Ka (pharaoh) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ka, also (alternatively) Sekhen, Jürgen von Beckerath: ''Handbuch der ägyptischen Königsnamen'', Münchner ägyptologische Studien, Heft 49, Mainz : P. von Zabern, 1999,
available online
see p. 36-37 was a Predynastic
 Ka ruled over
Ka ruled over
File:Ka vase.JPG, Vessel from Ka's tomb in Abydos bearing Ka's serekh on display at the
available online
see p. 36-37 was a Predynastic
pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty ( ...
of Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ', shortened to , , locally: ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the Nile River valley south of the delta and the 30th parallel North. It thus consists of the entire Nile River valley from Cairo south to Lake N ...
belonging to Dynasty 0. He probably reigned during the first half of the 32nd century BC. The length of his reign is unknown.
Name
The correct reading of Ka's name remains uncertain. There are vessel inscriptions which show a serekh with a typical ''Ka''-symbol, both written upright correctly, but there are also inscriptions presenting an upright serekh with an upside-down ''Ka''-symbol inside. The second form of that writing indicates a reading as Sekhen (meaning "to embrace someone") rather than ''Ka''. It was also thought to be the birth name of Narmer. Because the reading of the name is so uncertain, Egyptologists and writing experts such as Ludwig David Morenz prefer a neutral reading as "King Arms". Ka's personal name may have been 'king Ap.'Reign
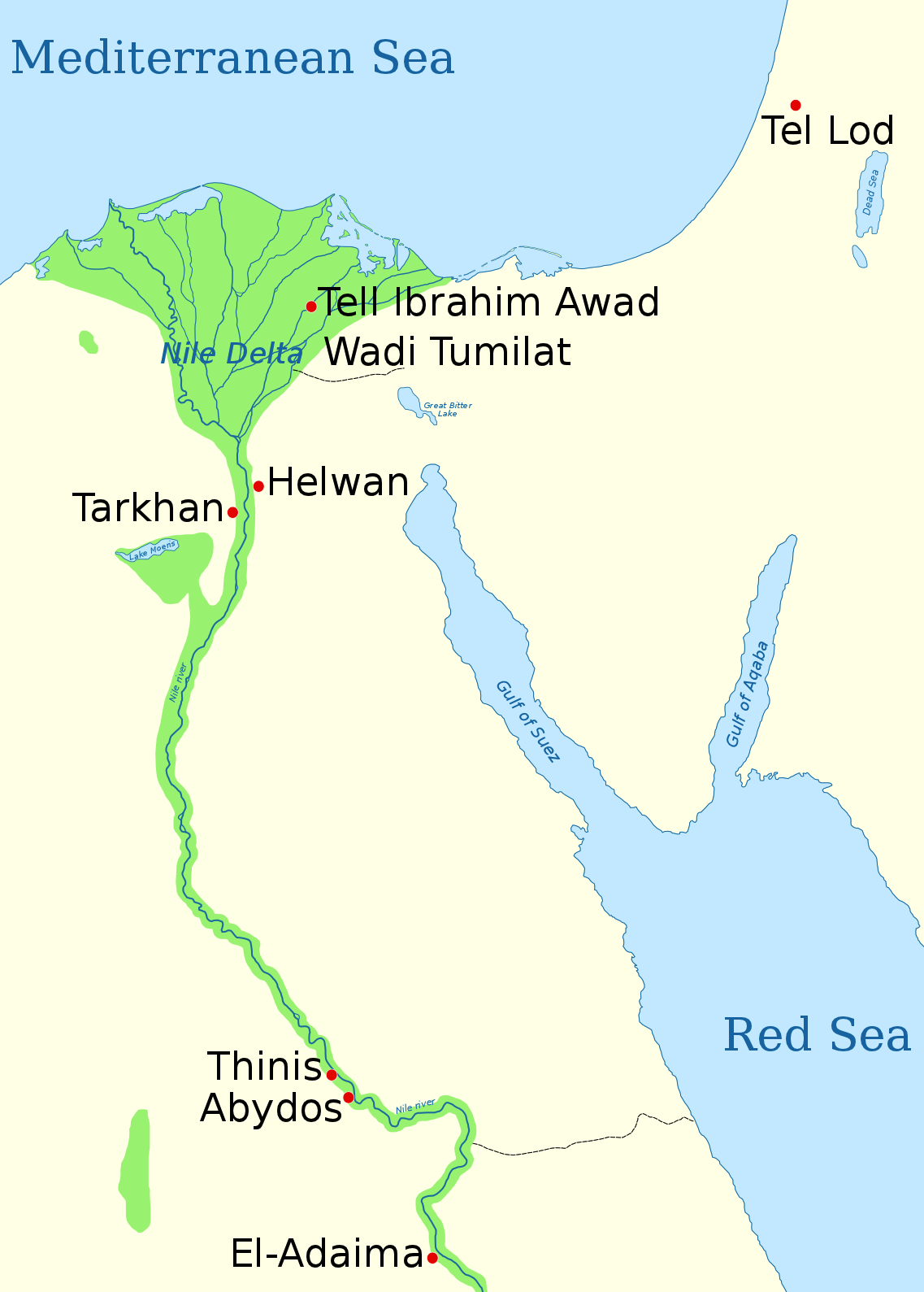
 Ka ruled over
Ka ruled over Thinis
Thinis ( Greek: Θίνις ''Thinis'', Θίς ''This'' ; Egyptian: Tjenu; ;
) was the capital city of pre- unification Upper Egypt. Thinis remains undiscovered but is well attested by ancient writers, including the classical historian Manetho ...
in the first half of the 32nd century BC and was buried at Umm el-Qa'ab
Umm El Qaʻāb (sometimes romanisation, romanised Umm El Gaʻab, ) is an archaeological site located at Abydos, Egypt. Its modern name, meaning "Mother of Pots", refers to the mound made of millions of broken pieces of pots which defines the landsc ...
. He most likely was the immediate successor to Iry-Hor and was succeeded either by Narmer or by Scorpion II. He is the earliest known Egyptian king with a '' serekh'' inscribed on a number of artifacts. This may thus be an innovation of his reign. Ka is one of the best attested predynastic kings with Narmer and Scorpion II. Beyond Abydos, he is attested in the predynastic necropolis of Adaima in Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ', shortened to , , locally: ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the Nile River valley south of the delta and the 30th parallel North. It thus consists of the entire Nile River valley from Cairo south to Lake N ...
and in the north in Tarkhan
Tarkhan (, or ; ; zh, c=達干/達爾罕/答剌罕; ; ; alternative spellings ''Tarkan'', ''Tarkhaan'', ''Tarqan'', ''Tarchan'', ''Turxan'', ''Tarcan'', ''Turgan, Tárkány, Tarján, Tarxan'') is an ancient Central Asian title used by various ...
, Helwan, Tell Ibrahim Awad, Tell el-Farkha (Eastern Nile Delta), Wadi Tumilat and as far north as Tel Lod in the Southern Levant.
The number of artifacts bearing Ka's serekh found outside Abydos is much greater than that of his predecessor. This may be the sign of an increasing influence and perhaps conquest of larger portions of Egypt by the Thinite kings.
Tomb
Two underground chambers, B7 and B9, in theUmm el-Qa'ab
Umm El Qaʻāb (sometimes romanisation, romanised Umm El Gaʻab, ) is an archaeological site located at Abydos, Egypt. Its modern name, meaning "Mother of Pots", refers to the mound made of millions of broken pieces of pots which defines the landsc ...
necropolis of Abydos are believed to be part of the tomb of King Ka. Each chamber is 1.90 m deep, B.7 is 6.0 × 3.2 m while B.9 is slightly smaller at 5.9 × 3.1 m; the two chambers are 1.80 m apart.
Ka's tomb was first excavated by Flinders Petrie in 1902. The excavations yielded fragments of flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
knife and pottery. In the southernmost chamber B7, more than forty inscriptions have been found on tall jars and cylinder vessels as well as a seal impression. The tomb of Ka (B7, B9) is close to that of Iry-Hor (B1, B2) and Narmer (B17, B18). Furthermore, it is located within a sequential order linking the older "U" cemetery with the First Dynasty tombs, thus suggesting that Ka succeeded Iry-Hor and preceded Narmer on the throne..
A cylinder jar found within the tomb, along with Ka's name, has inscribed the name "Ha, wife of the Horus Ka".
Gallery
British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
.
File:King ka seal.JPG, Seal impression with Ka's serekh. Note the absence of the Horus falcon. British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
.
File:Serekh of Ka.png, Shard bearing Ka's serekh from his tomb in Abydos.
File:KaSerekh2.png, Shard bearing Ka's serekh from his tomb.
File:Ka Tomb.jpg, Ka's tomb in the Umm el-Qa'ab
Umm El Qaʻāb (sometimes romanisation, romanised Umm El Gaʻab, ) is an archaeological site located at Abydos, Egypt. Its modern name, meaning "Mother of Pots", refers to the mound made of millions of broken pieces of pots which defines the landsc ...
File:Names of King Ka and Queen Ha on a jar.jpg, Names of Ka and Ha on a jar.
References
Bibliography
*External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Ka 32nd-century BC pharaohs Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown Wadi Tumilat