KELT-9 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
KELT-9b is an
Exoplanet Exploration Program 2017
/ref> The outer boundary of its atmosphere nearly reaches its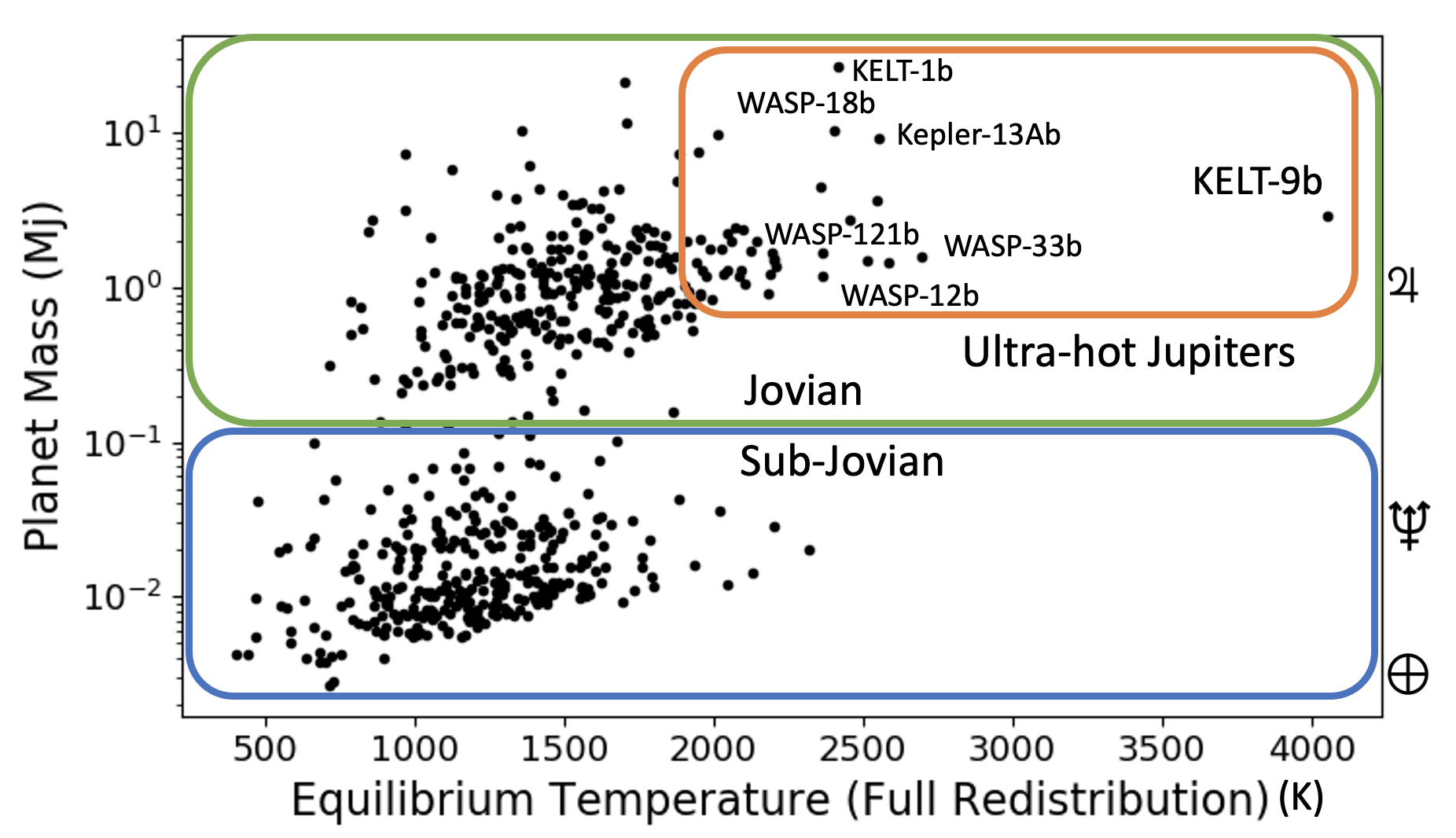 , KELT-9b is the hottest known exoplanet, with dayside temperatures approaching — warmer than some
, KELT-9b is the hottest known exoplanet, with dayside temperatures approaching — warmer than some
exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
and ultra-hot Jupiter that orbits the late B-type/early A-type star A type or type A may refer to: Science
* A-type asteroid, a type of relatively uncommon inner-belt asteroids
* A type blood, a type in the ABO blood group system
* A-type inclusion, a type of cell inclusion
* A-type potassium channel, a type of ...
KELT-9, located about 670 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year (ly or lyr), is a unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equal to exactly , which is approximately 9.46 trillion km or 5.88 trillion mi. As defined by the International Astr ...
s from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. Detected using the Kilodegree Extremely Little Telescope
The Kilodegree Extremely Little Telescope (or KELT) is an astronomical observation system formed by two robotic telescopes that are conducting a survey for transiting exoplanets around bright stars. The project is jointly administered by members ...
, the discovery of KELT-9b was announced in 2016. As of June 2017, it is the hottest known exoplanet.
Host star
The hoststar
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
, KELT-9, is 2 to 3 times larger and 2 to 3 times more massive than the sun. The surface temperature is , unusually hot for a star with a transit
Transit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Transit'' (1980 film), a 1980 Israeli film
* ''Transit'' (1986 film), a Canadian short film
* ''Transit'' (2005 film), a film produced by MTV and Staying-Alive about four people in countrie ...
ing planet. Prior to the discovery of KELT-9b, only six A-type stars were known to have planets, of which the warmest, WASP-33, is significantly cooler at ; no B-type stars were previously known to host planets. KELT-9, classified as B9.5-A0 could be the first B-type star known to have a planet. KELT-9b occupies a circular but strongly inclined orbit a mere 0.03462 AU from KELT-9 with an orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
of less than 1.5 day
A day is the time rotation period, period of a full Earth's rotation, rotation of the Earth with respect to the Sun. On average, this is 24 hours (86,400 seconds). As a day passes at a given location it experiences morning, afternoon, evening, ...
s.KELT-9 bExoplanet Exploration Program 2017
Physical properties
KELT-9b is a relatively largegiant planet
A giant planet, sometimes referred to as a jovian planet (''Jove'' being another name for the Roman god Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter), is a diverse type of planet much larger than Earth. Giant planets are usually primarily composed of low-boiling ...
at about 2.8 times the mass of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
; however given that its radius is nearly twice that of Jupiter, its density is less than half that of it. Like many hot Jupiter
Hot Jupiters (sometimes called hot Saturns) are a class of gas giant exoplanets that are inferred to be physically similar to Jupiter (i.e. Jupiter analogue, Jupiter analogues) but that have very short orbital periods (). The close proximity to t ...
s, KELT-9b is tidally locked
Tidal locking between a pair of co-orbiting astronomical bodies occurs when one of the objects reaches a state where there is no longer any net change in its rotation rate over the course of a complete orbit. In the case where a tidally locked ...
with its host star.NASA JPL, Pasadena CA (5 June 2017) Astronomers Find Planet Hotter Than Most Stars/ref> The outer boundary of its atmosphere nearly reaches its
Roche lobe
In astronomy, the Roche lobe is the region around a star in a binary system within which orbiting material is gravitationally bound to that star. It is an approximately teardrop-shaped region bounded by a critical gravitational equipotential, ...
, implying that the planet is experiencing rapid atmospheric escape
Atmospheric escape is the loss of planetary atmospheric gases to outer space. A number of different mechanisms can be responsible for atmospheric escape; these processes can be divided into thermal escape, non-thermal (or suprathermal) escape, and ...
driven by the extreme amount of radiation it receives from its host star. In 2020, atmospheric loss rate was measured to be equal to 18 - 68 Earth masses per billion years.
The planet's elemental abundances remain largely unknown as of 2022, but a low carbon-to-oxygen ratio is strongly suspected.
 , KELT-9b is the hottest known exoplanet, with dayside temperatures approaching — warmer than some
, KELT-9b is the hottest known exoplanet, with dayside temperatures approaching — warmer than some K-type stars K-type may refer to:
*AEC K-type, a bus chassis
*K-type star, a stellar spectral classification
*K-type filter, a type of electronic filter
*K-type asteroid
K-type asteroids are relatively uncommon asteroids with a moderately reddish spectrum shor ...
. Molecules on the day side are broken into their component atoms, so that normally sequestered refractory elements can exist as atomic species, including neutral oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
, neutral and singly ionize
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule i ...
d atomic iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
(Fe and Fe+) and singly ionized titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
(Ti+), only to temporarily reform once they reach the cooler night side, which is indirectly confirmed by measured enhanced heat transfer efficiency of 0.3 between dayside and nightside, likely driven by the latent heat of dissociation and recombination of the molecular hydrogen. Surprisingly, spectra taken in 2021 have unambiguously indicated a presence of metal oxides and hydrides in the planetary atmosphere, although higher resolution spectra taken in 2021 have not found any molecular emissions from the planetary dayside.
The thermosphere
The thermosphere is the layer in the Earth's atmosphere directly above the mesosphere and below the exosphere. Within this layer of the atmosphere, ultraviolet radiation causes photoionization/photodissociation of molecules, creating ions; the ...
layer of KELT-9b is expected to heat up to , driven by ionization of heavy metals atoms like iron.
See also
*51 Pegasi b
51 Pegasi b, officially named Dimidium (), is an extrasolar planet approximately away in the constellation of Pegasus. It was the first exoplanet to be discovered orbiting a main-sequence star, the Sun-like 51 Pegasi, and marked a breakthr ...
, the first-discovered Hot Jupiter
* List of hottest exoplanets
References
External links
* SIMBAD entry for HD 195689 {{Stars of Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Transiting exoplanets Exoplanets discovered in 2016 Exoplanets discovered by KELT Hot Jupiters