Josiah on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Josiah () or Yoshiyahu was the 16th king of Judah (–609 BCE). According to the
''Jewish Encyclopedia'' (1906). His grandfather Manasseh was one of the kings blamed for turning away from the worship of
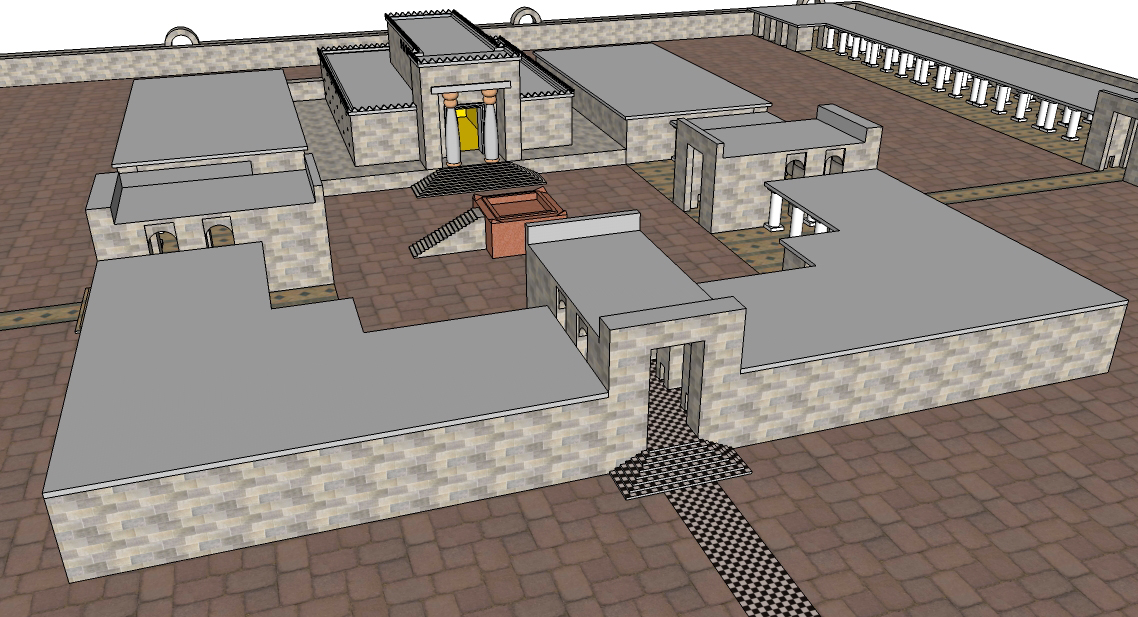 Josiah ordered Hilkiah, the High Priest, to use the tax money collected over the years to renovate the Temple. While Hilkiah was clearing the treasure room of the Temple, he allegedly discovered a scroll described in 2 Kings 22:8 as "a scroll of the Teaching" and in 2 Chronicles 34:14 as "the book of the Law of the LORD given by Moses". The phrase "scroll of the Teaching" () in 2 Kings 22:8 is identical to the phrase used in Joshua 1:8 and 8:34 to describe the sacred writings
Josiah ordered Hilkiah, the High Priest, to use the tax money collected over the years to renovate the Temple. While Hilkiah was clearing the treasure room of the Temple, he allegedly discovered a scroll described in 2 Kings 22:8 as "a scroll of the Teaching" and in 2 Chronicles 34:14 as "the book of the Law of the LORD given by Moses". The phrase "scroll of the Teaching" () in 2 Kings 22:8 is identical to the phrase used in Joshua 1:8 and 8:34 to describe the sacred writings 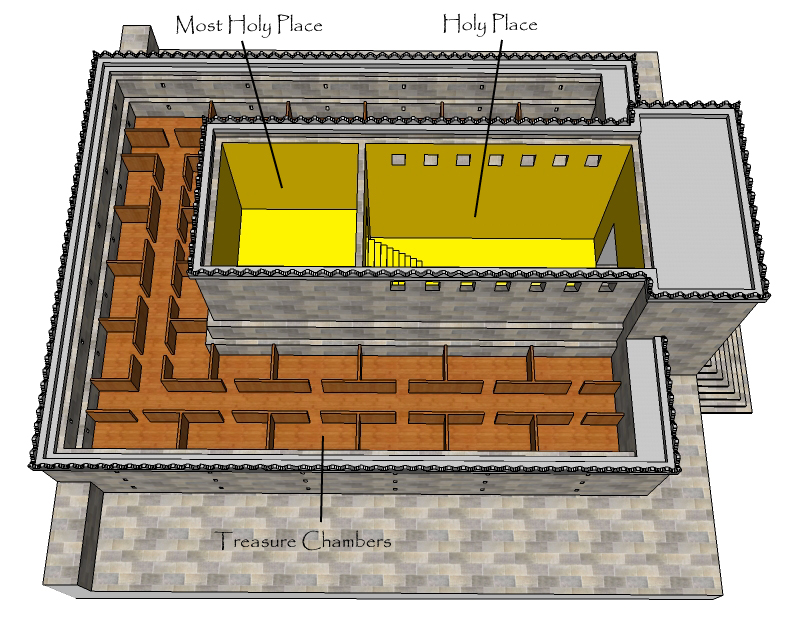 According to an unnamed "man of God" (sometimes identified as Iddo) had prophesied to King Jeroboam of the northern
According to an unnamed "man of God" (sometimes identified as Iddo) had prophesied to King Jeroboam of the northern
 The
The
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Kingdom of Judah The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries ...
at the age of eight, after the assassination of his father, King Amon, and reigned for 31 years, from 641/640 to 610/609 BCE.
Josiah is known only from biblical texts; no reference to him exists in other surviving texts of the period from . '' Kingdom of Judah The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries ...
ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
or Babylon, and no clear archaeological evidence, such as inscriptions bearing his name, has ever been found. However, a seal bearing the name " Nathan-melech," the name of an administrative official under King Josiah according to , dating to the 7th century BCE, was found in situ in an archeological site in Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
. The discoverers believe this seal represents the individual mentioned in 2 Kings 23:11. Additionally, most scholars believe that Josiah existed historically.
Biblical narrative
The Bible describes him as a righteous king in 2 Kings 22:2, "He did what was pleasing toGOD
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
and he followed all the ways of his forefather David; he did not deviate to the right or to the left." A similar phrase appears in 2 Chronicles 34:2. He is also one of the kings mentioned in the Gospel of Matthew
The Gospel of Matthew is the first book of the New Testament of the Bible and one of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells the story of who the author believes is Israel's messiah (Christ (title), Christ), Jesus, resurrection of Jesus, his res ...
, one of the two genealogies of Jesus in the New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
(cf. Matthew 1:10– 11).
Family
According to the biblical narrative, Josiah was the son of King Amon of Judah and Jedidah, daughter of Adaiah of Bozkath."Josiah"''Jewish Encyclopedia'' (1906). His grandfather Manasseh was one of the kings blamed for turning away from the worship of
Yahweh
Yahweh was an Ancient Semitic religion, ancient Semitic deity of Weather god, weather and List of war deities, war in the History of the ancient Levant, ancient Levant, the national god of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Judah, Judah and Kingdom ...
. Manasseh adapted the Temple for idolatrous worship. Josiah's great-grandfather was King Hezekiah, a noted reformer also respected by the biblical writers as having "done what was right in the sight of the LORD, as David had done.
Josiah had four sons: Johanan, and Eliakim (born c. 634 BCE), whose mother was Zebidah the daughter of Pedaiah of Ruma; and Shallum (633/632 BCE) and Mattanyahu (c. 618 BCE), whose mother was Hamutal, the daughter of Jeremiah of Libnah. Eliakim had his name changed by Necho II, the Pharaoh of Saïte Egypt, to Jehoiakim.
Shallum, his third son, succeeded Josiah as Jehoahaz according to 1 Chronicles 3:15 and Jeremiah 22:11. Eliakim succeeded Shallum as Jehoiakim in 2 Chronicles 36:4, and he was succeeded by his son Jeconiah in 2 Chronicles 36:8. Jeconiah was succeeded to the throne by his uncle Mattanyahu, under the name Zedekiah in 2 Kings 24:17. Zedekiah was the last king of Judah before the kingdom was conquered by the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
and the Babylonian captivity
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile was the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were forcibly relocated to Babylonia by the Neo-Babylonian Empire. The deportations occurred ...
began.
Religious reform
The Second Book of Chronicles records that Josiah was eight years old when he became king. In the eighth year of his reign, he "began to seek the God of his father David" and in the twelfth year of that reign he began a program of destruction of Baalist altars and images throughout Jerusalem and Judah according to 2 Chronicles 34:1-3. The Chronicler records in detail the execution of this program. In contrast, the account in 2 Kings begins with a restoration of Solomon's Temple in Jerusalem, which both accounts say was initiated in the eighteenth year of his reign. Josiah ordered Hilkiah, the High Priest, to use the tax money collected over the years to renovate the Temple. While Hilkiah was clearing the treasure room of the Temple, he allegedly discovered a scroll described in 2 Kings 22:8 as "a scroll of the Teaching" and in 2 Chronicles 34:14 as "the book of the Law of the LORD given by Moses". The phrase "scroll of the Teaching" () in 2 Kings 22:8 is identical to the phrase used in Joshua 1:8 and 8:34 to describe the sacred writings
Josiah ordered Hilkiah, the High Priest, to use the tax money collected over the years to renovate the Temple. While Hilkiah was clearing the treasure room of the Temple, he allegedly discovered a scroll described in 2 Kings 22:8 as "a scroll of the Teaching" and in 2 Chronicles 34:14 as "the book of the Law of the LORD given by Moses". The phrase "scroll of the Teaching" () in 2 Kings 22:8 is identical to the phrase used in Joshua 1:8 and 8:34 to describe the sacred writings Joshua
Joshua ( ), also known as Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' Literal translation, lit. 'Yahweh is salvation'), Jehoshua, or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Book of Exodus, Exodus and ...
had received from Moses. The book is not identified in the text and many scholars believe this was either a copy of the Book of Deuteronomy or a text that became a part of Deuteronomy.
The story of the Temple restoration is based on those ordered by an earlier Judean king, Joash in 2 Kings 12, who ruled c. 836 – 796 BCE .
Hilkiah brought this scroll to Josiah's attention. Josiah consulted the prophetess Huldah, who assured him that the evil foretold in the document for non-observance of its instructions, would come, but not in his day; "because", she said, "thine heart was tender and thou didst humble thyself before the Lord". An assembly of the elders of Judah and Jerusalem and of all the people was called, and Josiah then encouraged the exclusive worship of Yahweh, forbidding all other forms of worship. The instruments and emblems of the worship of Baal and " heavenly host" were removed from the Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. Accord ...
. Local sanctuaries, known as high places, were destroyed from Beersheba in the south to Bethel and the cities of Samaria
Samaria (), the Hellenized form of the Hebrew name Shomron (), is used as a historical and Hebrew Bible, biblical name for the central region of the Land of Israel. It is bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The region is ...
in the north. Josiah had pagan priests executed and even had the bones of the dead priests of Bethel exhumed from their graves and burned on their altars. Josiah also reinstituted Passover celebrations.
 According to an unnamed "man of God" (sometimes identified as Iddo) had prophesied to King Jeroboam of the northern
According to an unnamed "man of God" (sometimes identified as Iddo) had prophesied to King Jeroboam of the northern Kingdom of Israel (Samaria)
The Kingdom of Israel ( ), also called the Northern Kingdom or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israelite kingdom that existed in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Its beginnings date back to the firs ...
, approximately three hundred years earlier, that "a son named Josiah will be born to the house of David" and that he would destroy the altar at Bethel. And the only exception to this destruction was for the grave of an unnamed prophet he found in Bethel (), who had foretold that these religious sites Jeroboam erected would one day be destroyed (see ). Josiah ordered the double grave of the "man of God" and of the Bethel prophet to be left alone, as these prophecies had come true.
Josiah's reforms are described in two biblical accounts, 2 Kings 22–23, and 2 Chronicles 34–35. They began with the ending of ancient Israelite religious practices, and the astral cults that had become popular in the 8th century, and led to centralisation of worship in Jerusalem, and the destruction of the temple at Bethel. Some scholars have rejected the entire historicity of these accounts, while others have defended the historical existence of a religious reform under Josiah's reign.
According to the later account in 2 Chronicles, Josiah destroyed altars and images of pagan deities in cities of the tribes of Manasseh, Ephraim, "and Simeon
Simeon () is a given name, from the Hebrew (Biblical Hebrew, Biblical ''Šimʿon'', Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ''Šimʿôn''), usually transliterated in English as Shimon. In Greek, it is written Συμεών, hence the Latinized spelling Sy ...
, as far as Naphtali" (), which were outside of his kingdom, Judah, and returned the Ark of the Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant, also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, was a religious storage chest and relic held to be the most sacred object by the Israelites.
Religious tradition describes it as a wooden storage chest decorat ...
to the Temple.
Book of the Law
 The
The Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Hilkiah found a "Book of the Law" in the temple during the early stages of Josiah's temple renovation. Hilkiah then gave the scroll to his secretary Shaphan, who took it to King Josiah. According to the Bible, King Josiah then changed his form of leadership entirely, entering into a new form of covenant with the Lord. He wiped out all of the pagan cults that had formed within his land. He, along with his people, then entered into this new covenant with the Lord to keep the commandments of the Lord. For much of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, it was agreed among biblical scholars that this "Book of the Law" was an early version of the Book of Deuteronomy, but recent biblical scholarship sees it as a largely legendary narrative about one of the earliest stages of the creation of Deuteronomistic work. William G. Dever, for example, argues that the Book of the Law was actually composed by orthodox Yahwist priests, who attributed it to the legendary figure of Moses and then hid it in the Temple, where it would be dramatically discovered; in this way, a "miraculous new Word from
 When Josiah became king of Judah in about 641/640 BCE, the international situation was in flux. The
When Josiah became king of Judah in about 641/640 BCE, the international situation was in flux. The
 There are two accounts of Josiah's death in the Bible. The Second Book of Kings merely states that Necho II met Josiah at Megiddo and killed him (), whereas the second book of Chronicles () gives a lengthier account and states that Josiah was fatally wounded by Egyptian archers and was brought back to Jerusalem to die. His death in the latter account was attributed to him "not listening to what Necho had said at God's command..." when Necho stated: "What have I to do with you, king of Judah? I am not coming against you today, but against the house with which I am at war; and God has commanded me to hurry. Cease opposing God, who is with me, so that he will not destroy you." According to ,
There are two accounts of Josiah's death in the Bible. The Second Book of Kings merely states that Necho II met Josiah at Megiddo and killed him (), whereas the second book of Chronicles () gives a lengthier account and states that Josiah was fatally wounded by Egyptian archers and was brought back to Jerusalem to die. His death in the latter account was attributed to him "not listening to what Necho had said at God's command..." when Necho stated: "What have I to do with you, king of Judah? I am not coming against you today, but against the house with which I am at war; and God has commanded me to hurry. Cease opposing God, who is with me, so that he will not destroy you." According to ,
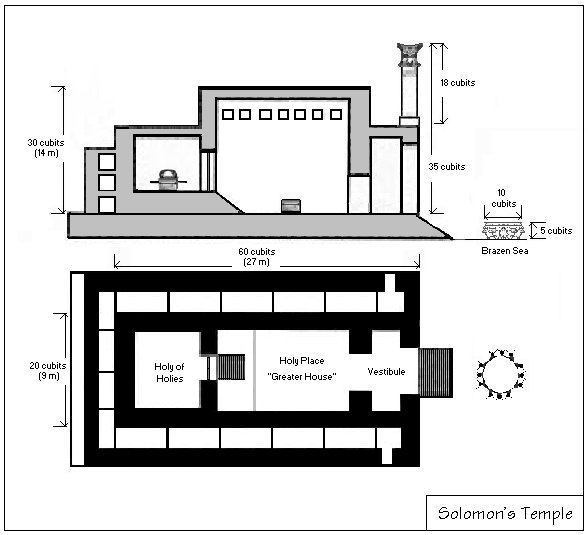 The only textual sources of information for Josiah's reign are from the Bible, notably and . No archaeological evidence for Josiah as a person exists. However, a bulla (impression seal) has been found in the "City of David" archaeological site in Jerusalem featuring the name of one of King Josiah's officials, Nathan-melech, mentioned in . The inscription of the ring says, "(belonging) to Netanmelek, Servant of the King". Although it may not directly mention King Josiah by name, it does appear to be from the same time period in which he would have lived. Seals and seal impressions from the period show a transition from those of an earlier period which bear images of stars and the moon, to seals that carry only names, a possible indication of Josiah's enforcement of monotheism. Other possible archaeological evidence of Josiah's religious reforms may have been discovered at
The only textual sources of information for Josiah's reign are from the Bible, notably and . No archaeological evidence for Josiah as a person exists. However, a bulla (impression seal) has been found in the "City of David" archaeological site in Jerusalem featuring the name of one of King Josiah's officials, Nathan-melech, mentioned in . The inscription of the ring says, "(belonging) to Netanmelek, Servant of the King". Although it may not directly mention King Josiah by name, it does appear to be from the same time period in which he would have lived. Seals and seal impressions from the period show a transition from those of an earlier period which bear images of stars and the moon, to seals that carry only names, a possible indication of Josiah's enforcement of monotheism. Other possible archaeological evidence of Josiah's religious reforms may have been discovered at
Jewish Encyclopedia: Josiah
Genealogy of the House of David- Josiah, King of Judah
{{Authority control 640s BC births 600s BC deaths 7th-century BCE kings of Judah Ancient child monarchs Deaths by arrow wounds Eastern Orthodox royal saints Military personnel killed in action Monarchs killed in action
. '' Hilkiah found a "Book of the Law" in the temple during the early stages of Josiah's temple renovation. Hilkiah then gave the scroll to his secretary Shaphan, who took it to King Josiah. According to the Bible, King Josiah then changed his form of leadership entirely, entering into a new form of covenant with the Lord. He wiped out all of the pagan cults that had formed within his land. He, along with his people, then entered into this new covenant with the Lord to keep the commandments of the Lord. For much of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, it was agreed among biblical scholars that this "Book of the Law" was an early version of the Book of Deuteronomy, but recent biblical scholarship sees it as a largely legendary narrative about one of the earliest stages of the creation of Deuteronomistic work. William G. Dever, for example, argues that the Book of the Law was actually composed by orthodox Yahwist priests, who attributed it to the legendary figure of Moses and then hid it in the Temple, where it would be dramatically discovered; in this way, a "miraculous new Word from
Yahweh
Yahweh was an Ancient Semitic religion, ancient Semitic deity of Weather god, weather and List of war deities, war in the History of the ancient Levant, ancient Levant, the national god of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Judah, Judah and Kingdom ...
" would seem to have appeared, giving Judah a chance to redeem itself and save itself from the advance of the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
.
Many scholars see the whole core narrative, from Joshua to 2 Kings, as comprising a Deuteronomistic History (DtrH) written during Josiah's reign. In fact, some recent European theologians even go so far as to posit that most of the Torah and Deuteronomistic History was composed and finalized several centuries later, during the Persian period. However, most biblical scholars are coming to believe that the Deuteronomistic History was composed using other earlier sources, including a brief chronicle of king's names, age at the beginning of their reign, and their mother's names.
Prophets and King Josiah
According to rabbinic interpretation, Huldah said to the messengers of King Josiah, "Tell the man that sent you to me ..." (), indicating by her unceremonious language that for her Josiah was like any other man. The king addressed her, and not Jeremiah, because he thought that women are more easily stirred to pity than men, and that therefore the prophetess would be more likely than Jeremiah to intercede with God in his behalf. Huldah was a relative of Jeremiah, both being descendants of Rahab by her marriage with Joshua. While Jeremiah admonished and preached repentance to the men, she did the same to the women. Huldah was not only a prophetess, but taught publicly in the school, according to some teaching especially the oral doctrine. It is doubtful whether "the Gate of Huldah" in theSecond Temple
The Second Temple () was the Temple in Jerusalem that replaced Solomon's Temple, which was destroyed during the Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), Babylonian siege of Jerusalem in 587 BCE. It was constructed around 516 BCE and later enhanced by Herod ...
(Middot 1:3) has any connection with the prophetess Huldah; it may have meant "Cat's Gate"; some scholars, however, associate the gate with Huldah's schoolhouse (Rashi to Kings l.c.).E. C. L. G.
The prophetic activity of Jeremiah began in the reign of Josiah; he was a contemporary of his relative the prophetess Hulda and of his teacher Zephaniah. These three prophets divided their activity: Hulda spoke to the women and Jeremiah to the men in the street, while Zephaniah preached in the synagogue. When Josiah restored the true worship, Jeremiah went to the exiled ten tribes, whom he brought to Israel under the rule of the pious king. Although Josiah went to war with Egypt against the prophet's advice, Jeremiah knew that this was an error by the otherwise pious king; and later he bitterly laments the king's death: the fourth chapter of Lamentations beginning with a dirge on Josiah.
King Josiah, who foresaw the impending national catastrophe, concealed the Ark and its contents (including Aaron's rod, the vial of manna and the anointing oil) within a hidden chamber which had been built by King Solomon] (Tosefta, Sotah, 13a); cf. Babylonian Talmud (''Kereithot'' 5b) and their whereabouts will remain unknown until, in the Messianic age, the prophet Elijah shall reveal them (Mekhilta l.c.).
Foreign relations
 When Josiah became king of Judah in about 641/640 BCE, the international situation was in flux. The
When Josiah became king of Judah in about 641/640 BCE, the international situation was in flux. The Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n Empire was beginning to disintegrate, the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
had not yet risen to replace it, and Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
to the west was still recovering from Assyrian rule. In this power vacuum, Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
was able to govern itself for the time being without foreign intervention.
In the spring of 609 BCE, Pharaoh Necho II led a sizable army up to the Euphrates River to aid the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East and parts of South Caucasus, Nort ...
, which was collapsing under the attacks of the Medes and the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to ancient Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC a ...
. Taking the coast route Via Maris into Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
at the head of a large army, consisting mainly of mercenaries; and supported by his Mediterranean fleet along the shore, Necho passed the low tracts of Philistia and Sharon. However, the passage over the ridge of hills which shuts in on the south of the great Jezreel Valley was blocked by the Judean army led by Josiah. The reason for Josiah attempting to halt the Egyptian campaign is not known, but he may have considered that the Assyrians and Egyptians were weakened by the death of pharaoh Psamtik I only a year earlier (610 BCE): Psamtik having been appointed and confirmed by Assyrian kings Esarhaddon and Ashurbanipal. According to the Biblical Books of Chronicles, Necho had not intended to do battle with the Judeans and was confused by Josiah's decision to attack him, supposedly sending a letter saying "what have we done to each other, king of Judah? I am not coming against you this day."
Josiah attempted to block the advance at Megiddo, where a fierce battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force co ...
was fought and Josiah was killed. Necho then joined forces with the Assyrian Ashur-uballit II and crossed the Euphrates to lay siege to Harran. The combined forces failed to capture the city, and Necho retreated to northern Syria.
Death
 There are two accounts of Josiah's death in the Bible. The Second Book of Kings merely states that Necho II met Josiah at Megiddo and killed him (), whereas the second book of Chronicles () gives a lengthier account and states that Josiah was fatally wounded by Egyptian archers and was brought back to Jerusalem to die. His death in the latter account was attributed to him "not listening to what Necho had said at God's command..." when Necho stated: "What have I to do with you, king of Judah? I am not coming against you today, but against the house with which I am at war; and God has commanded me to hurry. Cease opposing God, who is with me, so that he will not destroy you." According to ,
There are two accounts of Josiah's death in the Bible. The Second Book of Kings merely states that Necho II met Josiah at Megiddo and killed him (), whereas the second book of Chronicles () gives a lengthier account and states that Josiah was fatally wounded by Egyptian archers and was brought back to Jerusalem to die. His death in the latter account was attributed to him "not listening to what Necho had said at God's command..." when Necho stated: "What have I to do with you, king of Judah? I am not coming against you today, but against the house with which I am at war; and God has commanded me to hurry. Cease opposing God, who is with me, so that he will not destroy you." According to , Jeremiah
Jeremiah ( – ), also called Jeremias, was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition, Jeremiah authored the Book of Jeremiah, book that bears his name, the Books of Kings, and the Book of Lamentations, with t ...
wrote a lament for Josiah's death.
The account in Chronicles is considered unreliable by some scholars, as it is based on the description of the death of a different king, Ahab, in 1 Kings, and it meets the Chronicler's religious agenda to attribute the death of a righteous king to some form of sin.
Some researchers have concluded from the account in Kings that Josiah did not meet Necho in battle but was summoned by Necho as a vassal, investigated, and beheaded for failing to pay the correct tribute or tax to Egypt.
Rabbinic Literature remarks on Josiah's piety and his father Amon: "The fact that Amon was the most sinful of all the wicked kings of Judah (II Chron. xxxiii. 23) is brought out in the Talmud (Sanh. 103b) as follows:(Sanh. 104a) Ahaz suspended the sacrificial worship, Manasseh tore down the altar, Amon made it a place of desolation overed it with cobwebs Ahaz sealed up the scrolls of the Law (Isa. viii. 16), Manasseh cut out the sacred name, Amon burnt the scrolls altogether ompare Seder Olam, R. xxiv. This is derived from the story of the finding of the Book of the Law, II Kings, xxii. 8 Ahab permitted incest, Manasseh committed it himself, Amon acted as Nero was said to have done toward his mother Agrippina. And yet, out of respect for his son Josiah, Amon's name was not placed on the list of the kings excluded from the world to come." also that Josiah's death was brought about because despite his sincere religious reform, he had in fact been deceived; thus he refused to heed the Prophet Jeremiah, thinking that no sword would pass through the Land of Israel. He was struck by 300 darts; he made no complaint except to acknowledge "The Lord is righteous, for I rebelled against His commandment."
Succession
After the setback in Harran, the Pharaoh Necho left a sizeable force in Judah and returned toEgypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. On his return march, Necho found that Jehoahaz had succeeded his father Josiah as King of Judah. () Necho deposed Jehoahaz, who had been king of Judah for only three months, and replaced him with Jehoahaz's older brother, Jehoiakim. Necho imposed on Judah a levy of a hundred talents of silver (about 3 tons or about 3.4 metric tons) and a talent of gold (about 75 pounds or about 34 kilograms). Necho then took Jehoahaz back to Egypt as his prisoner.
Necho had left Egypt in 609 BCE to relieve the Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n Harran under Babylonian siege. Josiah's actions may have provided aid to the Babylonians by engaging the Egyptian army.
Sources
 The only textual sources of information for Josiah's reign are from the Bible, notably and . No archaeological evidence for Josiah as a person exists. However, a bulla (impression seal) has been found in the "City of David" archaeological site in Jerusalem featuring the name of one of King Josiah's officials, Nathan-melech, mentioned in . The inscription of the ring says, "(belonging) to Netanmelek, Servant of the King". Although it may not directly mention King Josiah by name, it does appear to be from the same time period in which he would have lived. Seals and seal impressions from the period show a transition from those of an earlier period which bear images of stars and the moon, to seals that carry only names, a possible indication of Josiah's enforcement of monotheism. Other possible archaeological evidence of Josiah's religious reforms may have been discovered at
The only textual sources of information for Josiah's reign are from the Bible, notably and . No archaeological evidence for Josiah as a person exists. However, a bulla (impression seal) has been found in the "City of David" archaeological site in Jerusalem featuring the name of one of King Josiah's officials, Nathan-melech, mentioned in . The inscription of the ring says, "(belonging) to Netanmelek, Servant of the King". Although it may not directly mention King Josiah by name, it does appear to be from the same time period in which he would have lived. Seals and seal impressions from the period show a transition from those of an earlier period which bear images of stars and the moon, to seals that carry only names, a possible indication of Josiah's enforcement of monotheism. Other possible archaeological evidence of Josiah's religious reforms may have been discovered at Tel Dothan
Dothan (Hebrew language, Hebrew: ) (also Dotan) was a location mentioned twice in the Hebrew Bible. It has been identified with Tel Dothan (), also known as Tel al-Hafireh, located adjacent to the Palestinian people, Palestinian town of Bir al-Bas ...
and Mordot Arnona in Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
.
The date of Josiah's death can be established fairly accurately. The Babylonian Chronicles date the battle at Harran between the Assyrians and their Egyptian allies against the Babylonians from Tammuz (July–August) to Elul
Elul (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Standard , Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ) is the twelfth month of the civil year and the sixth month of the Jewish religious year, religious year in the Hebrew calendar. It is a m ...
(August–September) 609 BCE. On that basis, Josiah was killed in the month of Tammuz (July–August) 609 BCE, when the Egyptians were on their way to Harran.Thiele, ''Mysterious Numbers'' 182, 184–185.
See also
* List of artifacts in biblical archaeologyNotes
References
Further reading
* '' The Bible Unearthed: Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts'' for the possible role of Josiah in creation of the Bible. * Hertz, J. H. (1936). ''The Pentateuch and Haftoras''. ''Deuteronomy''. Oxford University Press, London. * Friedman, R. (1987). ''Who Wrote the Bible?'' New York: Summit Books.External links
Jewish Encyclopedia: Josiah
Genealogy of the House of David- Josiah, King of Judah
{{Authority control 640s BC births 600s BC deaths 7th-century BCE kings of Judah Ancient child monarchs Deaths by arrow wounds Eastern Orthodox royal saints Military personnel killed in action Monarchs killed in action