Joint Hypermobility Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable
Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable
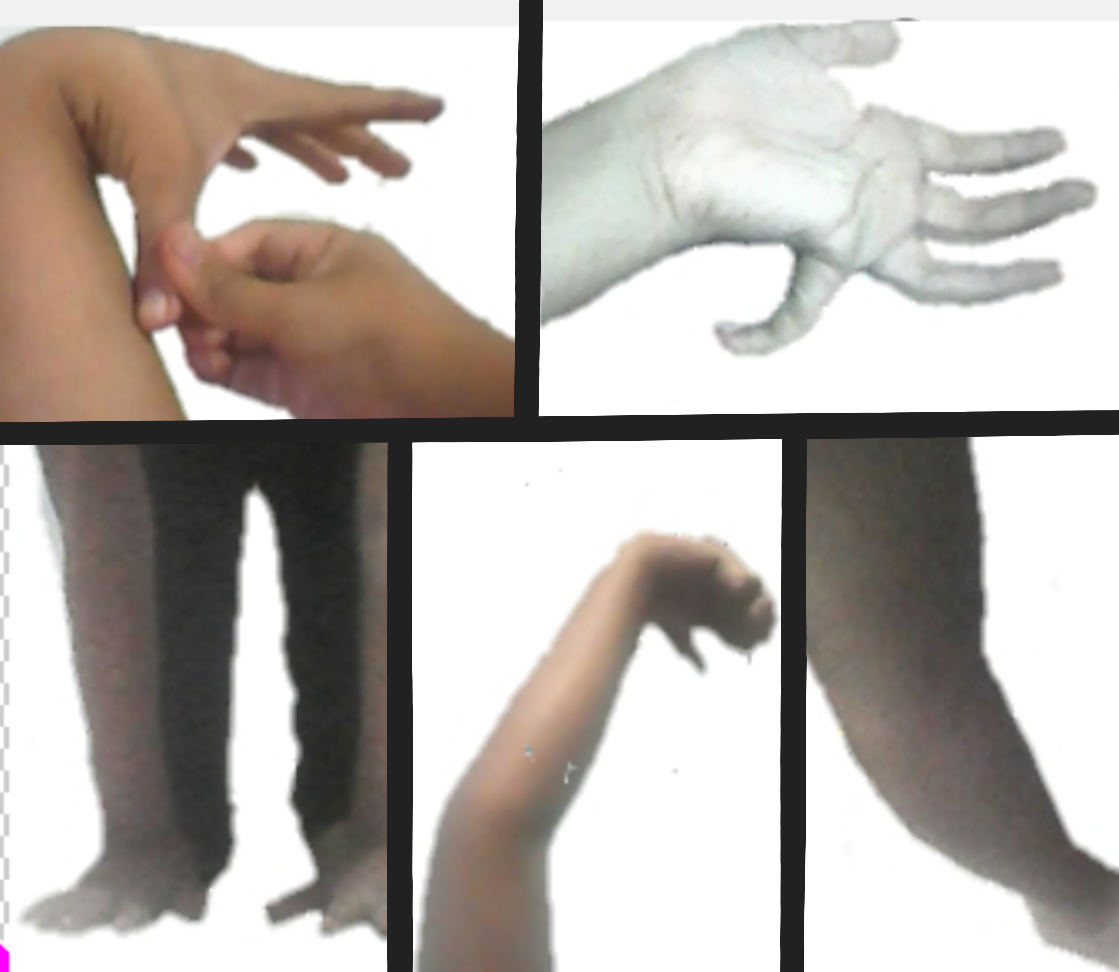 Being diagnosed with hypermobility syndrome can be a difficult task. There is a lack of wide understanding of the condition and it can be considered a zebra condition. As hypermobility syndrome can be easily mistaken for being double-jointed or categorised as nothing more than perhaps an achy body from lack of exercise, medical professionals may diagnose those affected incorrectly and not adequately investigate the symptoms. Due to these circumstances many affected individuals can live not knowing they have it. As a result, those affected without a proper diagnosis can easily injure themselves and not take proper care to ensure they go about working safely.
The Beighton score can be used to determine generalised joint hypermobility (GJH) related to hypermobility syndrome. The newer term "generalised hypermobility spectrum disorder" includes people with generalised joint hypermobility, often determined using the Beighton score, and other symptoms. Those who do not meet the Beighton score criteria may be diagnosed with historical joint hypermobility spectrum disorder, peripheral hypermobility spectrum disorder, or localised hypermobility spectrum disorder.
In comparison to the diagnostic criteria of
Being diagnosed with hypermobility syndrome can be a difficult task. There is a lack of wide understanding of the condition and it can be considered a zebra condition. As hypermobility syndrome can be easily mistaken for being double-jointed or categorised as nothing more than perhaps an achy body from lack of exercise, medical professionals may diagnose those affected incorrectly and not adequately investigate the symptoms. Due to these circumstances many affected individuals can live not knowing they have it. As a result, those affected without a proper diagnosis can easily injure themselves and not take proper care to ensure they go about working safely.
The Beighton score can be used to determine generalised joint hypermobility (GJH) related to hypermobility syndrome. The newer term "generalised hypermobility spectrum disorder" includes people with generalised joint hypermobility, often determined using the Beighton score, and other symptoms. Those who do not meet the Beighton score criteria may be diagnosed with historical joint hypermobility spectrum disorder, peripheral hypermobility spectrum disorder, or localised hypermobility spectrum disorder.
In comparison to the diagnostic criteria of
/ref>E. Connelly, A. Hakim, S. Davenport, J. Simmonds. "A study exploring the prevalence of joint hypermobility syndrome in patients attending a musculoskeletal triage clinic." Physiother. Pract. Res., 36 (1) (2015), pp. 43-53
 Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable
Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable connective tissue disorder
Connective tissue diseases (also termed connective tissue disorders, or collagen vascular diseases), are medical conditions that affect connective tissue.
Connective tissues protect, support, and provide structure for the body's other tissues a ...
that affects joints and ligaments. Different forms and sub-types have been distinguished, but it does not include asymptomatic joint hypermobility, sometimes known as double-jointedness.
Symptoms can include the inability to walk properly or for long distances, and pain in affected areas. Some people with HSD have hypersensitive nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
s and a weaker immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
. It can also cause severe fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
and some cases cause depressive episodes. It is somewhat similar to other genetic connective tissue disorders such as Ehlers–Danlos syndromes.
There is a strong association between HSD and neurodevelopmental disorder
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of mental conditions negatively affecting the development of the nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. According to the American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manu ...
s such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple con ...
and autism spectrum disorder
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing di ...
.
Classification
Hypermobility spectrum disorders are diagnosed when individuals have symptomatic joint hypermobility but do not meet the criteria for other connective tissue disorders, such asEhlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
.
In March 2017, the International Consortium on the Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes published a revised classification naming two syndromes: hypermobile EDS (hEDS), which has narrowly defined criteria, and hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD) for those with some but not all the features of hEDS. This reclassification aimed to address the overlap between joint hypermobility syndrome and what was previously termed EDS-hypermobile type (EDS-HT). Patients who have a diagnosis of EDS-HT or JHS will fall into one of these two new categories.
Hypermobility spectrum disorder does not include people with asymptomatic hypermobility or people with double-jointedness but no other symptoms. Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome and hypermobility spectrum disorders may be equally severe.
HSD is further classified into different subtypes, which include:
* Generalized HSD (G-HSD): Involves widespread joint hypermobility affecting multiple joints.
* Localized HSD (L-HSD): Limited to a few joints, without generalized involvement.
* Peripheral HSD (P-HSD): Affects joints in the hands and feet.
* Historical HSD (H-HSD): Diagnosed when there is a history of joint hypermobility that is no longer present, along with other symptoms.
These classifications help in identifying the specific pattern and extent of joint hypermobility and in determining the appropriate management strategies.
Signs and symptoms
Some common symptoms of hypermobility spectrum disorder may include:Musculoskeletal symptoms
* Joint instability and soft tissue injuries: Dislocations, subluxations, or damage to muscles, ligaments, tendons, synovium, or cartilage as a result of excessive joint movement. * Chronic pain: Recurrent joint pain that can develop intohyperalgesia
Hyperalgesia ( or ; ''hyper'' from Greek ὑπέρ (''huper'') 'over' + ''-algesia'' from Greek ἄλγος (algos) 'pain') is an abnormally increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves and ...
, with a higher rate of small fiber neuropathy in some individuals.
* Disturbed proprioception: Reduced proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position.
Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of propri ...
and muscle weakness, creating a cycle of increasing activity limitations
Extra-articular symptoms
* Autonomic dysfunction/dysautonomia: Symptoms may include orthostatic intolerance, dizziness, palpitations,Raynaud's phenomenon
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically the fingers, and, less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rare ...
, and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS).
* Functional gastrointestinal disorders: Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, early satiety, reflux, and irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
.
* Pelvic and bladder dysfunction: Symptoms include pelvic pain, dyspareunia
Dyspareunia ( ) is painful sexual intercourse due to somatic or psychological causes. The term ''dyspareunia'' covers both female dyspareunia and male dyspareunia, but many discussions that use the term without further specification concern the f ...
, bladder dysfunction, organ prolapse, and association with conditions like polycystic ovaries
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or polycystic ovarian syndrome, (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The name is a misnomer, as not all women with this condition develop cysts on their ovaries. The name origin ...
, fibroids, or endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease in which Tissue (biology), tissue similar to the endometrium, the lining of the uterus, grows in other places in the body, outside the uterus. It occurs in women and a limited number of other female mammals. Endomet ...
.
* Fatigue: Profound fatigue, often linked to sleep disturbances, nonrestorative sleep, and nocturnal musculoskeletal pain, affecting concentration and quality of life.
* Mood disorders: Anxiety, depression, panic attacks, and emotional distress, often related to chronic pain and reduced physical function.
Symptom expression varies widely, with different combinations and severities seen in individuals. Symptoms may fluctuate over time, often triggered by physical exertion, stress, illness, or injury.
Diagnosis
 Being diagnosed with hypermobility syndrome can be a difficult task. There is a lack of wide understanding of the condition and it can be considered a zebra condition. As hypermobility syndrome can be easily mistaken for being double-jointed or categorised as nothing more than perhaps an achy body from lack of exercise, medical professionals may diagnose those affected incorrectly and not adequately investigate the symptoms. Due to these circumstances many affected individuals can live not knowing they have it. As a result, those affected without a proper diagnosis can easily injure themselves and not take proper care to ensure they go about working safely.
The Beighton score can be used to determine generalised joint hypermobility (GJH) related to hypermobility syndrome. The newer term "generalised hypermobility spectrum disorder" includes people with generalised joint hypermobility, often determined using the Beighton score, and other symptoms. Those who do not meet the Beighton score criteria may be diagnosed with historical joint hypermobility spectrum disorder, peripheral hypermobility spectrum disorder, or localised hypermobility spectrum disorder.
In comparison to the diagnostic criteria of
Being diagnosed with hypermobility syndrome can be a difficult task. There is a lack of wide understanding of the condition and it can be considered a zebra condition. As hypermobility syndrome can be easily mistaken for being double-jointed or categorised as nothing more than perhaps an achy body from lack of exercise, medical professionals may diagnose those affected incorrectly and not adequately investigate the symptoms. Due to these circumstances many affected individuals can live not knowing they have it. As a result, those affected without a proper diagnosis can easily injure themselves and not take proper care to ensure they go about working safely.
The Beighton score can be used to determine generalised joint hypermobility (GJH) related to hypermobility syndrome. The newer term "generalised hypermobility spectrum disorder" includes people with generalised joint hypermobility, often determined using the Beighton score, and other symptoms. Those who do not meet the Beighton score criteria may be diagnosed with historical joint hypermobility spectrum disorder, peripheral hypermobility spectrum disorder, or localised hypermobility spectrum disorder.
In comparison to the diagnostic criteria of hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Hypermobility, also known as double-jointedness, describes joints that stretch farther than normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists, bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the h ...
, the criteria for hypermobile spectrum disorder are less strict. However, these criteria are differentiated from criteria of other EDS types and therefore its less-strict criteria are only comparable to the criteria of hEDS. As those with HSD experience a considerable amount of discomfort, it is important to focus on the treatment, not the labels. The severity of each condition can be equivalent. In particular, musculoskeletal involvement is a requirement for diagnosis with any form of hypermobility spectrum disorder but not for hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Like hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, hypermobility spectrum disorders are associated with orthostatic tachycardia, gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
disorders, and pelvic and bladder dysfunction.
Treatment
Treating hypermobility syndrome can be difficult. The condition has no direct cure, but its symptoms can be treated.Physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
, particularly exercise, is the main treatment for the condition, although there is only limited evidence for its effectiveness.
Treatments for pain include:
* Bandaging the affected area;
* Placing an ice pack on the affected area;
* Taking over the counter pain killers such as paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
or ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
.
Prevalence
Prevalence of HSD alone is unknown, though previous estimates have placed the combined prevalence of hEDS and HSD between 194.2 per 100 000 (0.19%) or 1 in 500 people. The condition is relatively common in those attending musculoskeletal services.Palmer et al., 2017/ref>E. Connelly, A. Hakim, S. Davenport, J. Simmonds. "A study exploring the prevalence of joint hypermobility syndrome in patients attending a musculoskeletal triage clinic." Physiother. Pract. Res., 36 (1) (2015), pp. 43-53
References
{{reflist Syndromes affecting joints Syndromes with ADHD