Kanishka on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kanishka I, also known as Kanishka the Great, was an emperor of the
File:Kushanmap.jpg, Kushan territories (full line) and maximum extent of Kushan dominions under Kanishka (dotted line). The conquests in India are according to the
Bactrian (official from )
Gandhari Prakrit
Hybrid
 A few coins at the beginning of his reign have a legend in the
A few coins at the beginning of his reign have a legend in the
Greek deities, with Greek names are represented on these early coins: * (, Hēlios), (,
 In Buddhist tradition Kanishka is regarded as of utmost importance. Although he never converted to Buddhism, he encouraged its teachings and provided royal sponsorship. Notably, he administered the 4th Buddhist Council in
In Buddhist tradition Kanishka is regarded as of utmost importance. Although he never converted to Buddhism, he encouraged its teachings and provided royal sponsorship. Notably, he administered the 4th Buddhist Council in
 Only six Kushan coins of the Buddha are known in gold (the sixth one is the centerpiece of an ancient piece of jewellery, consisting of a Kanishka Buddha coin decorated with a ring of heart-shaped ruby stones). All these coins were minted in gold under Kanishka I, and are in two different denominations: a
Only six Kushan coins of the Buddha are known in gold (the sixth one is the centerpiece of an ancient piece of jewellery, consisting of a Kanishka Buddha coin decorated with a ring of heart-shaped ruby stones). All these coins were minted in gold under Kanishka I, and are in two different denominations: a
 The Shakyamuni Buddha (with the legend "Sakamano Boudo", i.e. Shakamuni Buddha, another name for the historic Buddha Siddharta Gautama), standing to front, with left hand on hip and forming the abhaya mudra with the right hand. All these coins are in copper only, and usually rather worn.
The gown of the Shakyamuni Buddha is quite light compared to that on the coins in the name of Buddha, clearly showing the outline of the body, in a nearly transparent way. These are probably the first two layers of monastic clothing the '' antaravasaka'' and the '' uttarasanga''. Also, his gown is folded over the left arm (rather than being held in the left hand as above), a feature only otherwise known in the Bimaran casket and suggestive of a scarf-like '' uttariya''. He has an abundant topknot covering the
The Shakyamuni Buddha (with the legend "Sakamano Boudo", i.e. Shakamuni Buddha, another name for the historic Buddha Siddharta Gautama), standing to front, with left hand on hip and forming the abhaya mudra with the right hand. All these coins are in copper only, and usually rather worn.
The gown of the Shakyamuni Buddha is quite light compared to that on the coins in the name of Buddha, clearly showing the outline of the body, in a nearly transparent way. These are probably the first two layers of monastic clothing the '' antaravasaka'' and the '' uttarasanga''. Also, his gown is folded over the left arm (rather than being held in the left hand as above), a feature only otherwise known in the Bimaran casket and suggestive of a scarf-like '' uttariya''. He has an abundant topknot covering the
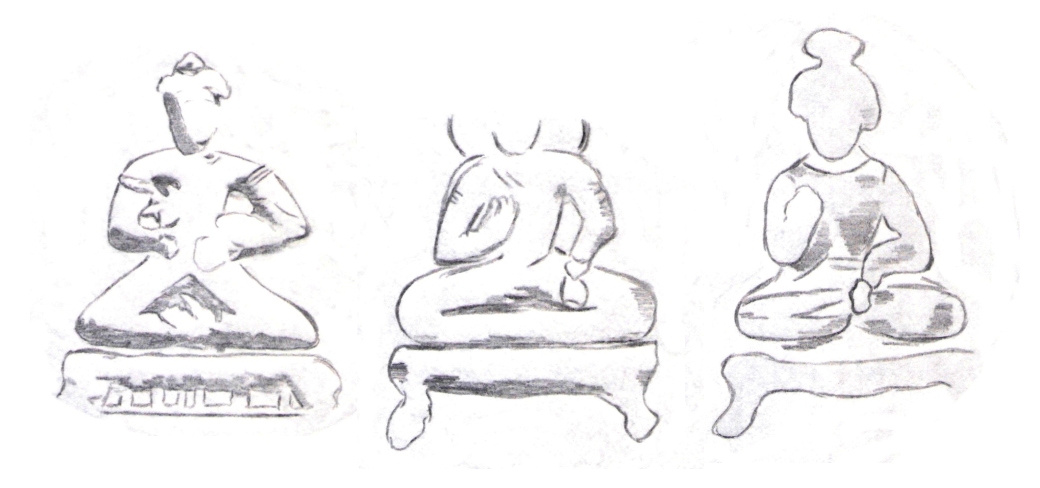 The Bodhisattva
The Bodhisattva
 The same story is repeated in a
The same story is repeated in a
Accessed: 20/12/2010
* Spooner, D. B. (1908–9): "Excavations at Shāh-jī-kī Dhērī."; ''Archaeological Survey of India, 1908-9''. * Wood, Frances (2003). ''The Silk Road: Two Thousand Years in the Heart of Asia''. University of California Press. Hbk (2003), ; pbk. (2004)
A rough guide to Kushana history.Coins of Kanishka
{{Authority control Kushan emperors 2nd-century Indian monarchs Indian Buddhist monarchs
Kushan dynasty
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
, under whose reign (–150 CE) the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises (Kushan language: ŒöŒøŒ∂ŒøœÖŒªŒøœÖ ŒöŒ±Œ¥œÜŒπŒ∂ŒøœÖ, also ŒöŒøŒ∂ŒøŒªŒ± ŒöŒ±Œ¥Œ±œÜŒµœÇ; Kharosthi: ê®êê®Çê®óê®Çê®´ ê®êê®Ø, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ', '; ; r. 30‚Äì80 CE, or 40‚Äì90 CE accor ...
, founder of the Kushan empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
, Kanishka came to rule an empire extending from Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
and Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
to Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
on the Gangetic plain. The main capital of his empire was located at ''Puru·π£apura'' (Peshawar
Peshawar is the capital and List of cities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by population, largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is the sixth most populous city of Pakistan, with a district p ...
) in Gandhara, with another major capital at Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
. Coins of Kanishka were found in Tripuri (present-day Jabalpur
Jabalpur, formerly Jubbulpore, is a city situated on the banks of Narmada River in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is the 3rd-largest urban agglomeration of the state and the 38th-largest of the country. Jabalpur is the administrative h ...
).
Although he never converted to the religion, his conquests and patronage of Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
played an important role in the development of the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
, and in the transmission of Mahayana Buddhism from Gandhara across the Karakoram
The Karakoram () is a mountain range in the Kashmir region spanning the border of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwestern extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range is withi ...
range to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. Around 127 CE, he replaced Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
with Bactrian as the official language of administration in the empire.
Earlier scholars believed that Kanishka ascended the Kushan throne in 78 CE, and that this date was used as the beginning of the Saka calendar era. However, historians no longer regard this date as that of Kanishka's accession. Falk estimates that Kanishka came to the throne in 127 CE.
Genealogy
There are two theories about Kanisha's origins, both based on the supposition of a separate Kanishka dynasty. The earlierSten Konow
image:StenKonow.jpg, Sten Konow
Sten Konow (17 April 1867 – 29 June 1948) was a Norwegian Indologist. He was a professor of Indian philology at the University of Oslo, Christiania University, Oslo, from 1910, until moving to Hamburg Universi ...
's is that Kanishka came from Khotan
Hotan (also known by #Etymology, other names) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region in Northwestern China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become an ...
, having been summoned as an ethnic ally at the time of troubles after Vima's reign. Konow supports this theory by citing a Tibetan tradition that a Khotanese expedition to India of about A.D. 120 was commanded by a King ''Vijayakirti'' along with a King ''Kanika'' and the king of ''Guzan''.
Roman Ghirshman's similar theory is that Kanishka was originally king of Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
before becoming suzerain of the dynasty as a whole. He cites the above-mentioned Khalatse epigraph, which may allude to Kushan power reaching the northeast corner of Kashmir, and also the Rajatarangini
''RƒÅjatara·πÖgi·πჴ'' (Sanskrit: Devanagari, ý§∞ý§æý§úý§§ý§∞ý§ôý•çý§óý§øý§£ý•Ä, IAST, romanized: ''rƒÅjatara·πÖgi·πჴ'', International Phonetic Alphabet, IPA: Help:IPA/Sanskrit, æ…ëÀê.dÕ° ë…ê.tÙ…êÀà…æ…ê≈ã.…°i.…≥iÀê ) is a metrical legend ...
, in which the list of Kushan kings of Kashmir gave Kanishka's name as the third of a sequence, along with the names of ''Hushka'' and ''Jushka''. Finally, testimony of Kanishka's activity in Kashmir in favor of the Buddhist faith suggests that he favored the region above others and that he founded Peshawar
Peshawar is the capital and List of cities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by population, largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is the sixth most populous city of Pakistan, with a district p ...
as his capital to be close to Kashmir.
He was of Yuezhi
The Yuezhi were an ancient people first described in China, Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defea ...
ethnicity and his native language was probably Tocharian. Kanishka was the successor of Vima Kadphises, as demonstrated by an impressive genealogy of the Kushan kings, known as the Rabatak inscription
The Rabatak Inscription is a stone inscribed with text written in the Bactrian language and Greek script, found in 1993 at Rabatak, near Surkh Kotal in Afghanistan. The inscription relates to the rule of the Kushan emperor Kanishka, and gives ...
. The connection of Kanishka with other Kushan rulers is described in the Rabatak inscription as Kanishka makes the list of the kings who ruled up to his time: Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises (Kushan language: ŒöŒøŒ∂ŒøœÖŒªŒøœÖ ŒöŒ±Œ¥œÜŒπŒ∂ŒøœÖ, also ŒöŒøŒ∂ŒøŒªŒ± ŒöŒ±Œ¥Œ±œÜŒµœÇ; Kharosthi: ê®êê®Çê®óê®Çê®´ ê®êê®Ø, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ', '; ; r. 30‚Äì80 CE, or 40‚Äì90 CE accor ...
as his great-grandfather, Vima Taktu as his grandfather, Vima Kadphises as his father, and himself Kanishka: "for King Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises (Kushan language: ŒöŒøŒ∂ŒøœÖŒªŒøœÖ ŒöŒ±Œ¥œÜŒπŒ∂ŒøœÖ, also ŒöŒøŒ∂ŒøŒªŒ± ŒöŒ±Œ¥Œ±œÜŒµœÇ; Kharosthi: ê®êê®Çê®óê®Çê®´ ê®êê®Ø, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ', '; ; r. 30‚Äì80 CE, or 40‚Äì90 CE accor ...
(his) great grandfather, and for King Vima Taktu (his) grandfather, and for King Vima Kadphises (his) father, and *also for himself, King Kanishka".
Conquests in India and Central Asia
Kanishka's empire was certainly vast. It extended from southernUzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
and Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
, north of the Amu Darya (Oxus
The Amu Darya ( ),() also shortened to Amu and historically known as the Oxus ( ), is a major river in Central Asia, which flows through Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Ku ...
) in the north west to Northern India, as far as Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
in the south east (the Rabatak inscription
The Rabatak Inscription is a stone inscribed with text written in the Bactrian language and Greek script, found in 1993 at Rabatak, near Surkh Kotal in Afghanistan. The inscription relates to the rule of the Kushan emperor Kanishka, and gives ...
even claims he held Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
and Sri Champa), and his territory also included Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
, where there was a town Kanishkapur (modern day Kanispora), named after him not far from the Baramulla Pass and which still contains the base of a large stupa. The Buddhist text ''Śrīdharmapiṭakanidānasūtra''—known via a Chinese translation made in AD 472—refers to the conquest of Pataliputra by Kanishka.
Knowledge of his hold over Central Asia is less well established. The '' Hou Hanshu'', states that general Ban Chao
Ban Chao (; 32–102 CE), courtesy name Zhongsheng, was a Chinese diplomat, explorer, and military general of the Eastern Han dynasty. He was born in Fufeng (region), Fufeng, now Xianyang, Shaanxi. Three of his family members—father Ban Biao, ...
fought battles near Khotan
Hotan (also known by #Etymology, other names) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region in Northwestern China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become an ...
with a Kushan army of 70,000 men led by an otherwise unknown Kushan viceroy named Xie ( zh, 謝) in 90 AD. Ban Chao claimed to be victorious, forcing the Kushans to retreat by use of a scorched-earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy of destroying everything that allows an enemy military force to be able to fight a war, including the deprivation and destruction of water, food, humans, animals, plants and any kind of tools and i ...
policy. The territories of Kashgar
Kashgar () or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is a city in the Tarim Basin region of southern Xinjiang, China. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, located near the country's border with Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. For over 2,000 years, Kashgar ...
, Khotan
Hotan (also known by #Etymology, other names) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region in Northwestern China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become an ...
and Yarkand
Yarkant County,, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also SASM/GNC ro ...
were Chinese dependencies in the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Xinjiang, Northwestern China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, Ch ...
, modern Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People' ...
. Several coins of Kanishka have been found in the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Xinjiang, Northwestern China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, Ch ...
.
Kanishka possibly fought off an invasion by the Parthian Empire in his reign. The war is attested in a single source, a Chinese translation of a lost Sanskrit original, '' A History of the Buddha's Successors''.
Rabatak inscription
The Rabatak Inscription is a stone inscribed with text written in the Bactrian language and Greek script, found in 1993 at Rabatak, near Surkh Kotal in Afghanistan. The inscription relates to the rule of the Kushan emperor Kanishka, and gives ...
, the northern expansion into the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Xinjiang, Northwestern China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, Ch ...
is mainly suggested by coin finds and Chinese chronicles.
, capital = Peshawar
Peshawar is the capital and List of cities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by population, largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is the sixth most populous city of Pakistan, with a district p ...
( ''Puru·π£apura'')Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the Pothohar region of Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the ...
(''Takṣaśilā'')Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
(''Mathurā'')
, common_languages = Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
(official until )Bactrian (official from )
Gandhari Prakrit
Hybrid
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
File:Probable statue of Kanishka, Surkh Kotal. Kabul Museum (2nd century CE).jpg, Probable statue of Kanishka, Surkh Kotal, 2nd century CE. Kabul Museum.
File:Bronze coin of Kanishka found in Khotan.jpg, Bronze coin of Kanishka, found in Khotan
Hotan (also known by #Etymology, other names) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region in Northwestern China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become an ...
, modern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
.
File:Bengal. Samatata. Coin of Vira Jadamarah imitative of Kushan coinage of Kanishka I. Circa 2nd-3rd century CE.jpg, Samatata
Samata·π≠a (Brahmi script: ''sa-ma-ta-·π≠a'') was an ancient geopolitical division of Bengal in the eastern Indian subcontinent. The Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman account of Sounagoura is linked to the kingdom of Samatata. Its territory corres ...
coinage of king Vira Jadamarah, in imitation of the Kushan coinage of Kanishka I
Kanishka I, also known as Kanishka the Great, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (–150 CE) the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadp ...
. Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
, .
Kanishka's coins
Kanishka's coins portray images of Indian,Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, Iranian
Iranian () may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Iran
** Iranian diaspora, Iranians living outside Iran
** Iranian architecture, architecture of Iran and parts of the rest of West Asia
** Iranian cuisine, cooking traditions and practic ...
and even Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
o-Elamite
Elamite, also known as Hatamtite and formerly as Scythic, Median, Amardian, Anshanian and Susian, is an extinct language that was spoken by the ancient Elamites. It was recorded in what is now southwestern Iran from 2600 BC to 330 BC. Elamite i ...
divinities, demonstrating the religious syncretism
Religious syncretism is the blending of religious belief systems into a new system, or the incorporation of other beliefs into an existing religious tradition.
This can occur for many reasons, where religious traditions exist in proximity to each ...
in his beliefs. Kanishka's coins from the beginning of his reign bear legends in Greek language and script and depict Greek divinities. Later coins bear legends in Bactrian, the Iranian language
The Iranian languages, also called the Iranic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian language ...
that the Kushans evidently spoke, and Greek divinities were replaced by corresponding Iranian ones. All of Kanishka's coins – even ones with a legend in the Bactrian language – were written in a modified Greek script that had one additional glyph (Ϸ) to represent /š/ (''sh''), as in the word 'Ku''sh''an' and 'Kani''sh''ka'.
On his coins, the king is typically depicted as a bearded man in a long coat and trousers gathered at the ankle, with flames emanating from his shoulders. He wears large rounded boots, and is armed with a long sword as well as a lance. He is frequently seen to be making a sacrifice on a small altar. The lower half of a lifesize limestone relief of Kanishka similarly attired, with a stiff embroidered surplice beneath his coat and spurs attached to his boots under the light gathered folds of his trousers, survived in the Kabul Museum until it was destroyed by the Taliban.
Hellenistic phase
 A few coins at the beginning of his reign have a legend in the
A few coins at the beginning of his reign have a legend in the Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
and script: , " oinof Kanishka, king of kings." Greek deities, with Greek names are represented on these early coins: * (, Hēlios), (,
Hephaistos
Hephaestus ( , ; eight spellings; ) is the Greek god of artisans, blacksmiths, carpenters, craftsmen, fire, metallurgy, metalworking, sculpture and volcanoes.Walter Burkert, ''Greek Religion'' 1985: III.2.ii; see coverage of Lemnos-based ...
), (, Selene
In ancient Greek mythology and Ancient Greek religion, religion, Selene (; , meaning "Moon")''A Greek–English Lexicon's.v. σελήνη is the goddess and personification of the Moon. Also known as Mene (), she is traditionally the daughter ...
), (, Anemos)
The inscriptions in Greek are full of spelling and syntactical errors.
Iranian / Indic phase
Following the transition to the Bactrian language on coins, Iranian and Indic divinities replace the Greek ones: * ŒëŒ°ŒîŒüŒß''œ∑''Œü (''ardoxsho'', Ashi Vanghuhi) * ŒõŒ°ŒüŒüŒëŒ£ŒÝŒü (''lrooaspo'', Drvaspa) * ŒëŒò''œ∑''Œü (''adsho'', Atar) * Œ¶ŒëŒ°Œ°Œü (''pharro'', personified khwarenah) * ŒúŒëŒü (''mao'', Mah) * ŒúŒôŒòŒ°Œü, ŒúŒôŒôŒ°Œü, ŒúŒôŒüŒ°Œü, ŒúŒôŒ•Œ°Œü (''mithro'', ''miiro'', ''mioro'', ''miuro'', variants ofMithra
Mithra ( ; ) is an ancient Iranian deity ('' yazata'') of covenants, light, oaths, justice, the Sun, contracts, and friendship. In addition to being the divinity of contracts, Mithra is also a judicial figure, an all-seeing protector of Truth ( ...
)
* ΜΟΖΔΟΟΑΝΟ (''mozdaooano'', "Mazda
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Fuch≈´, Hiroshima (town), Fuch≈´, Hiroshima Prefecture, Hiroshima, Japan. The company was founded on January 30, 1920, as Toyo Cork Kogyo Co., Ltd. ...
the victorious?")
* ΝΑΝΑ, ΝΑΝΑΙΑ, ΝΑΝΑ''Ϸ''ΑΟ (variants of pan-Asiatic ''Nana'', Sogdian ''nny'', in a Zoroastrian context Aredvi Sura Anahita
Anahita is the Old Persian form of the name of an Iranian goddess and appears in complete and earlier form as ('), the Avestan name of an Indo-Iranian cosmological figure venerated as the divinity of "the Waters" ( Aban) and hence associat ...
)
* ΜΑΝΑΟΒΑΓΟ (''manaobago'', Vohu Manah )
* ΟΑΔΟ (''oado'', Vata)
* ΟΡΑΛΑΓΝΟ (''orlagno'', Verethragna
Verethragna or Bahram () is a Zoroastrian yazata.
The neuter noun ''verethragna'' is related to Avestan ''verethra'', 'obstacle' and ''verethragnan'', 'victorious'. Representing this concept is the divinity Verethragna, who is the Hypostasis ( ...
)
Only a few Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
divinities were used as well:
* ΒΟΔΔΟ (''boddo'', Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was ...
),
* ''Ϸ''ΑΚΑΜΑΝΟ ΒΟΔΔΟ (''shakamano boddho'', Shakyamuni Buddha)
* ΜΕΤΡΑΓΟ ΒΟΔΔΟ (''metrago boddo'', the bodhisattava Maitreya
Maitreya (Sanskrit) or Metteyya (Pali), is a bodhisattva who is regarded as the future Buddhahood, Buddha of this world in all schools of Buddhism, prophesied to become Maitreya Buddha or Metteyya Buddha.Williams, Paul. ''Mahayana Buddhism: Th ...
)
Only a few Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
divinities were used as well:
* ΟΗ''Ϸ''Ο ('' oesho'', Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, …ê…¶aÀêdÙeÀê ã…êh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
). A recent study indicate that ''oesho'' may be Avestan
Avestan ( ) is the liturgical language of Zoroastrianism. It belongs to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family and was First language, originally spoken during the Avestan period, Old ...
Vayu
Vayu (; ), also known as Vata () and Pavana (), is the Hindu deities, Hindu god of the winds as well as the divine messenger of the gods. In the ''Vedic scriptures'', Vayu is an important deity and is closely associated with Indra, the king o ...
conflated with Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, …ê…¶aÀêdÙeÀê ã…êh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
.
Kanishka and Buddhism
 In Buddhist tradition Kanishka is regarded as of utmost importance. Although he never converted to Buddhism, he encouraged its teachings and provided royal sponsorship. Notably, he administered the 4th Buddhist Council in
In Buddhist tradition Kanishka is regarded as of utmost importance. Although he never converted to Buddhism, he encouraged its teachings and provided royal sponsorship. Notably, he administered the 4th Buddhist Council in Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
as the head of the council. It was presided by Vasumitra and Ashwaghosha. Images of the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was ...
based on 32 physical signs were made during his time.
He encouraged both the Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
school of Greco-Buddhist Art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of t ...
and the Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
school of art (an inescapable religious syncretism pervades Kushana rule). Kanishka personally seems to have embraced both Buddhism and the Persian attributes but he favored Buddhism, proven by his devotion to Buddhist teachings and prayer styles depicted in various books related to kushan empire.
His greatest contribution to Buddhist architecture was the Kanishka stupa at Purushapura, modern day Peshawar
Peshawar is the capital and List of cities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by population, largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is the sixth most populous city of Pakistan, with a district p ...
. Archaeologists who rediscovered the base of it in 1908–1909 estimated that this stupa had a diameter of 286 feet (87 metres). Reports of Chinese pilgrims such as Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mok·π£adeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making ...
indicate that its height was 600 to 700 (Chinese) "feet" (= roughly 180–210 metres or 591–689 ft.) and it was covered with jewels.
Kanishka is said to have been particularly close to the Buddhist scholar Ashvaghosha, who became his religious advisor in his later years.
Buddhist coinage
The Buddhist coins of Kanishka are comparatively rare (well under one percent of all known coins of Kanishka). Several show Kanishka on the obverse and the Buddha standing on the reverse. A few also show the Shakyamuni Buddha andMaitreya
Maitreya (Sanskrit) or Metteyya (Pali), is a bodhisattva who is regarded as the future Buddhahood, Buddha of this world in all schools of Buddhism, prophesied to become Maitreya Buddha or Metteyya Buddha.Williams, Paul. ''Mahayana Buddhism: Th ...
. Like all coins of Kanishka, the design is rather rough and proportions tend to be imprecise; the image of the Buddha is often slightly overdone, with oversize ears and feet spread apart in the same fashion as the Kushan king.
Three types of Kanishka's Buddhist coins are known:
Standing Buddha
 Only six Kushan coins of the Buddha are known in gold (the sixth one is the centerpiece of an ancient piece of jewellery, consisting of a Kanishka Buddha coin decorated with a ring of heart-shaped ruby stones). All these coins were minted in gold under Kanishka I, and are in two different denominations: a
Only six Kushan coins of the Buddha are known in gold (the sixth one is the centerpiece of an ancient piece of jewellery, consisting of a Kanishka Buddha coin decorated with a ring of heart-shaped ruby stones). All these coins were minted in gold under Kanishka I, and are in two different denominations: a dinar
The dinar () is the name of the principal currency unit in several countries near the Mediterranean Sea, with a more widespread historical use. The English word "dinar" is the transliteration of the Arabic دينار (''dīnār''), which was bor ...
of about 8 gm, roughly similar to a Roman aureus
The ''aureus'' ( ''aurei'', 'golden') was the main gold coin of ancient Rome from the 1st century BC to the early 4th century AD, when it was replaced by the ''solidus (coin), solidus''. This type of coin was sporadically issued during the Roman ...
, and a quarter dinar of about 2 gm. (about the size of an obol).
The Buddha is represented wearing the monastic robe, the '' antaravasaka'', the '' uttarasanga'', and the overcoat '' sanghati''.
The ears are extremely large and long, a symbolic exaggeration possibly rendered necessary by the small size of the coins, but otherwise visible in some later Gandharan statues of the Buddha typically dated to the 3rd–4th century CE (''illustration, left''). He has an abundant topknot covering the usnisha, often highly stylised in a curly or often globular manner, also visible on later Buddha statues of Gandhara.
In general, the representation of the Buddha on these coins is already highly symbolic, and quite distinct from the more naturalistic and Hellenistic images seen in early Gandhara sculptures. On several designs a mustache is apparent. The palm of his right hand bears the Chakra
A chakra (; ; ) is one of the various focal points used in a variety of ancient meditation practices, collectively denominated as Tantra, part of the inner traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism.
The concept of the chakra arose in Hinduism. B ...
mark, and his brow bear the urna. An aureola
An aureola or aureole (diminutive of Latin ''aurea'', "golden") is the radiance of luminous cloud which, in paintings of sacred personages, surrounds the whole figure.
In Romance languages, the noun Aureola is usually more related to the d ...
, formed by one, two or three lines, surrounds him.
The full gown worn by the Buddha on the coins, covering both shoulders, suggests a Gandharan model rather than a Mathuran one.
"Shakyamuni Buddha"
 The Shakyamuni Buddha (with the legend "Sakamano Boudo", i.e. Shakamuni Buddha, another name for the historic Buddha Siddharta Gautama), standing to front, with left hand on hip and forming the abhaya mudra with the right hand. All these coins are in copper only, and usually rather worn.
The gown of the Shakyamuni Buddha is quite light compared to that on the coins in the name of Buddha, clearly showing the outline of the body, in a nearly transparent way. These are probably the first two layers of monastic clothing the '' antaravasaka'' and the '' uttarasanga''. Also, his gown is folded over the left arm (rather than being held in the left hand as above), a feature only otherwise known in the Bimaran casket and suggestive of a scarf-like '' uttariya''. He has an abundant topknot covering the
The Shakyamuni Buddha (with the legend "Sakamano Boudo", i.e. Shakamuni Buddha, another name for the historic Buddha Siddharta Gautama), standing to front, with left hand on hip and forming the abhaya mudra with the right hand. All these coins are in copper only, and usually rather worn.
The gown of the Shakyamuni Buddha is quite light compared to that on the coins in the name of Buddha, clearly showing the outline of the body, in a nearly transparent way. These are probably the first two layers of monastic clothing the '' antaravasaka'' and the '' uttarasanga''. Also, his gown is folded over the left arm (rather than being held in the left hand as above), a feature only otherwise known in the Bimaran casket and suggestive of a scarf-like '' uttariya''. He has an abundant topknot covering the ushnisha
The ushnisha (, Pali: ''u·πáhƒ´sa'') is a protuberance on top of the head of a Buddha. In Buddhist literature, it is sometimes said to represent the "crown" of a Buddha, a symbol of Enlightenment and status the King of the Dharma.
Descripti ...
, and a simple or double halo
HALO, halo, halos or haloes may refer to:
Most common meanings
* Halo (optical phenomenon)
* Halo (religious iconography), a ring of light around the image of a head
* ''Halo'' (franchise), a sci-fi video game series (2001–2021)
Arts and en ...
, sometimes radiating, surrounds his head.
"Maitreya Buddha"
 The Bodhisattva
The Bodhisattva Maitreya
Maitreya (Sanskrit) or Metteyya (Pali), is a bodhisattva who is regarded as the future Buddhahood, Buddha of this world in all schools of Buddhism, prophesied to become Maitreya Buddha or Metteyya Buddha.Williams, Paul. ''Mahayana Buddhism: Th ...
(with the legend "Metrago Boudo") cross-legged on a throne, holding a water pot, and also forming the Abhaya mudra. These coins are only known in copper and are quite worn out .
On the clearest coins, Maitreya seems to be wearing the armbands of an Indian prince, a feature often seen on the statuary of Maitreya. The throne is decorated with small columns, suggesting that the coin representation of Maitreya was directly copied from pre-existing statuary with such well-known features.
The qualification of "Buddha" for Maitreya is inaccurate, as he is instead a Bodhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva is a person who has attained, or is striving towards, '' bodhi'' ('awakening', 'enlightenment') or Buddhahood. Often, the term specifically refers to a person who forgoes or delays personal nirvana or ''bodhi'' in ...
(he is the Buddha of the future).
The iconography of these three types is very different from that of the other deities depicted in Kanishka's coinage. Whether Kanishka's deities are all shown from the side, the Buddhas only are shown frontally, indicating that they were copied from contemporary frontal representations of the standing and seated Buddhas in statuary. Both representations of the Buddha and Shakyamuni have both shoulders covered by their monastic gown, indicating that the statues used as models were from the Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
school of art, rather than Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
.
Buddhist statuary under Kanishka
Several Buddhist statues are directly connected to the reign of Kanishka, such as several Bodhisattva statues from theArt of Mathura
The Art of Mathura refers to a particular school of Indian art, almost entirely surviving in the form of sculpture, starting in the 2nd century BCE, which centered on the city of Mathura, in central northern India, during a period in which Bu ...
, while a few other from Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
are inscribed with a date in an era which is now thought to be the Yavana era, starting in 186 to 175 BCE.
Kanishka stupa
The " Kanishka casket" or "Kanishka reliquary", dated to the first year of Kanishka's reign in 127 CE, was discovered in a deposit chamber under Kanishka stupa, during the archaeological excavations in 1908–1909 in Shah-Ji-Ki-Dheri, just outside the present-day Ganj Gate of the old city of Peshawar. It is today at the Peshawar Museum, and a copy is in theBritish Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
. It is said to have contained three bone fragments of the Buddha, which are now housed in Mandalay
Mandalay is the second-largest city in Myanmar, after Yangon. It is located on the east bank of the Irrawaddy River, 631 km (392 mi) north of Yangon. In 2014, the city had a population of 1,225,553.
Mandalay was founded in 1857 by Ki ...
, Burma.
The casket is dedicated in Kharoshthi. The inscription reads:
: "(*mahara)jasa kanishkasa kanishka-pure nagare aya gadha-karae deya-dharme sarva-satvana hita-suhartha bhavatu mahasenasa sagharaki dasa agisala nava-karmi ana*kanishkasa vihare mahasenasa sangharame"
The text is signed by the maker, a Greek artist named ''Agesilas'', who oversaw work at Kanishka's stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
s (caitya), confirming the direct involvement of Greeks with Buddhist realisations at such a late date: "The servant Agisalaos, the superintendent of works at the vihara of Kanishka in the monastery of Mahasena" ("dasa agisala nava-karmi ana*kaniskasa vihara mahasenasa sangharame").
The lid of the casket shows the Buddha on a lotus pedestal, and worshipped by Brahma
Brahma (, ) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the triple deity, trinity of Para Brahman, supreme divinity that includes Vishnu and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity, Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp. 212– ...
and Indra
Indra (; ) is the Hindu god of weather, considered the king of the Deva (Hinduism), Devas and Svarga in Hinduism. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. volumes
Indra is the m ...
. The edge of the lid is decorated by a frieze of flying geese. The body of the casket represents a Kushan monarch, probably Kanishka in person, with the Iranian sun and moon gods on his side. On the sides are two images of a seated Buddha, worshiped by royal figures, can be assumed as Kanishka. A garland, supported by cherubs
A cherub (; : cherubim; ''kərūḇ'', pl. ''kərūḇīm'') is one type of supernatural being in the Abrahamic religions. The numerous depictions of cherubim assign to them many different roles, such as protecting the entrance of the Garden of ...
goes around the scene in typical Hellenistic style.
The attribution of the casket to Kanishka has been recently disputed, essentially on stylistic ground (for example the ruler shown on the casket is not bearded, to the contrary of Kanishka). Instead, the casket is often attributed to Kanishka's successor Huvishka.
Kanishka in Buddhist tradition
In Buddhist tradition, Kanishka is often described as an aggressive, hot tempered, rigid, strict, and a bit harsh kind of King before he got converted to Buddhism of which he was very fond, and after his conversion to Buddhism, he became an openhearted, benevolent, and faithful ruler. As in the Sri-dharma-pitaka-nidana sutra: :"At this time the King of Ngan-si (Pahlava) was very aggressive and of a violent nature....There was a bhikshu (monk) arhat who seeing the harsh deeds done by the king wished to make him repent. So by his supernatural force he caused the king to see the torments of hell. The king was terrified and repented and cried terribly and hence dissolved all his negatives within him and got self realised for the first time in life ." ' Additionally, the arrival of Kanishka was reportedly foretold or was predicted by the Buddha, as well as the construction of his stupa: :". . . the Buddha, pointing to a small boy making a mud tope....aid
In international relations, aid (also known as international aid, overseas aid, foreign aid, economic aid or foreign assistance) is – from the perspective of governments – a voluntary transfer of resources from one country to another. Th ...
that on that spot would erect a tope by his name." ''Vinaya sutra''
 The same story is repeated in a
The same story is repeated in a Khotan
Hotan (also known by #Etymology, other names) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region in Northwestern China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become an ...
ese scroll found at Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Sachu (Dunhuang) was ...
, which first described how Kanishka would arrive 400 years after the death of the Buddha. The account also describes how Kanishka came to raise his stupa:
:"A desire thus arose in anishka to build a vast stupa...at that time the four world-regents learnt the mind of the king. So for his sake they took the form of young boys.... ndbegan a st≈´pa of mud....the boys said to anishka'We are making the .'....At that time the boys changed their form.... ndsaid to him, 'Great king, by you according to the Buddha's prophecy is a to be built wholly (?) with a large st≈´pa and hither relics must be invited which the meritorious good beings...will bring."
Chinese pilgrims to India, such as Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mok·π£adeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making ...
, who travelled there around 630 CE also relays the story:
:" became sovereign of all Jambudvƒ´pa (Indian subcontinent) but he did not believe in Karma, but he treated Buddhism with honor and respect as he himself converted to Buddhism intrigued by the teachings and scriptures of it. When he was hunting in the wild country a white hare appeared; the king gave a chase and the hare suddenly disappeared at he site of the future stupa... hen the construction of the st≈´pa was not going as plannedthe king lost his patience and took the matter in his own hands and started resurrecting the plans precisely, thus completing the stupas with utmost perfection and perseverance. These two stupas are still in existence and were resorted to for cures by people afflicted with diseases."
King Kanishka because of his deeds was highly respected, regarded, honored by all the people he ruled and governed and was regarded the greatest king who ever lived because of his kindness, humbleness and sense of equality and self-righteousness among all aspects. Thus such great deeds and character of the king Kanishka made his name immortal and thus he was regarded "THE KING OF KINGS"Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mok·π£adeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making ...
, quoted in: Kumar (1973), p. 93.
Transmission of Buddhism to China
Buddhist monks from the region ofGandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
played a key role in the development and the transmission of Buddhist ideas in the direction of northern Asia from the middle of the 2nd century CE. The Kushan monk, Lokaksema (), became the first translator of Mahayana
Mahāyāna ( ; , , ; ) is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, Buddhist texts#Mahāyāna texts, texts, Buddhist philosophy, philosophies, and practices developed in ancient India ( onwards). It is considered one of the three main ex ...
Buddhist scriptures into Chinese and established a translation bureau at the Chinese capital Loyang. Central Asian and East Asian Buddhist monks appear to have maintained strong exchanges for the following centuries.
Kanishka was probably succeeded by Huvishka. How and when this came about is still uncertain. The inscription on The Sacred Rock of Hunza also shows the signs of Kanishka.
See also
*Menander I
Menander I Soter (, ; ), sometimes called Menander the Great, was an Indo-Greek king (reigned /155Bopearachchi (1998) and (1991), respectively. The first date is estimated by Osmund Bopearachchi and R. C. Senior, the other Boperachchi –1 ...
* Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism or Graeco-Buddhism was a cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism developed between the 4th century BC and the 5th century AD in Gandhara, which was in present-day Pakistan and parts of north-east Afghanis ...
Footnotes
References
* * Chavannes, √âdouard. (1906) "Trois G√©n√©raux Chinois de la dynastie des Han Orientaux. Pan Tch'ao (32‚Äì102 p. C.); ‚Äì son fils Pan Yong; ‚Äì Leang K'in (112 p. C.). Chapitre LXXVII du ''Heou Han chou''." ''T'oung pao'' 7, (1906) p. 232 and note 3. * Dobbins, K. Walton. (1971). ''The St≈´pa and VihƒÅra of Kanishka I''. The Asiatic Society of Bengal Monograph Series, Vol. XVIII. Calcutta. * Falk, Harry (2001): "The yuga of Sphujiddhvaja and the era of the Ku·π£√¢·πáas." In: ''Silk Road Art and Archaeology'' VII, pp. 121‚Äì136. * Falk, Harry (2004): "The Kani·π£ka era in Gupta records." In: ''Silk Road Art and Archaeology'' X (2004), pp. 167‚Äì176. * Foucher, M. A. 1901. "Notes sur la geographie ancienne du Gandh√¢ra (commentaire √Ý un chapitre de Hiuen-Tsang)." ''BEFEO'' No. 4, Oct. 1901, pp. 322‚Äì369. *Gnoli, Gherardo (2002). "The "Aryan" Language." ''JSAI'' 26 (2002). * Hargreaves, H. (1910‚Äì11): "Excavations at ShƒÅh-jƒ´-kƒ´ Dhƒìrƒ´"; ''Archaeological Survey of India, 1910‚Äì11''. * ** * Hill, John E. (2009) ''Through the Jade Gate to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes during the Later Han Dynasty, 1st to 2nd centuries CE''. BookSurge, Charleston, South Carolina. . * * Kumar, Baldev. 1973. ''The Early ''. New Delhi, Sterling Publishers. * Sims-Williams, Nicholas and Joe Cribb (1995/6): "A New Bactrian Inscription of Kanishka the Great." ''Silk Road Art and Archaeology'' 4 (1996), pp. 75‚Äì142. * Sims-Williams, Nicholas (1998): "Further notes on the Bactrian inscription of Rabatak, with an Appendix on the names of Kujula Kadphises and Vima Taktu in Chinese." ''Proceedings of the Third European Conference of Iranian Studies Part 1: Old and Middle Iranian Studies''. Edited by Nicholas Sims-Williams. Wiesbaden. 1998, pp. 79‚Äì93. * Sims-Williams, Nicholas.Accessed: 20/12/2010
* Spooner, D. B. (1908–9): "Excavations at Shāh-jī-kī Dhērī."; ''Archaeological Survey of India, 1908-9''. * Wood, Frances (2003). ''The Silk Road: Two Thousand Years in the Heart of Asia''. University of California Press. Hbk (2003), ; pbk. (2004)
External links
*A rough guide to Kushana history.
{{Authority control Kushan emperors 2nd-century Indian monarchs Indian Buddhist monarchs