Joint Guardian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kosovo Force (KFOR) is a
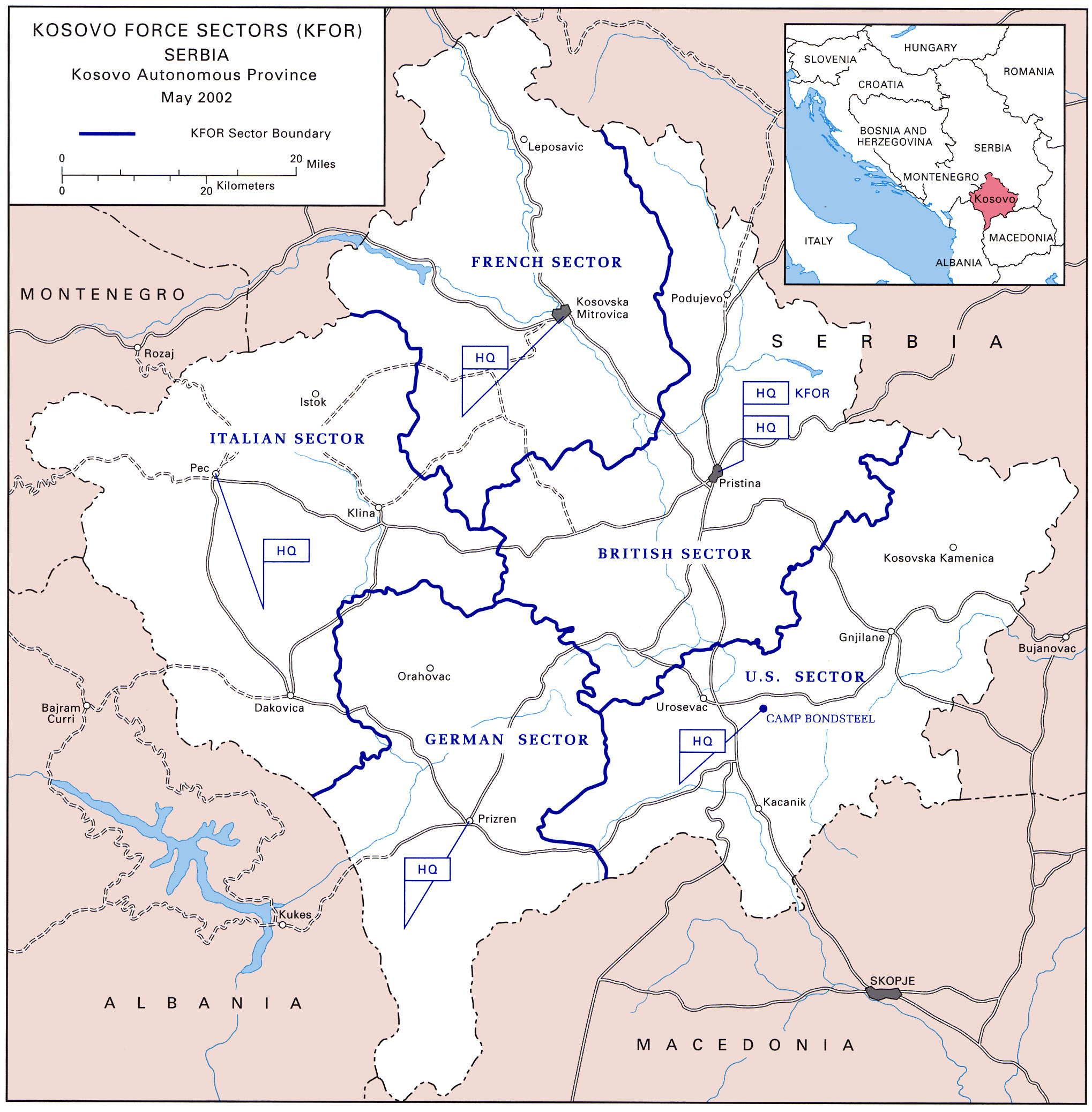 KFOR focuses on building a secure environment and guaranteeing the freedom of movement through all Kosovo territory for all citizens, irrespective of their ethnic origins, in accordance with
KFOR focuses on building a secure environment and guaranteeing the freedom of movement through all Kosovo territory for all citizens, irrespective of their ethnic origins, in accordance with
 KFOR contingents were grouped into five multinational brigades and a lead nation designated for each multinational brigade. All national contingents pursued the same objective to maintain a secure environment in Kosovo.
In August 2005, the
KFOR contingents were grouped into five multinational brigades and a lead nation designated for each multinational brigade. All national contingents pursued the same objective to maintain a secure environment in Kosovo.
In August 2005, the

 At its height, KFOR troops consisted of 50,000 men and women coming from 39 different NATO and non-NATO nations. The official KFOR website indicated that in 2008 a total 14,000 soldiers from 34 countries were participating in KFOR. The following list shows the number of troops which have participated in the KFOR mission. Most of the force has been downsized since 2008; current numbers are reflected here as well:
At its height, KFOR troops consisted of 50,000 men and women coming from 39 different NATO and non-NATO nations. The official KFOR website indicated that in 2008 a total 14,000 soldiers from 34 countries were participating in KFOR. The following list shows the number of troops which have participated in the KFOR mission. Most of the force has been downsized since 2008; current numbers are reflected here as well:

 On 14 January 2017, the Belgrade-Kosovska Mitrovica train incident happened when rhetoric was exchanged between Kosovo and Serbian Officials after Serbia announced restarting train service between Kosovo and Serbia and Kosovo responded stating that the train would be stopped at the border. The initial train was painted in the colors of the Serbian flag with the words “ Kosovo is Serbia” printed down the side which was considered provocative by Kosovo Officials and Kosovo Officials stated that Police would stop it at the border. The train traveled from Belgrade to the border town of Raska and returned never crossing into Kosovo. Train service between Kosovo and Serbia remains non-existent.
On 21 March 2018, Kosovo's Assembly ratified the border agreement with Montenegro. The European Union set ratification as a condition before it would grant Kosovo nationals visa-free access to the pass-port free
On 14 January 2017, the Belgrade-Kosovska Mitrovica train incident happened when rhetoric was exchanged between Kosovo and Serbian Officials after Serbia announced restarting train service between Kosovo and Serbia and Kosovo responded stating that the train would be stopped at the border. The initial train was painted in the colors of the Serbian flag with the words “ Kosovo is Serbia” printed down the side which was considered provocative by Kosovo Officials and Kosovo Officials stated that Police would stop it at the border. The train traveled from Belgrade to the border town of Raska and returned never crossing into Kosovo. Train service between Kosovo and Serbia remains non-existent.
On 21 March 2018, Kosovo's Assembly ratified the border agreement with Montenegro. The European Union set ratification as a condition before it would grant Kosovo nationals visa-free access to the pass-port free
 Since the KFOR entered Kosovo in June 1999, soldiers from Argentina, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Luxembourg, Morocco, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and the United States were killed in the line of duty.
The biggest fatal event is that of the 42 Slovak soldiers dead in a 2006 military plane crash in Hungary. In 20 years, more than 200 NATO soldiers have died as part of KFOR.
Since the KFOR entered Kosovo in June 1999, soldiers from Argentina, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Luxembourg, Morocco, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and the United States were killed in the line of duty.
The biggest fatal event is that of the 42 Slovak soldiers dead in a 2006 military plane crash in Hungary. In 20 years, more than 200 NATO soldiers have died as part of KFOR.
KFOR Placemap
KFOR official site (NATO)
K-For: The task ahead
(from
First deaths in K-For operation
(from
Memorial honors soldiers' sacrifices
June 2002: 68 soldiers have died since KFOR entered Kosovo.
Radio KFOR
{{Authority control Kosovo War NATO-led peacekeeping in the former Yugoslavia United States Marine Corps in the 20th century Military units and formations established in 1999 1999 establishments in Serbia 1999 establishments in Kosovo Military of Kosovo Military operations involving India Military operations involving Portugal
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
-led international peacekeeping force
Peacekeeping comprises activities, especially military ones, intended to create conditions that favor lasting Peace, peace. Research generally finds that peacekeeping reduces Casualty (person), civilian and battlefield deaths, as well as redu ...
and military of Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
. KFOR is the third security responder, after the Kosovo Police
The Kosovo Police (Albanian language, Albanian: ''Policia e'' ''Kosovës'') is the national police, policing law enforcement agency of Kosovo. It was established in 1999 and took its current form with the 2008 police law. It consists of five dep ...
and the EU Rule of Law (EULEX
The European Union Rule of Law Mission in Kosovo, known as EULEX Kosovo or simply as EULEX,About EULEX
accessed 15 Jan ...
) mission, respectively, with whom NATO peacekeeping forces work in close coordination. Its operations are gradually reducing until the accessed 15 Jan ...
Kosovo Security Force
The Kosovo Security Force (KSF) is the military of Kosovo. The KSF is tasked with defending the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Kosovo, military support for civilian authorities, and participation in international Peacekeeping, peacekee ...
, established in 2009, becomes self-sufficient.
KFOR entered Kosovo on 12 June 1999, one day after the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
adopted the UNSC Resolution 1244. At the time, Kosovo was facing a grave humanitarian crisis, with military forces from Yugoslavia
, common_name = Yugoslavia
, life_span = 1918–19921941–1945: World War II in Yugoslavia#Axis invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia, Axis occupation
, p1 = Kingdom of SerbiaSerbia
, flag_p ...
in action against the Kosovo Liberation Army
The Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA; , UÇK) was an Albanians, ethnic Albanian separatist militia that sought the separation of Kosovo, the vast majority of which is inhabited by Albanians, from the Republic of Serbia (1992–2006), Republic of R ...
(KLA) in daily engagements. Nearly one million people had fled Kosovo as refugees by that time, many of whom left permanently.
Currently, 28 states contribute to the KFOR, with a combined strength of approximately 4,686 military personnel.
Objectives
 KFOR focuses on building a secure environment and guaranteeing the freedom of movement through all Kosovo territory for all citizens, irrespective of their ethnic origins, in accordance with
KFOR focuses on building a secure environment and guaranteeing the freedom of movement through all Kosovo territory for all citizens, irrespective of their ethnic origins, in accordance with UN Security Council Resolution 1244
United Nations Security Council resolution 1244, adopted on 10 June 1999, after recalling resolutions 1160 (1998), 1199 (1998), 1203 (1998) and 1239 (1999), authorised an international civil and military presence in the Federal Republic of Yu ...
.
The Contact Group countries have said publicly that KFOR will remain in Kosovo to provide the security necessary to support the final settlement of Kosovo authorities.
Structure
North Atlantic Council
The North Atlantic Council (NAC) is the principal political decision-making body of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), consisting of permanent representatives of its member countries. It was established by wikisource:North Atlantic ...
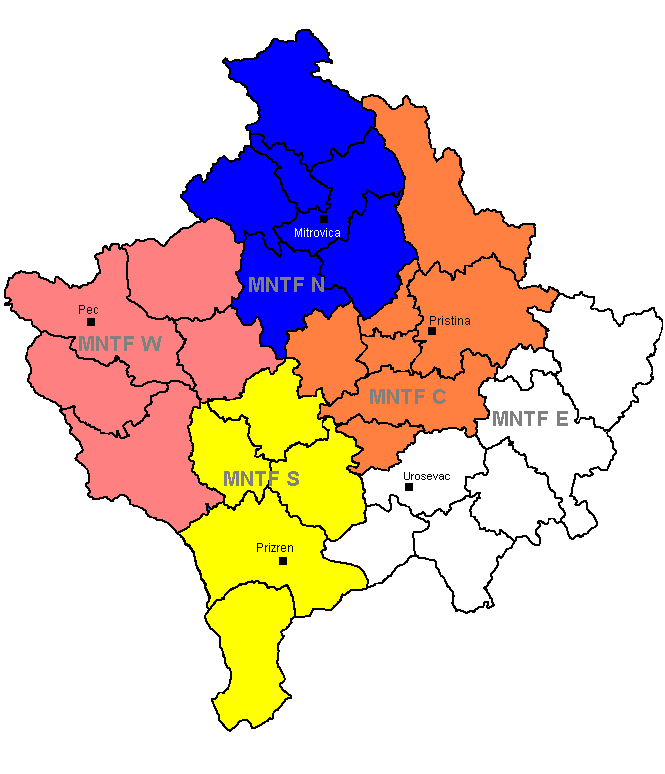
decided to restructure KFOR, replacing the five existing multinational brigades with five task forces, to allow for greater flexibility with, removing restrictions on the cross-boundary movement of units based in different sectors of Kosovo. Then in February 2010, the Multinational Task Forces became Multinational Battle Groups, and in March 2011, KFOR was restructured again, into just two multinational battlegroups; one based at Camp Bondsteel
Camp Bondsteel is the operation headquarters of the Kosovo Force (KFOR) in Kosovo. It is located near Ferizaj in southeastern Kosovo. It is the Regional Command-East headed by the United States Army (U.S. Army) and it is supported by troops from ...
, and one based at Peja
Peja or Peć, ), is the fifth most populous city in Kosovo and serves as the seat of the Peja Municipality and the District of Peja. It is located in the Rugova region on the eastern section of the Accursed Mountains along the Peja's Lumbar ...
.
In August 2019, the KFOR structure was streamlined. Under the new structure, the former Multinational Battlegroups are reflagged as Regional Commands, with Regional Command-East (RC-E) based at Camp Bondsteel, and Regional Command-West (RC-W) based at Camp Villaggio Italia.
Structure 2023
* Kosovo Force, at Camp Film City,Pristina
Pristina or Prishtina ( , ), . is the capital and largest city of Kosovo. It is the administrative center of the eponymous municipality and District of Pristina, district.
In antiquity, the area of Pristina was part of the Dardanian Kingdo ...
*** Headquarters Support Group (HSG), at Camp Film City;
*** Joint Logistics Support Group (JLSG), in Pristina (Logistics and engineering support)
*** Intelligence Surveillance and Reconnaissance Battalion (ISRBN), at Camp Film City
** Regional Command-East (RC-E), at Camp Bondsteel
Camp Bondsteel is the operation headquarters of the Kosovo Force (KFOR) in Kosovo. It is located near Ferizaj in southeastern Kosovo. It is the Regional Command-East headed by the United States Army (U.S. Army) and it is supported by troops from ...
near Ferizaj
Ferizaj or Uroševac,, or Uroševac sr-Cyrl, Урошевац, . Also formerly known as Ferizovići (). is a city and a municipality in Kosovo. It is the third largest city in Kosovo by population and also the seat of Ferizaj Municipality and ...
(U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United Stat ...
force supported by Greece, Italy, Finland, Hungary, Poland, Slovenia, Switzerland and Turkey)
** Regional Command-West (RC-W), at Camp Villaggio Italia near Peja
Peja or Peć, ), is the fifth most populous city in Kosovo and serves as the seat of the Peja Municipality and the District of Peja. It is located in the Rugova region on the eastern section of the Accursed Mountains along the Peja's Lumbar ...
(Italian Army
The Italian Army ( []) is the Army, land force branch of the Italian Armed Forces. The army's history dates back to the Italian unification in the 1850s and 1860s. The army fought in colonial engagements in China and Italo-Turkish War, Libya. It ...
force supported by Austria, Croatia, Moldova, North Macedonia, Poland, Slovenia, Switzerland and Turkey)
** Multinational Specialized Unit (MSU), in Pristina (Military Police
Military police (MP) are law enforcement agencies connected with, or part of, the military of a state. Not to be confused with civilian police, who are legally part of the civilian populace. In wartime operations, the military police may supp ...
, crowd and riot control, peacekeeping operations regiment composed entirely of Italian Carabinieri
The Carabinieri (, also , ; formally ''Arma dei Carabinieri'', "Arm of Carabineers"; previously ''Corpo dei Carabinieri Reali'', "Royal Carabineers Corps") are the national gendarmerie of Italy who primarily carry out domestic and foreign poli ...
)
** KFOR Tactical Reserve Battalion (KTRBN), at Camp Novo Selo (composed entirely of Hungarian Army
The Hungarian Ground Forces (, ) constitute the land branch of the Hungarian Defence Forces, responsible for ground activities and troops, including artillery, tanks, Armoured Personnel Carriers (APCs), Infantry Fighting Vehicles (IFVs), and g ...
troops)
*Kosovo Force Office, at Skopje International Airport
Skopje International Airport (, ) , also known as Skopje Airport (, ) and Petrovec Airport is the larger and busier of the two international airports in North Macedonia, with the other being the St. Paul the Apostle Airport in Ohrid, which is l ...
Contributing states

 At its height, KFOR troops consisted of 50,000 men and women coming from 39 different NATO and non-NATO nations. The official KFOR website indicated that in 2008 a total 14,000 soldiers from 34 countries were participating in KFOR. The following list shows the number of troops which have participated in the KFOR mission. Most of the force has been downsized since 2008; current numbers are reflected here as well:
At its height, KFOR troops consisted of 50,000 men and women coming from 39 different NATO and non-NATO nations. The official KFOR website indicated that in 2008 a total 14,000 soldiers from 34 countries were participating in KFOR. The following list shows the number of troops which have participated in the KFOR mission. Most of the force has been downsized since 2008; current numbers are reflected here as well:
KFOR commanders
# Sir Michael Jackson (United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, 10 June 1999 – 8 October 1999)
# Klaus Reinhardt (Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, 8 October 1999 – 18 April 2000)
#Juan Ortuño Such (Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, 18 April 2000 – 16 October 2000)
# (Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, 6 April 2001 – 3 October 2001)
# (France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, 3 October 2001 – 4 October 2002)
# (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 4 October 2002 – 3 October 2003)
# Holger Kammerhoff (Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, 3 October 2003 – 1 September 2004)
# (France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, 1 September 2004 – 1 September 2005)
# (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 1 September 2005 – 1 September 2006)
# (Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, 1 September 2006 – 31 August 2007)
# Xavier de Marnhac (France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, 31 August 2007 – 29 August 2008)
# (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 29 August 2008 – 8 September 2009)
# (Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, 8 September 2009 – 1 September 2010)
#Erhard Bühler
General Erhard Bühler (born 20 January 1956) is a retired officer of the German Army, and the former Director General for Planning German Ministry of Defence in Berlin, Germany. He was the commander of KFOR, from September 2010 to September 201 ...
(Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, 1 September 2010 – 9 September 2011)
# (Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, 9 September 2011 – 7 September 2012)
# (Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, 7 September 2012 – 6 September 2013)
# Salvatore Farina (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 6 September 2013 – 3 September 2014)
# Francesco Paolo Figliuolo (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 3 September 2014 – 7 August 2015)
#Guglielmo Luigi Miglietta (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 7 August 2015 – 1 September 2016)
#Giovanni Fungo (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 1 September 2016 – 15 November 2017)
# Salvatore Cuoci (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 15 November 2017 – 28 November 2018)
# Lorenzo D'Addario (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 28 November 2018 – 19 November 2019)
# Michele Risi (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 19 November 2019 – 13 November 2020 )
#Franco Federici
Franco may refer to:
Name
* Franco (name)
* Francisco Franco (1892–1975), Spanish general and dictator of Spain from 1939 to 1975
* Franco Luambo (1938–1989), Congolese musician, the "Grand Maître"
* Franco of Cologne (mid to late 13th cent ...
(Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 13 November 2020 – 15 October 2021)
# Ferenc Kajári (Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, 15 October 2021 – 14 October 2022 )
# Angelo Michele Ristuccia (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 14 October 2022 – 10 October 2023 )
# Özkan Ulutaş (Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, 10 October 2023 – 10 October 2024)
# Enrico Barduani (Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, 11 October 2024 – present)
Note: The terms of service are based on the official list of the KFOR commanders and another article.
Kosovo peacekeeping

Events
On 9 June 1999 the Military Technical Agreement or Kumanovo Agreement between KFOR and the Governments of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Republic of Serbia was signed by NATO General Sir Mike Jackson and Yugoslavia Colonel General Svetozar Marjanovic concluding theKosovo War
The Kosovo War (; sr-Cyrl-Latn, Косовски рат, Kosovski rat) was an armed conflict in Kosovo that lasted from 28 February 1998 until 11 June 1999. It ...
. This agreement outlined a rapid withdrawal of Federal Republic of Yugoslavia Forces from Kosovo, assigning to the KFOR Commander the airspace control over Kosovo and pending the later United Nations Security Council Resolution's approval, the deployment of KFOR to Kosovo. On 10 June 1999 the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
adopted the UNSC Resolution 1244 authorizing the deployment in Kosovo of an international civil and security presence for an initial period of 12 months, and to continue thereafter unless the UNSC decides otherwise. The civil presence was represented by the United Nations Mission In Kosovo (UNMIK), while the security presence was led by KFOR.
Following the adoption of UNSCR 1244, General Jackson, acting on the instructions of the North Atlantic Council, made immediate preparations for the rapid deployment of the security force (Operation Joint Guardian), mandated by the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
. The first NATO-led elements entered Kosovo at 5 a.m. on 12 June. On 21 June, the UCK undertaking of demilitarization and transformation was signed by COMKFOR and the Commander in Chief of the UCK (Mr. Hashim Thaci
Hashim () is a common male Arabic given name.
Notable people with the name include:
*Hashim ibn Abd Manaf
* Hashim Amir Ali
*Hashim Shah
*Hashim Amla
* Hashim Thaçi
* Hashim Khan
* Hashim Qureshi
* Mir Hashim Ali Khan
*Hashim al-Atassi
* Hashim ...
), moving KFOR into a new phase of enforcing the peace and supporting the implementation of a civil administration under the auspices of the United Nations.
Within three weeks of KFOR entry, more than half a million out of those who had left during the bombing were back in Kosovo. However, in the months following KFOR deployment, approximately 150,000 Serbs, Romani and other non-Albanians fled Kosovo while many of the remaining civilians were subjected to violence and intimidation from ethnic Albanians.
October 28, 2000 the first Municipal Assembly Elections were held. The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe(OSCE) announced that approximately 80% of the population participated in this vote for local representatives. The final results were certified by the Special Representative for Kosovo of the UN Secretary-General, Bernard Kouchner
Bernard Kouchner (born 1 November 1939) is a French politician and doctor. He is the co-founder of Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) and Médecins du Monde. From 2007 until 2010, he was the French Minister of Foreign and European Affairs in t ...
, on 7 November.
KFOR was initially composed of 40,000 troops from NATO countries. Troop levels were reduced to 26,000 by June 2003, then to 17,500 by the end that year. Combat troops were reduced more than support troops. KFOR tried to deal with this by transferring tasks to UNMIK and the Kosovo Police Service (KPS), but UNMIK was also reducing its number of international police, and KPS were not numerous enough or competent enough to take over from KFOR.
The 2004 unrest in Kosovo
On 17–18 March 2004, violence erupted in Kosovo, leaving hundreds wounded and at least 19 people dead. The unrest was precipitated by unsubstantiated reports in the Kosovo Albanian media which claimed that three Kosovo Albanian boys had drow ...
was the worst ethnic violence since 1999, leaving hundreds wounded and at least 14 people dead. On 17 and 18 March 2004, a wave of violent riots swept through Kosovo, triggered by two incidents perceived as ethnically motivated acts. The first incident, on 15 March 2004, an 18-year-old Serb was shot near the all Serb village of Čaglavica, near Pristina.
On 16 March, three Albanian children drowned in the Ibar River in the village of Čabar, near the Serb community of Zubin Potok. A fourth boy survived. It was speculated that he and his friends had been chased into the river by Serbs in revenge for the shooting of Ivić the previous day, but this claim has not been proven. According to Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. Headquartered in New York City, the group investigates and reports on issues including War crime, war crimes, crim ...
, the violence in March 2004 left 19 dead, 954 wounded, 550 homes destroyed, twenty-seven Orthodox churches and monasteries burned, and leaving approximately 4,100 Serbs, Roma, Ashkali (Albanian-speaking Roma), and other non-Albanian minorities displaced. Nineteen people, eight Kosovo Serbs and eleven Kosovo Albanians, were killed and over a thousand wounded-including more than 120 KFOR soldiers and UNMIK police officers, and fifty-eight Kosovo Police Service (KPS) officers.
The 10 February 2007 protest in Kosovo resulted in 2 deaths and many injuries. A crowd of ethnic Albanians in Pristina protested against a UN plan, also known as the Ahtisaari Plan
The Ahtisaari Plan, formally the Comprehensive Proposal for the Kosovo Status Settlement (CSP), is a status settlement proposed by former President of Finland Martti Ahtisaari covering a wide range of issues related to the status of Kosovo.
Some ...
, they felt fell short of granting full independence for Kosovo. The proposals, unveiled 2 February, recommended a form of self-rule and was strongly opposed by Serbia. The UN Security Council did not endorse the plan.
On February 17, 2008 unrest followed Kosovo's declaration of independence . Some Kosovo Serbs opposed to secession boycotted the move by refusing to follow orders from the central government in Pristina and attempted to seize infrastructure and border posts in Serb-populated regions. There were also sporadic instances of violence against international institutions and governmental institutions, predominantly in North Kosovo. After declaring independence, the Kosovo government introduced new customs stamps, a symbol of their newly declared sovereignty. Serbia refused to recognize the customs stamps which led to the de facto prohibition of both direct import of goods from Kosovo to Serbia, as well as transit to third countries. Goods from Serbia, however, could still be freely imported into Kosovo. Pursuant to the Statement by the President of the Security Council on 26 November 2008 (S/PRST/2008/44), UNMIK was restructured and its rule of law executive tasks were transferred to EULEX. EULEX maintains a limited residual capability as a second security responder and provides continued support to Kosovo Police's crowd and riot control capability.
The 25 August 2009 Pristina protests resulted in vehicle damages and multiple injuries.
On 22 July 2010, the International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; , CIJ), or colloquially the World Court, is the only international court that Adjudication, adjudicates general disputes between nations, and gives advisory opinions on International law, internation ...
delivered its advisory opinion on Kosovo's declaration of independence
''Accordance with International Law of the Unilateral Declaration of Independence in Respect of Kosovo'' was a request in 2008 for an advisory opinion referred to the International Court of Justice by the United Nations General Assembly regarding ...
declaring that "the adoption of the declaration of independence of the 17 February 2008 did not violate general international law because international law contains no 'prohibition on declarations of independence'," nor did the adoption of the declaration of independence violate UN Security Council Resolution 1244, since this did not describe Kosovo's final status, nor had the Security Council reserved for itself the decision on final status.
20 July 2011 Kosovo banned all imports from Serbia and introduced 10 percent tax for imports from Bosnia as both countries blocked exports from Kosovo. On 26 July 2011, a series of confrontations in North Kosovo began with a Kosovo Police operation to seize two border outposts along the Kosovo Serbia border and consequent clashes continued until 23 November. The clashes, resulting in multiple deaths and injuries, were over differences between who would administer the border crossings between Kosovo and Serbia along with what would happen with the revenue collected from the customs and removal of roadblocks to secure freedom of movement. On 3 September 2011, a deal to unblock the impasse between Serbia and Kosovo over exports was struck at EU-led negotiations in Brussels. Serbia agreed to accept goods marked “Kosovo Customs”, while Pristina gave up including state emblems, coats of arms, flags, or use of the word “republic” allowing Kosovo to interpret the label as referring to the customs of independent Kosovo, whereas Serbia could see it as a provincial customs label.
On 14 and 15 February 2012, an advisory referendum on accepting the institutions of the Republic of Kosovo was held in North Kosovo. 1 June 2012 Kosovo Serbs and a KFOR soldier were wounded when peacekeepers tried to dismantle Serb barricades, among the last on major roads yet to be dismantled, blocking traffic.
On 8 February 2013, a series of protests began against increases in electricity bills which later turned into protests against corruption. On 19 April 2013, the Belgrade Pristina Normalization Agreement was signed between the governments of Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
and Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
. Prior, North Kosovo
North Kosovo (, ); also known as the Ibar Kolašin (, or ''Kollashini i Ibrit''); earlier Old Kolašin, (, or ''Kollashini i Vjetër'') and colloquially known as the North (, ) is a region in the northern part of Kosovo, generally understood ...
functioned independently from the institutions in Kosovo by refusing to recognize Kosovo's 2008 declaration of independence and the Government of Kosovo
The Government of Kosovo (, ) exercises executive authority in the Republic of Kosovo. It is composed of government ministers, and is led by the prime minister. The prime minister is elected by the Assembly of the Republic of Kosovo. Ministe ...
opposed any parallel government for Serbs. The Brussels Agreement abolished the parallel structures and both governments agreed upon creating a Community of Serb Municipalities
The Community of Serb Municipalities (, ZSO; , AKS) is a planned inter-municipal association of Serbs in Kosovo, ethnic Serb majority Municipalities of Kosovo, municipalities in Kosovo.
The proposal for the association came as a result of the 20 ...
. The association was expected to be officially formed in 2016 but continued discussions has resulted in not forming the Community. By signing the Agreement, the European Union's Commission considered Serbia had met key steps in its relations with Kosovo and recommended that negotiations for accession of Serbia to the European Union be opened. Several days after the agreement was reached, the European Commission recommended authorizing the launch of negotiations between the EU and Kosovo on the Stabilisation and Association Process
In talks with countries that have expressed a wish to join the European Union, the EU typically concludes Association Agreements in exchange for commitments to political, economic, trade, or human rights reform in that country. In exchange, th ...
.
The 2014 student protest in Kosovo demanded the resignation or dismissal of the University of Pristina Rector. Students threw red paint and rocks at the Kosovo Police who responded with tear gas. 30 Kosovo Police officers were injured and more than 30 students were arrested. The upper airspace over Kosovo, skies over 10,000 feet, was re-opened for civilian traffic overflights on 3 April 2014. This followed a decision by the North Atlantic Council
The North Atlantic Council (NAC) is the principal political decision-making body of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), consisting of permanent representatives of its member countries. It was established by wikisource:North Atlantic ...
to accept the offer by the Government of Hungary to act as a technical enabler through its national air navigation service provider, Hungarocontrol.
The 2015 Kosovo protests were a series of violent protests calling for the resignation of a Minister and the passage of a bill on Trepca Mines ownership. On 6 January protestors claiming that among the pilgrims visiting a local church for Orthodox Christmas included displaced Serbs from Gjakova involved in war crimes against Albanians in 1998-1999 threw blocks of ice at the bus breaking one of its windows. Kosovo Police arrested two protestors. The Minister For Community and Return, who accompanied the pilgrims, made a statement that was perceived by Kosovo Albanians as an ethnic slur leading to riots. The rioters, which included students and opposition parties, demanded his resignation and he was dismissed by the Kosovo Prime Minister. The Kosovo government's announcement it was postponing a decision on the privatization process of the Trepca mining complex after Serb Kosovo Parliamentary Representatives protested claiming that the Serbian government had the right to retain ownership was met with student-led protests in Pristina, Lipljan and Ferizaj/Urosevac, Kosovo Albanian Miners in South Trepca and Kosovo Serbian Miners in North Trepca. Trepca's lead, zinc, and silver mines once accounted for 75 percent of the mineral wealth of socialist Yugoslavia, employing 20,000 people. Trepca now operates at a minimum level to keep the mines alive employing several thousand miners. The Trepca mines are under the oversight of the Kosovo Privatization Agency.
9 January 2016, thousands of protestors wanted the government to withdraw from a border demarcation agreement with Montenegro and an agreement to set up a Community of Serb Municipalities
The Community of Serb Municipalities (, ZSO; , AKS) is a planned inter-municipal association of Serbs in Kosovo, ethnic Serb majority Municipalities of Kosovo, municipalities in Kosovo.
The proposal for the association came as a result of the 20 ...
. Police fired tear gas responding to protesters who threw Molotov cocktails and set fire to a government building. The Kosovo Assembly later withdrew the agreements.
 On 14 January 2017, the Belgrade-Kosovska Mitrovica train incident happened when rhetoric was exchanged between Kosovo and Serbian Officials after Serbia announced restarting train service between Kosovo and Serbia and Kosovo responded stating that the train would be stopped at the border. The initial train was painted in the colors of the Serbian flag with the words “ Kosovo is Serbia” printed down the side which was considered provocative by Kosovo Officials and Kosovo Officials stated that Police would stop it at the border. The train traveled from Belgrade to the border town of Raska and returned never crossing into Kosovo. Train service between Kosovo and Serbia remains non-existent.
On 21 March 2018, Kosovo's Assembly ratified the border agreement with Montenegro. The European Union set ratification as a condition before it would grant Kosovo nationals visa-free access to the pass-port free
On 14 January 2017, the Belgrade-Kosovska Mitrovica train incident happened when rhetoric was exchanged between Kosovo and Serbian Officials after Serbia announced restarting train service between Kosovo and Serbia and Kosovo responded stating that the train would be stopped at the border. The initial train was painted in the colors of the Serbian flag with the words “ Kosovo is Serbia” printed down the side which was considered provocative by Kosovo Officials and Kosovo Officials stated that Police would stop it at the border. The train traveled from Belgrade to the border town of Raska and returned never crossing into Kosovo. Train service between Kosovo and Serbia remains non-existent.
On 21 March 2018, Kosovo's Assembly ratified the border agreement with Montenegro. The European Union set ratification as a condition before it would grant Kosovo nationals visa-free access to the pass-port free Schengen area
The Schengen Area ( , ) encompasses European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their common borders. As an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it ...
. 8 September, Serbia's president visited North Kosovo's Gazivode Lake, an important source of Kosovo's water. The following day, his planned visit to the majority-Serb village Banje was cancelled by the Kosovo government after Kosovo Albanian protestors put up barricades at the village's entrance. 29 Sept, Kosovo's president visited Gazivode Lake. Serbia accused Kosovo police of seizing control of the lake and briefly detaining workers and Kosovo said police were there to provide security for the visit and nobody was detained. A Kosovo Serbian representative said Serbia was putting its military as well as police under high alert as a result. 20 November The international police agency (INTERPOL), rejected Kosovo's membership. On 21 November, Kosovo imposed an import tax on Serbian and Bosnia Herzogovina goods. Kosovo said the tariff would be lifted when Serbia recognizes its sovereignty and stops blocking it from joining international organizations and Serbia said it will not participate in further dialogue until the measure is lifted.
On 1 July 2021, NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg
Jens Stoltenberg (; born 16 March 1959) is a Norwegian politician from the Labour Party. Since 2025, he has been the Minister of Finance in the Støre Cabinet. He has previously been the prime minister of Norway and secretary general of NATO.
...
confirmed that the KFOR mission would continue.
On 29 May 2023, more than 30 NATO peacekeeping soldiers defending three town halls in northern Kosovo were injured in clashes with Serb protesters, while Serbia's president put the army on the highest level of combat alert.
The tense situation developed after ethnic Albanian mayors took office in northern Kosovo's Serb-majority area after elections that the Serbs boycotted.
On 29 September 2023, the NATO Secretary-General
The secretary general of NATO is the chief civil servant of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), an intergovernmental military alliance with 32 member states. The officeholder is an international diplomat responsible for coordinating th ...
announced the authorisation of additional forces to address the build up of Serbian troops on the border of Kosovo and Serbia in order to keep peace within the region.
KFOR fatalities
 Since the KFOR entered Kosovo in June 1999, soldiers from Argentina, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Luxembourg, Morocco, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and the United States were killed in the line of duty.
The biggest fatal event is that of the 42 Slovak soldiers dead in a 2006 military plane crash in Hungary. In 20 years, more than 200 NATO soldiers have died as part of KFOR.
Since the KFOR entered Kosovo in June 1999, soldiers from Argentina, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Luxembourg, Morocco, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and the United States were killed in the line of duty.
The biggest fatal event is that of the 42 Slovak soldiers dead in a 2006 military plane crash in Hungary. In 20 years, more than 200 NATO soldiers have died as part of KFOR.
Notes and references
References
External links
KFOR Placemap
KFOR official site (NATO)
K-For: The task ahead
(from
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
, 13 June 1999)
First deaths in K-For operation
(from
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
, 14 June 1999)
Memorial honors soldiers' sacrifices
June 2002: 68 soldiers have died since KFOR entered Kosovo.
Radio KFOR
{{Authority control Kosovo War NATO-led peacekeeping in the former Yugoslavia United States Marine Corps in the 20th century Military units and formations established in 1999 1999 establishments in Serbia 1999 establishments in Kosovo Military of Kosovo Military operations involving India Military operations involving Portugal