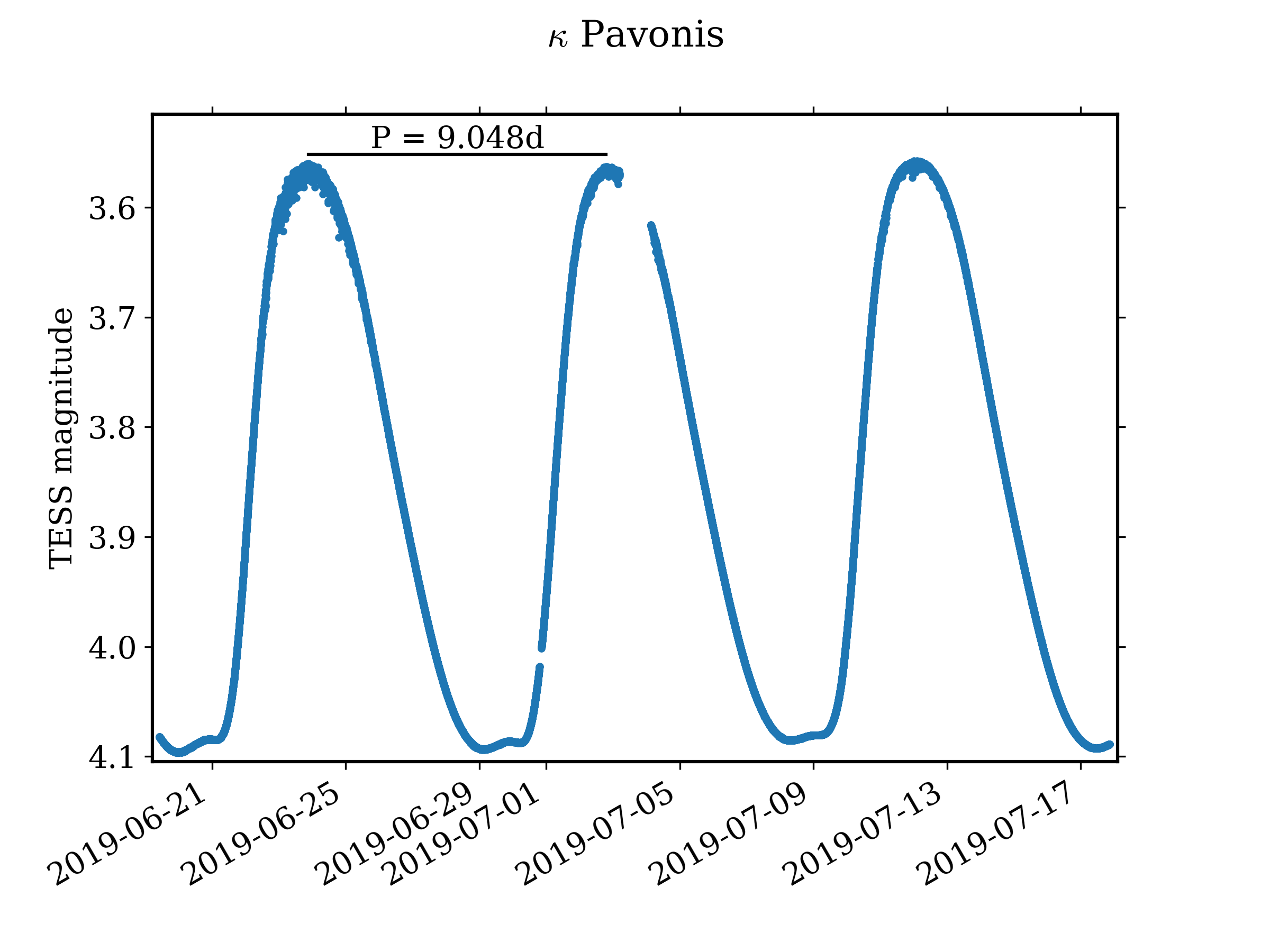 κ Pavonis ranges between apparent magnitudes 3.91 and 4.78, and spectral types F5 to G5, over a period of 9.1 days. It is a W Virginis variable, a type II Cepheid thought to be evolving along a blue loop from the thermal pulsing asymptotic giant branch.
κ Pav shows sudden small changes in the period of its otherwise highly regular pulsations. The period has changed at times by as much as 16 minutes from its average of around 9 days and 2 hours. The star also is considered peculiar compared to other W Virginis stars such as
κ Pavonis ranges between apparent magnitudes 3.91 and 4.78, and spectral types F5 to G5, over a period of 9.1 days. It is a W Virginis variable, a type II Cepheid thought to be evolving along a blue loop from the thermal pulsing asymptotic giant branch.
κ Pav shows sudden small changes in the period of its otherwise highly regular pulsations. The period has changed at times by as much as 16 minutes from its average of around 9 days and 2 hours. The star also is considered peculiar compared to other W Virginis stars such as
constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
Pavo. It is the brightest W Virginis variable in the sky.
Discovery
In 1901, κ Pavonis was reported to be a variable star with a magnitude range of 3.8 to 5.2 with a period of 9.0908 days. Further observations revealed radial velocity variations in time with the brightness variations, but this was assumed to indicate a spectroscopic binary system. The brightness variations were then interpreted as eclipses. Less than 10 years later, was κ Pav was listed as a likely Cepheid variable. In 1937 it was used as part of the effort to calibrate the Cepheid distance scale. Only years later were the separate period luminosity relationships for population I and II Cepheid variables identified, and κ Pav was assigned to the type II group.Variability
 κ Pavonis ranges between apparent magnitudes 3.91 and 4.78, and spectral types F5 to G5, over a period of 9.1 days. It is a W Virginis variable, a type II Cepheid thought to be evolving along a blue loop from the thermal pulsing asymptotic giant branch.
κ Pav shows sudden small changes in the period of its otherwise highly regular pulsations. The period has changed at times by as much as 16 minutes from its average of around 9 days and 2 hours. The star also is considered peculiar compared to other W Virginis stars such as
κ Pavonis ranges between apparent magnitudes 3.91 and 4.78, and spectral types F5 to G5, over a period of 9.1 days. It is a W Virginis variable, a type II Cepheid thought to be evolving along a blue loop from the thermal pulsing asymptotic giant branch.
κ Pav shows sudden small changes in the period of its otherwise highly regular pulsations. The period has changed at times by as much as 16 minutes from its average of around 9 days and 2 hours. The star also is considered peculiar compared to other W Virginis stars such as W Virginis
W Virginis is the prototype W Virginis variable, a subclass of the Cepheid variable stars. It is located in the constellation Virgo (constellation), Virgo, and varies between magnitudes 9.46 and 10.75 over a period of approximately 17 day ...
itself. A sub-group of W Virginis stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), or Nubecula Major, is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a distance of around 50 kiloparsecs (≈160,000 light-years), the LMC is the second- or third-closest galaxy to the Milky Way, after the ...
have been discovered to be hotter and more luminous than expected and given a ''pW'' (peculiar W Virginis) classification. It is proposed that κ Pav should also be given a pW classification. The peculiarities in the LMC stars may be due to binary interactions, although κ Pav is not known to be a binary star.
Properties
κ Pavonis is a large star several hundred times more luminous than the sun. Its spectral type varies as it pulsates, between F5 and G5 as the temperature changes, and the luminosity class changes from a bright giant to a supergiant. The luminosity class is relatively high for a star of this luminosity, due to the low surface gravity caused by a low mass pulsating star. The pulsations cause the star's radius to change by about above and below the mean size. The angular diameter of the disc has been directly observed to change during the pulsations.References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kappa Pavonis Pavo (constellation) F-type supergiants Pavonis, Kappa W Virginis variables F-type bright giants 093015 7107 174694 Durchmusterung objects G-type bright giants G-type supergiants