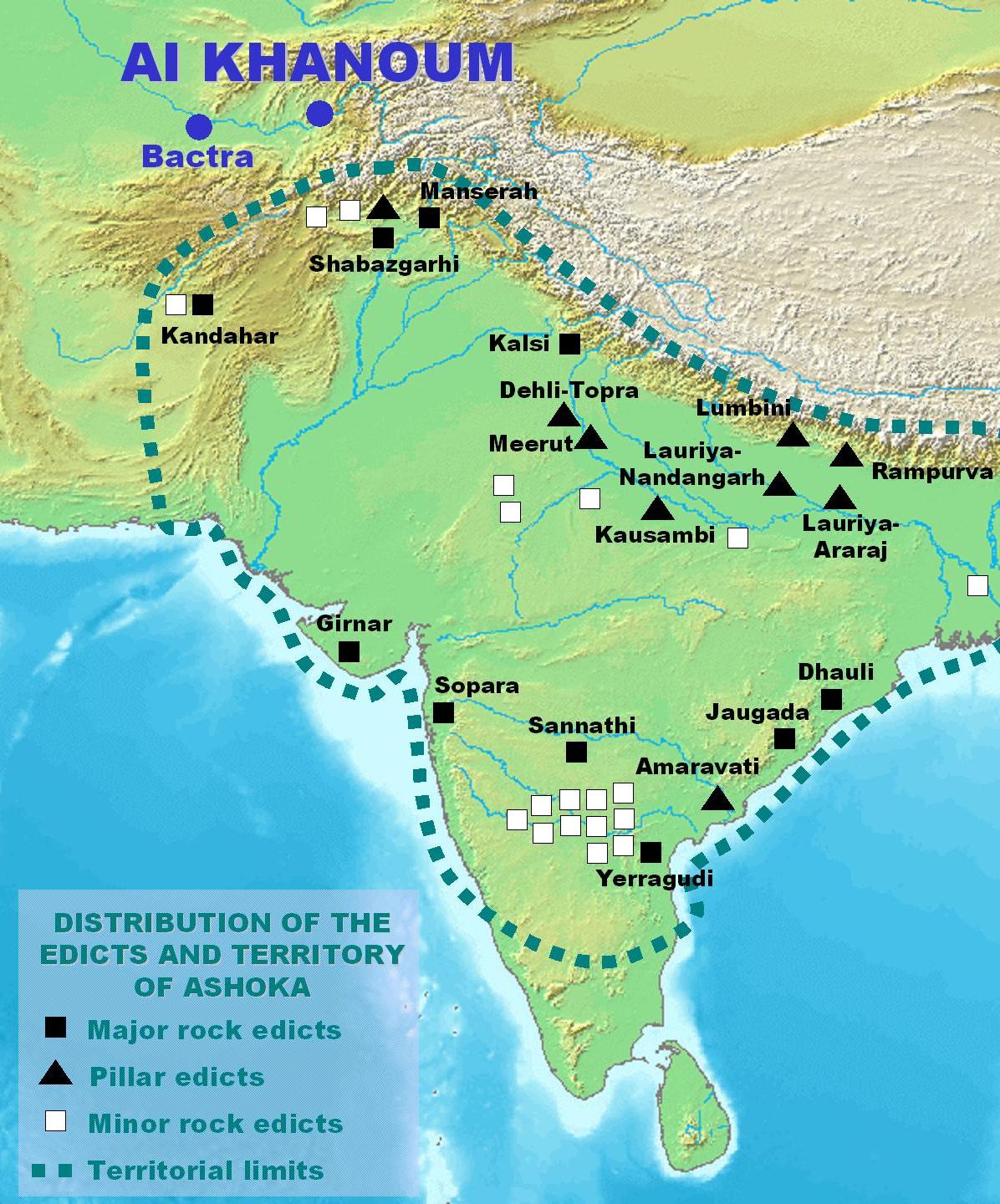
Kandahar Greek Edicts Of Ashoka on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kandahar Greek Edicts of Ashoka are among the
/ref> The beginning and the end of the fragment are lacking, which suggests the inscription was original significantly longer, and may have included all 14 of Ashoka's Edicts in Greek, as in several other locations in India. The plaque with the inscription was bought in the Kandahar market by the German doctor Seyring, and French archaeologists found that it had been excavated in

 The Edict is a Greek version of the end of the 12th Edict (which describes moral precepts) and the beginning of the 13th Edict (which describes the King's remorse and conversion after the war in Kalinga), which makes it a portion of a Major Rock Edict. This inscription does not use another language in parallel, contrary to the famous
The Edict is a Greek version of the end of the 12th Edict (which describes moral precepts) and the beginning of the 13th Edict (which describes the King's remorse and conversion after the war in Kalinga), which makes it a portion of a Major Rock Edict. This inscription does not use another language in parallel, contrary to the famous
 The
The
The Oxford Handbook of Ancient Greek Religion
', Esther Eidinow, Julia Kindt, Oxford University Press, 2015
File:AsokaKandahar.jpg,
Major Rock Edicts
The Major Rock Edicts of Indian emperor Ashoka refer to 14 separate major Edicts of Ashoka which are significantly detailed and represent some of the earliest dated rock inscriptions of any Indian monarch. These edicts are preceded chronologica ...
of the Indian Emperor Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
(reigned 269-233 BCE), which were written in the Greek language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), south ...
and Prakrit language. They were found in the ancient area of Old Kandahar
Old Kandahar (locally known as Zorr Shaar, ; also Shahr-i-Kona, , meaning 'Old City') is a historical section of the city of Kandahar in southern Afghanistan.
The citadel
It is widely believed that after conquering Mundigak in 330 BC, Alexander ...
(known as Zor Shar in Pashto
Pashto ( , ; , ) is an eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family, natively spoken in northwestern Pakistan and southern and eastern Afghanistan. It has official status in Afghanistan and the Pakistani province of Khyb ...
, or Shahr-i-Kona in Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
) in Kandahar in 1963. It is thought that Old Kandahar
Old Kandahar (locally known as Zorr Shaar, ; also Shahr-i-Kona, , meaning 'Old City') is a historical section of the city of Kandahar in southern Afghanistan.
The citadel
It is widely believed that after conquering Mundigak in 330 BC, Alexander ...
was founded in the 4th century BCE by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
, who gave it the Ancient Greek name Ἀλεξάνδρεια Ἀραχωσίας ( Alexandria of Arachosia).
The extant edicts are found in a plaque of limestone, which probably belonged to a building, and its size is and it is about thick. These are the only Ashoka inscriptions thought to have belonged to a stone building.Une nouvelle inscription grecque d'Açoka, Schlumberger, Daniel, Comptes rendus des séances de l'Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres Année 1964 Volume 108 Numéro 1 pp. 126-14/ref> The beginning and the end of the fragment are lacking, which suggests the inscription was original significantly longer, and may have included all 14 of Ashoka's Edicts in Greek, as in several other locations in India. The plaque with the inscription was bought in the Kandahar market by the German doctor Seyring, and French archaeologists found that it had been excavated in
Old Kandahar
Old Kandahar (locally known as Zorr Shaar, ; also Shahr-i-Kona, , meaning 'Old City') is a historical section of the city of Kandahar in southern Afghanistan.
The citadel
It is widely believed that after conquering Mundigak in 330 BC, Alexander ...
. The plaque was then offered to the Kabul Museum, but its current location is unknown following the looting of the museum in 1992–1994.
Background
Greek communities lived in the northwest of the Mauryan empire, currently inPakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, notably ancient Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
near the current Pakistani capital of Islamabad
Islamabad (; , ; ) is the capital city of Pakistan. It is the country's tenth-most populous city with a population of over 1.1 million and is federally administered by the Pakistani government as part of the Islamabad Capital Territory. Bu ...
and in the region of Gedrosia
Gedrosia (; , ) is the Hellenization, Hellenized name of the part of coastal Balochistan that roughly corresponds to today's Makran. In books about Alexander the Great and his Diadochi, successors, the area referred to as Gedrosia runs from the I ...
, and presently in Southern Afghanistan, following the conquest and the colonization efforts of Alexander the Great around 323 BCE. These communities therefore were significant in the area of Afghanistan during the reign of Ashoka.
Content

 The Edict is a Greek version of the end of the 12th Edict (which describes moral precepts) and the beginning of the 13th Edict (which describes the King's remorse and conversion after the war in Kalinga), which makes it a portion of a Major Rock Edict. This inscription does not use another language in parallel, contrary to the famous
The Edict is a Greek version of the end of the 12th Edict (which describes moral precepts) and the beginning of the 13th Edict (which describes the King's remorse and conversion after the war in Kalinga), which makes it a portion of a Major Rock Edict. This inscription does not use another language in parallel, contrary to the famous Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription
The Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription, also known as the Kandahar Edict of Ashoka and less commonly as the Chehel Zina Edict, is an inscription in the Ancient Greek, Greek and Aramaic languages that dates back to 260 BCE and was carved b ...
in Greek language and Aramaic, discovered in the same general area.
The Greek language used in the inscription is of a very high level and displays philosophical refinement. It also displays an in-depth understanding of the political language of the Hellenic world in the 3rd century BCE. This suggests the presence of a highly cultured Greek presence in Kandahar at that time.
Implications
The proclamation of this edict in Kandahar is usually taken as proof that Ashoka had control over that part ofAfghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, presumably after Seleucus I had ceded this territory to Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (Sanskrit: elp:IPA/Sanskrit, t̪͡ɕɐn̪d̪ɾɐgupt̪ɐ mɐʊɾjɐ (reigned 320 BCE – c. 298 BCE) was the founder and the first emperor of the Maurya Empire, based in Magadha (present-day Bihar) in the Indian ...
in their 305 BCE peace agreement. The Edict also shows the presence of a sizable Greek population in the area where great efforts were made to convert them to Buddhism. At the same epoch, the Greeks were established in the Greco-Bactrian kingdom
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Ancient Greece, Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central Asia, Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid Empire, Seleucid satrap Diodotus I, Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, ...
, and particularly in the border city of Ai-Khanoum
Ai-Khanoum (, meaning 'Lady Moon'; ) is the archaeological site of a Hellenistic city in Takhar Province, Afghanistan. The city, whose original name is unknown, was likely founded by an early ruler of the Seleucid Empire and served as a mili ...
, in the northern part of Afghanistan.
Translation
Other inscriptions in Greek in Kandahar
 The
The Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription
The Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription, also known as the Kandahar Edict of Ashoka and less commonly as the Chehel Zina Edict, is an inscription in the Ancient Greek, Greek and Aramaic languages that dates back to 260 BCE and was carved b ...
, discovered in 1958, is the other well-known Greek inscription by Ashoka in the area of Kandahar. It was found on the mountainside of the Chil Zena outcrop on the western side of the city of Kandahar.
Two other inscriptions in Greek are known at Kandahar. One is a dedication by a Greek man who names himself "son of Aristonax" (3rd century BCE). The other is an elegiac composition by Sophytos son of Naratos (2nd century BCE).The Oxford Handbook of Ancient Greek Religion
', Esther Eidinow, Julia Kindt, Oxford University Press, 2015
Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription
The Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription, also known as the Kandahar Edict of Ashoka and less commonly as the Chehel Zina Edict, is an inscription in the Ancient Greek, Greek and Aramaic languages that dates back to 260 BCE and was carved b ...
in Greek and Aramaic, by Emperor Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
, 3rd century BCE, Kandahar.
File:Kandahar son of Aristonax inscription.jpg, Inscription in Greek by the "son of Aristonax", 3rd century BCE, Kandahar.
File:Kandahar Sophytes Inscription.jpg, Kandahar Sophytos Inscription, 2nd century BCE, Kandahar.
File:Kandahar_fortifications.jpg, Plan of ancient fortifications of Kandahar.
See also
*Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who ruled most of the Indian subcontinent from 268 BCE to 2 ...
* Gandharan Buddhism
Gandhāran Buddhism was the Buddhist culture of ancient Gandhāra, which was a major center of Buddhism in the northwestern Indian subcontinent from the 3rd century BCE to approximately 1200 CE.Kurt Behrendt, Pia Brancaccio, Gandharan Buddhism ...
* Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism or Graeco-Buddhism was a cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism developed between the 4th century BC and the 5th century AD in Gandhara, which was in present-day Pakistan and parts of north-east Afghanis ...
* Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
* Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription
The Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription, also known as the Kandahar Edict of Ashoka and less commonly as the Chehel Zina Edict, is an inscription in the Ancient Greek, Greek and Aramaic languages that dates back to 260 BCE and was carved b ...
* List of Edicts of Ashoka
* Pillars of Ashoka
The pillars of Ashoka are a series of Monolith, monolithic columns dispersed throughout the Indian subcontinent, erected—or at least inscribed with Edicts of Ashoka, edicts—by the 3rd Mauryan Emperor Ashoka the Great, who reigned from to ...
References
{{Central Asian history Archaeological discoveries in Afghanistan Edicts of Ashoka Kandahar Greek inscriptions