Julia (unidentified Sound) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The following is a list of unidentified, or formerly unidentified, sounds. All of the NOAA sound files in this article have been sped up by at least a factor of 16 to increase intelligibility by condensing them and raising the frequency from
 Upsweep is an unidentified sound detected on the American NOAA's equatorial autonomous
Upsweep is an unidentified sound detected on the American NOAA's equatorial autonomous
 Bloop is the name given to an ultra-low-frequency and extremely powerful underwater sound detected by the U.S.
Bloop is the name given to an ultra-low-frequency and extremely powerful underwater sound detected by the U.S.
/ref> The name was given because the sound slowly decreases in
/ref> The sound has been picked up several times each year since 1997. One of the
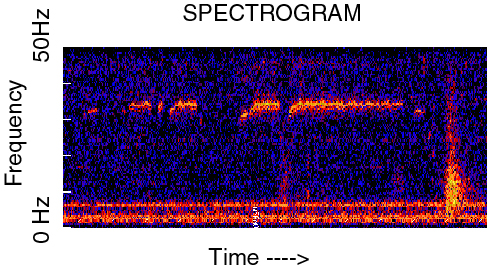 The Sea Train is the name given to a sound recorded on March 5, 1997, on the Equatorial Pacific Ocean autonomous hydrophone array. The sound rises to a quasi-steady frequency. According to the NOAA, the origin of the sound is most likely generated by a very large iceberg grounded in the
The Sea Train is the name given to a sound recorded on March 5, 1997, on the Equatorial Pacific Ocean autonomous hydrophone array. The sound rises to a quasi-steady frequency. According to the NOAA, the origin of the sound is most likely generated by a very large iceberg grounded in the
Canadian military investigating mysterious 'ping' sound scaring sea animals
/ref>
infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low frequency sound or incorrectly subsonic (subsonic being a descriptor for "less than the speed of sound"), describes sound waves with a Audio frequency, frequency below the lower limit of human audibility ...
to a more audible and reproducible range.
Formerly unidentified sounds
NOAA
The following previously unidentified sounds have been detected by the U.S.National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
(NOAA) using its Equatorial Pacific Ocean autonomous hydrophone array. Researchers have since posited volcanic and glacial origins for the sounds.
Upsweep
 Upsweep is an unidentified sound detected on the American NOAA's equatorial autonomous
Upsweep is an unidentified sound detected on the American NOAA's equatorial autonomous hydrophone
A hydrophone () is a microphone designed for underwater use, for recording or listening to underwater sound. Most hydrophones contains a piezoelectric transducer that generates an electric potential when subjected to a pressure change, such as a ...
arrays. This sound was present when the Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory began recording its sound surveillance system, SOSUS
Sound Surveillance System (SOSUS) was the original name for a submarine detection system based on passive sonar developed by the United States Navy to track Soviet Navy, Soviet submarines. The system's true nature was classified with the name a ...
, in August 1991. It consists of a long train of narrow-band upsweeping sounds of several seconds in duration each. The source level is high enough to be recorded throughout the Pacific.
The sound appears to be seasonal, generally reaching peaks in spring and autumn, but it is unclear whether this is due to changes in the source or seasonal changes in the propagation environment. The source can be roughly located at , between New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
. Scientists/researchers of NOAA speculate the sound to be underwater volcanic activity. The Upsweep's level of sound (volume) has been declining since 1991, but it can still be detected on NOAA's equatorial autonomous hydrophone arrays.
Whistle
This sound, dubbed the Whistle, was recorded by the eastern Pacific autonomous hydrophone deployed at on July 7, 1997 at 07:30 GMT. According to NOAA, the Whistle is similar to volcanogenic sounds previously recorded in the Marianavolcanic arc
A volcanic arc (also known as a magmatic arc) is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate, with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc ...
of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
. NOAA also stated that locating the source of an event requires at least three recording instruments, and since the Whistle was only recorded on the NW hydrophone, the sound could have traveled a great distance from its source volcano before detection.
Bloop
 Bloop is the name given to an ultra-low-frequency and extremely powerful underwater sound detected by the U.S.
Bloop is the name given to an ultra-low-frequency and extremely powerful underwater sound detected by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
(NOAA) in 1997. The sound is consistent with the noises generated by icequake
A cryoseism, ice quake or frost quake, is a seismic event caused by a sudden cracking action in frozen soil or rock saturated with water or ice, or by stresses generated at frozen lakes. As water drains into the ground, it may eventually freeze ...
s in large icebergs, or large icebergs scraping the ocean floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as seabeds.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
.
The sound's source was roughly triangulated to a remote point in the south Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
west of the southern tip of South America, and the sound was detected several times by the Equatorial Pacific Ocean autonomous hydrophone array.
According to the NOAA description, it "rises rapidly in frequency over about one minute and was of sufficient amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
to be heard on multiple sensors, at a range of over ." NOAA's Christopher Fox did not believe its origin was man-made, such as a submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
or bomb
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechan ...
. While the audio profile of Bloop does resemble that of a living creature, the source was a mystery both because it was different from known sounds and because it was several times louder than the loudest recorded animal, the blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known ever to have existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can ...
.
The NOAA Vents Program has attributed Bloop to a large icequake
A cryoseism, ice quake or frost quake, is a seismic event caused by a sudden cracking action in frozen soil or rock saturated with water or ice, or by stresses generated at frozen lakes. As water drains into the ground, it may eventually freeze ...
. Numerous icequakes share similar spectrograms with Bloop, as well as the amplitude necessary to spot them despite ranges exceeding . This was found during the tracking of iceberg A53a as it disintegrated near South Georgia Island
South Georgia is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic Ocean that is part of the British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. It lies around east of the Falkland Islands. ...
in early 2008, suggesting that the iceberg(s) involved in generating the sound were most likely between Bransfield Straits and the Ross Sea
The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land and within the Ross Embayment, and is the southernmost sea on Earth. It derives its name from the British explorer James Clark Ross who ...
, or possibly at Cape Adare
Cape Adare is a prominent cape of black basalt forming the northern tip of the Adare Peninsula and the north-easternmost extremity of Victoria Land, East Antarctica.
It is the site of the first confirmed landing on the Antarctic mainlan ...
in Antarctica, a well-known source of cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
The 13th International Institute of Refrigeration's (IIR) International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington, DC in 1971) endorsed a univers ...
signals.
Julia
Julia is a sound recorded on March 1, 1999, by the U.S.National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
(NOAA). NOAA said the source of the sound was most likely a large iceberg that had run aground off Antarctica. It was loud enough to be heard over the entire Equatorial Pacific Ocean autonomous hydrophone array, with a duration of about 2 minutes and 43 seconds. Due to the uncertainty of the arrival azimuth
An azimuth (; from ) is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north, in a local or observer-centric spherical coordinate system.
Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer ( origin) to a point ...
, the point of origin could only be narrowed to between Bransfield Straits and Cape Adare
Cape Adare is a prominent cape of black basalt forming the northern tip of the Adare Peninsula and the north-easternmost extremity of Victoria Land, East Antarctica.
It is the site of the first confirmed landing on the Antarctic mainlan ...
.
Slow Down
Slow Down is a sound recorded on May 19, 1997, in the EquatorialPacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
. The source of the sound was most likely a large iceberg as it became grounded.NOAA Cryogenic "Slow Down"/ref> The name was given because the sound slowly decreases in
frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
over about seven minutes. It was recorded using an autonomous hydrophone array.NOAA page/ref> The sound has been picked up several times each year since 1997. One of the
hypotheses
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific method, scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educ ...
on the origin of the sound is moving ice in Antarctica. Sound spectrograms of vibrations caused by friction closely resemble the spectrogram of the Slow Down. This suggests the source of the sound could have been caused by the friction of a large ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice s ...
moving over land.
Sea Train
 The Sea Train is the name given to a sound recorded on March 5, 1997, on the Equatorial Pacific Ocean autonomous hydrophone array. The sound rises to a quasi-steady frequency. According to the NOAA, the origin of the sound is most likely generated by a very large iceberg grounded in the
The Sea Train is the name given to a sound recorded on March 5, 1997, on the Equatorial Pacific Ocean autonomous hydrophone array. The sound rises to a quasi-steady frequency. According to the NOAA, the origin of the sound is most likely generated by a very large iceberg grounded in the Ross Sea
The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land and within the Ross Embayment, and is the southernmost sea on Earth. It derives its name from the British explorer James Clark Ross who ...
, near Cape Adare
Cape Adare is a prominent cape of black basalt forming the northern tip of the Adare Peninsula and the north-easternmost extremity of Victoria Land, East Antarctica.
It is the site of the first confirmed landing on the Antarctic mainlan ...
.
Other identified sounds
* Bio-duck, a quacking-like sound produced by theAntarctic minke whale
The Antarctic minke whale or southern minke whale (''Balaenoptera bonaerensis'') is a species of minke whale within the suborder of baleen whales. It is the second smallest rorqual after the common minke whale and the third smallest baleen whale ...
.
* Moodus noises, strange sounds heard in Moodus, Connecticut, later attributed to microquakes.
Currently unidentified sounds
*The Hum
The Hum is persistent and invasive low-frequency humming, rumbling, or droning noise audible to many but not all people. Hums have been reported in many countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia and Canada. They are so ...
, a persistent and invasive low-frequency humming, rumbling, or droning noise audible to many but not all people. Different causes have been attributed, including local mechanical sources, often from industrial plants, as well as manifestations of tinnitus or other biological auditory effects.
* Mistpouffers or skyquake
A skyquake is a phenomenon where a loud sound is reported to originate from the sky. It often manifests as a banging, or a horn-like noise. The sound may cause noticeable effects on buildings, including vibration in ceilings or across the walls of ...
s, a phenomenon generally occurring near large bodies of water. Sound has been compared to distant cannon fire or thunder.
* The Ping, described as "hums and buzzes" whose "sound scare sea animals." It was detected by shipboard sonars in the Fury and Hecla Strait
Fury and Hecla Strait is a narrow (from wide) Arctic seawater channel located in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.
Geography
Situated between Baffin Island to the north and the Melville Peninsula to the south, it connects Foxe Basin o ...
of northern Canada during the summer of 2016. It was investigated by Canadian military authorities, who did not detect any anomalies on the seabed, where the sound originated. Possible causes include local sonar surveys or the acoustics of Arctic ice./ref>
See also
*52-hertz whale
The 52-hertz whale, colloquially referred to as 52 Blue, is an individual whale of unidentified species that calls at the unusual frequency of 52 hertz. This is a higher frequency than usual for any whale species with migration patterns mo ...
*Lists of unsolved problems
List of unsolved problems may refer to several notable conjectures or open problems in various academic fields:
Natural sciences, engineering and medicine
* Unsolved problems in astronomy
* Unsolved problems in biology
* Unsolved problems in ch ...
*Numbers station
A numbers station is a shortwave radio station characterized by broadcasts of formatted numbers, which are believed to be addressed to intelligence officers operating in foreign countries. Most identified stations use speech synthesis to voca ...
*Pareidolia
Pareidolia (; ) is the tendency for perception to impose a meaningful interpretation on a nebulous stimulus (physiology), stimulus, usually visual, so that one detects an object, pattern, or meaning where there is none. Pareidolia is a specific bu ...
*Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to noise power, often expressed in deci ...
*Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a condition when a person hears a ringing sound or a different variety of sound when no corresponding external sound is present and other people cannot hear it. Nearly everyone experiences faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely ...
* UVB-76
References
{{Reflist unexplained sounds unexplained